Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
A SYSTEM FOR PROCESSING,
ACTIVATING AND REDEEMING VALUE ADDED PREPAID CARDS
[0001]
BACKGROUND
[0002] The present invention generally relates to a processing and
activation system providing
consumers with the ability to purchase a stored value card, i.e., a gift card,
of various affiliated or
non-affiliated service providers with additional value added beyond the
purchase price.
[0003] The market for stored value cards such as merchant gift cards
continues to grow. The
marketplace is currently filled with many types of stored value cards offered
by numerous card
issuers. Some of the cards are tailored to be redeemed from a single merchant
while others may be
redeemed by several merchants. Because the consumer has numerous choices in
selecting a stored
value card, such as a gift card, it is becoming increasingly difficult for
card issuers to distinguish
themselves in the marketplace from other issuers of stored value cards.
Therefore, it would be
desirable to have a method and system that provided card issuers and redeeming
merchants a
mechanism for promoting their card and/or store in order to encourage a
consumer to purchase a
stored value card from them or redeem a stored value card with them.
[0004] Clients such as corporate clients and other larger buyers have
significant leverage and
buying power. As a result, such clients can command discounts from certain
merchants selling
goods or services. Thus, the clients direct their entities (buyers) purchasing
on their behalf to
1
CA 2846601 2020-04-02
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
purchase from the certain merchants that have agreed to provide a discount. As
an example, an
insurer has significant leverage and buying power and can command discounts
from certain
merchants selling goods or services provided to an insured. When fulfilling a
claim for their
insured entity (e.g., buyer or their representative), an insurer directs their
insured entity to purchase
from the certain merchants that have agreed to provide to the insurer a
discount. There is a need
for systems, methods and a tangible computer readable storage medium which
facilitate,
implement, control and monitor the above.
SUMMARY
[0005] Disclosed herein is a computer implemented method and system for
adding value to a
stored value card in excess of the purchase price for the stored value card.
In one embodiment a
stored value card transaction processor receives an activation or redemption
request for a stored
value card from a point of sale terminal. The request comprises an activation
or redemption
amount and at least one of a card identification, a point of sale terminal
identification, a merchant
identification, and a time of activation. The stored value card transaction
processor compares at
least one of the card identification, the point of sale terminal
identification, the merchant
identification, and the time of activation to data stored in a stored value
card datastore to determine
if the stored value card to be activated or redeemed is eligible for a value
added award. The
processor then determines the value added award to be added to an account
associated with the
stored value card to be activated or redeemed when the stored value card is
determined to be
eligible for the value added award and modifies the request to include the
value added award. The
processor then transmits the modified request to the card issuer authorization
system and receives a
response from the card issuer authorization system. The processor transmits
the response to the
point of sale terminal wherein the response includes a value added award
reference when the stored
value card has been determined to be eligible for the value added award and
the value added award
has been authorized.
(0006] Also disclosed herein is a system used by a client that implements
transactions between
a buyer and merchants providing a discount to the client. In a preferred
embodiment the
transactions are funded by the client. In another embodiment, the transactions
are partially funded
by the client and partially funded by the buyer.
[0007] Also disclosed herein is a method used by a client that implements
transactions
between a buyer and merchants providing a discount to the client. In a
preferred embodiment the
2
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
transactions are funded by the client. In another embodiment the transactions
are partially funded
by the client and partially funded by the buyer. The method includes computer-
executable
instructions executed by a processor.
[0008] Also disclosed herein is a tangible computer readable storage medium
used by a client
implements transactions between a buyer and merchants providing one or more
discounts to the
client. In a preferred embodiment the transactions are funded by the client.
In another
embodiment, the transactions are partially funded by the client and partially
funded by the buyer.
The tangible computer readable storage medium includes computer executable
instructions
executable by a processor.
100091 As used herein, a discount may be monetary or may be another form of
value
differentiation, including points, rebates, cost reductions, coupons, ad-on
merchandise, credits, and
the like.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0010] Figure 1 is a schematic representation of the stored value card
transaction system.
[0011] Figures 2A and 2B are front perspective views of representative
individual stored value
cards.
[0012] Figure 3AA is a flowchart depicting an exemplary process utilized by
a stored value
card transaction computer for processing a stored value card with value
differentiation.
[0013] Figures 3A and 3B are flowcharts depicting exemplary processes
utilized by a stored
value card transaction computer for activating a stored value card with a
value added bonus.
[0014] Figures 4A and 4B are flowcharts depicting exemplary processes
utilized by a stored
value card transaction computer for redeeming a stored value card and awarding
a value added
bonus during the redemption process.
[0015] Figure 5 is a flowchart depicting an exemplary process for redeeming
a specific product
and/or service that has been awarded to a stored value card.
[00161 Figure 6 illustrates an exemplary general purpose computer system
suitable for
implementing the several embodiments of the disclosure.
3
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
10017] Figure 7 is a sequence diagram illustrating a net discount of 10%
distributed between a
merchant and a corporate client.
[0018] Figure 8 is a sequence diagram illustrating a net discount of 20%
distributed between a
merchant and a corporate client wherein the discount is based on an option
selected by the
merchant at the POS.
[0019] Figure 9 is a sequence diagram illustrating a net discount of 20%
distributed between
an administrator and a corporate client.
[0020] Figure 10 is a block diagram of a system illustrating the various
interactions between
components of the system.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0021] As used herein, stored value card refers to a card that may be used
to transact business
with a party willing to accept the card, for example as tender for a purchase.
Examples of such
cards include gift cards, prepaid telephone cards, loyalty cards, membership
cards, ticket cards,
entertainment cards, sports cards, prepaid cards, and the like. Typically,
such cards are wallet-
sized and made of plastic but may also be in electronic form. In various
embodiments, the
transaction card may be a type of card such as a gift or prepaid card that
requires activation at a
point of sale. For example, a stored value card may be purchased and activated
at a point of sale
by a consumer and subsequently used by the consumer or another (e.g., the
recipient of the card as
a gift) to transact business.
[0022] Consumer use of stored value cards typically involves a card vendor,
a redeeming
merchant, and a card issuer. In various embodiments, the card vendor,
redeeming merchant and
card issuer may be the same, different, or related entities. The point of sale
where stored value
cards are purchased and activated may be referred to as the card vendor or
simply vendor. An
entity that will accept a stored value card for business transactions, for
example as tender for a
purchase, may be referred to as a redeeming merchant. An entity that provides
the financial
backing and/or payment processing accessed via the stored value card may be
referred to as the
card issuer or simply issuer.
[0023] Typically, the issuer is identified on the stored value card and
associates a unique issuer
account code with each stored value card. Card issuers include direct issuers
of cards such as
store-branded cards, and in some embodiments the card vendor may also be the
card issuer and/or
4
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
the redeeming merchant. Card issuers also include banks, financial
institutions, and transaction
processors such as VISA, Mastercard, American Express, etc., and cards issued
by such
institutions may be readily accepted by a number of redeeming merchants to
conduct transactions
such as purchases. In some instances, the redeeming merchant may be identified
on the stored
value card (for example, a retailer branded card such as Store X), and such
cards may be sold at the
same or different card vendor (e.g., card vendor is Store X or a different or
unrelated Store Z). In
such instances, the Store X branded stored value card may be issued by Store
X, by Store Z, or by
a third party such as bank or financial institution.
[0024] Customers (which can be used interchangeably with buyers, herein)
may be offered
incentives to purchase and/or redeem a card (or cards) via value
differentiation between the
purchase and redemption values of said card (or cards).
[0025] In an embodiment, a card with a face value of $25 may be purchased
by a customer for
$25, but the card may be activated for $30 ¨ the $25 purchase price plus an
additional $5 added as
an incentive to purchase the card. Alternatively, rather than adding cash
value to the card, the card
may be encoded, in addition to the face value of the card, with a redemption
coupon for a specific
product or service. For example, a $15 gift card to a coffee house may have an
electronic
redemption coupon for a free shot of the customer's syrup of choice to be
added to any coffee
purchased at the coffee house. The free shot of syrup may be redeemed in
connection with
redeeming a portion or all of the gift card amount or the free shot of syrup
may be redeemed
separately.
[0026] In another embodiment, a card vendor is able to offer customers
incentives to redeem a
stored value card, such as a gift card, by adding value in addition to the
value of the stored value
card at the time the customer redeems the stored value card. For example, a
merchant could run a
promotion in which it offers customers an additional $5 credit when the
customer uses a gift card
for a purchase at one of the merchant's retail stores during a specified
period of time.
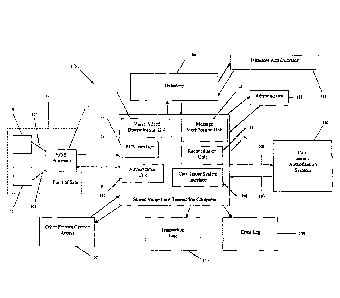
10027] Figure 1 illustrates an exemplary stored value card transaction
system 100 in
accordance with one embodiment of the present invention. In one embodiment,
the stored value
card transaction system comprises: (a) at least one point of sale component
111; (b) a stored value
card transaction computer 150; (c) a datastore 180 containing stored value
card identifiers, stored
value card account information, value added award conditions (herein "value
added award" is
synonymous with "value added bonus," "value added bonus award," "value added
award bonus,"
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
and "value differentiation"), and other information related to activating,
redeeming, and managing
stored value cards; (d) at least one individual card issuers' authorization
system 160; and (e) any
other component included in the system by the stored-value card transaction
computer
administrator 151. In one embodiment, the stored value card transaction
computer 150 comprises
a value added determination component 153, a POS interface 152, a message
modification
component 154, a reconciliation component 155, a card issuer system interface
156, and an
authorization component 157. The POS Interface 152 provides a means for the
stored value card
transaction computer 150 to communicate with the point of sale component 111
via, for example,
the Internet, a Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), or an independent
dedicated network.
Likewise, the stored value card transaction computer 150 may communicate with
the card issuers'
authorization system 160 via, for example, the Internet, a Public Switched
Telephone Network
(PSTN), or an independent dedicated network. Communications 106, 107 between
the PUS
interface 152 and the point of sale component 111 and communications 109, 110
between the card
issuer system interface 156 and the card issuers' authorization systems 160
may be encrypted for
added security and/or may utilize a virtual private network (VPN).
10028] As can be seen in Figure 1, at the point of sale component 111
(typically located at a
vendor and/or redeeming merchant), the card identifier on the stored value
card is interpreted 102
by a point of sale interpretation component 101 (e.g., a card reader). The
point of sale
interpretation component 101 can comprise a human, a bar code scanner,
magnetic strip reader,
optical character recognition device, or other device configured to interpret
the data encoded in the
card identifier on the stored value card.
100291 Contemporaneously with the interpretation of the card identifier, a
request for
activation, deactivation, or redemption 103 by a point of sale transaction
component 104 is made.
The point of sale transaction component 104 can comprise a human, an
electronic input device, a
register, a computer processing unit ("CPU"), or other means of requesting the
activation or
deactivation of the stored value card identifier interpreted by the point of
sale interpretation
component 101. In some embodiments, the actions performed by the point of sale
interpretation
component 101 and the point of sale transaction component 104 may be performed
by one
component capable of performing both actions that would be performed by the
individual
components.
6
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[0030] The point of sale interpretation component 101 and the point of sale
transaction
component 104 communicate with the point of sale processing component 105. The
point of sale
processing component 105 can comprise a CPU or other type of processing device
accepted for use
in the industry. The point of sale interpretation component 101 communicates
the card identifier to
the point of sale processing component 105. The point of sale transaction
component 104
communicates the request for activation or deactivation of the card identifier
interpreted by the
point of sale interpretation component 101 to the point of sale processing
component 105. The
point of sale processing component 105 communicates 106 with the stored value
card transaction
computer 150 (e.g., transmits a message requesting card activation,
deactivation or redemption). In
some embodiments, the actions performed by the point of sale interpretation
component 101, the
point of sale transaction component 104, and the point of sale processing
component 105 may all
be performed by one component (e.g., an integrated POS device such as a
computerized register)
capable of performing all the actions that would be performed by the
individual components.
[0031] The point of sale processing component 105 is connectable to the
stored value card
transaction computer 150 via a suitable network, such as the Internet, the
public switched
telephone network (PSTN), or an independent dedicated network. Each point of
sale processing
component 105 has an associated identifier that may be transmitted to the
stored value card
transaction computer 150 during the course of connecting the point of sale
processing component
105 to the stored value card transaction computer 150. Each point of sale
processing component
105 may include multiple point of sale transaction components 101, 104
corresponding to
individual terminals each with its own terminal identification.
[0032] As depicted in Figure 1, the stored value card transaction computer
150 is configured
to: (a) form a secure connection with the card vendor (e.g., via the point of
sale component 111),
the card issuers' authorization systems 160, and any other entities 190
authorized to access the
stored value card transaction computer 150 by the stored value card
transaction computer
administrator 151; (b) to communicate with card issuers' authorization systems
160 to request and
receive activation or deactivation of stored value cards as well as receive
value added information
for stored-value cards that are eligible for incentives; (c) to communicate
with card issuers'
authorization systems 160 to redeem all or a portion of the value, services,
or products associated
with the stored-value card; (d) generate and maintain a transaction log 170 of
all activities
performed; (e) generate and maintain an error log 175 of all activities
unsuccessfully completed
7
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
and reasons therefor; (f) communicate to the card vendor (e.g., via the POS
component 111) the
activation or deactivation of the stored value card and any information
concomitant with the
activation or deactivation of individual stored value card, i.e. the
communication of PINs
associated with activated stored value cards; and (g) communicate to the card
vendor (e.g., via the
POS component 111) any reasons why requested transactions cannot not be
completed.
