Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
DESCRIPTION
TITLE OF THE INVENTION: SOLE MEMBER OF FOOTWEAR
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001]
The present invention relates to a sole member of
footwear, and more particularly to a sole member of footwear
which absorbs impact during walking while providing feeling
of stable, comfortable walking, exhibits a massaging effect
through stimulation of the foot sole, and can prevent leakage
of liquid sealed therein.
BACKGROUND ART
[0002]
When the heel touches down on the ground, impact force
imposed on the heel is said to be about 1.25 times the body
weight during walking and about three times during jogging.
The impact is transmitted to the heel, the ankle, the knee,
and then the waist and imposes loads on these regions. Also,
it has been known that, as compared with impact applied when
the heel touches down on the ground, impact applied when the
toes kick the ground is greater.
[0003]
Thus, the inventors of the present invention have
proposed a shoe insole which disperses and absorbs impact
applied to the foot sole when the foot sole lands on the
1
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
ground during walking and which can exhibit a massaging
effect through stimulation of the foot sole (refer to, for
example, Patent Document 1).
[0004]
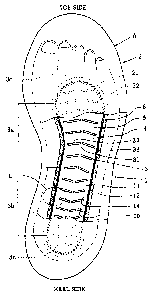
Referring to FIG. 17, the configuration of a shoe
midsole A described in Patent Document 1 mentioned above is
explained. The shoe midsole A described in Patent Document 1
includes a base plate 1 similar in shape to a shoe sole, and
a cover 2. Thermoplastic resin is used to form the base
plate 1 and the cover 2. The base plate 1 has a first
concave portion 11 equivalent to the shape of that portion of
the foot sole which comes into contact with the ground, and
the cover 2 has a second concave portion 21 which faces the
first concave portion.
[0005]
The base plate 1 has a plurality of blades 3 formed in
the first concave portion 11 in an integrally rising manner.
The plurality of blades 3 are disposed substantially
orthogonally to the longitudinal direction of the base plate
1 at predetermined intervals and are tilted toward the heel
side or the toe side. The base plate 1 has a partition 15
integrally rising therefrom between an inner peripheral wall
14 of the first concave portion 11 of the base plate 1 and
the laterally opposite ends of the blades 3.
[0006]
As viewed from the heel toward the toes in a direction
parallel to the base plate 1, each of the blades 3 has a
2
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
substantially trapezoidal shape such that its both outer ends
are inclined downward, and has two grooves 31 at laterally
intermediate positions for allowing movement of liquid 4.
[0007]
The base plate 1 and the cover 2 are welded together at
a joint 6 which surrounds the outer peripheries of the first
and second recesses 11 and 21, and the liquid 4 such as water
or propylene glycol is sealed in a closed space 5 sandwiched
between the first concave portion and the second concave
portion.
[0008]
Next, the function of the shoe midsole A mentioned
above will be described. In walking, first, the heel of the
foot touches down on the ground. Next, the ground contact
area expands toward the outside of the arch; then, the body
weight moves to the rounded parts (balls) at the roots of the
toes. Upon completion of imposition of the body weight on
the balls, the toes spread to right and left so as to
restrain shaking right and left and back and forth. Next,
while the center of gravity is being moved forward, the foot
sole begins to bend at the balls; the heel lifts; and then
the entire toes kick the ground.
[0009]
In a sequence of walking actions mentioned above, for
example, when the heel touches down on the ground, a pressing
force derived from the body weight is concentrically applied
to that portion of the insole A which is in contact with the
3
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
heel, and, according to Pascal's principle, the pressing
force is equally transmitted to every inner surface of the
closed space 5 through the liquid 4 which is sealed in the
closed space 5 sandwiched between the first concave portion
11 and the second concave portion 21.
[0010]
Meanwhile, when, for example, the heel comes into
contact with the closed space 5 in which the liquid 4 is
sealed, the contact portion moves downward and presses the
liquid 4 at the contact position. Since the liquid 4 such as
water or propylene glycol is noncompressible, the liquid 4
does not contract. Therefore, a portion of the liquid 4
corresponding to, for example, the heel contact portion
attempts to move to a different location where the pressing
force does not act.
