Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
1
ASSEMBLY COMPRISING A SECURITY APPARATUS
EQUIPPING A LIFTING DEVICE, IN PARTICULAR A WINCH,
AND SYSTEM FOR ACTUATING SAID APPARATUS
The present invention relates to an assembly comprising a security apparatus
equipping a lifting device, in particular a winch, and a system for actuating
said
apparatus.
It is known to equip a winch with a security apparatus comprising a toothed
wheel, wedged on the shaft of the winch, a worm meshing with the toothed
wheel, a
housing slidingly receiving the worm, a motor, termed "follow-up motor,"
making it
possible to rotate the worm so that it follows the rotation of the toothed
wheel during
normal operation of the winch, and means for damping the sliding of the worm
in the
housing in the case of an exceptional failure situation of the winch. This
security
apparatus, known under the "MotosuiveurTm" mark, is described in document
No. EP 1 253 102.
In a normal operating situation of the winch, the worm is in a normal position
bearing against said damping means, and the follow-up motor rotates the worm
at a
speed adapted to that of the toothed wheel, which in turn is rotated by the
winch; the
security apparatus is then inactive or "transparent," i.e. it does not
interfere with the
operation of the winch.
In the event the winch fails, the shaft thereof undergoes an immediate
acceleration generated by the weight of the load, which is transmitted to the
toothed
wheel of the security apparatus, and which the worm cannot follow; this
results in
sliding of the worm in the housing, from its aforementioned normal position
toward an
exceptional position stressing said damping means then, when the damping
capacities of said damping means are reached, up to a stop position.
In one embodiment, these damping means comprise a piston, against which
the worm bears, nozzles with a reduced section, through which the piston
forces oil in
which the worm soaks, elastic washers situated between the ends of the worm,
and
the stop formed by the housing. Such damping means are described in document
No. US 7,331,252.
CA 2868059 2018-07-09
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
2
The aforementioned security apparatus makes it possible to monitor said
exceptional failure situation by blocking the load against falling.
At the end of that blocking, it is necessary to regain control of the load so
as to
release the winch, which involves accessing the security apparatus so as to
rotate the
worm manually, since the follow-up motor is not powerful enough to rotate the
worm
(this is not its role).
However, in a certain number of situations, said access is not possible or is
restricted, for example when the winch is used in the nuclear industry.
Furthermore,
manually actuating the worm is a tedious operation, the pitch of the worm
being
relatively small and the diameter of the toothed wheel being relatively large.
The present invention aims to resolve these significant practical drawbacks.
Another exceptional situation exists in which the operation of the winch is
stopped, i.e. when a brake comprised by the winch tightens until it locks the
shaft of
the winch, for example in the event of an electrical power loss. It is then no
longer
possible to regain control of the load easily and quickly, i.e. without a
manual
intervention on the security apparatus or the winch.
The present invention also aims to resolve this gap.
The assembly covered by the invention comprises a "Motosuiveur" security
apparatus as described above, i.e. comprising a toothed wheel, wedged on the
shaft
of the lifting device, a worm meshing with said toothed wheel, a housing
slidingly
receiving the worm, a motor, termed "follow-up motor," allowing the worm to be
rotated so that the latter part follows the rotation of the toothed wheel
during normal
operation of the lifting device, and means for damping the sliding of the worm
in the
housing in the case of an exceptional failure situation of the lifting device,
up to a stop
position of this worm in this housing.
According to the invention, said assembly also comprises:
- a splined shaft secured to one end of the worm and axially extending said
worm;
- a pocketed wheel with inner and outer splines, slidingly engaged on the
splined shaft and rotationally engaged therewith;
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
3
- an elastic member whereof one end is connected to a stop piece secured to
the splined shaft and whereof the other end is connected to the pocketed
wheel;
- a drive wheel with a splined hub, with which the pocketed wheel is
capable of
engaging rotationally owing to the outer splines comprised by said pocketed
wheel;
- a motor, termed "back-up motor," capable of rotating the drive wheel,
the pocketed wheel being able to move with said splined shaft between a normal
disengaged position, which it occupies outside a failure situation of the
lifting device,
and in which it is not engaged with the drive wheel, and an exceptional
engaged
position, which it occupies in a failure situation of the lifting device, and
in which it is
rotationally engaged with the drive wheel and thus rotationally connects the
drive
wheel with the splined shaft and therefore with the worm.