[0033] The stored value card transaction computer 150 may comprise a
singular processing
unit (e.g., a centralized server or data center), a plurality of processing
units (e.g., a distributed
computing system with various components distributed and in communication with
each other), or
combinations thereof, with concomitant storage capabilities, each capable of
or designated for:
accessing the datastore 180; creating a transaction log 170; creating and
maintaining an error log
175; communicating with card vendors; communicating with the individual card
issuers'
authorization systems 160; processing individual transaction card activation
and or deactivation
requests; processing stored value card redemption requests, processing value
added functions to
add additional cash value or add an electronic redemption coupon for a
specific product(s) or
service(s), processing redemption request for electronic redemption coupons
for specific product(s)
and/or service(s), and communicating with other systems 190 capable of and
authorized to
communicate with the stored value card transaction computer 150.
[0034] Datastore 180 maintains records of accounts associated with each
stored value card
indicating: (a) whether each individual card has been activated or
deactivated, (b) whether the card
has been redeemed, (c) records and details of each individual redemption
request, (d) the amount
remaining on the card, (e) conditions required for activation and redeeming
the card, (f) identity of
the card issuer, (f) value added bonus awards, (g) conditions for redeeming
value added bonus
awards, and (h) any combination thereof. The datastore may also maintain
records of conditions
required for granting a value added bonus award to a stored value card.
[0035] The stored value card transaction computer 150 is also configured to
generate and
maintain a transaction log 170 of all activity involving the stored value card
transaction computer
150. The transaction log may comprise a detailed summary of: (a) requested
stored-value card
activations; (b) requested stored-value card deactivations; (c) the monetary
amount ascribed to card
activations; (d) the monetary amount ascribed to card deactivations; (e) the
value added amounts,
products, or services ascribed card activations; (f) the value added amounts,
products, or services
ascribed to card deactivations; (g) the time the cards were activated; (h) the
time the cards were
8
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
deactivated; (i) the transaction or communication performed with the card
issuer to activate the
cards; (j) the transaction or communication performed with the card issuer to
deactivate the cards;
(k) the PIN communicated to the card vendor in response to a request to
activate a card requiring
the input of a PIN for use; (I) any other information the stored value card
transaction computer
administrator 151 directs the stored value card transaction computer 150 to
maintain as a log entry;
and (m) any combination thereof.
[0036] The information contained in the transaction log 170 may be used to
generate
reconciliation reports, settlement reports, payment reports, audit reports, or
other forms of
information aggregation for the benefit of, use by, or for provision to, the
stored value card
transaction administrator 151, the datastore administrator 181, card vendors,
card issuers, card
issuers' authorization systems 160, redeeming merchants, or other interested
parties. For example,
the transaction log 170 contains information about each transaction performed
by stored value card
transaction computer 150 and may be utilized by the reconciliation component
155 when
reconciling accounts belonging to various vendors, merchants, card issuers and
the stored value
card transaction system administrator.
[0037] Oversight and maintenance of the stored value card transaction
computer is performed
by the stored value card transaction computer administrator 151. Although not
required, in an
alternative embodiment, the stored value card transaction computer
administrator 151 may also
function as the datastore administrator 181. The stored value card transaction
computer 150 is
configured to generate and maintain an error log of all transactions that were
not completed and
reasons therefor. In some embodiments, the error log is administered by the
stored value card
transaction computer administrator 151.
[0038] As noted above, the stored value card transaction computer 150
communicates with the
datastore 180 and/or the card issuers' authorization systems 160 to determine
whether the stored
value card to be activated is eligible for a value added award. The stored
value card transaction
computer 150 may compare one or more of the card identification, the terminal
identification,
vendor identification, and the time and date of the activation request
contained within the
activation request to data contained in the datastore 180 to determine whether
the stored value card
to be activated is eligible for a value added award. For example, a particular
card issuer may run a
promotion to encourage customers to purchase its stored value card in which
cards issued by that
card issuer that are purchased within a specified period of time receive a $5
bonus added to the
9
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
stored value card in addition to the purchase price for the card. Thus, a $25
gifl card may be
purchased for $25, but be authorized for $30. In another example, a vendor may
run a promotion
to encourage customers to purchase a stored value card, wherein stored value
cards purchased
within a specified period of time may be purchased for a price less than the
value designated by the
stored value card's markings and/or packaging. Thus, a customer could purchase
a $25 gift card
for some amount less than $25, e.g., $20. In either of the above examples, the
value differentiators,
e.gõ bonus added to a redemption value of a stored value card and reduction of
purchase price for a
designated value of a stored value card, may be applicable to bundled stored
value card packages
and the value differentiators distributed amongst and/or across the cards,
either equally or
disproportionately.
[0039] Upon receipt of an activation or deactivation request for a stored-
value card from the
card vendor, the stored value card transaction computer 150 accesses the
datastore 180 of stored
value card identifier data. The stored value card transaction computer 150
processes the
information contained in the datastore 180 and communicates 109, 110 with the
individual card
issuers' authorization systems 160 to effectuate activation or deactivation of
the transaction cards
secured by the package as well as to effectuate the addition of a value added
service, product, or
cash value amount. The stored value card transaction computer's 150
communication with the
individual card issuers' authorization systems 160 may occur simultaneously or
independently.
The stored value card transaction computer 150 is connectable to the
individual card issuers'
authorization systems as via a suitable network, such as the PSTN, the
Internet, or an independent
dedicated network. The stored value card transaction computer 150 is
configured to receive
communication 110 from the card issuers' authorization systems 160 concerning
the status of the
activation or deactivation of individual transaction cards.
[0040] The stored value card transaction computer 150 is also configured to
communicate to
the card vendor 107 the status of a request for activation or deactivation of
a stored-value card and
to communicate any necessary PIN information required by activated stored
value cards to the card
vendor in order for the card purchaser to be apprised of that information for
use of the purchased
individual transaction card. As previously discussed, is connectable to the
individual card issuers'
authorization systems as via a suitable network, such as the PSTN, the
Internet, or an independent
dedicated network.
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[00411 The stored value card transaction computer 150 is also configured to
communicate with
other entities 190 authorized to access the stored value card transaction
system and specifically
authorized to access the stored value card transaction computer 150. These
other entities may
comprise third party payment management systems, third party audit systems,
card issuer affiliated
entities, card vendor affiliated entities, redeeming merchants or redeeming
merchant affiliated
entities, financial institutions, such as banks and credit unions, or any
other entity provided access
by the stored value card transaction computer administrator 151.
100421 There may arise situations where an activation, deactivation, or
redemption request is
received by the stored value card transaction computer 150, but the
information in the datastore
180 pertaining to the stored value card identifier received by stored value
card transaction
computer 150 precludes completion of the request. For example, a card may have
been previously
activated, returned to the point of sale for a refund, but not deactivated
prior to reshelving. In that
case, when a subsequent customer purchases that card, and an activation
request is communicated
to the stored value card transaction computer 150, the datastore 180 file
accessed by the stored
value card transaction computer 150 will indicate that the card is already
activated. In another
example, the stored value card identifier received by the stored value card
transaction computer
150 may have already been redeemed for the entire amount associated with the
stored value card.
In these and other similar situations, the stored value card transaction
computer 150 will
communicate a message to the card vendor that the transaction cannot be
completed.
[00431 The value added determination component 153 uses information
contained within the
activation request or redemption request received from the point of sale
component 111 as well as
information contained in datastore 180 to determine whether the stored value
card which the point
of sale component 111 is attempted to have activated or redeemed is eligible
for a value added
award. The activation request from the point of sale component 111 may contain
one or more of
the following pieces of information: (a) stored value card identification, (b)
point of sale terminal
identification, (c) amount to be credited to an account associated with the
stored value card, (d) the
time of the activation request, (e) the date of the activation request, (1)
identification of the card
issuer for the stored value card, (g) identification of the activating vendor,
(h) location of activating
vendor, and (i) any combination thereof. The redemption request from the point
of sale component
111 may contain one or more of the following pieces of information: (a) stored
value card
identification, (b) point of sale terminal identification, (c) amount to be
debited from the account
11
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
associated with the stored value card, (d) the time of the redemption request,
(e) the date of the
redemption request, (f) identification of the card issuer for the stored value
card, (g) identification
of the redeeming merchant, (h) location of the redeeming merchant, (i)
identification of the
product(s) and/or service(s) being purchased, (j) and any combination thereof.
However, the
information contained within the activation and redemption requests is not
limited to the
enumerated list but may other items in addition to the items enumerated or in
place of the items
enumerated above.
[0044] For an
activation request, the value added determination component 153 compares the
information received in the activation request to information in the datastore
180 to determine if
any of the criteria for adding additional value to the stored value card or
discounting the price of
the stored value card to be activated are met. For example, the card issuer
may have provided that
stored value cards purchased during a certain period of time should receive an
additional value
added to the purchase amount. Alternatively, the card issuer may provide that
stored value cards of
a certain value or purchased during a specified time period be discounted such
that the card selling
vendor is only required to obtain an amount less than the face value of the
card. For example, the
face value of the stored value card may be $50, but the card issuer is running
a promotion to
encourage customers to purchase its cards by giving a $5 discount such that
the purchase amount
for the $50 card is only $45, but the card is activated for $50. Such a
promotion may encourage a
consumer to purchase the card issuer's card or encourage the consumer to
purchase the card
issuer's card rather than a competitor's card. Alternatively, the vendor
selling the card could run a
promotion in which cards purchased during a specified period of time receive
an additional value
added to the purchase amount of the stored value card. The vendor selling the
card may not be
related to the card issuer. However, by running such a promotion, the vendor
selling stored value
cards may encourage a consumer to purchase the stored value card from them
rather than another
vendor. The value added to the stored value card in excess of the purchase
amount of the stored
value card may be a monetary amount. For example, a $25 gift card purchased
for $25 may be
activated for $30 - $25 purchase amount plus a $5 value added award. Thus, the
gift card may be
used to purchase items totaling $30 even though the consumer only paid $25 for
the gift card.
However, the value added to the card need not be a monetary amount, but could
be an award of a
specific product or service. For example, the value added could be an
electronic coupon for a free
product or service if the stored value card is redeemed for a specified
product or service or is
12
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
redeemed during a specified period of time or is redeemed with a specified
merchant.
Furthermore, the value added, whether it be a monetary amount or for a
specific product or service,
may have an expiration date that is different from the purchased amount of the
stored value card.
Also, the value added, may be tied to other specific redemption criteria that
are different from the
redemption criteria of the purchase amount of the stored value card. For
example, the value added
portion of the stored value card may be required to be redeemed at a specific
location(s), specific
merchant(s), a specific time(s), or credited toward the purchase of a specific
product(s) or
service(s) while the remaining portion of the stored value card may have no
limitations on
redemption or have different limitations on redemption,.
[0045] For a redemption request, the value added determination component
153 compares the
information received in the redemption request to information in the datastore
180 to determine if
any of the criteria for adding additional value to the stored value card to be
redeemed are met.
Depending on the type of value added award specified by the card issuer or
redeeming merchant,
the value added, if a monetary amount, could be subtracted from the redemption
amount requested
or, alternatively, could be added to the account associated with the stored
value card to be
redeemed at a later time during a separate transaction.
[0046] The message modification component 154 modifies the messages 106 and
110 to add
value added information into the messages. For example, if it is determined by
the value added
determination component 153 that a stored value card to be activated is
eligible for a value added
bonus, the activation message 106 received from the point of sale component 1
1 I is modified by
the message modification component 154 to include the determined value added
bonus and is then
forwarded as message 109 to the appropriate card issuers' authorization system
160 for authorizing
the activation request for the amount specified in the activation request plus
the value added bonus.
As another example, if it is determined that the stored value card is eligible
to be purchased at a
discount, the activation message 106 received from the point of sale component
111 is modified by
the message modification component 154 (and forwarded as message 109) to
indicate to the
appropriate card issuers' authorization system 160 that the stored value card
to be activated will be
activated for one amount, but that the customer will be charged a lesser
amount reflecting the
discount associated with the stored value card.
[00471 The message modification component 154 also modifies messages 110
from the card
issuers' authorization systems 160 intended for the point of sale component
111 to include any
13
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
information regarding value added to the stored value card that may be printed
on the receipt
generated for the customer as well as information that may be presented to a
cashier on a terminal
101 or 104 that the cashier may communicate to the customer, and such modified
messages are
forwarded as messages 107 to the point of sale component 111.