[0011]
However, in order for such a pressed portion of the
liquid 4 to move to a different location where the pressing
force does not act, the closed space 5 must be deformed or
expanded. In order for the closed space 5 to be deformed or
expanded, the sheet-like first and second concave portions 11
and 21 which constitute the closed space must be stretched or
deformed; to that end, the pressure of the liquid 4 must be
increased.
[0012]
That is, when the pressed portion of the liquid 4 moves
to a different location where the pressing force does not act,
4
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
the liquid 4 in the closed space 5 increases in pressure, and
the pressed midsole portion receives a reaction force derived
from the increased pressure of the liquid 4. Therefore, when,
for example, the heel touches down on the ground, the
reaction force of the liquid 4 can absorb impact applied to
the heel.
[0013]
Meanwhile, in the case where the midsole A does not
have the blades 3, when, for example, the heel touches down
on the ground, since the sealed-in liquid 4 easily moves in
every direction within the closed space 5, that portion of
the cover 2 which is pressed by the heel easily touches the
base plate 1; therefore, impact force derived from the heel's
touch down on the ground is hardly mitigated. Also, if the
sealed-in liquid 4 easily moves in every direction within the
closed space 5, force with which the midsole A supports the
foot sole becomes unstable, resulting in poor foot comfort.
[0014]
In the case where the midsole A has the plurality of
blades 3, when, for example, the heel touches down on the
ground, the plurality of blades hinder movement of the
sealed-in liquid 4. When movement of the liquid 4 is
hindered, resistance force is generated against depression of
that portion of the cover 2 which is pressed by the heel;
accordingly, that portion becomes unlikely to touch the base
plate 1, whereby impact force derived from the heel's touch
down on the ground can be mitigated.
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
[0015]
Meanwhile, the plurality of blades 3 are tilted toward
the heel side or the toe side. In the case where the
plurality of blades 3 are tilted toward the heel side, when
the heel touches down on the ground, the liquid 4
corresponding to that portion of the midsole A which is
pressed by the heel attempts to move toward the toe side
within the closed space 5. However, since the blades 3 are
tilted in a direction opposite to the moving direction of the
liquid 4 directed toward the toe side; i.e., since the blades
3 are tilted toward the heel side, resistance force which
hinders the movement of the liquid is enhanced; therefore,
impact force derived from the heel's touches down on the
ground can be mitigated more effectively.
[0016]
In the case where the plurality of blades 3 are tilted
toward the toe side, impact force derived from the toes' kick
the ground can be mitigated more effectively. Furthermore,
in the case where some blades 3 are tilted toward the heel
side, and the other blades 3 are tilted toward the toe side,
impact forces derived from the heel's and the toes' landings,
respectively, on the ground can be mitigated more effectively.
[0017]
In addition to the above, the plurality of blades 3 are
formed in such a manner as to rise from the base plate 1 and
are, as mentioned above, tilted toward the heel side or the
toe side. Therefore, when the midsole A is pressed by, for
6
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
example, the heel, repulsive force is generated from elastic
force of the blades 3. Thus, by virtue of repulsive force of
the blades 3 in addition to the above-mentioned function of
the liquid 4, stronger resistance force is exhibited against
depression of the pressed portion of the cover 2.
[0018]
Thus, when the midsole A is pressed by, for example,
the heel, the cover 2 becomes unlikely to touch the base
plate 1, whereby impact force derived from the heel's touch
down on the ground can be mitigated further effectively.
Also, force to support the foot sole becomes stable, thereby
providing good foot comfort.
[0019]
Furthermore, in walking, the ridges of the blades 3
sequentially stimulate the foot sole through the cover 2,
thereby exhibiting the effect of massaging the foot sole. In
the case where the liquid 4 is not sealed in, force with
which the ridges of the blades 3 come into contact with the
foot sole through the cover 2 becomes strong and excessively
stimulates the foot sole, potentially causing pain.
[0020]
However, in the case where the liquid 4 is sealed in,
resistance force of the liquid appropriately restrains force
generated at the contact portions where the tips of the
blades 3 hit the foot sole through the cover 2, thereby
yielding a comfortable massaging effect.