During normal operation of the security apparatus, the pocketed wheel is in
the
disengaged position and the actuating system formed by the back-up motor and
the
drive wheel is therefore inactive.
In a failure situation of the lifting device, the worm is moved toward its
exceptional stop position, which, aside from blocking the load from falling,
causes the
compression of the elastic member and therefore causes the pocketed wheel to
press
against the driving wheel. Slowly rotating the back-up motor then makes it
possible to
rotate the drive wheel so as to make the splines of that drive wheel coincide
with the
splines of the pocketed wheel and allow the mutual engagement of said splines.
A
rotational connection of the drive wheel and the worm is thus produced,
allowing said
worm to be actuated using the back-up motor and therefore allowing the load to
be
actuated to move upward or downward. When the load ceases to weigh on the
cable
of the lifting device, the worm returns to its normal position, returning the
pocketed
wheel to the disengaged position.
The invention thus provides a system for actuating the security apparatus,
having a sufficient driving power to actuate the worm in such an exceptional
failure
situation of the winch, and therefore eliminating the need to access the worm
and
actuate said worm manually.
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
4
When the shaft of the lifting device is locked, in particular after automatic
tightening of a brake comprised by that device, the follow-up motor can be
actuated
so as to rotate the worm and, since the toothed wheel is then rotationally
immobile, to
thereby move said worm into said exceptional position for stressing the
damping
means, then into said stop position. In the same way as before, this movement
causes the pocketed wheel to press against the driving wheel, then the slow
rotation
of said drive wheel using the back-up motor makes the pocketed wheel go into
the
engaged position. The back-up motor then makes it possible to rotate the worm,
in
the direction of rotation preserving the aforementioned exception position of
said
worm, which makes it possible to force the rotation of the toothed wheel so as
to
overcome the frictional force generated by the brake of the lifting device.
Advantageously, the actuating system comprises means for locking the
pocketed wheel in the engaged position.
These locking means make it possible, when the worm is rotated by the back-
up motor in the direction of rotation making it leave its aforementioned
exceptional
position and moving it toward an opposite stop position, to keep the pocketed
wheel
in an engaged position notwithstanding that movement of the worm. The
possibility of
actuating the worm using the back-up motor is therefore kept.
According to one preferred embodiment of these locking means:
- the female splines of the driving wheel have a width greater than that of
the
male splines of the pocketed wheel, such that the flanks of said male splines
are,
depending on the direction of driving of the drive wheel, against first flanks
delimiting
the female splines of the drive wheel or against the two flanks delimiting
these same
female splines, opposite said first flanks;
- the male splines of the pocketed wheel have wider front portions, forming
lateral shoulders, said wider front portions being capable of protruding past
the drive
wheel in said engaged position of the pocketed wheel and, when said drive
wheel is
driven in the direction of rotation causing the worm to leave its exceptional
position
and moving said worm toward an opposite stop position, to bear against the
drive
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
wheel, thereby keeping the pocketed wheel in said engaged position, against
the
elastic force of the elastic member.
Once the drive wheel is driven in the opposite direction, said wider front
portions return opposite the female splines of the drive wheel, thereby
allowing the
5 pocketed wheel to return to said disengaged position.
Advantageously, said wider front portions have thinner front ends, which favor
the engagement thereof in the female splines of the drive wheel when the
pocketed
wheel enters the engaged position.
Preferably, the actuating system also comprises contactors, one of which
detects the arrival of the worm in said exceptional position and the other of
which
detects the fact that the pocketed wheel is in said engaged position or in
said
disengaged position.
Other features and advantages of the invention will appear in the following
description, done in reference to the appended diagrammatic drawing, which
shows,
as a non-limiting example, one possible embodiment of the concerned security
apparatus / actuating system assembly.