[00481 The reconciliation component 155 reconciles the accounts of various
card issuers,
selling vendors, and/or redeeming merchants, to credit and debit appropriate
merchants, vendors,
the stored value card transaction system administrator, and card issuers with
the value of various
transactions to reflect which entities received value from which other
entities. For example, if a
vendor A sells a stored value card issued by card issuer B for a specified
amount and receives
payment from a customer, then an account associated with the stored value card
is credited with
the payment amount, the selling vendor receives a percentage (e.g., retains a
percentage) of the
purchase amount and/or a predetermined amount, the stored value card system
administrator
receives a percentage of the purchase amount and/or predetermined amount, and
the card issuer
receives the remainder. If a stored value card issued by card issuer Y is
redeemed at merchant X to
purchase items, then the amount redeemed is debited to the card issuer Y and
credited to the
merchant X, sometimes minus a transaction fee collected by the card issuer
and/or a transaction fee
collected by the stored value card transaction system administrator.
[0049] Authorization component 157 is utilized when the stored value card
transaction
computer 150 is also the authorizing system such that the stored value card
transaction computer
150 authorizes activation, deactivation, and redemption requests rather than
transmitting the
request to the card issuers' authorization systems 160 for authorization. When
the authorization
component 157 is utilized, the stored value card transaction computer 150 may
transmit details of
transactions to the card issuers' authorization systems rather than
authorization requests. Also, in
some embodiments, the card issuer, the authorizing system, and the transaction
computer are part
of the same entity and, in such an embodiment, there would be no a card
issuers' authorization
systems 160 or the card issuers' authorization systems 160 would be under
common control with
the other components of the stored value card transaction computer 150 (for
example, a commonly
owned and operated computing system, that may be centralized (e.g., part of a
centralized data
center) and/or distributed within a commonly owned or controlled system or
network).
Furthermore, it should be noted that although components associated with the
stored value card
transaction computer 150 (e.g., components 152-157) are depicted as various
components within a
14
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
single data processing system for illustration and conceptual purposes, one or
more of components
152-157 could be implemented on separate computers, systems, or servers in a
distributed data
processing environment.
10050] Examples of stored value cards are depicted in Figures 2A and 2B.
Figure 2A depicts a
stored value card 200 in which the identification 211 is encoded on the card
200 by means of a bar
code capable of being read by an optical scanner. Figure 2B depicts a stored
value card 201 in
which the card identification 211 is encoded on a magnetic strip located on
the card 201. In some
embodiments, the stored value card may have a magnetic strip and a bar code
(or a plurality of
magnetic strips and/or bar codes), and one or more of such may contain the
identification 211. The
stored value cards 200, 201 are fabricated from a suitable first material,
such as plastic, paper, a
plastic-coated paper, laminates, or combinations thereof. The stored value
cards 200, 201 are
typically made in a thickness range of from about 0.005 to about 0.040 inch.
The stored value
cards 200, 201 each bear an identifier 211. The stored value card identifier
211 is unique to the
stored value card and associates the stored value card to a unique account
maintained by the card
issuer. The stored value card identifier 211 may be encoded in a bar code as
depicted in Figure 2A
on stored value card 200, a magnetic strip as depicted in Figure 2B on stored
value card 201, a
series of numerals, a series of letters, or a combination thereof. The stored
value cards 200, 201
may also be fashioned with personal identification numbers, or PlNs, to be
entered during the
course of the transaction, that correspond to the particular stored value card
identifier 211 and
allows access and/or use of the stored value card account. The PIN may be
encoded in a bar code,
a magnetic strip, a series of numeral, a series of letters, or a combination
thereof. The PIN may be
obscured from view by packaging, by an obscuring material such as a scratch-
off strip or peel-off
label, or combinations thereof. In some embodiments, the stored value card may
comprise a card
security code (CSC), a card verification value (CVV or CV2), a card
verification value code
(CVVC), card verification code (CVC), verification code (V-code or V code),
card code
verification (CCV), credit card ID (COD), or combinations thereof.
[0051] Figure 2B depicts a stored value card 201 in which the card
identification 211 is
encoded on a magnetic strip located on the card 201. The magnetic strip may be
made
conventional construction, such as one deposited from a slurry, positioned on
the card 201 so that it
can be scanned in well-known magnetic strip reading equipment, A terminal such
as a Trattz 380
made by Verifone is suitable in this application. For additional security, the
card identification 211
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
may also be subjected to an encryption algorithm, many of which are well-known
in the art, prior
to encoding on the magnetic strip.
[0052] In an embodiment of the stored value card identifier 211, the stored
value card 200
comprises a bar code of conventional construction, such as a UPC code (e.g., a
GS1-128 or
UCC/EAN-128), positioned on the stored value card 201 so that it can be
scanned by well-known
bar code reading equipment. Encoded in the bar code on the stored value card
is a representation
of the stored value card identifier 211.
[0053] In other embodiments of the stored value card identifier, radio
frequency identification
(RFD) tags, microprocessors, and/or microchips may be placed on the stored
value card 200 and
201 to be interpreted by specifically configured devices. The RFLD tags,
microprocessors, and/or
microchips may be used in addition to or in place of the bar code 255 on
stored value card 200 and
magnetic strip 256 on stored value card 201, or may be used in combination
with these or other
means of encoding the stored value card identifier on the stored value card.
[0054] In further embodiments, series of numerals, series of letters, or
combinations thereof,
may be placed on the stored value cards 200 and 201 to be read or interpreted
by a human or a
device, i.e. optical character recognition device, configured to interpret a
series of shapes
corresponding to the package identifier.
[0055] An exemplary process utilized by a stored value card transaction
computer 150 for
activating a stored value card with a value differentiation in accordance with
one embodiment of
the present invention is depicted in Figure 3AA. To begin, in block 3002, the
stored value card
transaction computer 150 receives a transaction request from a point of sale
terminal. The
transaction request comprises one or more of the following: (a) identity of
the terminal, (b) the
identity of the stored value card, (c) a request for activation of the stored
value card, (d) a request
for redemption of the stored value card, (e) an amount of the card activation,
(f) an amount of the
card redemption, (g) the identity of the stored value card issuer, (h) the
identity of the activating
vendor, (i) the identity of the requesting location, (j) the time of the
transaction request, (k) the date
of the transaction request, and (1) any combination thereof. The transaction
request may comprise
other information in addition to or in place of the above enumerated items.
Using information
contained within the transaction request received form the point of sale
component 111 and on
information obtained from datastore 180, in block 3004, the stored value card
transaction computer
150 determines whether the card to be transacted is eligible for value
differentiation. The value
16
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
differentiation may be an additional monetary value credited to an account
associated with the
stored value card (e.g., a monetary redemption value amount) in excess of the
purchase price of the
stored value card, an award of a specific product(s) or service(s) to the
purchaser or redeemer of
the stored value card (e.g., a non-monetary redemption value), a discount on
the purchase price of
the stored value card, or combinations thereof. The value differentiation
portion of the transaction
may have conditions of use that are different from the primary purchased
amount of the stored
value card. For example, the value differentiation amount/offering may have an
expiration date or
specified dates of use that arc different from any expiration dates associated
with the primary
stored value card. Furthermore, the value differentiation amount/offering may
specify specific
merchants, locations, and/or products that the value differentiation
amount/offering may be utilized
with which may be different from any conditions associated with the primary
purchased amount of
the stored value card.
[00561 If the stored value card is not eligible for value differentiation,
then in block 3006, the
stored value card transaction computer 150 forwards the transaction request as
received from the
point of sale component 111 to the appropriate one of the card issuers'
authorization systems 160
without modifying the request to include value differentiation. The
transaction request, however,
may be modified for other reasons unrelated to the value differentiation
decision prior to
forwarding to the appropriate one of the card issuers' authorization systems
160. The method
proceeds to block 3012 as described in more detail below.
100571 If the stored value card is eligible for value differentiation, then
in block 3008, the
stored value card transaction computer 150 modifies the transaction request to
add the value
differentiation amount/offering to the transaction request. In block 3010, the
stored value card
transaction computer 150 then forwards the modified transaction request with
the value
differentiation to the appropriate one of the card issuers' authorization
systems 160, which receives
the modified transaction request and acts upon same, for example authorizing
and/or processing
the request to activate or redeem the card along with the appropriate value
differentiation
amount/offering and updating a datastore accordingly. The card issuers'
authorization systems 160
sends a response message back to the stored value card transaction computer
150. In an alternative
embodiment where the stored value card transaction computer 150 performs the
functions of the
card issuers' authorization systems 160, the method may proceed directly from
block 3004 or 3008
to block 3014.
17
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[0058] The stored value card transaction computer 150 receives the response
message from the
appropriate one of the card issuers' authorization systems 160 in block 3012.
At block 3014, the
stored value card transaction computer 150 optionally updates an account
associated with the
stored value card in the datastore to reflect the concomitant changes in the
status of the stored value
card. For example, the datastore is updated to include any value
differentiation amount/offering
associated with the stored value card and the conditions for redeeming the
stored value card's
principal balance as well as for redeeming the value differentiation
amount/offereing, if any. In an
alternative embodiment, such updates are performed additionally or
alternatively by the card
issuer's authorization systems 160 and stored in a datastore associated
therewith. A transaction log
170 may be updated by the stored value card transaction computer 150 in block
3016 to record the
details about the transaction. The account information to be stored in the
datastore 180 (or
alternatively or additionally in a datastore associated with the card issuer's
authorization systems
160) as well as the details of the transaction recorded in the transaction log
may include (a) the
time and date of the transaction, (b) whether the stored value card was
activated, (c) the reason the
stored value card was not activated if the activation request was denied, (d)
the amount credited to
the stored value card account when activated, (e) conditions associated with
redeeming the stored
value card, (f) the type and amount of any value differentiation, (g) the
conditions for redeeming
the value differentiation amount/offering, (h) the identity of the activating
vendor, (i) the identity
of the card issuer, (j) the location of the activating vendor, (k) the
identity of the terminal activating
the stored value card, (1) the identity of the entity granting the value
differentiation
amount/offering, (m) the identity of the account to be debited for the value
differentiation
amount/offering, (n) the requested redemption amount, (o) the reason the
stored value card was not
redeemed if the transaction request was denied, (p) the amount debited from
the stored value card
account when redeemed, (q) the identity of the redeeming merchant vendor, (r)
the location of the
redeeming merchant, (s) the identity of the terminal redeeming the stored
value card, and (t) any
combination thereof. The transaction log may include other information in
addition to or in place
of the items enumerated above.
[0059] The stored value card transaction computer 150, in block 3018, then
forwards the
response message to the point of sale component 111. The stored value card
transaction computer
150, prior to forwarding the response message to the point of sale component
111, may modify the
response message as necessary to include information that may be printed on a
receipt for the
18
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
customer and/or presented on a display to the store clerk operating the point
of sale component
111. At block 3020, the stored value card transaction computer 150 reconciles
the accounts of the
various vendors, merchants, card issuers, the stored value card transaction
system administrator,
and other entities involved with issuing, selling, redeeming, and marketing
the stored value card to
debit and credit appropriate accounts and, in some embodiments, initiate funds
transfers between
appropriate bank accounts belonging to the various entities. Alternatively,
reconciliation of
accounts may be performed periodically (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly, etc.)
rather than after each
transaction. In such an embodiment, the information from the transaction log
170 may be utilized
to reconcile the various entities involved with the sale or redemption of
various stored value cards
thus requiring fewer funds transfers to be initiated. In various embodiments,
the sequence of
events depicted in blocks 3014, 3016, 3018, and 3020 may be varied, and thus
may be carried out
in any desired order, sequentially or simultaneously. Moreover, the requested
transaction may
involve multiple stored value cards and multiple value differentiators. In
such an scenario, the
transaction process proceeds as described above, however the transaction
request will comprise
multiple sets of transaction information, i.e., information such: (a) identity
of the terminal, (b) the
identity of the stored value card, (c) a request for activation of the stored
value card, (d) a request
for redemption of the stored value card, (e) an amount of the card activation,
(f) an amount of the
card redemption, (g) the identity of the stored value card issuer, (h) the
identity of the activating
vendor, (i) the identity of the requesting location, (j) the time of the
transaction request, (k) the date
of the transaction request, and (1) any combination thereof, for each of the
multiple of stored value
cards comprising the instant transaction request. Further, in the multiple
stored value card
transaction scenario, any activation amount, redemption amount, or value
differentiation
amount/offering may be allocated across the multiple stored value cards
equally or
disproportionately as desired by any of the card transaction interested
parties and/or card
purchasers/redeemers.
100601 An
exemplary process utilized by a stored value card transaction computer 150 for
activating a stored value card with a value added bonus in accordance with one
embodiment of the
present invention is depicted in Figure 3A. To begin, in block 302, the stored
value card
transaction computer 150 receives an activation request from a point of sale
terminal. The
activation request comprises one or more of the following: (a) identity of the
terminal, (b) the
identity of the stored value card to be activated, (c) the amount of the card
activation, (d) the
19
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
identity of the stored value card issuer, (e) the identity of the activating
vendor, (f) the identity of
the activating location, (g) the time of the activation request, (h) the date
of the activating request,
and (i) any combination thereof The activation request may comprise other
information in
addition to or in place of the above enumerated items. Using information
contained within the
activation request received form the point of sale component 111 and on
information obtained
from datastore 180, in block 304, the stored value card transaction computer
150 determines
whether the card to be activated is eligible for a value added bonus. The
value added bonus may
be an additional monetary value credited to an account associated with the
stored value card to be
activated, an award of a specific product(s) or service(s), or a discount on
the purchase price of the
stored value card. The value added portion of the activation may have
conditions of use that are
different from the primary purchased amount of the stored value card. For
example, the value
added bonus may have an expiration date or specified dates of use that are
different from any
expiration dates associated with the primary stored value card. Furthermore,
the value added
bonus may specify specific merchants, locations, and/or products that the
value added bonus may
be utilized with which may be different from any conditions associated with
the primary purchased
amount of the stored value card.
