Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
81780341
1 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR NARROW BANDWIDTH DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
11 FIELD OF THE INVENTION
12 The present
invention provides for methods and systems for
13 digitally processing narrow bandwidth digital signals.
14 Specifically, some embodiments relate to digitally processing an
audio signal where the audio content is restricted to only a few
16 octaves.
17
18 BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
19 Narrow
bandwidth audio processing has a variety of
applications, including voice communications in extreme first
21 responder environments, auscultation of various body sounds,
22 hydrophones, telecommunications, or unusual speaker/microphone
23 situations where the available information is of very poor
24 quality. In these
situations, the audio content is generally
1
CA 2854086 2017-12-21
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\I-PAT\PkI 2013\APP\1245-13 Bonglovi
Acoustic8\Patent_4pp1ication_FIled_1245.doc
1 restricted to only a few octaves.
2
Although traditional, full spectrum audio enhancement
3 systems and methods are capable of enhancing the sound quality
4 of narrow bandwidth audio content, these standard configurations
tend to be underutilized and fall short of achieving stellar
6 quality enhancements.
Accordingly, it would be beneficial to
7 improve audio processing and enhancement for narrow bandwidth
8 audio content throughout various applications, in order to
9 produce a clear and easily interpretable audio output. Further,
it would be beneficial to allow a user to calibrate the audio
11 processing for different applications having different narrow
12 bandwidth frequency ranges.
13
14 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention meets the existing needs described
16 above by providing for a system and method for narrow bandwidth
17 processing of an audio signal, in order to create a clear and
18 easily, interpretable audio output.
19
Accordingly, in initially broad terms, an audio input
signal is first filtered through a high pass filter. The high
21 pass filter may comprise a resonant high pass filter with a
22 first frequency. As
such, the frequencies of the audio input
23 signal above the first frequency are passed through to a first
24 compressor as a filtered signal. The first compressor comprises
2
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
=
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 BonglovL
Acoustz.cs\Patent_App1Ication_FL1ed_1245.doc
1 dynamic gain compression capabilities in order to modulate the
2 filtered signal.
3 In
some embodiments, the modulated signal is then
4 transmitted to a clipping module in order to create a partially
processed signal. The
clipping module limits the gain of the
6 modulated signal in order to create a partially processed
7 signal. In
other embodiments, the filtered signal from the
8 first compressor is transmitted as the partially processed
9 signal, without the use of a clipping module.
In some embodiments, the partially processed signal is sent
11 to a transmitter for transmission to a receiver over a
12 communications network, the receiver then transmits the
13 partially processed signal to a splitter. In other embodiments,
14 the partially processed signal is sent directly to the splitter
without the use of a transmitter or receiver.
16 The
partially processed signal is then split in the
17 splitter into a first signal and a second signal. The
first
18 signal, is then filtered through a low pass filter. The low pass
19 filter may comprise a resonant low pass filter with a second
frequency. The
frequencies below the second frequency are
21 passed through. In a preferred embodiment, and counterintuitive
22 to expected function, the second frequency is selected to be
23 lower .than the first frequency. This
allows the resultant
24 signal to be used to rebuild usable dynamics from the low
3
81780341
1 frequencies. The second signal is transmitted to a pass through
2 module. The pass through module may be configured to adjust the gain
3 of the second signal. The pass through module may simply pass
4 through the second signal without any modification. Further, the
gain adjustment may be a static adjustment. The filtered first
6 signal and gain-adjusted are then combined in a mixer in order to
7 create a combined signal.
8 In some embodiments, the combined signal is then processed by a
9 tone control module. The tone control module may comprise a
parametric equalizer or other equalizer configured to fine tune the
11 signal. In at least one embodiment, the processed signal from the
12 tone control module may then be modulated by a second compressor.
13 The modulated signal is then sent as the output signal. In other
14 embodiments, the combined signal, from the mixer may be directly
sent as the output signal, without the use of the tone control
16 module or the second compressor.