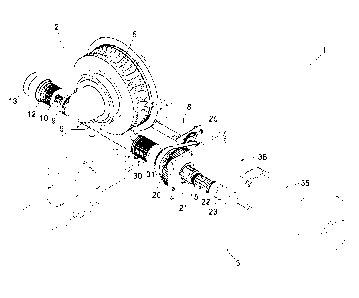
Figure 1 is a perspective view of said apparatus, the assembly of the housing
and the cases comprised by the apparatus having been removed, as well as the
contactors also comprised by said apparatus;
figure 2 is an overall side view, in a normal position of a worm it comprises
in a
disengaged position of a pocketed wheel it also comprises;
figure 3 is a view similar to figure 2, in an exceptional position of the worm
and
in an engaged position of the pocketed wheel;
figure 4 is a perspective view of the pocketed wheel and a drive wheel with
which said pocketed wheel is intended to be rotationally engaged;
figure 5 is a view of the pocketed wheel similar to figure 4, on a larger
scale;
figure 6 is a partial view of said assembly, in perspective and with a partial
cross-section, the pocketed wheel being in the disengaged position;
figure 7 is a view similar to figure 6, the pocketed wheel being in the
engaged
position; and
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
6
figure 8 is a view similar to figure 7, the pocketed wheel being in a locked
engaged position.
Figures 1 to 3 show an assembly 1 comprising a security apparatus 2
equipping a lifting device, in particular a winch, and a system 3 for
actuating said
apparatus 2.
The security apparatus 2 is of the type known under the "Motorsuiveur" mark,
the principle of which is described by document No. EP 1 253 102. It comprises
a
toothed wheel 5, wedged on the shaft of the lifting device (not shown), a worm
6
meshing with said toothed wheel 5, a housing 7 slidingly receiving the worm 6,
a
motor 8, termed "follow-up motor," making it possible to rotate the worm 6 so
that it
follows the rotation of the toothed wheel 5 during normal operation of the
lifting
device, and means 9 to 13 for damping the sliding of the worm 6 in the housing
7 in
the case of an exceptional failure situation of the lifting device, as far as
a maximal
stop position of said worm 6.
The worm 6 extends axially over one side of the wheel 5 by a splined shaft 15
integral therewith. This splined shaft 15 successively comprises a drive wheel
20, an
engaging/disengaging pocketed wheel 21, a spring 22 and a stop piece 23,
described
later, which are part of the actuating system 3.
As shown in figures 2 and 3, the housing 7 forms an upper central portion 7a,
comprising a bore for receiving the toothed wheel 5 in an adjusted manner, a
lower
central portion 7b, comprising a bore for receiving the worm 6 in an adjusted
manner,
and two coaxial extensions 7c, extending said bore, one of which receives said
means 9 to 13 for damping the worm 6.
The follow-up motor 8 is situated along said lower central portion 7b and
drives
the worm 6 via a wheel 24 and a belt 25.
In the illustrated example, the weight of the load lifted by the lifting
device
tends to rotate the toothed wheel 5 in the clockwise direction as shown in
figures 2
and 3, so that in the event said lifting device fails, the worm 6 moves from
right to left
in said figures 2 and 3. The damping means 9 to 13 are therefore situated at
the
extension 7c located on the left of the security apparatus 2.
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
7
These damping means comprise a piston 9, against which the worm 6 bears, a
tube 10 comprising nozzles 11 with a reduced section formed through the wall
thereof, elastic washers 12, and a stop piece 13 secured to the housing 7,
against
which the washers 12 are situated.
The piston 9 forms an inner chamber 26, with which the tube 10
communicates. When it is pressed by the worm 6 in case of failure of the
lifting
device, this piston 9 forces the oil present between it and the washers 12
through the
nozzles 11, said oil then flowing in the chamber 26 (cf. figures 2 and 3 in
comparison). The nozzles 11 are aligned axially on the tube 10 and are
gradually
covered by the piston 9 during the movement of the worm 6, so that the section
of the
oil passage is gradually reduced during the movement of that piston 9, thereby
increasing the damping produced. After having gone past the last nozzle 11,
the
piston 9, if it continues its travel, crushes the washers 12 as far as the
compressibility
limit thereof, which defines the stop position of the worms 6 in the housing
7.
At the opposite extension 7c (i.e. the extension located on the right in
figures 2
and 3), the apparatus comprises a series of washers 30 and a stop piece 31
that are
similar to the aforementioned washers 12 and stop piece 13, making it possible
to
damp the movement of the worm 6 from left to right in certain situations, as
will be
described later.