[0021]
7
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
As explained above, during walking, the shoe midsole A
described in Patent Document 1 disperses and absorbs impact
force applied to the foot sole when the foot sole lands on
the ground, and exhibits excellent massaging effect through
stimulation of the foot sole, by means of the liquid 4 sealed
in the midsole, and the plurality of tilted blades 3 which
rise from the bottom plate 1.
[0022]
However, in a sequence of walking or jogging actions,
when the heel, the outside region of the arch, the balls, and
the toes touch down on the ground, a large pressing force is
repeatedly applied to the midsole A mentioned above. When a
portion of the midsole A is pressed, the liquid 4
corresponding to that portion of the midsole A is also
pressed, and the pressing force causes an abrupt increase in
pressure of the sealed-in liquid 4. Furthermore, the pressed
portion of the liquid 4 quickly moves to a different location
where the pressing force does not act, thereby generating
impact force.
[0023]
That is, in walking or the like, in addition to tensile
stress, compressive stress, shearing stress, or bending
stress, an abruptly built high pressure of the liquid 4 and
impact force induced by quick movement of the liquid are
repeatedly generated in the base plate 1 and the cover 2 of
the midsole A. Thus, the base plate 1 and the cover 2 have
been required to take means to prevent outward leakage of the
8
CA 02873158 2014-13-16
liquid 4. Particularly, prevention of leakage of the liquid
4 from the joint 6 between the base plate 1 and the cover 2
has been required.
[0024]
Thus, the inventors of the present invention have
proposed the following means to prevent leakage of the
sealed-in liquid 4 in the shoe midsole A.
[0025]
An increase has been given to the thickness of the
joint portion 6 located at the outer peripheries of the first
concave portion 11 of the base plate 1 and the second concave
portion 21 of the cover 2 where the base plate 1 and the
cover 2 are joined together (see Patent Documents 1 and 2).
This is for increasing the strength of the joint 6.
[0026]
Also, the width of the joint portion 6 has been
rendered uniform along the entire periphery of the joint
portion 6 (refer to Patent Documents 1 and 3). This is for
rendering the joining strength per unit area of the joint
portion 6 uniform along the entire periphery of the joint
portion 6, so as to avoid emergence of a portion of weakened
joining strength.
[0027]
Furthermore, the partition 15 integrally rising from
the base plate 1 has been formed between the inner peripheral
wall 14 of the first concave portion 11 of the base plate 1
and the both lateral ends of the blades 3, along the entire
9
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
periphery of the inner peripheral wall 14 (see Patent
Document 1). This is for avoiding direct impact against the
joint portion 6 which is generated by the liquid 4 that moves
quickly as a result of the midsole A being pressed, so as to
render leakage of the liquid 4 unlikely to arise.
Patent Document 1: International Publication W02010/023793
Patent Document 2: Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open
(kokai) No. H06-14805
Patent Document 3: Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open
(kokai) No. 2000-236908
DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION
[0028]
However, despite of employment of the above-mentioned
means for preventing leakage of liquid, leakage of liquid
from the joint between the base plate and the cover has
occurred. Thus, it has become clear that, in order to
prevent outward leakage of the sealed-in liquid, further
improvement is required.
[0029]
The inventors of the present invention carried out
extensive studies and found that reducing impact force
against the joint by restraining rapid movement of the liquid,
and restraining increase in pressure locally generated by
hindering the liquid flow are effective for prevention of
outward leakage of sealed-in liquid; on the basis of the
CA 02873158 2016-03-09
finding, the inventors accomplished the present invention.
[0030]
A sole member of footwear according to the present
invention comprises a base plate, a cover, a plurality of
blades, and liquid. The base plate has a first region having
a shape equivalent to a foot sole, and a first horizontal
flange portion surrounding the entire periphery of the first
region. The cover has a second region that faces the first
region, and a second horizontal flange portion that faces the
first horizontal flange portion.
[0031]
The blades are formed in such a manner as to rise from
an upper surface of the first region. The blades are
disposed at predetermined intervals
substantially
orthogonally to a center line extending from a toe side to a
heel side of the base plate. The blades each comprise a
plurality of flat-shaped blade elements separated from each other
by slits. Each blade has two outer side portions. The flat-shaped
blade elements of each of the blades are tilted toward the toe
side or the heel side.