17 In some embodiments, there is provided a system for narrow
18 bandwidth digital signal processing of an input audio signal comprising:
19 a high pass filter configured to filter the input audio signal to create
a filtered signal, a first processing module configured to process the
21 filtered signal to create a partially processed signal, a splitter
22 configured to split the partially processed signal into a first signal
23 and a second signal, a low pass filter configured to filter the first
24 signal, a pass through module configured to adjust the gain of the
second signal, and a second processing module configured to process the
4
CA 2854086 2017-12-21
81780341
1 filtered first signal and gain-adjusted second signal to create an
2 output signal, wherein said second processing module comprises: a
3 mixer configured to combine the filtered first signal and gain
4 adjusted second signal in order to create a combined signal; a tone
control module configured to process the combined signal in order to
6 create a controlled signal; and a second compressor configured to
7 modulate the controlled signal to create the output signal.
8 In
some embodiments, there is provided a system for narrow
9 bandwidth digital signal processing of an input audio signal
comprising: a pre-transmission module configured to receive the
11 input audio signal and create a partially processed signal, wherein
12 said pre-transmission module comprises: a high pass filter
13 configured to filter the input audio signal to create a filtered
14 signal, a first processing module configured to process the filtered
signal to create the partially processed signal, a transmitter
16 structured to transmit the partially processed signal, a receiver
17 structured to receive the partially processed signal, and a post-
18 transmission module configured to further process the partially
19 processed signal to create an output signal, wherein said post-
transmission module comprises: a splitter configured to split the
21 received signal into a first signal and a second signal, a low pass
22 filter configured to filter the first signal to create a filtered
23 first signal, a pass through module configured to adjust the gain of
24 the second signal to create a gain-adjusted second signal, a second
processing module configured to process the filtered first signal
26 and gain-adjusted second signal to create the output signal, wherein
4a
CA 2854086 2017-12-21
81780341
1 said second processing module comprises: a mixer configured to
2 combine the filtered first signal and gain-adjusted second signal to
3 create a combined signal; a tone control module configured the
4 process the combined signal to create a controlled signal; and a
second compressor configured to modulate the controlled signal to
6 create the output signal.
7 In
some embodiments, there is provided a method for narrow
8 bandwidth digital signal processing of an input audio signal
9 comprising: filtering the input audio signal with a high pass filter
to create a filtered signal, processing the filtered signal with a
11 first processing module to create a partially processed signal,
12 splitting the partially processed signal with a splitter into a
13 first signal and a second signal, filtering the first signal with a
14 low pass filter to create a filtered first signal, adjusting the
gain on the second signal with a pass through module to create a
16 gain-adjusted second signal, processing the filtered first signal
17 and gain-adjusted second signal with a second processing module to
18 create an output signal, wherein the processing the filtered first
19 signal and gain adjusted second signal comprises: combining the
filtered first signal and gain-adjusted second signal with a mixer
21 to create a combined signal; processing the combined signal with a
22 tone control module to create a controlled signal; and modulating
23 the controlled signal with a second compressor to create the output
24 signal.
4b
CA 2854086 2017-12-21
81780341
1 In some embodiments, there is provided a system for narrow
2 bandwidth digital signal processing of an input audio signal
3 comprising: a high pass filter configured to filter the input audio
4 signal to create a filtered signal, a first processing module
configured to process the filtered signal to create a partially
6 processed signal, wherein said first processing module comprises a
7 first compressor configured to modulate the filtered signal to
8 create the partially processed signal, a splitter configured to
9 split the partially processed signal into a first signal and a
second signal, a low pass filter configured to filter the first
11 signal, a pass through module configured to adjust the gain of the
12 second signal, and a second processing module configured to process
13 the filtered first signal and gain-adjusted second signal to create
14 an output signal, wherein said second processing module comprises a
mixer configured to combine the filtered first signal and gain-
16 adjusted second signal to create the output signal.
17 Applications of the present invention may include voice
18 communication, such as those in extreme first responder environments
19 or where the available audio content is of poor or very poor
quality. In these applications, the present invention may filter out
21 background noise, and selectively enhance the frequency range of
22 voice applications in order to yield a clear and interpretable audio
23 output. In these embodiments, the first frequency may be selected
24 from the range of 2.5 kHz to 3.2 kHz,
4c
CA 2854086 2017-12-21
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Boagiovi
Acoustics\Patent_App1ication_Fi1ed_1245.doc
1 and the second frequency may be selected from the range of 700
2 Hz to 1000 Hz.
3 Other applications may include hydroohones or sonar, such
4 as those used for underwater or underground resource
exploration, and appropriate frequency ranges for such
6 applications. In body auscultations, the present invention may
7 also be used to enhance respiratory sounds, for instance as part
8 of an electronic stethoscope. The present invention may also be
9 used to enhance heart sounds, for instance as part of a device
for phonocardiogram or echocardiograph, as well as other
11 detection methods. The present invention may also be embedded
12 as part of, or connected to a computer in order to analyze pre-
13 recorded narrow bandwidth audio content. Accordingly, the first
14 and second frequency ranges, as well as gain control and
compression elements, may be set or calibrated accordingly
16 depending on the type of audio content.