Aside from the drive wheel 20, the pocketed wheel 21, the spring 22 and the
stop part 23, the actuating system 3 comprises a motor 35, termed "back-up
motor,"
and a step-down gear 36 driven by said motor 35.
The drive wheel 20 meshes with the pinion 37 (figure 6) at the output of the
gear 36 and is therefore driven by the motor 35. As shown more particularly in
figure
4, it comprises a splined hub capable of engaging with the outer splines
comprised by
the pocketed wheel 21.
The latter part, visible in figures 4 and 5, comprises inner splines allowing
it to
engage rotationally with the splined shaft 15 and allowing it the possibility
of sliding
axially thereon, and the aforementioned outer splines allow it to engage with
the drive
wheel 20. The pocketed wheel 21 can move with the splined shaft 15, and
therefore
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
8
with the worm 6, between a normal disengaged position, which it occupies
outside a
failure situation of the lifting device, and in which it is not engaged with
the drive
wheel 20 (cf. figures 2 and 6), and an exceptional engaged position, which it
occupies
in a failure situation of the lifting device, and in which it is rotationally
engaged with
the drive wheel 20 and thereby produces a rotational connection of said drive
wheel
20 with the splined shaft 15 and therefore with the worm 6 (cf. figures 3 and
7).
Furthermore,
- the female splines 20f of the hub of the drive wheel 20 have a width larger
than that of the male outer splines 21m of the pocketed wheel 21, such that
the flanks
of said male outer splines 21c come, depending on the driving direction of the
drive
wheel 20 relative to the shaft 15, against first flanks laterally delimiting
said female
splines 20f or against the second flanks laterally delimiting these same
female splines
20f, opposite said first flanks;
- each male outer spline 21m has a wider front portion 21a, forming a lateral
shoulder 21e that protrudes laterally relative to one of the lateral flanks of
the spline
21m.
As shown in figure 5, each wider front portion 21a has lateral flanks that
converge toward one another in the direction of the front end of the pocketed
wheel
21, thereby favoring the engagement of those portions 21a in the female
splines 20f.
As will be understood in reference to figures 6 to 8, these wider front
portions
21a can protrude past the drive wheel 20 in said engaged position; when said
drive
wheel 20 is driven in the direction of rotation moving the worm 6 from left to
right in
figures 2 and 3 (which is the counterclockwise direction of said wheel 20 as
seen in
figures 6 to 8), toward a stop position of said worm 6 against the washers 30,
said
lateral shoulders 21a protrude laterally past the female splines 20f and bear
against
the drive wheel 20, thereby keeping the pocketed wheel 21 in said engaged
position
(cf. figure 8). These lateral shoulders 21e consequently form, with the drive
wheel 20,
means for locking the pocketed wheel 21 in said engaged position.
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
9
The spring 22 is engaged on the shaft 15 while being inserted between the
pocketed wheel 21 and the stop piece 23 and is connected to the pocketed wheel
21
by one end and to the stop piece 23 by the other end.
Said spring 22 is relaxed in the disengaged position of the pocketed wheel 21
shown in figures 1, 2 and 6, so that it defines that disengaged position. When
the
worm 6 is moved from right to left until it comes into contact with the
washers 12, the
stop piece 23 is moved with the shaft 15, which makes the pocketed wheel 21
bear
against the hub of the drive wheel 20 and compresses the spring 22.
Furthermore, as shown by figures 2, 3, and 6 to 8, the actuating system 3
comprises:
- an assembly for detecting the normal position of the worm 6-shaft 15-stop
piece 23 assembly, formed by a groove arranged in the stop piece 23 and by a
contactor 40 whereof the detection member is moved radially depending on
whether
its end is engaged in said groove; and
- an assembly for detecting the engaged position of the pocketed wheel 21,
formed by a sleeve 41 provided with a shoulder, covering the spring 22 and
connected to the pocketed wheel 21, and by a contactor 42 whereof the
detection
member is moved radially depending on whether its end is opposite said
shoulder.
During normal operation of the security apparatus 2, the pocketed wheel 21 is
in the disengaged position and the actuating system 3 is therefore inactive
(cf. figures
2 and 6).