[0061] If the stored value card is not eligible for a value added bonus,
then in block 306, the
stored value card transaction computer 150 forwards the activation request as
received from the
point of sale component 111 to the appropriate one of the card issuers'
authorization systems 160
without modifying the request to include a value added bonus. The activation
request, however,
may be modified for other reasons unrelated to the value added bonus decision
prior to forwarding
to the appropriate one of the card issuers' authorization systems 160. The
method proceeds to
block 312 as described in more detail below.
[0062] If the stored value card is eligible for a value added bonus, then
in block 308, the stored
value card transaction computer 150 modifies the activation request to add the
additional value
added bonus to the activation request. In block 310, the stored value card
transaction computer
150 then forwards the modified activation request with the value added bonus
to the appropriate
one of the card issuers' authorization systems 160, which receives the
modified activation request
and acts upon same, for example authorizing and/or processing the request to
activate the card
along with the appropriate value added bonus and updating a datastore
accordingly. The card
issuers' authorization systems 160 sends a response message back to the stored
value card
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
transaction computer 150. In an alternative embodiment where the stored value
card transaction
computer 150 performs the functions of the card issuers' authorization systems
160, the method
may proceed directly from block 304 or 308 to block 314.
[00631 The stored value card transaction computer 150 receives the
activation message from
the appropriate one of the card issuers' authorization systems 160 in block
312. At block 314, the
stored value card transaction computer 150 optionally updates an account
associated with the
stored value card in the datastore to reflect that the stored value card is
activated and the amount
for which the stored value card is activated. Additionally, the datastore is
updated to include any
value added bonus awarded to the stored value card and the conditions for
redeeming the stored
value card's principal balance as well as for redeeming the value added bonus,
if any. In an
alternative embodiment, such updates are performed additionally or
alternatively by the card
issuer's authorization systems 160 and stored in a datastore associated
therewith. A transaction log
170 may be updated by the stored value card transaction computer 150 in block
316 to record the
details about the activation transaction. The account information to be stored
in the datastore 180
(or alternatively or additionally in a datastore associated with the card
issuer's authorization
systems 160) as well as the details of the transaction recorded in the
transaction log may include (a)
the time and date of the activation, (b) whether the stored value card was
activated, (c) the reason
the stored value card was not activated if the activation request was denied,
(d) the amount credited
to the stored value card account when activated, (e) conditions associated
with redeeming the
stored value card, (f) the type and amount of any value added bonus, (g) the
conditions for
redeeming the value added bonus, (h) the identity of the activating vendor,
(i) the identity of the
card issuer, (j) the location of the activating vendor, (k) the identity of
the terminal activating the
stored value card, (1) the identity of the entity granting the value added
bonus, (m) the identity of
the account to be debited for the value added bonus, and (n) any combination
thereof. The
transaction log may include other information in addition to or in place of
the items enumerated
above.
[0064] The stored value card transaction computer 150, in block 318, then
forwards the
activation message to the point of sale component Ill. The stored value card
transaction computer
150, prior to forwarding the activation message to the point of sale component
111, may modify
the activation message as necessary to include information that may be printed
on a receipt for the
customer and/or presented on a display to the store clerk operating the point
of sale component
21
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
111. At block 320, the stored value card transaction computer 150 reconciles
the accounts of the
various vendors, merchants, card issuers, the stored value card transaction
system administrator,
and other entities involved with issuing, selling, and marketing the stored
value card to debit and
credit appropriate accounts and, in some embodiments, initiate funds transfers
between appropriate
bank accounts belonging to the various entities. Alternatively, reconciliation
of accounts may be
performed periodically (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly, etc.) rather than after
each transaction, In
such an embodiment, the information from the transaction log 170 may be
utilized to reconcile the
various entities involved with the sale or redemption of various stored value
cards thus requiring
fewer funds transfers to be initiated. In various embodiments, the sequence of
events depicted in
blocks 314, 316, 318, and 320 may be varied, and thus may be carried out in
any desired order,
sequentially or simultaneously. Moreover, the requested transaction may
involve multiple stored
value cards and multiple value added awards. In such an scenario, the
transaction process proceeds
as described above, however the transaction request will comprise multiple
sets of transaction
information, i.e., information such: (a) identity of the terminal, (b) the
identity of the stored value
card, (c) a request for activation of the stored value card, (d) a request for
redemption of the stored
value card, (e) an amount of the card activation, (f) an amount of the card
redemption, (g) the
identity of the stored value card issuer, (h) the identity of the activating
vendor, (i) the identity of
the requesting location, (j) the time of the transaction request, (k) the date
of the transaction
request, and (1) any combination thereof, for each of the multiple of stored
value cards comprising
the instant transaction request. Further, in the multiple stored value card
transaction scenario, any
activation amount, redemption amount, or value added awards may be allocated
across the multiple
stored value cards equally or disproportionately as desired by any of the card
transaction interested
parties and/or card purchasers/redeemers.
[00651 An
exemplary process utilized by a stored value card transaction computer for
activating a stored value card with a value added bonus in accordance with
another embodiment of
the present invention is depicted in Figure 3B. In the example depicted in
Figure 3B, the stored
value card transaction computer 150 also serves to authorize activation. The
process begins in
block 352 with the receipt of an activation request by the stored value card
transaction computer
150 from the point of sale component 111. In block 354, the stored value card
transaction
computer 150 determines whether to activate the card based on the information
contained in the
activation request as compared to information stored in datastore 180. If the
stored value card
22
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
transaction computer 150 determines that the activation is denied, an
activation denied (or rejected)
response message is generated in block 356. The activation denied response is
then transmitted to
the point of sale component 111 in block 366 and the datastore and transaction
log are updated to
reflect the details of the transaction in block 368. The stored value card
transaction computer 150
then notifies the card issuer of the details of the transaction in block 370
and, if necessary,
reconciles the various accounts among the appropriate vendors, merchants, card
issuers, stored
value card transaction system administrator, and other entities involved in
block 372.
[0066] If the stored value card transaction computer 150 determines that
the card should be
activated based upon the information received in the activation request, then
the stored value card
transaction computer 150 determines whether the card is eligible for a value
added bonus in block
358. If the card is not eligible for a value added bonus, then, in block 360,
the stored value card
transaction computer 150 generates an activation approval response message and
transmits this
activation approval message back to the point of sale component 111 in block
366. The account
associated with the stored data card in the datastore and the transaction log
are updated by the
stored value card transaction computer 150 in block 368 and the card issuer is
notified of the
transaction details in block 370. At block 370, the stored value card
transaction computer 150
reconciles the various accounts among the appropriate vendors, merchants, card
issuers, stored
value card transaction system administrator, and other entities involved with
issuing, selling, and
marketing the stored value card to debit and credit appropriate accounts and,
in some
embodiments, initiate funds transfers between appropriate bank accounts.
Alternatively,
reconciliation of accounts may be performed periodically (e.g., daily, weekly,
monthly, etc.) rather
than after each transaction. In such an embodiment, the information from the
transaction log 170
may be utilized to reconcile the various entities involved with the sale or
redemption of various
stored value cards thus requiring fewer funds transfers to be initiated.
[0067] If the stored value card transaction computer 150 determines in
block 358 that the
stored value card is eligible for a value added bonus, then the appropriate
bonus is determined in
block 362. An activation approval message including the value added bonus
information is
generated in block 364. The activation approval message may include
information to be printed
onto the customer's receipt at the point of sale component 111 that provides
the details of the value
added bonus that has been added to the stored value card and the redemption
details for redeeming
the value added bonus. The activation approval response is then transmitted to
the point of sale
23
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
component 111 by the stored value card transaction computer 150 in block 366.
In block 368, the
account associated with the stored value card that has been activated is
updated in datastore 180 as
well as the transaction log is updated to reflect the details of the
transaction. The account
information to be stored in the datastore 180 as well as the details of the
transaction recorded in the
transaction log may include (a) the time and date of the activation, (b)
whether the stored value
card was activated, (c) the reason the stored value card was not activated if
the activation request
was denied, (d) the amount credited to the stored value card account when
activated, (e) conditions
associated with redeeming the stored value card, (1) the type and amount of
any value added bonus,
(g) the conditions for redeeming the value added bonus, (h) the identity of
the activating vendor, (i)
the identity of the card issuer, (j) the location of the activating vendor,
(k) the identity of the
terminal activating the stored value card, (1) the identity of the entity
granting the value added
bonus, (m) the identity of the account to be debited for the value added
bonus, and (n) any
combination thereof. The account associated with the stored value card and the
transaction log
may include other information in addition to or in place of the items
enumerated above. In various
embodiments, the sequence of events depicted in blocks 366, 368, 370, and 372
may be varied, and
thus may be carried out in any desired order, sequentially or simultaneously.
[00681 An
exemplary process utilized by a stored value card transaction computer for
adding a
value added bonus to a stored value card during a redemption request in
accordance with one
embodiment of the present invention is depicted in Figure 4A. To begin, in
block 402, the stored
value card transaction computer 150 receives a redemption request from a point
of sale component
111. The redemption request includes at least one of the following items of
information: (a) an
amount to be deducted from the stored value card toward the purchase, (b) an
identity of the
redeeming terminal, (c) an identity of the redeeming merchant, (d) an identity
of the location of the
redeeming merchant, (e) an indication of the identity of the item(s) to be
purchased with the stored
value card, (f) a stored value card identification, (g) the identity of the
stored value card issuer, (h)
the date of the redemption request, (i) the time of the redemption request,
and (j) any combination
thereof. Using the information contained in the redemption request as well as
information obtained
from datastore 180, the stored value card transaction computer 150, in block
404, determines
whether the stored value card is eligible for a value added bonus. The value
added bonus may be
an award of additional cash value to be added to the stored value card, a
reduction in the amount to
24
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
be debited to the account associated with the stored value card, and/or an
award of a specific
product(s) or service(s).
10069] If the card is not eligible for a value added bonus, then in block
406, the stored value
card transaction computer 150 forwards the redemption request (e.g., forwards
an unmodified
redemption request) to the appropriate card issuers' authorization system 160
for authorization to
redeem the card. The redemption request, however, may be modified for other
reasons unrelated
to the value added bonus decision prior to forwarding to the appropriate one
of the card issuers'
authorization systems 160. The method proceeds to block 412 as described in
more detail below.
[0070] If the stored value card is eligible for a value added bonus, then
in block 408, the stored
value card transaction computer 150 modifies the redemption request to add the
additional value
added bonus to the redemption request. In block 410, the stored value card
transaction computer
150 then forwards the modified redemption request with the value added bonus
to the appropriate
one of the card issuers' authorization systems 160, which receives the
modified redemption request
and acts upon same, for example authorizing and/or processing the request to
redeem the card
along with the appropriate value added bonus and updating a datastore
accordingly. The card
issuers' authorization systems 160 sends a response message back to the stored
value card
transaction computer 150. In an alternative embodiment where the stored value
card transaction
computer 150 performs the functions of the card issuers' authorization systems
160, the method
may proceed directly from block 404 or 408 to block 414.
100711 The stored value card transaction computer 150 then receives a
redemption message
from the card issuer either authorizing redemption or denying redemption in
block 412. The
redemption message is then forwarded to the point of sale component 111 by the
stored value card
transaction computer 150 in block 414. The stored value card transaction
computer 150, prior to
forwarding the redemption message to the point of sale component 111, may
modify the
redemption message as necessary to include information that may be printed on
a receipt for the
customer and/or presented on a display to the store clerk operating the point
of sale component
111. At block 416, the stored value card transaction computer 150 optionally
updates an account
in datastore 180 associated with the stored value card to be redeemed to
include the details of the
redemption approval or denial. In an alternative embodiment, such account
updates are performed
additionally or alternatively by the card issuer's authorization systems 160
and stored in a datastore
associated therewith. The transaction log is also updated to include
appropriate details in block
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
418. The account information to be stored in the datastore 180 as well as the
details of the
transaction recorded in the transaction log may include (a) the time and date
of the redemption, (b)
whether the stored value card was redeemed, (c) the reason the stored value
card was not redeemed
if the redemption request was denied, (d) the amount debited to the stored
value card account when
redeemed, (e) conditions associated with redeeming the stored value card, (f)
the type and amount
of any value added bonus, (g) the conditions for redeeming the value added
bonus, (h) the identity
of the redeeming merchant, (i) the identity of the card issuer, 6) the
location of the redeeming
merchant, (k) the identity of the terminal redeeming the stored value card,
(1) the identity of the
entity granting the value added bonus, (m) the identity of the account to be
debited for the value
added bonus, and (n) any combination thereof. The account associated with the
stored value card
and the transaction log may include other information in addition to or in
place of the items
enumerated above. The stored value card transaction computer 150 at block 420
then reconciles
the various accounts among the appropriate vendors, merchants, card issuers,
stored value card
transaction system administrator, and other entities involved in selling,
issuing, or redeeming the
stored value card (collectively "card transaction interested parties") and may
initiate funds transfers
between bank accounts belonging to the various vendors, merchants, card
issuers, stored value card
transaction system administrator, and other involved entities as appropriate.