17 These and other objects, features and advantages of the
18 present invention will become clearer when the drawings as well
19 as the detailed description are taken into consideration.
21 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
22 For a fuller understanding of the nature of the present
23 invention, reference should be had to the following detailed
24 description taken in connection with the accompanying drawings
5
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAI\PAI 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovi
Acoustics\Patent_App1icatIon_Fi1ed_1245.doc
1 in which:
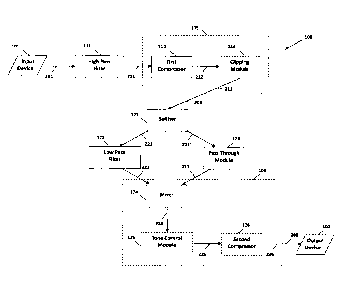
2 Figure 1 illustrates a schematic of one embodiment of the
3 present invention directed to a system for narrow bandwidth
4 processing.
Figure 2 illustrates a schematic of another embodiment of
6 the present invention directed to a broadcast variation of the
7 system of Figure 1.
8 Figure 3 illustrates a schematic of another embodiment of
9 the present invention directed to a system for narrow bandwidth
processing.
11 Figure 4 illustrates a schematic of another embodiment of
12 the present invention directed to a broadcast variation of the
13 system of Figure 3
14 Figure 5 illustrates a block diagram of another embodiment
of the present invention directed to a method for narrow
16 bandwidth processing.
17 Figure 6 illustrates a block diagram of another embodiment
18 directed to a broadcast variation for the method of Figure 5.
19 Figure 7 illustrates a block diagram of another embodiment
of the present invention directed to a method for narrow
21 bandwidth processing.
22 Figure 8 illustrates a block diagram of another embodiment
23 directed to a broadcast variation for the method of Figure 7.
24 Like reference numerals refer to like parts throughout the
6
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bonglovi
Acoustics\Patent_Application_Fi1ed_1245.doc
1 several views of the drawings.
2
3 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE EMBODIMENT
4 As
illustrated by the accompanying drawings, the present
invention is directed to systems and methods for narrow
6 bandwidth digital signal processing.
7 As
schematically represented, Figure 1 illustrates at least
8 one preferred embodiment of a system 100 for narrow bandwidth
9 digital signal processing.
Accordingly, and in these
embodiments, the system 100 generally comprises an input device
11
101, a high pass filter 111, a first processing module 105, a
12 splitter 121, a resonant low pass filter 122, a pass through
. 13 module 123, a second processing module 106, and finally an
14 output. device 102.
The input device 101 is at least partially structured or
16 configured to transmit an input audio signal 201 into the high
17 pass filter 111.
The input audio signal 201 may comprise the
18 full audible range, but will in certain applications comprise
19 less than half of the 20 Hz to 20 kHz audible range. The input
device 101 may comprise at least portions of an audio device
21 capable of audio playback.
The input device 101 for instance,
22 may comprise a stereo system, a portable music player, a mobile
23 device, a computer, a sound or audio card, or any other device
24 or combination of electronic circuits suitable for audio
7
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-AT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovl
Acoustics\Patent_App1IcatIon_FI1ed_1245.doc
1 playback.
2
The high pass filter 111 is configured to pass through high
3 frequencies of the input audio signal 201, while attenuating
4 lower frequencies, based on a first frequency. In other words,
the frequencies above the first frequency are transmitted as a
6 filtered signal 211 to the first compressor 112. In
at least
7 one embodiment, such as those for voice applications, the first
8 frequency may be selected from a range between 2.5 kHz and 3.2
9 kHz.
The first frequency however, may vary depending on the
source signal. The first frequency may further be tunable by a
11 user, or alternatively be statically set. The high pass filter
12 111 may comprise a resonant high pass filter.
The high pass
. 13 filter 111 may further comprise any circuits or combinations
14 thereof structured to pass through high frequencies above a
first frequency, and attenuate or filter out the lower
16 frequencies.