[0032]
The flat-shaped blade elements which occupy both outer
side portions of each of the blade with respect to a lateral
direction of the first region are disposed in such a manner
as to be divergent toward the toe side or the heel side as
viewed from above. The first horizontal flange portion and
the second horizontal flange portion are joined together,
thereby forming a space defined by the first region and the
11
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
second region, and the liquid is sealed in the space.
[0033]
No particular limitation is imposed on the material of
the "base plate," the "cover," and the "blade;" however,
desirably, the material has elasticity. Examples of the
material include thermoplastic resin, thermosetting resin,
synthetic rubber, and natural rubber. Desirably, the "base
plate," the "cover," and the "blades" are formed by injection
molding or press molding. Furthermore, desirably, the "base
plate" and the "blades" are integrally molded.
[0034]
The "shape equivalent to a foot sole" means a shape
substantially similar to the shape of that portion of the
foot sole which comes into contact with the ground in walking
and jogging and in a halt position. Desirably, the shape
does not encompass five toes and their roots.
[0035]
Desirably, the "first region" and the "second region"
are concave region formed on planes where the base plate and
the cover face each other; however, may be flat without
concave regions. Desirably, the outer peripheral shapes of
the "first horizontal flange portion" and the "second
horizontal flange portion" are substantially similar to the
inner peripheral shape of an outsole; however, more desirably,
the outer peripheral shapes are rendered greater so as to
match the size of the outsole by trimming off outer
peripheries thereof.
12
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
[0036]
The "slits" desirably extend from the upper ends to the
bases of the blades so as to divide the blades; however, the
"slits" include those which have a depth of 50% or more of
the blade height from the upper ends to the bases.
[0037]
The expression "the flat-shaped blade elements which
occupy both outer side portions of each of the blades with
respect to a lateral direction of the first region are
disposed in such a manner as to be divergent toward the toe
side or the heel side as viewed from above" means that, for
example, in the case where the blade is composed of four
flat-shaped blade elements, at least two flat-shaped blade
elements which occupy both outer side portions of each of the
blades are disposed in such a manner as to be divergent
toward the toe side or the heel side as viewed from above.
That is, the disposition of the remaining two flat-shaped
blade elements includes two dispositions in which the flat-
shaped blade elements are divergent, and the flat-shaped
blade elements are aligned in a row.
[0038]
"Footwear" in "sole member of footwear" includes men's
shoes and women's shoes and corresponds to sports shoes,
sneakers, sandals with or without straps, business shoes, ski
boots, golf shoes, hiking shoes, walking shoes, boots, high
boots, indoor shoes, Japanese sandals, slippers, socks, etc.
The "sole member" includes so-called midsole and outsoles.
13
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
[0039]
Next, the functions and effects of the present
invention will be described. Similar to the above-mentioned
conventional technique, by means of liquid sealed in the
insole, and a plurality of tilted blades rising from the
bottom plate, the sole member of footwear according to the
present invention disperses and absorbs impact applied to the
foot sole when the foot sole lands on the ground during
walking, and exhibits an excellent massaging effect through
stimulation of the foot sole. Additionally, the sole member
of footwear according to the present invention more
effectively prevents leakage of liquid sealed in the sole
member.
[0040]
Next will be described the function and effect of
preventing leakage of sealed-in liquid when the heel touches
down on the ground as an example. The sole member of
footwear according to the present invention is configured as
follows: the blades each comprise a plurality of flat-shaped
blade elements separated each other by slits, and, as viewed
from above, the flat-shaped blade elements which occupy both
outer side portions of each of the blade with respect to the
lateral direction of the first region are disposed in such a
manner as to be divergent toward the toe side or the heel
side.
[0041]
When the heel, for example, presses a portion of the
14
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
surface of the cover, the liquid corresponding to the pressed
portion is also pressed and moves abruptly to an unpressed
portion of the closed space. However, plurality of blades
are provided at predetermined intervals in the closed space.
Thus, movement of pressed liquid is hindered by the plurality
of blades; accordingly, the liquid moves abruptly in the
lateral direction of the midsole along gaps between the
blades.