In various
embodiments, the sequence of events depicted in blocks 414, 416, 418, and 420
may be varied, and
thus may be carried out in any desired order, sequentially or simultaneously.
[00721 In an alternative embodiment, an exemplary process utilized by a
stored value card
transaction computer for adding a value added bonus to a stored value card
during an activation
request in which the stored value card transaction computer also makes the
authorization
determination in accordance with the method shown in Figure 4B, with the
understanding that each
reference to redemption within the method is generally replaced with a
corresponding reference to
activation.
[0073] An exemplary process utilized by a stored value card transaction
computer for adding a
value added bonus to a stored value card during a redemption request in which
the stored value
card transaction computer also makes the authorization determination in
accordance with another
embodiment of the present invention is depicted in Figure 4B. The process
begins in block 452
with the receipt of a redemption request from a point of sale component 1 l 1
by the stored value
card transaction computer 150. The stored value card transaction computer 150
determines if the
26
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
card is eligible for a value added bonus in block 454 and, if not, proceeds
with a normal
redemption process based on the redemption request amount in block 456,
followed by block 460.
The stored value card transaction computer 150 then determines whether to
authorize redemption
in the amount requested in block 460 and generates and sends a redemption
message to the point of
sale terminal either authorizing or denying the redemption request in block
462. The stored value
card transaction computer 150 then modifies the account information associated
with the stored
value card in the datastore 180 to reflect the details of the redemption
request and response in block
464. If the redemption request was approved, then the account associated with
the stored value
card is debited by the amount of the activation request. The stored value card
transaction computer
150 notifies the card issuer of the details of the transaction in block 468.
In block 470, the stored
value card transaction computer 150 reconciles the accounts of the various
vendors, merchants,
card issuers, stored value card transaction system administrator, financial
institutions, and other
entities that were involved in the issuing, selling, or redeeming of the
stored value card to credit
and debit the appropriate accounts. The stored value card transaction computer
150 may initiate
funds transfers between bank accounts belonging to the various vendors,
merchants, card issuers,
stored value card transaction system administrator, and other entities as
appropriate.
[0074] If the
stored value card transaction computer 150 determines that the stored value
card
is eligible for a value added bonus at block 454, then the stored value card
transaction computer
150 determines the specific value added bonus to be applied to the stored
value card in block 458.
The value added bonus may be an additional monetary value credited to an
account associated with
the stored value card to be activated, an award of a specific product(s) or
service(s), or reduce the
amount to be debited to the account associated with the stored value card by a
specified amount
during the redemption process. For example, if the stored value card is used
to purchase items
totaling $50, but is eligible for a $5 discount, then the purchase is
approved, but the account
associated with the stored value card is only debited by $45 rather than the
entire $50 of the
purchase. Depending on the entity granting the bonus award, the merchant with
which the stored
value card is used to purchase items may receive the difference between the
amount debited from
the stored value card and the actual amount of the purchase from the entity
granting the bonus
award. If the entity granting the bonus award is also the merchant whose
product(s) and/or
service(s) are being purchased using the stored value card, then the
transaction may merely require
reconciliation of various accounting books without a transfer of funds between
entities.
27
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[0075] It should also be noted that the value added portion of the
activation may have
conditions of use that are different from the primary purchased amount of the
stored value card.
For example, the value added bonus may have an expiration date or specified
dates of use that are
different from any expiration dates associated with the primary stored value
card. Furthermore, the
value added bonus may specify specific merchants, locations, and/or products
that the value added
bonus may be utilized with which may be different from any conditions
associated with the
primary purchased amount of the stored value card.
[0076] The process then proceeds with determining whether to authorize
redemption in block
460, and generating and sending a redemption message to the point of sale
component 111 in block
462. The redemption message may include information indicating the amount
and/or type of value
added bonus that the customer is receiving to be printed on the customer's
receipt. The redemption
message may also include the conditions associated with redeeming the value
added bonus if the
value added bonus was not used during the current redemption process. For
example, the value
added bonus may be a coupon for a free item during a subsequent visit by the
customer to the
merchant. In block 464, the stored value card transaction computer 150 then
modifies the account
information associated with the stored value card in datastore 180 to debit
the account by the
appropriate amount in cases where the transaction was approved and to store
other information
associated with the transaction. The stored value card transaction computer
150 also updates the
transaction log in block 466 with the details of the transaction. The account
information to be
stored in the datastore 180 as well as the details of the transaction recorded
in the transaction log
may include (a) the time and date of the redemption, (b) whether the stored
value card was
redeemed, (c) the reason the stored value card was not redeemed if the
redemption request was
denied, (d) the amount debited to the stored value card account when redeemed,
(e) conditions
associated with redeeming the stored value card, (f) the type and amount of
any value added bonus,
(g) the conditions for redeeming the value added bonus, (h) the identity of
the redeeming merchant,
(i) the identity of the card issuer, (j) the location of the redeeming
merchant, (k) the identity of the
terminal redeeming the stored value card, (1) the identity of the entity
granting the value added
bonus, (m) the identity of the account to be debited for the value added
bonus, and (n) any
combination thereof. The account associated with the stored value card and the
transaction log
may include other information in addition to or in place of the items
enumerated above. The stored
value card transaction computer 150 then reconciles the various accounts among
the appropriate
28
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
vendors, merchants, card issuers, stored value card transaction system
administrator, and other
entities involved in selling, issuing, or redeeming the stored value card and
may initiate funds
transfers between bank accounts belonging to the various vendors, merchants,
card issuers, stored
value card transaction system administrator, and other entities as appropriate
in block 470. In
various embodiments, the sequence of events depicted in blocks 462, 464, 466,
468, and 470 may
be varied, and thus may be carried out in any desired order, sequentially or
simultaneously.
100771 In an alternative embodiment, an exemplary process utilized by a
stored value card
transaction computer for adding a value added bonus to a stored value card
during a redemption
request in which the stored value card transaction computer also makes the
authorization
determination in accordance with the method shown in Figure 3B, with the
understanding that each
reference to activation within the method is generally replaced with a
corresponding reference to
redemption.
[0078] An exemplary process utilized by a stored value card transaction
computer for
redeeming a stored value card for a specific product or service that has been
awarded to the stored
value card in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention is
depicted in Figure 5. To
begin, in block 502, the stored value card transaction computer 150 receives a
redemption request
for a value added bonus of a specific product and/or service for a stored
value card from a point of
sale component 111. In block 504, the stored value card transaction computer
150 determines
whether to authorize the request. If it is determined that the request should
be denied, then the
stored value card transaction computer 150 generated a redemption denied
message in block 506
and transmits the redemption denied message to the point of sale component 111
in block 518.
The redemption denied message may include a reason for denying the redemption
request.
Reasons for denial of the redemption request may include one or more of: (a)
the specific items
has already been redeemed previously, (b) the time and/or date that the bonus
is attempted to be
redeemed fall outside the date and time windows specified for redemption of
the bonus, (c) the
item attempted to be redeemed using the bonus differs from the item associated
with the bonus, (d)
the location and/or identity of the merchant does not correspond to the
location and/or identity of
the merchant required for redemption of the bonus award, (e) the account
associated with the
stored value card in datastore 180 does not contain the requested bonus award;
and (f) any
combination thereof. The method continues at block 520 as described in more
detail below.
29
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[0079] If the stored value card transaction computer 150 determines that
the redemption
request is to be authorized in block 504, then the stored value transaction
computer 150 determines
the identity of the entity granting the value added bonus in block 508. The
stored value card
transaction computer 150 then determines if the entity granting the value
added bonus is different
from the redeeming merchant in block 510. If the entity granting the value
added bonus is the
same as the redeeming merchant, the method proceeds to block 512 et seq. as
described herein. If
the entity granting the value added bonus is different from the redeeming
merchant, then the stored
value card transaction computer 150 determines a reimbursement monetary value
for service(s)
and/or product(s) being redeemed with the value added bonus on the stored
value card in block
514. The stored value card transaction computer 150 then reconciles the
accounts between the
redeeming merchant and the value added bonus authorizing entity to credit the
redeeming
merchant with the monetary amount associated with the redemption and debit the
value added
bonus authorizing entity in block 516. The stored value card transaction
computer 150 may also
initiate a transfer of funds between an account associated with the value
added bonus authorizing
entity and the redeeming merchant for the appropriate amount. Alternatively,
funds transfers may
be the responsibility of other entities or may be performed periodically
(e.g., daily, weekly,
monthly) using information from the transaction log in order to minimize the
number of funds
transfers between entities.
[0080] The stored value card transaction computer 150 then generates a
redemption accepted
message in block 512 and transmits this response message to the point of sale
terminal 101, 104 in
block 518. The stored value card transaction computer 150 then updates the
transaction log with
the details of the redemption transaction in block 520, notifies the card
issuer of the details of the
transaction in block 522, and, in block 524, updates the account associated
with the stored value
card in the datastore 180 to reflect the details of the transaction and
indicate that the specific value
added bonus has been redeemed. The account information to be stored in the
datastore 180 as well
as the details of the transaction recorded in the transaction log may include
(a) the time and date of
the redemption, (b) whether the stored value card was redeemed, (c) the reason
the stored value
card was not redeemed if the redemption request was denied, (d) the product(s)
and/or services
redeemed with the stored value card account when redeemed, (e) the identity of
the redeeming
merchant, (f) the identity of the entity granting the value added bonus, (g)
the identity of the card
issuer, (h) the location of the redeeming merchant, (i) the identity of the
terminal redeeming the
stored value card, (k) the identity of the account to be debited for the value
added bonus, and (1)
any combination thereof. The account associated with the stored value card and
the transaction log
may include other information in addition to or in place of the items
enumerated above. In various
embodiments, the sequence of events depicted in blocks 512, 518, 520, 522, and
524 may be
varied, and thus may be carried out in any desired order, sequentially or
simultaneously.
[0081] In an alternative embodiment, an exemplary process utilized by a
stored value card
transaction computer for activating a stored value card for a specific product
or service that has
been awarded to the stored value card in accordance with the method shown in
Figure 5, with the
understanding that each reference to redemption within the method is generally
replaced with a
corresponding reference to activation.
[0082] An exemplary process utilized by a stored value card transaction
computer for
activating a stored value card for a specific product or service that has been
awarded to the stored
value card in accordance with one embodiment
[0083] The stored value card transaction computer 150 above may be
implemented on any
general-purpose computer with sufficient processing power, memory resources,
and network
throughput capability to handle the necessary workload placed upon it. Figure
6 illustrates a
typical, general-purpose computer system suitable for implementing one or more
embodiments
disclosed herein. The computer system 680 includes a processor 682 (which may
be referred to as
a central processor unit or CPU) that is in communication with memory devices
including
secondary storage 684, read only memory (ROM) 686, random access memory (RAM)
688,
input/output (I/O) 690 devices, and network connectivity devices 692. The
processor may be
implemented as one or more CPU chips.
100841 It is understood that by programming and/or loading executable
instructions onto the
computer system 680, at least one of the CPU 682, the RAM 688, and the ROM 686
are changed,
transforming the computer system 680 in part into a particular machine or
apparatus having the
novel functionality taught by the present disclosure. It is fundamental to the
electrical engineering
and software engineering arts that functionality that can be implemented by
loading executable
software into a computer can be converted to a hardware implementation by well
known design
rules. Decisions between implementing a concept in software versus hardware
typically hinge on
considerations of stability of the design and numbers of units to be produced
rather than any issues
involved in translating from the software domain to the hardware domain.
Generally, a design that
is still subject to frequent change may be preferred to be implemented in
software, because re-
31
CA 2846601 2020-04-02
spinning a hardware implementation is more expensive than re-spinning a
software design.
Generally, a design that is stable that will be produced in large volume may
be preferred to be
implemented in hardware, for example in an application specific integrated
circuit (ASIC), because
for large production runs the hardware implementation may be less expensive
than the software
implementation. Often a design may be developed and tested in a software form
and later
transformed, by well known design rules, to an equivalent hardware
implementation in an
application specific integrated circuit that hardwires the instructions of the
software. In the same
manner as a machine controlled by a new ASIC is a particular machine or
apparatus, likewise a
computer that has been programmed and/or loaded with executable instructions
may be viewed as
a particular machine or apparatus.
[0085] The secondary storage 684 is typically comprised of one or more disk
drives or tape
drives and is used for non-volatile storage of data and as an over-flow data
storage device if RAM
688 is not large enough to hold all working data. Secondary storage 684 may be
used to store
programs which are loaded into RAM 688 when such programs are selected for
execution. The
ROM 686 is used to store instructions and perhaps data which are read during
program execution.
ROM 686 is a non-volatile memory device which typically has a small memory
capacity relative to
the larger memory capacity of secondary storage. The RAM 688 is used to store
volatile data and
perhaps to store instructions. Access to both ROM 686 and RAM 688 is typically
faster than to
secondary storage 684.