17
The first processing module 105 is configured to process
18 the filtered signal 211 and transmit a partially processed
19 signal, 205 to the splitter 121.
Accordingly, the first
processing module 105 may comprise a first compressor 112 in at
21 least one embodiment. The first processing module 105 may also
22 comprise both a first compressor 112 in other embodiments.
23 In
at least one embodiment, the first compressor 112 is
24 configured to modulate the filtered signal 211 and transmit a
8
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovi
Acoustics\Patent_1pp1ication_Filed_1245.doc
1 modulated signal 212 to the clipping module 113. In
other
2 embodiments, the first compressor 112 may transmit the modulated
3 signal 212 as the partially processed signal 205 to the
4 splitter.
The first compressor 112 may comprise an automatic
gain controller. The first compressor 112 may comprise standard
6 dynamic range compression controls such as threshold, ratio,
7 attack and release.
Threshold allows the first compressor 112
8 to reduce the level of the filtered signal 211 if its amplitude
9 exceeds a certain threshold. Ratio allows the first compressor
112 to reduce the gain as determined by a ratio. Attack and
11 release determines how quickly the first compressor 112 acts.
12 The attack phase is the period when the first compressor 112 is
. 13 decreasing gain to reach the level that is determined by the
14 threshold.
The release phase is the period that the first
compressor 112 is increasing gain to the level determined by the
16 ratio. The first compressor 112 may also feature soft and hard
17 knees to control the bend in the response curve of the output or
18 modulated signal 212, and other dynamic range compression
19 controls appropriate for the dynamic compression of an audio
signal. The
first compressor 112 may further comprise any
21 device or combination of circuits that is structured and
22 configured for dynamic range compression.
23
The clipping module 113, in at least one embodiment, is
24 configured to limit the gain of the modulated signal 212 and
9
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F,\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bonglovi
Acou8tiCs\Patent_Application_Filed_1245.doc
1 transmit a partially processed signal 213 to the splitter 121.
2 Specifically, in at least one embodiment, the clipping module
3 113 is configured to limit or remove transients from the
4 modulated signal 212. A transient is a short burst of gain or
amplitude in the audio signal. Transients may be generated if,
6 for instance, the first compressor used slower attack times in
7 the creation of the modulated signal 212. This
would ensure
8 minimum dynamic range of the partially processed signal 213. A
9 minimum dynamic range may further facilitate the transmission of
a signal over a communication network due to its smaller
11 bandwidth or file size. The clipping module 113 may comprise a
12 clipper or clipping circuit. The
clipping module 113 may
13 comprise series clippers, shunt clippers, or any combination of
14 circuits capable and appropriate for clipping or limiting
amplitude or gain of an audio signal. Additionally, the
16 clipping module 113 may also comprise soft clipping, or devices
17 or circuits capable of soft clipping in order to avoid sharp
18 points in the transfer characteristic of a signal.
19 The
splitter 121 is configured to split the partially
processed signal 213 into a first signal 221 and a second signal
21 221'. The
first signal 221 is transmitted to a low pass filter
22 122, while the second signal is transmitted to a pass through
23 module 123. In at
least one embodiment, the splitter 121 is
24 configured such that the first signal 221 and second signal 221'
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovr
Acoustics\Patent_App1icatron_Fi1ed_1245.doc
1 are substantially the same signal as the partially processed
2 signal 213, i.e. correspondingly identical amplitude and phase.
3 In other embodiments, slight variations may result due to signal
4 degradation.
The low pass filter 122 is configured to Pass through low
6 frequencies of the first signal 221, while attenuating higher
7 frequencies, based on a second frequency. In
other words, the
8 frequencies below the second frequency are transmitted as a
9 filtered first signal 222 to the mixer 124. In
at least one
embodiment, and counterintuitive to expected function, the
11 second frequency is set below that of the first frequency. In
12 voice applications the second frequency can be selected from a
. 13 range between 700 Hz and 1000 Hz.
The second frequency may
14 further be tunable by a user, or alternatively be statically
set. The resultant first filtered signal 222 is used to rebuild
16 usable dynamics from the low frequencies.