[0042]
As viewed from above, the flat-shaped blade elements
which occupy both outer side portions of each of the blade
with respect to the lateral direction of the sole member are
disposed in such a manner as to be divergent toward the toe
side or the heel side. Therefore, the flat-shaped blade
elements which occupy both outer side portions of each of the
blade bend the flow path of the liquid which abruptly moves
in the lateral direction along the gaps between the blades;
thus, the liquid flows out obliquely toward the toe side or
the heel side from the both sides of the gaps between the
blades.
[0043]
Accordingly, the liquid which flows out from the both
sides of the gaps between the blades impinges obliquely on
the joint between the base plate and the cover which is
located externally of the blades. In other words, when the
abruptly moving liquid obliquely impinges on the joint
between the base plate and the cover, impact force of the
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
moving liquid applied to the impingement portion can be
greatly reduced, as compared with orthogonal impingement on
the joint.
[0044]
Also, when the abruptly moving liquid obliquely
impinges on the joint between the base plate and the cover,
the flow direction of the moving liquid can be smoothly
changed toward the heel side or the toe side, as compared
with orthogonal impingement on the joint. In the other wards,
when the liquid orthogonally impinges on the joint between
the base plate and the cover, the impinging liquid becomes
unlikely to be released toward the heel side or the toe side
and is dammed; as a result, static pressure of the liquid
increases at the impingement portion.
[0045]
Thus, when the liquid obliquely impinges on the joint
between the bottom plate and the cover, the impinging liquid
is readily released toward the heel side or the toe side,
whereby there can be restrained an increase in static
pressure of liquid at the impingement portion.
[0046]
Through employment of the configuration in which the
blades each comprise a plurality of flat-shaped blade
elements separated each other by slits, the following
function and effect can be exhibited. In the case of
provision of no slits, the flat-shaped blade elements
disposed in a divergent arrangement do not easily lean even
16
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
when pressed from above, and thus apply excessively strong
stimulation to the foot sole and may possibly cause pain.
The provision of the slits avoids an excessive increase in
bending rigidity of the flat-shaped blade elements and
enables application of appropriate stimulation to the foot
sole, whereby a comfortable massaging effect can be exhibited.
[0047]
The provision of slits between the flat-shaped blade
elements allows liquid pressed by the heel or the like to
flow toward the heel side or the toe side through the slits.
Thus, the velocity of liquid flowing in the lateral direction
along the gaps between the blades can be restrained, along
with confinement pressure, whereby impact force of liquid
applied to the joint can be reduced.
[0048]
By using flat plates for forming the blade elements,
bending rigidity of the blade elements can be reduced, the
appropriate stimulation to the foot sole can be obtained and
the comfortable massaging effect can be exhibited.
[0049]
Regarding the configuration in which one group of the
blades are located on one side and the other group of the
blades are located on the other side with respect to the
center portion of longitudinal length of the first region of
the base plate, when the tilting directions of both groups of
the blades are reversed each other, impact force can be
effectively mitigated when the heel touches down on the
17
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
ground and also when the toe kicks the ground.
[0050]
Thus, in another sole member of footwear according to
the present invention, the plurality of blades are composed
of a plurality of toe-side blades located in a toe-side range
from a center portion of longitudinal length of the first
region to toe side, and composed of a plurality of heel-side
blades located in a heel side range from a center portion of
longitudinal length of the first region to heel side. A
plurality of the flat-shaped blade elements of each of the
toe-side blades are tilted toward the toe side or the heel
side.
[0051]
A plurality of the flat-shaped blade elements of each
of the heel-side blades are tilted in a direction opposite to
that of the flat-shaped blade elements of toe-side blades.
The flat-shaped blade elements which occupy both outer side
portions of each of the toe-side blades with respect to the
lateral direction of the first region are inclined in such a
manner as to be divergent toward the toe side or the heel
side as viewed from above. The flat-shaped blade elements
which occupy both outer side portions of each of the heel-
side blades with respect to the lateral direction of the
first region are inclined in such a manner as to be divergent
in a direction opposite to that of the flat-shaped blade
elements of the toe-side blades as viewed from above.