[0086] I/O 690 devices may include printers, video monitors, liquid crystal
displays (LCDs),
touch screen displays, keyboards, keypads, switches, dials, mice, track balls,
voice recognizers,
card readers, paper tape readers, or other well-known input devices. The
network connectivity
devices 692 may take the form of modems, modem banks, ethernet cards,
universal serial bus
(USB) interface cards, serial interfaces, token ring cards, fiber distributed
data interface (FDD1)
cards, wireless local area network (WLAN) cards, radio transceiver cards such
as code division
multiple access (CDMA) and/or global system for mobile communications (GSM)
radio
transceiver cards, and other well-known network devices. These network
connectivity 692 devices
may enable the processor 682 to communicate with an Internet or one or more
intranets. With
such a network connection, it is contemplated that the processor 682 might
receive information
from the network, or might output information to the network in the course of
performing the
above-described method steps. Such information, which is often represented as
a sequence of
32
CA 2846601 2020-04-02
instructions to be executed using processor 682, may be received from and
outputted to the
network, for example, in the form of a computer data signal embodied in a
carrier wave
[0087] Such information, which may include data or instructions to be
executed using
processor 682 for example, may be received from and outputted to the network,
for example, in the
form of a computer data baseband signal or signal embodied in a carrier wave.
The baseband
signal or signal embodied in the carrier wave generated by the network
connectivity 692 devices
may propagate in or on the surface of electrical conductors, in coaxial
cables, in waveguides, in
optical media, for example optical fiber, or in the air or free space. The
information contained in
the baseband signal or signal embedded in the carrier wave may be ordered
according to different
sequences, as may be desirable for either processing or generating the
information or transmitting
or receiving the information. The baseband signal or signal embedded in the
carrier wave, or other
types of signals currently used or hereafter developed, referred to herein as
the transmission
medium, may be generated according to several methods well known to one
skilled in the art.
[0088] The processor 682 executes instructions, codes, computer programs,
scripts which it
accesses from hard disk, floppy disk, optical disk (these various disk based
systems may all be
considered secondary storage 684), ROM 686, RAM 688, or the network
connectivity devices 692.
[0089] In other embodiments systems, methods and tangible computer readable
storage
mediums apply discounts at a point of sale by a merchant 700, that can be
shared by a client 700,
an administrator 702 and/or the merchant 701 (see Fig. 10). The shared amount
is based on a
discount or value differentiation arrangement 1001 in place between the
administrator 702 and the
merchant 701. For example, an insurance company as the client 700 can use such
systems,
methods, and instructions to reduce the cost of services or materials
purchased as part of an
insurance claim by an insured. The insured or their representative, as a buyer
705, is provided with
an account from the account administrator 702 to purchase goods or services to
fulfill the claim.
Preferably, the account is a merchant-filtered account and is only usable at
certain merchants 701
(although this aspect may be optional), wherein such certain merchants 701
have agreed to
discounts or value differentiation arrangements 1001 with the administrator
702. In another
embodiment, some merchants 701 have a discount or value differentiation
arrangement 1001 with
the administrator 702 while others do not and an incentive, such as a customer
or buyer targeted
33
CA 2846601 2020-04-02
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
discount or value differentiation, may be provided to the buyer 705 related to
such certain
merchants 701 or a subset thereof.
[0090] In one embodiment, when the buyer 705 uses the account for a
purchase, the full
purchase price is initially charged to the account and the discount is
subsequently taken. Thus, the
discount is hidden from the buyer 705 and the transaction appears to the buyer
705 to be a standard
transaction. However, the settlement of the transaction results in a discount
provided by the
merchant 701 which can be shared by the merchant 701, the client 702 and/or
the administrator
700. In one form, the merchant 701 is willing to provide such a discount
because of the likelihood
of increased sales volume since the merchant is one of a select few merchants
(or possibly the only
merchant) authorized to accept the account (e.g., the account is a merchant
filtered account). The
administrator 702 can implement the account so that it is only approved when
involving the
selected merchants 701 which have a discount arrangement 1001 with the
administrator 702.
100911 In another embodiment, when the buyer 705 uses the account for a
purchase, the
purchase price reflects a customer or buyer targeted discount or value
differentiation, including
reward points that can be used for the merchant or for a group of merchants
such as the certain
merchants 701 and an additional client/administrator targeted discount or
value differentiation is
subsequently taken. Thus, a portion of the total discount or value
differentiation is realized
amongst the buyer or customer 705, the client 702 and the administrator 702.
Such an approach
can incentivize all parties involved in the purchase, the buyer, the client,
the administrator, and the
certain merchants that stand to gain an increased use from buyers or
customers. Herein, where an
embodiment describes only a client/administrator targeted discount or value
differentiation,
another embodiment would include a buyer/customer targeted discount or value
differentiation as
described above.
[0092] In general, after a user account has been properly activated, the
value associated with
the account may be used to facilitate a transaction. In an exemplary
transaction, the account (or a
proxy for the account such as a stored value card) may be presented at a point
of sale (POS) to
effectuate the transaction. For example, the card may be swiped at the POS
system of a merchant
to initiate a card-based transaction, e.g., the swiping of the card's magnetic
stripe to convey card
transaction information to the POS, in alternative embodiments the card's
transaction information
may be conveyed to the POS via mnemonic transfer, QR code, barcode, NFC chip,
or
combinations thereof) via a keypad, keyboard, voice recognition device,
scanning device, swiping
34
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
device, NFC communication device, Bluetooth communication device, Wi-Fl, or
combinations
thereof. In alternative embodiments, the point of sale may be located at a
vendor and/or redeeming
merchant or retailer, but alternatively located at a kiosk or at a user's
home, office, or other
public/private areas where a personal computer, or other electronic device, is
configured to act as a
point of sale, for example during an on-line transaction. In alternative
embodiments the card may
be a physical card or a virtual card, wherein the virtual card is an
electronic representation of the
card and may be stored on a cardholder's personal electronic devices, e.g.,
home computer,
portable computer, tablet computer, smart phone, or other similar devices. In
additional
embodiments, the virtual card may be stored in a cardholder's electronic
wallet. The following
descriptions of the Figures illustrate some exemplary scenarios implementing
the above described
concepts along with additional activities and functions pertinent to the
instantly disclosed methods
and systems.
[0093] Figure 7 illustrates an exemplary transaction flow in accordance
with one embodiment
of the present invention. After activation by the client at 70, the card 704
is swiped at the POS
(Point of Sale) system at 71 (the POS operator performs the transaction as any
other purchase
procedure) of the merchant 701 or used t the merchant online website to
initiate a card-based
transaction, e.g., the swiping of the card's magnetic stripe to convey card
transaction information
to the POS. The merchant's POS system sends an authorization request to the
network (via their
acquirer and the card processor) at 72. The card processor authorizes the
transaction if the
merchant 701 is one of the select, authorized merchants, and reduces the funds
on the card
accordingly at 73. Steps 70 through 73 reflect a typical payment network
example. The dashed
line 77 indicates a traditional payment sequence; the systems, methods, and
instructions herein
replace the dashed line 77 for merchants 701 which have a discount arrangement
1001 with the
administrator 702. In some implementations, transactions involving merchants
who do not have a
discount arrangement 1001 with the administrator 702 are rejected by the card
processor 703.
[0094] Continuing with Figure 7, at 74, the merchant discount fee (which is
maintained by an
ancillary system) is deducted from the authorization amount and stored in a
master account
(separate from the cardholder account). At 75, the daily settlement (ROC-
record of charge) is
reduced by the merchant fee (commission) as determined at 74. At 75, the
settlement amount
(ROC) paid to the merchant 701 (e.g., merchant fee are maintained in an
ancillary system with a
unique commission/fee rate for each participating merchant.
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[0095] The discount amount (commission-fee, e.g., $10) is in the control of
the administrator
702 (e.g., issuer) and can then be re-distributed to the supply chain per the
individual discount
arrangements 1001 in the applicable, various settlement agreements between the
administrator 702,
the client 700 and/or each merchant 701 (see Fig. 10).
[0096] The settlement and the commission may be netted daily. This
eliminates the need to
invoice the fees from the card issuer (i.e., administrator 702 as the program
manager) and
eliminates the need to pay the invoice by the merchant 701. The systems,
methods, and instructions
expedite cash flow and reduce risks of bad debt by eliminating accounts
receivables from the
merchant 701 to the administrator 702.
[0097] Where a customer/buyer discount or value differentiation is included
in the transaction,
the discount or value may be provided by the merchant through its online
website or at the point of
sale. One example is that the customer/buyer, upon using the payment card,
which includes stored
value cards and electronic stored value cards, may be provided a discount code
to use for that or
subsequent purchases which may be by customer election. Such discount or value
differentiation
may apply automatically to the transaction or may be credited to an applicable
customer/buyer
account, such as an electronic wallet.
10098] Figure 8 illustrates an exemplary transaction flow in accordance
with another
embodiment of the present invention wherein the point of sale discount offered
by merchants 701
to program participating cardholders. The volume discount is not intended for
the cardholder
(buyer 705) as it is to be distributed to one or more clients 700 in the
supply chain.
[0099] After a client 700 activates funds to an account at 80, the card 704
is swiped at the POS
(Point of Sale) system 81 of the merchant 701. Optionally, the POS operator
selects an appropriate
discount level (e.g. level 3) at 88 based upon the program parameters. The
merchant's POS system
sends an authorization request to the network (via their acquirer and the card
processor) at 82.
1001001 At 83, the card processor 703 authorizes the transaction and
reduces the funds on the
card accordingly. Steps 80 through 83 reflect a typical payment network
example. The dashed
line 87 indicates a traditional payment sequence; the systems, methods, and
instructions herein
replace the dashed line 87 for merchants 701 which have a discount arrangement
1001 with the
administrator 702. In some implementations, transactions involving merchants
who do not have a
discount arrangement 1001 with the administrator 702 are rejected by the card
processor 703.
36
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[00101] At 84,
the merchant discount fee (which is maintained by an ancillary system) is
deducted from the authorization amount and stored in a master account
(separate from the
cardholder account). The daily settlement (ROC-record of charge) at 85 is
reduced by the
merchant fee (commission) as determined at 84.
[00102] The
discount amount (commission-fee, e.g., $20) may triggered at the POS by the
merchant 701 in accordance with contracted volume discounts. The discount
amount is in the
control of the administrator 702 and can then be re-distributed to the supply
chain per the
individual discount arrangements 1001 in the applicable, various settlement
agreements between
the administrator 702 and each merchant 701 (see Fig. 10).
[00103] As shown in Figure 8, program managers are allowed to aggregate like-
type purchases
and drive similar buyers (cardholders) to the merchant for volume discounts,
etc. The settlement
and the commission may be netted daily. This eliminates the need to invoice
the fees from the card
issuer (program manager) and eliminates the need to pay the invoice by the
merchant. The systems,
methods, and instructions expedite cash flow and reduce risks of bad debt by
eliminating accounts
receivables from the merchant to the card issuer (program manager).
100104] Figure 9 illustrates a sequence diagram implementing a net discount of
20% distributed
between an administrator 702 and a corporate client 700. Figure 4 is a block
diagram of a system
illustrating the various interactions between components of the system. In one
form, the client 700,
the card administrator 702 and the merchant 701 illustrated in Figure 10 can
be a processor or
server providing electronic communication there between, although some of the
communication as
indicated by the arrows may be implemented by verbal or written
correspondence. In various
embodiments and as described previously, a card can be a physical credit or
debit card, a smart
card, an NFC (near field communication) chip account on an mobile device or a
virtual card which
is essentially an account number or account. Similarly, as used herein, an
account can be any of an
account for a physical credit or debit card, a smart card or an NFC chip
account on a mobile
device. In some implementations, transactions involving merchants who do not
have a discount
arrangement 1001 with the administrator 702 are rejected by the card
processor.
[00105] The
system as illustrated is for use by a client 700 to implement transactions
between a
buyer 705 and merchants 701 providing a discount to the client 700. In this
scenario, the
transactions are funded by the client 700. As noted, the blocks in Fig. 10 may
each be
37
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
implemented as one or more processors for executing computer executable
instructions stored on a
tangible computer readable storage medium. The executed instructions implement
the following.
[00106] Referring to Figures 9 and 10, at 91, responsive to input from the
client 700 at 90
providing instructions to activate an account with funds for use in
transactions on behalf of the
client 700. At 92, responsive to receiving an authorization request from a
merchant 701 for a
particular transaction for a particular purchase amount using the activated
account, instructions
approve the particular transaction when the merchant 701 is an authorized
merchant and when the
particular purchase amount is less than or equal to the remaining funds in the
activated account. At
93, responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions reduce the
funds of the activated
account by the particular purchase amount of the particular transaction. The
dashed line 991
indicates a traditional payment sequence; the systems, methods, and
instructions herein replace the
dashed line 991 for merchants 701 which have a discount arrangement 1001 with
the administrator
702. At 94, responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions
transfer a discount
amount of the funds in the activated account to an administrator 702 of the
account. At 95,
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions transfer a
settlement amount (ROC)
of the funds in the activated account to the merchant 701. At 96, responsive
to the approved
particular transaction, instructions transfer a net discount of the discount
amount to an account of
the client 700, the administrator 702 and/or the merchant 701.