17
The pass through module 123 is configured to pass through
18 the second signal 221'. In
at least one embodiment, the pass
19 through module 123 will also adjust the gain of the second
signal. For instance, in voice applications only a small amount
21 of the signal is sufficient to achieve desired results, and the
22 gain of the second signal 221' will be adjusted downward
23 accordingly. One example of the pass through module 123 may be
24 to restore sibilance in voice applications. Other examples may
11
=
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAI\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bonglovi
Acoustics\Patent_App1icatIon_FIled_245.doc
1 include the restoration of other high frequency content if the
2 low pass filter 122 removes too much. In at
least one
3 embodiment, the level or gain adjustment of the pass through
4 module 123 is a static adjustment. The gain adjustment may also
be zero. In
other embodiments, dynamic or adjustable gain
6 reduction may be desired and used. In at least one embodiment,
7 the pass through module may simply pass through a signal without
8 any modification.
9 The
second processing module 106 is configured to process
the filtered first signal 222 and the gain-adjusted second
11 signal 223 and transmit an output signal to the output device
12 102. Accordingly, the second processing module 106 may comprise
13 a mixer 124, a tone control module 125, a second compressor 126,
14 and any combinations thereof.
The mixer 124 is configured to combine the filtered first
16 signal 222 and the gain-adjusted second signal 223 and transmit
17 a combined signal 224 to the tone control module 125 in at least
18 one embodiment. In some embodiments the combined signal 224 is
19 transmitted as the output signal 206 of the second processing
module 106. In other
embodiments the combined signal 224 is
21 further transmitted to a tone control module 125. The mixer 124
22 may comprise an electronic mixer structured to combine two or
23 more signals into a composite or combined signal. The mixer 124
24 may similarly comprise any circuit or combination of circuits
12
=
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
Fa\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovi Acoustics\Patent
Application_Filed_1245.doc
1 structured or configured to combine two or more signals.
2
The tone control module 125 processes the combined signal
3 224 and transmits a controlled signal 225 to the second
4 compressor 126 in at least one embodiment. In some embodiments
the controlled signal 225 is transmitted as the output signal
6 206, in other embodiments the controlled signal 225 is further
7 transmitted to the second compressor 126. In
at least one
8 embodiment, the tone control module 125 comprises a parametric
9 equalizer. Further, the parametric equalizer may comprise one,
two, three, or four bands. In
other embodiments, the tone
11 control module 125 may comprise a graphic equalizer. The tone
12 control module 125 may further be any device or combination of
. 13 circuits appropriate for the equalization of an audio signal.
14
The second compressor 126, in at least one embodiment, is
configured to modulate the controlled signal 225 and transmit an
16 output signal 226 to the output device 102.
The second
17 compressor 126 may be similar in structure and/or configuration
18 as the first compressor 112. Accordingly, the second compressor
19 126 may comprise any device or combination of circuits that is
structured and configured for dynamic range compression or
21 static compression or level adjustment.
22
The output device 102 may be structured to further process
23 the output signal 226.
The output device 102 may also be
24 structured and/or configured for playback of the output signal
13
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\mm DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovl_ Acoustics
\Patent_Application_Filed_1245.doc
1 226.
2 As
schematically represented, Figure 2 illustrates at least
3 one preferred embodiment of a system 100 for narrow bandwidth
4 digital signal processing in broadcasting applications.
Accordingly, and in these embodiments, the system 200 generally
6 comprises the same or similar components as system 100 as
7 illustrated in Figure 1, namely an input device 101, a high pass
8 filter' 111, a first compressor 112, a clipping module 113, a
9 splitter 121, a resonant low pass filter 122, a pass through
module 123, a mixer 124, a tone control module 125, a second
11
compressor 126, and an output device 102. In the broadcasting
12 embodiment of Figure 2 as illustrated by system 200, these
13 components may be split between a pre-transmission module 110
14 and a post-transmission module 120. Accordingly, the system 200
includes the addition of a transmitter 131, a communications
16 network 132, and a receiver 133 in between the pre-transmission
17 module 110 and post-transmission module 120.
18 In
effect, the embodiment of system 200 separates out
19 various components of the present invention into at least two
modules, such that the pre-transmission module or modules 110
21 and post-transmission module or modules 120 may be placed in
22 different locations or embedded into different devices in
23 communication with one another. The network 132 may comprise a
24 wired or wireless network, such as cellular, satellite,
14
81780341
1 terrestrial, and any variety of LAN, WAN, local wireless or near
TM
2 field communications including but not limited to Wifi,
3 BluetootO infrared technologies, as well as any other
4 appropriate technologies for the transmission of a digital audio
signal. Accordingly,
the transmitter 131 and corresponding
6 receiver 133 are configured to send and receive the partially
7 processed signal 213 from the pre-transmission module 110 to the
8 post-transmission module 120. In the
embodiment of Figure 2,
9 the partially processed signal 213 is transmitted from the
clipping module 113 to the transmitter 131, sent over the
11 network 132 to the receiver 133, and then is transmitted to the
12 splitter 121.