In a failure situation of the lifting device, the worm 6 is moved toward its
exceptional position abutting against the washers 12, which, aside from
blocking the
load from falling, causes the pocketed wheel 21 to abut against the hub of the
drive
wheel 20 and the compression of the spring 22, which thereby exerts pressure
on the
pocketed wheel 21. Slowly rotating the back-up motor 35 then makes it possible
to
rotate the drive wheel 20 so as to make the splines 20f of that drive wheel 20
coincide
with the portions 21a of the splines 21m and thereby allow the mutual
engagement of
said splines. A rotational connection of the drive wheel 20 and the worm 6 is
thus
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
produced, allowing said worm to be actuated by the back-up motor 35 and
therefore
allowing the load to be moved upward or downward.
When the toothed wheel 5 is immobilized, in particular when the load is set
down and ceases to weigh on the security apparatus, the worm 6, through its
rotation,
5 returns to its normal position. When said worm 6 has been actuated in its
screwing
direction relative to the toothed wheel 5 (clockwise driving of the drive
wheel 20), the
front ends 21a of the splines 21m are opposite the female splines 20f and the
direct
return of the pocketed wheel 21 to the disengaged position is thus made
possible
under the effect of the elastic return of the spring 22; when the worm 6 has
been
10 actuated in the unscrewing direction thereof relative to the toothed
wheel 5
(counterclockwise driving of the drive wheel 20), the front ends 21a of the
splines
21m are angularly offset relative to the female splines 20f and the shoulders
21e bear
against the drive wheel 20, then the spring 22 is stretched; a slow rotation
of the drive
wheel 20 in the clockwise direction, using the back-up motor 35, makes it
possible to
bring the female splines 20f opposite the front ends 21a of the splines 21 and
therefore to free the shoulders 21e from their bearing against the drive wheel
20,
thereby allowing the pocketed wheel 21 to return to the disengaged position
under the
effect of the elastic return of the spring 22.
In a locking situation of the shaft of the lifting device, in particular
following the
automatic tightening of a brake comprised by that device, the follow-up motor
is
actuated so as to rotate the worm 6 in the screwing direction thereof relative
to the
toothed wheel 5. Since the toothed wheel 5 is then rotationally immobile, this
driving
moves the worm 6 toward the washers 12 as far as the stop position of said
worm
against the latter parts. In the same way as before, this movement causes the
pocketed wheel 21 to press against the drive wheel 20, then the slow rotation
of said
drive wheel by the back-up motor 35 causes the pocketed wheel 21 to go to the
engaged position. The back-up motor 35 then makes it possible to rotate the
worm 6
in the screwing direction relative to the toothed wheel 5 (driving of the
wheel 20 in the
clockwise direction), which makes it possible to force the rotation of said
toothed
CA 02868059 2014-09-22
WO 2012/131595 PCT/IB2012/051486
11
wheel 5 so as to overcome the frictional force generated by the brake of the
lifting
device and to thereby move the load downward.
If one wishes to move the load upward, the worm 6 is then rotated by the back-
up motor 35 in the unscrewing direction thereof relative to the toothed wheel
5
(driving of the wheel 20 in the counterclockwise direction), which brings said
worm 6
to a stop position against the washers 30; as of the beginning of this
movement of the
worm 6, the shoulders 21e bear against the drive wheel 20, thereby making it
possible to keep the pocketed wheel 21 in the engaged position. When the load
is
under control, the drive wheel 20 is then driven in the clockwise direction so
as to
return the female splines 20f opposite the wider front ends 21a of the male
splines
21m, thereby freeing the return of the pocketed wheel 21 to the disengaged
position.
As appears from the preceding, the invention provides an assembly comprising
a security apparatus 2 termed "Motosuiveur (Di" and a system 3 for actuating
that
apparatus, with the following decisive advantages:
- the actuating system 3 has a sufficient drive power to actuate the worm 6 in
a
failure situation of the lifting device, and therefore eliminates the need to
access the
worm 6 and actuate said worm manually;
- in a stop situation of the operation of the lifting device, in particular
when a
brake comprised by the device tightens until it blocks the shaft of said
device, said
assembly 1 makes it possible to regain control of the load easily and quickly,
i.e.
without manual intervention on the security apparatus or the lifting device,
and to
move that load both upward and downward.
The invention has been described above in reference to one preferred
embodiment. It is of course not limited to that embodiment, but on the
contrary
extends to all other embodiments covered by the appended claims.