[00107] In one form, the client 700 is an insurer and the buyer 700 is an
insured of the insurer
or a representative of the insured.
[00108] In one form, responsive to receiving an indication from the
merchant 701 for a
particular discount or value differentiation option to be applied to the
transaction, the instructions
transfer a discount amount at 97. In particular, the instructions transfer a
discount amount
corresponding to the indicated discount option indicated by the merchant 701.
[00109] In one form, instructions a 98 transfer to the client 700 any
remaining funds in the
activated account after a preset period of time.
[001101 In one form, at 99, a portion of the discount amount transferred to
the administrator is
retained by the administrator as an administrative fee.
[00111] In one form, the instructions transferring the net discount of the
discount amount are
executed in real-time at the time of the transaction.
38
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[001121 In one form, the system includes a plurality of clients 700, a
plurality of buyers 705
and a plurality of merchants 701. Each of the merchants 701 has a unique
settlement agreement
specifying a unique discount arrangement 1001 with the administrator 702. The
settlement amount
(ROC) of the funds in the activated account is paid to the merchant 701 in
accordance with the
unique settlement agreement of each merchant 701.
[00113] The discount (commission-fee, e.g., $10) is in the control of the
administrator 702
(e.g., issuer) and can then be re-distributed back to the supply chain per the
discount arrangements
1001 in the applicable settlement agreements.
[00114] The following is a non-exhaustive list of some examples of payments
types of the
systems, methods, and instructions herein: Prepaid Debit Account (open loop
cards with
transactions over networks such as American Express, Discover, MasterCard and
Visa); Debit
Account (open loop cards with transactions over networks such as American
Express, Discover,
MasterCard and Visa); Credit Card Account (open loop cards with transactions
over networks such
as American Express, Discover, MasterCard and Visa), Closed Loop Accounts
(filtered gift cards,
universal gift cards, proxy cards). The foregoing are exemplary as other types
are contemplated
and known in the art.
[00115] The following is a non-exhaustive list of some examples of payments
form factors of
the systems, methods, and instructions herein: Traditional Plastic Card ¨ one
or more cards may be
associated with an account; Virtual Card (eSVC or Card not present) ¨ an
account for an open loop
(prepaid, debit or credit) may be used for an on-line transaction; Mobile Card
¨ a contactless, EMV
or any mobile device with appropriate account credentials that are validated
at the POS. The
foregoing are exemplary as other types are contemplated and known in the art.
[00116] In another form, the client 700 can be an employer and the buyer 705
can be an
employee or agent of the buyer 705 purchasing on behalf of the employer or
purchasing for the
employee's or agent's use. Thus, systems, methods and instructions as noted
herein can also be
used in an employer/employee relationship. In another form, a coupon situation
can be
implemented; the sequence is similar: a coupon is in effect a discount off an
item. This allows for
real-time value of moving funds rather than waiting for days or even a month
for the settlement
process to occur.
39
[00117] The embodiments herein can be implemented in real-time by a merchant-
filtered card
or account, such as described in U.S. Patent No. 5,689,100, and does not
require settlement of
monthly invoicing back to each merchant.
[00118] For purposes of illustration, programs and other executable program
components, such
as the operating system, are illustrated herein as discrete blocks. It is
recognized, however, that
such programs and components reside at various times in different storage
components of a
computing device, and are executed by a data processor(s) of the device.
[00119] Although described in connection with an exemplary computing system
environment,
embodiments of the aspects of the invention are operational with numerous
other general purpose
or special purpose computing system environments or configurations. The
computing system
environment is not intended to suggest any limitation as to the scope of use
or functionality of any
aspect of the invention. Moreover, the computing system environment should not
be interpreted as
having any dependency or requirement relating to any one or combination of
components
illustrated in the exemplary operating environment. Examples of well-known
computing systems,
environments, and/or configurations that may be suitable for use with aspects
of the invention
include, but are not limited to, personal computers, server computers, hand-
held or laptop devices,
multiprocessor systems, microprocessor-based systems, set top boxes,
programmable consumer
electronics, mobile telephones, network PCs, minicomputers, mainframe
computers, distributed
computing environments that include any of the above systems or devices, and
the like.
[00120] Embodiments of the aspects of the invention may be described in the
general context
of data and/or processor-executable instructions, such as program modules,
stored one or more
tangible, non-transitory storage media and executed by one or more processors
or other devices.
Generally, program modules include, but are not limited to, routines,
programs, objects,
components, and data structures that perform particular tasks or implement
particular abstract data
types. Aspects of the invention may also be practiced in distributed computing
environments
where tasks are performed by remote processing devices that are linked through
a communications
network. In a distributed computing environment, program modules may be
located in both local
and remote storage media including memory storage devices.
[00121] In operation, processors, computers and/or servers may execute the
processor-
executable instructions (e.g., software, firmware, and/or hardware) such as
those illustrated herein
to implement aspects of the invention.
CA 2846601 2020-04-02
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
[00122]
Embodiments of the aspects of the invention may be implemented with processor-
executable instructions. The processor-executable instructions may be
organized into one or more
processor-executable components or modules on a tangible processor readable
storage medium.
Aspects of the invention may be implemented with any number and organization
of such
components or modules. For example, aspects of the invention are not limited
to the specific
processor-executable instructions or the specific components or modules
illustrated in the figures
and described herein. Other embodiments of the aspects of the invention may
include different
processor-executable instructions or components having more or less
functionality than illustrated
and described herein.
[00123] While several embodiments have been provided in the present
disclosure, it should be
understood that the disclosed systems and methods may be embodied in many
other specific forms
without departing from the spirit or scope of the present disclosure. The
present examples are to be
considered as illustrative and not restrictive, and the intention is not to be
limited to the details
given herein. For example, the various elements or components may be combined
or integrated in
another system or certain features may be omitted, or not implemented.
Moreover, one or more of
the embodiments disclosed herein may be combined with one or more of the other
embodiments
disclosed herein to reflect the needs, desires and preferences of the entity
or entities implementing
the methods and systems disclosed herein.
[00124] The ordering of steps in the various processes, data flows, and
flowcharts presented are
for illustration purposes and do not necessarily reflect the order that
various steps must be
performed. The steps may be rearranged in different orders in different
embodiments to reflect the
needs, desires and preferences of the entity implementing the systems.
Furthermore, many steps
may be performed simultaneously with other steps in some embodiments.
[00125] Also, techniques, systems, subsystems and methods described and
illustrated in the
various embodiments as discrete or separate may be combined or integrated with
other systems,
modules, techniques, or methods without departing from the scope of the
present disclosure.
Other items shown or discussed as directly coupled or communicating with each
other may be
coupled through some interface or device, such that the items may no longer be
considered
directly coupled to each other but may still be indirectly coupled and in
communication, whether
electrically, mechanically, or otherwise with one another. Other examples of
changes,
41
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
substitutions, and alterations are ascertainable by one skilled in the art and
could be made without
departing from the spirit and scope disclosed herein.
[00126] When introducing elements of aspects of the invention or the
embodiments thereof,
the articles "a," "an," "the," and "said" are intended to mean that there are
one or more of the
elements. The terms "comprising," "including," and "having" are intended to be
inclusive and
mean that there may be additional elements other than the listed elements.
[00127] In view of the above, it will be seen that several advantages of
the aspects of the
invention are achieved and other advantageous results attained.
[001281 Not all of the depicted components illustrated or described may be
required. In
addition, some implementations and embodiments may include additional
components.
Variations in the arrangement and type of the components may be made without
departing from
the spirit or scope of the claims as set forth herein. Additional, different
or fewer components
may be provided and components may be combined. Alternatively or in addition,
a component
may be implemented by several components.
[001291 The above description illustrates the aspects of the invention by
way of example and
not by way of limitation. This description enables one skilled in the art to
make and use the
aspects of the invention, and describes several embodiments, adaptations,
variations, alternatives
and uses of the aspects of the invention, including what is presently believed
to be the best mode
of carrying out the aspects of the invention. Additionally, it is to be
understood that the aspects of
the invention is not limited in its application to the details of construction
and the arrangement of
components set forth in the following description or illustrated in the
drawings. The aspects of the
invention are capable of other embodiments and of being practiced or carried
out in various ways.
Also, it will be understood that the phraseology and terminology used herein
is for the purpose of
description and should not be regarded as limiting.
[00130] Having described aspects of the invention in detail, it will be
apparent that
modifications and variations are possible without departing from the scope of
aspects of the
invention as defined in the appended claims. It is contemplated that various
changes could be
made in the above constructions, products, and methods without departing from
the scope of
aspects of the invention. In the preceding specification, various preferred
embodiments have been
described with reference to the accompanying drawings. It will, however, be
evident that various
modifications and changes may be made thereto, and additional embodiments may
be
42
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
implemented, without departing from the broader scope of the aspects of the
invention as set forth
in the claims that follow. The specification and drawings are accordingly to
be regarded in an
illustrative rather than restrictive sense.
[00131] There has been described herein a stored value card transaction system
that allows
stored value card vendors to add additional value to a card at the time the
card is purchased or
redeemed in order to provide incentives to customers to purchase or redeem a
particular card or
provide discounts to clients whom authorize funding of a stored value card. It
will be apparent to
those skilled in the art that modifications may be made without departing from
the spirit and
scope of the invention. The embodiments described are representative only, and
are not intended
to be limiting. Many variations, combinations, and modifications of the
applications disclosed
herein are possible and are within the scope of the invention. Accordingly,
the scope of
protection is not limited by the description set out above, but is defined by
the claims which
follow, that scope including all equivalents of the subject matter of the
claims.
[00132] Reference is further made to the following specific embodiments:
1. A
computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card transaction
comprising:
receiving in a stored value card transaction computer a transaction request
for a stored
value card from a point of sale terminal, wherein the transaction request
comprises at least one of a
card identification, a point of sale terminal identification, a vendor
identification, a merchant
identification, and a time of activation;
comparing at least one of the card identification, the point of sale terminal
identification,
the vendor identification, the merchant identification, and the time of
activation to stored data in a
stored value card datastore to determine if the stored value card is eligible
for a value
differentiation;
determining the value differentiation to be attributed to an account
associated with the
stored value card when the stored value card is determined to be eligible for
the value
differentiation;
transmitting the transaction request to the card issuer authorization system;
receiving a response from the card issuer authorization system; and
transmitting the response to the point of sale terminal.
43
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
2. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 1, wherein the transaction request further comprises an activation
request.
3. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 1, wherein the transaction request further comprises a redemption
request.
4. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 1, 2, or 3 further comprising:
modifying the transaction request to include the value differentiation when
the stored value
card is determined to be eligible for the value differentiation; and
transmitting a modified transaction request to the card issuer authorization
system.
5. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 1,2, 3, or 4, wherein the response comprises a reference to the
value differentiation.
6. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5, wherein the value differentiation comprises a
monetary redemption
value amount for the stored value card that differs from a purchase price of
the stored value card.
7. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 6, wherein the monetary redemption value amount for the stored
value card exceeds
the purchase price of the stored value card.
8. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 6, wherein the purchase price of the stored value card is less than
the monetary
redemption value for the stored value card.
9. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8, wherein the value differentiation
comprises a non-monetary
redemption value.
10. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9, further comprising reconciling
accounts of card transaction
interested parties.
11. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 10, wherein the card transaction interested parties comprise card
vendors, card
merchants, card issuers, a stored value card transaction system administrator,
and combinations
thereof.
44
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
12. A computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction
comprising:
receiving in a stored value card transaction computer a transaction request
for a stored
value card from a point of sale terminal, wherein the transaction request
comprises at least one of a
card identification, a point of sale terminal identification, a vendor
identification, a merchant
identification, and a time of activation;
comparing at least one of the card identification, the point of sale terminal
identification,
the vendor identification, the merchant identification, and the time of
activation to stored data in a
stored value card datastore to determine if the stored value card is eligible
for a value added award;
determining the value added award to be attributed to an account associated
with the stored
value card when the stored value card is determined to be eligible for the
value added award;
transmitting the transaction request to the card issuer authorization system;
receiving a response from the card issuer authorization system; and
transmitting the response to the point of sale terminal.
13. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 12, wherein the transaction request further comprises an activation
request
14. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 12, wherein the transaction request further comprises a redemption
request.
15. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 12, 13, or 14 further comprising:
modifying the transaction request to include the value added award when the
stored value
card is determined to be eligible for the value added award; and
transmitting a modified transaction request to the card issuer authorization
system.
16. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 12, 13, 14, or 15, wherein the response comprises a reference to
the value added
award.
17. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 12, 13, 14, 15, or 16, wherein the value added award comprises a
monetary
redemption value amount for the stored value card that differs from a purchase
price of the stored
value card.
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
18. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 17, wherein the monetary redemption value amount for the stored
value card exceeds
the purchase price of the stored value card.
19. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 17, wherein the purchase price of the stored value card is less
than the monetary
redemption value for the stored value card.
20. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, or 19, wherein the value added award
comprises a non-
monetary redemption value.
21. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, or 20, further comprising
reconciling accounts of card
transaction interested parties.
22. The computer implemented method for conducting a stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 21, wherein the card transaction interested parties comprise card
vendors, card
merchants, card issuers, a stored value card transaction system administrator,
and combinations
thereof.