13 As
schematically represented, Figure 3 illustrates at least
14 one preferred. embodiment of a system 300 for narrow bandwidth
digital' signal processing. Generally
speaking, the system 300
16 is a simpler variation of the embodiment of system 100, and has
17 fewer components than the system 100 recited above. As such,
18 the system 300 comprises an input device 101, a high pass filter
19 111, a first compressor 112, a splitter 121, a low pass filter
122, a' pass through module 123, a mixer 124, and an output
21 device 102. However, it
should be understood that the system
22 300 embodiment may comprise the addition of the clipping module
23 113, tone control module 125, second compressor 126, and any
24 combinations thereof.
CA 2854086 2017-12-21
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F,\MM DOCS\1-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovi
Acoustica\Patent_Application_Filed 124b.doc
1
Structurally and in at least one embodiment, the components
2 recited in system 300 are similar to or the same as the
3 components in system 100 above. Modulated signal 212 from the
4 first compressor 112 however, is transmitted directly to the
splitter 121.
Further, the combined signal 224 from mixer 124
6 is sent directly to the output device 102.
7 As
schematically represented, Figure 4 illustrates at least
8 one preferred embodiment of a broadcast variation of the system
9 of Figure 3. In
this embodiment, system 400 comprises a pre-
transmission module 110' and a post-transmission module 120'.
11 The pre-transmission module 110' comprises a high pass filter
12 111 and a first compressor 112. The
post-transmission module
. 13 120' comprises a splitter 121, a low pass filter 122, a pass
14 through module 123, and a mixer 124.
Structurally, the
components are as those recited in system 300 and system 200
16 above in at least one embodiment.
17 As
diagrammatically represented, Figure 5 illustrates
18 another embodiment directed to a method for narrow bandwidth
19 processing, which may, in various embodiments, incorporate the
components from the systems referenced above. In
this
21 embodiment, an input audio signal is first filtered, as in 501,
22 with a high pass filter. In
at least one embodiment, the high
23 pass filter comprises a resonant filter that passes frequencies
24 above a first frequency and attenuates frequencies below the
16
81780341
1 first frequency. Further, the first frequency may be selected
2 from a range between 2.5 kHz and 3.2 kHz,
3 The filtered
signal comprising frequencies above the first
4 frequency are then processed by the first processing module, as
in 1001, to create a partially processed signal. This step may
6 further comprise modulating the filtered signal with a first
7 compressor to create a modulated signal. The first
8 compressor may comprise an automatic gain controller, or other
9 device, or combination of circuits capable of dynamic range
compression. In some
embodiments, the first compressor may
11 comprise any device or combination of circuits capable of static
12 level adjustments. The modulated signal may be transmitted as
13 the partially processed signal, or may further be transmitted to
14 a clipping module to limit the gain of the modulated signal
in order to create the partially processed signal. The
16 clipping module may comprise a clipper or clipping circuit
17 configured to limit the amplitude or gain of an audio signal.
18 The clipping module may further comprise soft clipping in order
19 to avoid sharp points in the transfer characteristics of the
signal.
21 The
partially processed signal is then split using a
22 splitter, as in 504, into a first signal and a second signal.
23 In at least one embodiment, the splitter is configured such that
24 the first and second signals are substantially the same signal
17
CA 2854086 2017-12-21
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\?AT 2013\1\PP\1245-13 Bonglovi
AcoustIcs\Patent_ApplicatIon_Filed_1245.doc
1 as the partially processed signal. In
other words, the
2 partially processed signal diverges into a first signal and a
3 second signal at the splitter.
4 The
first signal is filtered, as in 505, with a low pass
filter. In at
least one embodiment, the low pass filter
6 comprises a resonant filter that passes frequencies below a
7 second frequency and attenuates frequencies above the second
8 frequency. Further, and counterintuitive to expected function,
9 the second frequency is set to be lower than the first
frequency. In at least one embodiment, the second frequency may
11 further be selected from the range between 700 Hz and 1000 Hz.