[0052]
18
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
Meanwhile, regarding the blade located at nearest
position to toe side or heel side, when liquid flows out
through a slit which separates the flat-shaped blade elements
thereof, impact force of the liquid is directly applied to
the joint at a position which faces the slit. Particularly,
in the case where the flat-shaped blade elements which occupy
both outer side portions of the toe-side blade located at
nearest position to toe side are inclined in such a manner as
to be divergent toward the heel side, or in the case where
the flat-shaped blade elements which occupy both outer side
portions of the heel-side blade located at nearest position
to heel side are inclined in such a manner as to be divergent
toward the toe side, liquid flows out faster through the
slit; accordingly, impact force of liquid becomes stronger.
[0053]
Thus, as to the toe-side blade located at nearest
position to toe side and heel-side blade located at nearest
position to heel side, by forming those blades with a single
flat blade element having no slit, there can be prevented
generation of impact force of liquid flowing out through the
slit.
[0054]
Meanwhile, when the heel, for example, presses a
portion of sealed-in liquid, the pressed liquid moves in the
lateral direction of the base plate along the gaps between
the blades, flows out from the both sides of the gaps between
the blades, and impinges on the joint between the base plate
19
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
and the cover which is located externally of the blades.
Thus, if liquid flowing out from the both sides of the gaps
between the blades does not directly impinge on the joint,
leakage of liquid can be effectively prevented. Thus, the
inventors of the present invention have employed, as
described in Patent Document 1, a means of forming a single
partition integrally rising from the base plate between the
both sides of the blades and the inner peripheral wall of the
first concave portion of the base plate, along the entire
periphery of the inner peripheral wall.
[0055]
However, it has become clear that the provision of only
a single partition fails to prevent leakage of liquid from
the joint located externally of the partition. Specifically,
when the heel, for example, presses sealed-in liquid, the
pressed portion of liquid moves to a different location where
the pressing force does not act, and deforms and expands a
corresponding portion of the closed space.
[0056]
Thus, at the unpressed portion, a contact portion
between the upper end of the single partition and the lower
surface of the cover opens, and moving liquid flows through a
clearance of the opening and impinges directly on the joint
located externally of the partition. Therefore, the liquid
becomes likely to leak from the joint.
[0057]
Thus, in another sole member of footwear according to
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
the present invention, a first partition is formed between an
inner peripheral wall of the first region and both lateral
ends of the plurality of blades in such a manner as to rise
from the upper surface of the first region. Also, a second
partition is formed on an inner periphery side or an outer
periphery side of the first partition in such a manner as to
rise from a lower surface of the second region with a
predetermined gap formed between the first partition and the
second partition.
[0058]
Furthermore, the first partition and the second
partition have a plurality of grooves or cuts formed therein.
Also, the grooves or cuts formed in the first partition and
the grooves or cuts formed in the second partition are
disposed in such a manner as not to overlap each other as
viewed from a direction along center lines of the grooves or
cuts.
[0059]
That is, through employment of dual partition such that
one partition is formed in such a manner as to rise from the
bottom plate, whereas the other partition is formed in such a
manner as to be suspended from the cover, even though, as a
result of movement of liquid, a clearance is formed between
the upper end of the partition and the lower surface of the
cover, liquid which passes through a clearance which opens at
the upper end of the inner partition is blocked by the base
of the outer partition, so that there can be avoided direct
21
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
impingement of liquid on the joint located externally of the
outer partition.
[0060]
Also, by virtue of provision of the grooves or cuts in
the first and second partitions, liquid which flows into the
gap between the outer partition and the inner periphery of
the joint is easily released, through the grooves or cuts, to
the inside of the first and second partitions, thereby
avoiding confinement of liquid in the gap; thus, an increase
in pressure resulting from the confinement can be restrained.
[0061]
Furthermore, by means of the grooves or cuts formed in
the first partition and the grooves or cuts formed in the
second partition being disposed in such a manner as not to
overlap each other as viewed from a direction along center
lines of the grooves or cuts, there can be avoided an
incident in which liquid that flows out from both sides of
gaps between the blades as a result of press impinges
directly on the joint between the base plate and the cover
through the grooves or cuts.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0062]
[FIG. 1] Top view showing a shoe midsole with a portion of a
cover cut away.
[FIG. 2] Sectional view taken along a longitudinal direction
in a state in which a base plate and the cover are separated
22
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
from each other.