23. A stored value card transaction system comprising:
a datastore maintaining account information for a plurality of stored value
cards, conditions
for receiving a value differentiation, and conditions for redeeming the value
differentiation;
a point of sale interface for receiving and transmitting a transaction message
with a point of
sale terminal;
a value added determination component to determine whether a stored value card
is eligible
for value differentiation and a type of value differentiation to be awarded to
an account associated
with a stored value card when the stored value card is eligible for the value
differentiation;
a card issuer system interface for transmitting the transaction message to,
and receiving a
response to the transaction message from, the card issuer system;
an authorization component for authorizing the stored value card transaction.
24. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 23, wherein the
transaction
message comprises an activation request.
25. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 23, wherein the
transaction
message comprises a redemption request.
46
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
26. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 23, 24, or 25
further comprising a
message modification component for modifying messages to at least one of the
point of sale
terminal and the card issuer system to indicate information about the value
differentiation
associated with a stored value card transaction.
27. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 23, 24, 25, or
26, wherein the
response comprises a reference to the value differentiation.
28. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 23, 24, 25, 26,
or 27, wherein the
value differentiation comprises a monetary redemption value amount for the
stored value card that
differs from a purchase price of the stored value card.
29. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 28, wherein the
monetary
redemption value amount for the stored value card exceeds the purchase price
of the stored value
card.
30. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 28, wherein the
purchase price of
the stored value card is less than the monetary redemption value for the
stored value card.
31. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 23, 24, 25, 26,
27, 28, 29, or 30,
wherein the value differentiation comprises, and when applicable further
comprises, a non-
monetary redemption value.
32. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 23, 24, 25, 26,
27, 28, 29, 30, or
31, further comprising a reconciliation component for reconciling accounts of
card transaction
interested parties.
31 The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 32, wherein the
card transaction
interested parties comprise card vendors, card merchants, card issuers, a
stored value card
transaction system administrator, and combinations thereof.
34. A stored value card transaction system comprising:
a datastore maintaining account information for a plurality of stored value
cards, conditions
for receiving a value added award, and conditions for redeeming the value
added award;
a point of sale interface for receiving and transmitting a transaction message
with a point of
sale terminal;
a value added determination component to determine whether a stored value card
is eligible
for the value added award and a type of value added award to be awarded to an
account associated
with a stored value card when the stored value card is eligible for the value
added award;
47
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
a card issuer system interface for transmitting the transaction message to,
and receiving a
response to the transaction message from, the card issuer system;
an authorization component for authorizing the stored value card transaction.
35. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 34, wherein the
transaction
message comprises an activation request.
36. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 34, wherein the
transaction
message comprises a redemption request.
37. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 34, 35, or 36
further comprising a
message modification component for modifying messages to at least one of the
point of sale
terminal and the card issuer system to indicate information about the value
added award associated
with a stored value card transaction.
38. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 34, 35, 36, or
37, wherein the
response comprises a reference to the value added award.
39. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 34, 35, 36, 37,
or 38, wherein the
value added award comprises a monetary redemption value amount for the stored
value card that
differs from a purchase price of the stored value card.
40. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 39, wherein the
monetary
redemption value amount for the stored value card exceeds the purchase price
of the stored value
card.
41. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 39, wherein the
purchase price of
the stored value card is less than the monetary redemption value for the
stored value card.
42. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 34, 35, 36, 37,
38, 39, 40, or 41,
wherein the value added award comprises, and when applicable further
comprises, a non-monetary
redemption value.
43. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 34, 35, 36, 37,
38, 39, 40, 41, or
42, further comprising a reconciliation component for reconciling accounts of
card transaction
interested parties.
44. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 43, wherein the
card transaction
interested parties comprise card vendors, card merchants, card issuers, a
stored value card
transaction system administrator, and combinations thereof.
48
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
45. A computer implemented method for conducting the stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,18, 19,
20, 21, or 22, wherein the
stored value card transaction request further comprises transaction
information for at least two
stored value cards.
46. The computer implemented method for conducting the stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 45, wherein the value differentiation, when present, is allocated
equally between the
at least two stored value cards.
47. The computer implemented method for conducting the stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 45, wherein the value differentiation, when present, is allocated
disproportionately
between the at least two stored value cards.
48. The computer implemented method for conducting the stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 46 or 47, wherein value differentiation allocation, when performed,
is directed by
card transaction interested parties, card purchasers, card redeemers, or a
combination thereof.
49. The computer implemented method for conducting the stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 45, wherein the value added award, when present, is allocated
equally between the at
least two stored value cards.
50. The computer implemented method for conducting the stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 45, wherein the value added award, when present, is allocated
disproportionately
between the at least two stored value cards.
51. The computer implemented method for conducting the stored value card
transaction of
embodiment 46 or 47, wherein value added award allocation, when performed, is
directed by card
transaction interested parties, card purchasers, card redeemers, or a
combination thereof
52. The stored value card transaction system of embodiment 23, 24, 25, 26,
27, 28, 29, 30, 31,
32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, or 44, wherein the stored
value card transaction
system comprises a component for allocating, when present, an activation
amount, a redemption
amount, the value added award, the value differentiation, or combinations
thereof across multiple
stored value cards.
53. A computer implemented method for adding value to a stored value card
in excess of the
purchase price for the stored value card, comprising:
receiving in a stored value card transaction processor an activation request
for a stored
value card from a point of sale terminal, wherein the activation request
comprises an activation
49
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
amount and at least one of a card identification, a point of sale terminal
identification, a vendor
identification, a merchant identification, and a time of activation;
comparing at least one of the card identification, the point of sale terminal
identification,
the vendor identification, the merchant identification, and the time of
activation to stored data in a
stored value card datastore to determine if the stored value card to be
activated is eligible for a
value added award, wherein the stored value card datastore comprises a
computer readable media;
determining the value added award to he added to an account associated with
the stored
value card to be activated when the stored value card is determined to be
eligible for the value
added award;
modifying the activation request to include the value added award when the
stored value
card is determined to be eligible for the value added award;
transmitting the modified activation request to the card issuer authorization
system;
receiving an activation response from the card issuer authorization system;
and
transmitting the activation response to the point of sale terminal.
54. A stored
value card transaction system for activating and redeeming stored value cards
with
value added bonuses, comprising:
a datastore maintaining account information for a plurality of stored value
cards, conditions
for receiving a value added bonus, and conditions for redeeming a value added
bonus;
a point of sale interface for receiving and transmitting activation and
redemption messages
with a point of sale terminal;
a value added determination component to determine whether a stored value card
is eligible
for a value added bonus and the type of value added bonus to be awarded to an
account associated
with a stored value card when the stored value card is eligible for a value
added bonus;
a card issuer system interface for transmitting and receiving messages with a
card issuer
system;
a message modification component for modifying messages to one of the point of
sale
terminal and the card issuer system to indicate information about a value
added bonus associated
with one of an activation and a redemption of the stored value card; and
an authorization component for authorizing at least one of the awarding of a
value added
bonus, the redemption of a value added bonus, the activating of the stored
value card, and the
redemption of the stored value card.
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
55. A system for use by a client to implement transactions between a buyer
and merchants
providing a discount to the client, wherein the transactions are funded by the
client, said system
comprising:
one or more processors for executing computer executable instructions stored
an a
tangible computer readable storage medium, said instructions comprising:
responsive to input from the client, instructions for activating an account
with funds for
use in transactions for the client;
responsive to receiving an authorization request from a merchant for a
particular
transaction for a particular purchase amount using the activated account,
instructions for approving the particular transaction when the merchant is an
authorized merchant and when the particular purchase amount is less than or
equal to the remaining funds in the activated account;
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for reducing
the funds of
the activated account by the particular purchase amount of the particular
transaction;
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a discount
amount of the funds in the activated account to an administrator of the
account;
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a
settlement amount (ROC) of the funds in the activated account to the merchant;
and
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a net
discount of the discount amount to an account of the client or the merchant.
56. The system of embodiment 55 wherein the client is an insurer and the buyer
is an insured of
the insurer.
57. The system of embodiment 55 wherein responsive to receiving an indication
from the
merchant for a particular discount option to be applied to the transaction,
the instructions for
transferring a discount amount comprise instructions for transferring a
discount amount
corresponding to the indicated discount option indicated by the merchant.
58. The system of embodiment 55 further comprising instructions for
transferred to the client
any remaining funds in the activated account after a preset period of time.
51
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
59. The system of embodiment 55 wherein a portion of the discount amount
transferred to the
administrator is retained by the administrator as an administrative fee.
60. The system of embodiment 55 wherein the instructions for transferring the
net discount of
the discount amount are executed in real-time at the time of the transaction.
61. The system of embodiment 55 wherein there a plurality of clients, a
plurality of buyers and a
plurality of merchants, wherein each of the merchants has a unique settlement
agreement
specifying a unique discount arrangement with the administrator, and wherein
the settlement
amount (ROC) of the funds in the activated account are paid to the merchant in
accordance with
the unique settlement agreement of the merchant.
62. A method for use by a client to implement transactions between a buyer and
merchants
providing a discount to the client, wherein the transactions are funded by the
client, said method
comprising computer-executable instructions executed by a processor, said
instructions
comprising:
responsive to input from the client, instructions for activating an account
with funds for
use in transactions for the client;
responsive to receiving an authorization request from a merchant for a
particular
transaction for a particular purchase amount using the activated account,
instructions for approving the particular transaction when the merchant is an
authorized merchant and when the particular purchase amount is less than or
equal to the remaining funds in the activated account;
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for reducing
the funds of
the activated account by the particular purchase amount of the particular
transaction;
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a discount
amount of the funds in the activated account to an administrator of the
account;
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a
settlement amount (ROC) of the funds in the activated account to the merchant;
and
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a net
discount of the discount amount to an account of the client or the merchant.
52
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
63. The method of embodiment 62 wherein the client is an insurer and the buyer
is an insured of
the insurer.
64. The method of embodiment 62 wherein responsive to receiving an indication
from the
merchant for a particular discount option to be applied to the transaction,
the instructions for
transferring a discount amount comprise instructions for transferring a
discount amount
corresponding to the indicated discount option indicated by the merchant.
65. The method of embodiment 62 further comprising instructions for
transferred to the client
any remaining funds in the activated account after a preset period of time.
66. The method of embodiment 62 wherein a portion 8f the discount amount
transferred to the
administrator is retained by the administrator as an administrative fee.
67. The method of claim 8 wherein the instructions for transferring the net
discount of the
discount amount are executed in real-time at the time of the transaction.
68. The method of embodiment 62 wherein there a plurality of clients, a
plurality of buyers and
a plurality of merchants, wherein each of the merchants has a unique
settlement agreement
specifying a unique discount arrangement with the administrator, and wherein
the settlement
amount (ROC) of the funds in the activated account are paid to the merchant in
accordance with
the unique settlement agreement of the merchant.
69. A tangible computer readable storage medium for use by a client to
implement transactions
between a buyer and merchants providing a discount to the client, wherein the
transactions are
funded by the client, said tangible computer readable storage medium
comprising computer
executable instructions executable by a processor, said instructions
comprising:
responsive to input from the client, instructions for activating an account
with funds for
use in transactions for the client;
responsive to receiving an authorization request from a merchant for a
particular
transaction for a particular purchase amount using the activated account,
instructions for approving the particular transaction when the merchant is an
authorized merchant and when the particular purchase amount is less than or
equal to the remaining funds in the activated account;
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for reducing
the funds of
the activated account by the particular purchase amount of the particular
transaction;
53
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a discount
amount of the funds in the activated account to an administrator of the
account;
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a
settlement amount (ROC) of the funds in the activated account to the merchant;
and
responsive to the approved particular transaction, instructions for
transferring a net
discount of the discount amount to an account of the client or the merchant.
70. The tangible computer readable storage medium of embodiment 69 wherein the
client is an
insurer and the buyer is an insured of the insurer.
71. The tangible computer readable storage medium of embodiment 69 wherein
responsive to
receiving an indication from the merchant for a particular discount option to
be applied to the
transaction, the instructions for transferring a discount amount comprise
instructions for
transferring a discount amount corresponding to the indicated discount option
indicated by the
merchant.
72. The tangible computer readable storage medium of embodiment 69 further
comprising
instructions for transferred to the client any remaining funds in the
activated account after a
preset period of time.
73. The tangible computer readable storage medium of embodiment 69 wherein a
portion of the
discount amount transferred to the administrator is retained by the
administrator as an
administrative fee.
74. The tangible computer readable storage medium of embodiment 69 wherein the
instructions
for transferring the net discount of the discount amount are executed in real-
time at the time of
the transaction.
75. The tangible computer readable storage medium of embodiment 69 wherein
there a plurality
of clients, a plurality of buyers and a plurality of merchants, wherein each
of the merchants has a
unique settlement agreement specifying a unique discount arrangement with the
administrator,
and wherein the settlement amount (ROC) of the funds in the activated account
are paid to the
merchant in accordance with the unique settlement agreement of the merchant.
76. The embodiments described above wherein such embodiments include a
customer/buyer
discount or value differentiation that may be an additional discount or value
differentiation
54
CA 02846601 2014-03-14
determined by the unique settlement agreements of the merchants or
alternatively may be
provided by administrator as a portion of the client/administrator discount.