12 The
second signal is passed through the pass through
13 module, as in 506. The gain of the second signal is adjusted in
14 at least one embodiment. The gain adjustment may be zero, may
be adjusted downwards or upwards. In some embodiments the gain
16 adjustment may be static, in others dynamic. In
yet other
17 embodiments, the pass through module may not comprise a gain
18 adjustment component. Accordingly, the pass through module may
19 comprise a device or circuit(s) for the dynamic or static gain
adjustment of the signal.
21 The
filtered first signal and gain-adjusted second signal
22 are then processed with a second processing module, as in 1002.
23 This step may further comprise combining the filtered first
24 signal, and the gain-adjusted second signal with a mixer in order
18
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PhT\PAT 2013\APP\1215-13 Bongiovi
Acoustics\Patent_App1ication.3i1ed_1245.doc
1 to create a combined signal.
The mixer is structured and/or
2 configured to combine at least two signals and output a
3 composite signal. The combined signal may be transmitted as the
4 output signal, or may be further processed with a tone control
module to create a controlled signal. The tone control module
6 may comprise any device or combination of circuits appropriate
7 for the equalization of an audio signal. In
at least one
8 embodiment, the tone control module comprises a parametric
9 equalizer.
The parametric equalizer may comprise one, two,
three, or four bands. In
other embodiments, the tone control
11 module may comprise graphic equalizers or other equalizers. The
12 controlled signal may be output as the output signal, or may be
. 13 further modulated with a second compressor to create the output
14 signal.
The second compressor may comprise any device or
combination of circuits capable of dynamic range compression or
16 static compression.
17
Finally, the output signal is transmitted to an output
18 device, as in 510.
The output device may be configured for
19 additional processing, or may be configured for playback of the
output signal.
21 As
diagrammatically represented, Figure 6 illustrates
22 another embodiment directed to a broadcasting variation of a
23 method for narrow bandwidth processing.
Structural and or
24 configurable components of this embodiment may be the same or
19
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovi
Acoustics\Patent_Application_Filed_1245.doc
1 similar as those recited above.
2 In
the embodiment of Figure 6, an input audio signal is
3 filtered, as in 501, with a high pass filter. In
at least one
4 embodiment, the high pass filter comprises a resonant filter
that passes frequencies above a first frequency and attenuates
6 frequencies below the first frequency.
Further, the first
7 frequency may be selected from a range between 2.5 kHz and 3.2
8 kHz.
9 The
filtered signal is then processed by the first
processing module, as in 1001. This
step may comprise
11 modulation by a first compressor, limiting the gain with a
12 clipping module, or combinations thereof, in order to create a
. 13 partially processed signal.
14 The
partially processed signal is then transmitted with a
transmitter, as in 601. The transmitter may comprise any device
16 or combination of circuits capable of transmitting a signal,
17 wired or wireless, over a communication network or platform.
18 The partially processed signal is received with a receiver, as
19 in 602. The receiver may comprise any device or combination of
circuits capable of receiving the partially processed signal
21 being transmitted by the transmitter.
22 The
partially processed signal received by the receiver is
23 then split into a first signal and second signal, as in 504,
24 with a splitter.
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\XPP\1245-13 BongLovi
Acoustic8\Patent_App1ication_Fi1ed_1245.doc
1 The
first signal is filtered with a low pass filter, as in
2 505. In at least one embodiment, the low pass filter comprises
3 a resonant filter that passes frequencies below a second
4 frequency and attenuates frequencies above the second frequency.
Further, and counterintuitive to expected function, the second
6 frequency is set to be lower than the first frequency. In
at
7 least one embodiment, the second frequency may further be
8 selected from the range between 700 Hz and 1000 Hz.
9 The
second signal is passed through a pass through module,
as in 506. In at least one embodiment, the gain of the second
11 signal is adjusted with the pass through module.
12 The
filtered first signal and gain-adjusted second signal
. 13 are then processed with a second processing module, as in 1002.
14 This step may comprise combination of the two signals with a
mixer, further processing with a tone control module, modulating
16 with a second compressor, and combinations thereof, in order to
17 create the output signal. Finally, the second processing module
18 transmits an output signal as in 510 to the output device.
19 As
diagrammatically represented, Figure 7 illustrates
another embodiment directed to a method for narrow bandwidth
21 processing.
Structural and or configurable components of this
22 embodiment may be the same or similar as those recited above.