[FIG. 3] Sectional view taken along the longitudinal
direction in a state in which the base plate and the cover
are joined together.
[FIG. 4] Sectional view taken along a lateral direction in a
state in which the base plate and the cover are joined
together.
[FIG. 5] Fragmentary, enlarged front views showing a slit
which separates flat-shaped blade elements from each other.
[FIG. 6] Fragmentary, enlarged top view showing a first
partition and a second partition.
[FIG. 7] Enlarged views showing grooves and cuts formed in
the first and second partitions as viewed from a direction
along the center lines of the grooves and cuts.
[FIG. 8] Top views showing examples of dispositions of the
flat-shaped blade elements.
[FIG. 9] Top views showing other examples of dispositions of
the flat-shaped blade elements.
[FIG. 10] Top views showing examples of divergent directions
of the flat-shaped blade elements.
[FIG. 11] Top view and sectional view showing a relation
between the divergent directions and the tilting directions
of the flat-shaped blade elements.
[FIG. 12] Top view and sectional view showing another
relation between the divergent directions and the tilting
directions of the flat-shaped blade elements.
[FIG. 13] Enlarged sectional views showing examples of the
23
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
first partition and the second partition.
[FIG. 14] Top view of a shoe midsole showing desirable
positions where grooves or cuts are not provided in the first
partition and the second partition.
[FIG. 15] Exploded perspective view of a portion of a shoe,
showing the position of a midsole.
[FIG. 16] Exploded perspective view of a portion of a shoe,
showing the position of an outsole.
[FIG. 17] Top view showing a conventional shoe midsole with a
portion of a cover cut away.
DESCRIPTION OF REFERENCE NUMERALS
[0063]
1: base plate
2: cover
3, 3c, 3d: blade
3a: toe-side blade
3b: heel-side blade
4: liquid
5: closed space
6: joint
11: first region
12: first horizontal flange portion
14: inner peripheral wall
15: first partition
21: second region
22: second horizontal flange portion
24
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
31: slit
32, 33: flat-shaped blade element
A: midsole
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
[0064]
A sole member of footwear according to the present
invention will next be described while referring to a shoe
midsole, with reference to FIGS. 1 to 7. As shown in FIG. 1,
the shoe midsole A according to the present invention
includes a base plate 1, a cover 2, a plurality of blades 3,
and liquid 4.
[0065]
The base plate 1 has a first region 11 having a shape
equivalent to a foot sole, and a first horizontal flange
portion 12 surrounding the entire periphery of the first
region. The cover 2 has a second region 21 which faces the
first region 11 of the base plate 1, and a second horizontal
flange portion 22 which faces the first horizontal flange
portion 12. As is apparent from FIG. 1, the first region 11
of the base plate 1 has a length extending from the heel to
the portion near to the roots of the toes, and a width of the
portion where foot sole contacts with, when foot sole touches
down on the ground.
[0066]
As shown in FIGS. 2 to 4, the first region 11 has a
concave shape which is slightly depressed downward from the
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
upper surface of the first horizontal flange portion 12, and
the second region 21 has a concave shape which is slightly
depressed upward from the lower surface of the second
horizontal flange portion 22. The upper surface of the first
region 11 and the lower surface of the second region 21 are
connected to each other through inner peripheral walls 14 and
24 which are gently inclined toward a mating surface between
the first horizontal flange portion 12 and the second
horizontal flange portion 22, thereby avoiding stress
concentration.
[0067]
As shown in FIGS. 1 to 4, a plurality of the blades 3
are formed in the first region 11 of the bottom plate 1 in
such a manner as to integrally rise from the base plate. The
plurality of blades 3 are disposed at predetermined intervals
substantially orthogonally to a center line extending from
the toe side to the heel side of the base plate 1. As shown
in FIGS. 1 and 4, each of the blades 3 is composed of two
flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33 separated each other by
a slit 31.
[0068]
As shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, the blades 3 are tilted in
opposite directions with respect to a central portion of
longitudinal length of the first region 11.
[0069]
Specifically, the blades located in a range from the
central portion of longitudinal length of the first region to
26
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
the toe side (hereinafter called the "toe-side blades 3a")
are tilted toward the heel side, whereas the blades located
in a range from the central portion to the heel side
(hereinafter called the "heel-side blades 3b") are tilted
toward the toe side.