23 In the embodiment of Figure 7, an input audio signal is
24 filtered, as in 701, with a high pass filter. In
at least one
21
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\1-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovi
Acoustics\Patent_Application_Fi1ed_1245.doc
1 embodiment, the high pass filter comprises a resonant filter
2 that passes frequencies above a first frequency and attenuates
3 frequencies below the first frequency.
Further, the first
4 frequency may be selected from a range between 2.5 kHz and 3.2
kHz.
6 The
filtered signal is then modulated by a first
7 compressor, as in 702, in order to create a partially processed
8 signal. The
partially processed signal is then split into a
9 first signal and second signal, as in 703, with a splitter.
The first signal is filtered with a low pass filter, as in
11 704. In at least one embodiment, the low pass filter comprises
12 a resonant filter that passes frequencies below a second
, 13 frequency and attenuates frequencies above the second frequency.
14 Further, and counterintuitive to expected function, the second
frequency is set to be lower than the first frequency. In at
16 least one embodiment, the second frequency may further be
17 selected from the range between 700 Hz and 1000 Hz.
18 The
second signal is passed through a pass through module,
19 as in 705. In
at least one embodiment, the gain of the second
signal is adjusted with the pass through module. The
filtered
21 first signal and gain-adjusted second signal are combined in a
22 mixer, as in 706.
Finally, the combined signal is transmitted
23 as an output signal, as in 707.
24 As
diagrammatically represented, Figure 8 illustrates
22
= CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovi Acoustics\Patent
Application_Flled 1245.doc
1 another embodiment directed to a broadcasting variation of a
2 method for narrow bandwidth processing.
Structural and or
3 configurable components of this embodiment may be the same or
4 similar as those recited above.
In the embodiment of Figure 8, an input audio signal is
6 filtered, as in 701, with a high pass filter. In
at least one
7 embodiment, the high pass filter comprises a resonant filter
8 that passes frequencies above a first frequency and attenuates
9 frequencies below the first frequency.
Further, the first
frequency may be selected from a range between 2.5 kHz and 3.2
11 kHz. The
filtered signal is then modulated by a first
12 compressor, as in 702, in order to create a partially processed
. 13 signal.
14 The
partially processed signal is then transmitted with a
transmitter, as in 801. The transmitter may comprise any device
16 or combination of circuits capable of transmitting a signal,
17 wired .or wireless, over a communication network or platform.
18 The partially processed signal is received with a receiver, as
19 in 802. The receiver may comprise any device or combination of
circuits capable of receiving the partially processed signal
21 being transmitted by the transmitter.
22 The
partially processed signal received by the receiver is
23 then split into a first signal and second signal, as in 703,
24 with a splitter.
23
=
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
F,\MM DOCS\1-2Ai\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovl
Acoustics\Patent_ApplIcation_Filed_1245.doc
1 The
first signal is filtered with a low pass filter, as in
2 704. In at least one embodiment, the low pass filter comprises
3 a resonant filter that passes frequencies below a second
4 frequency and attenuates frequencies above the second frequency.
Further, and counterintuitive to expected function, the second
6
frequency is set to be lower than the first frequency. In at
7 least one embodiment, the second frequency may further be
8 selected from the range between 700 Hz and 1000 Hz.
9 The
second signal is passed through a pass through module,
as in 705. In at least one embodiment, the gain of the second
11 signal is adjusted with the pass through module. The filtered
12 first signal and gain-adjusted second signal are combined in a
. 13 mixer,
as in 706. Finally, the combined signal is transmitted
14 as an output signal, as in 707.
The above methods may be completed in sequential order in
16 at least one embodiment, though they may be completed in any
17 other order. In at least one embodiment, the above methods may
18 be exclusively performed, but in other embodiments, one or more
19 steps of the methods as described may be skipped.
Since many modifications, variations and changes in detail
21 can be made to the described preferred embodiment of the
22 invention, it is intended that all matters in the foregoing
23 description and shown in the accompanying drawings be
24 interpreted as illustrative and not in a limiting sense. Thus,
24
CA 02854086 2014-06-11
=
F:\MM DOCS\l-PAT\PAT 2013\APP\1245-13 Bongiovi
Acoustics\Patent_App1ication_Filed_1245.doc
1 the scope of the invention should be determined by the appended
2 claims and their legal equivalents.
3 Now that the invention has been described,