[0070]
However, all of the blades 3 may be tilted toward the
toe side or the heel side; also, the toe-side blades 3a may
be tilted toward the toe side, whereas the heel-side blades
3b may be tilted toward the heel side. Furthermore, the
boundary between the toe-side blades 3a and the heel-side
blades 3b may be moved toward the toe side or the heel side
instead of being set at the central portion of longitudinal
length.
[0071]
As shown in FIG. 1, as viewed from above, the two flat-
shaped blade elements 32 and 33 which constitute each of the
blades 3 are disposed in such a manner as to be divergent
toward the toe side or the heel side.
[0072]
Specifically, the flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33
which constitute the toe-side blades 3a are disposed in such
a manner as to be divergent toward the heel side, whereas the
flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33 which constitute the
heel-side blades 3b are disposed in such a manner as to be
divergent toward the toe side.
[0073]
27
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
As shown in FIG. 1, the blades 3c, 3d located at the
positions nearest to toe side and heel-side are formed of a
single flat-shaped blade element having no slit. The blade
3c located at the position nearest to toe side is tilted
toward the heel side, whereas the blade 3d located at the
positions nearest to heel side is tilted toward the toe side.
[0074]
In a certain use mode of shoes, the single flat-shaped
blade element having no slit may be eliminated, two or more
of such blade elements may be formed being adjacent to one
another, and such blade elements may be provided at any
position between the heel side and the toe side.
[0075]
Desirably, the slit 31 shown in FIG. 4 separates the
flat-shaped blades 32 and 33 from each other with a range
from their upper ends to their bases as shown in FIG. 5(A).
However, as shown in FIG. 5(B), the slit 31 may be formed in
such a manner as to separate the blades 32 and 33 from each
other with depth of 50% or more of the blade height from
their upper ends to their bases so as to leave a connecting
portion above their bases.
[0076]
As shown in FIGS. 1 to 4, a first partition 15 is
formed between an inner peripheral wall 14 of the first
region 11 of the base plate 1 and both sides of the blades 3
in such a manner as to rise from the upper surface of the
first region. Also, a second partition 25 is formed on an
28
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
inner periphery side of the first partition 15 in such a
manner as to rise from the lower surface of the second region
21 with a predetermined gap formed between the first
partition and the second partition. For the purpose of easy
understanding of shape and constitution, FIGS. 2 to 4 show
the first partition 15 and the second partition 25 in a size
greater than an actual size.
[0077]
As shown in FIGS. 6 and 7(A), the first partition 15
and the second partition 25 have a plurality of grooves 151
and 251, respectively. The grooves 151 provided in the first
partition 15 and the grooves 251 provided in the second
partition 25 are disposed in such a manner as not to overlap
each other as viewed from a direction along the center lines
of the grooves.
[0078]
In place of the grooves 151 and 251 provided in the
first and second partitions 15 and 25, cuts 151 and 251 may
be provided as shown in FIG. 7(B).
[0079]
The first partition 15 and the second partition 25 may
be reversed in position. Moreover, in addition to the first
partition 15 and the second partition 25, a third partition
may be provided with a predetermined gap formed between the
same and the first or second partition, and a fourth
partition may be provided further.
[0080]
29
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 3, the first horizontal flange
portion 12 of the base plate 1 and the second horizontal
flange portion 22 of the cover 2 are joined together by a
belt-like joint 6, thereby forming a closed space 5
sandwiched between the first region 11 and the second region
21. The liquid 4 is injected into the closed space 5 from an
inlet (not shown) provided on the heel side; then, the inlet
is closed for sealing.
[0081]
The belt-like joint 6 is formed at inner peripheral
portions of the first and second flange portions 12 and 22
and has uniform width along the entire periphery of the inner
peripheral portions. Desirably, the joint 6 is formed
through thermal welding by use of a high-temperature press;
however, adhesive may be used to bond.
[0082]
The bottom plate 1 and the cover 2 are formed through
injection molding by use of thermoplastic resin such as vinyl
chloride resin.
Desirably, the liquid 4 has low water
permeability, is less susceptible to evaporation, and does
not rot. Furthermore, more desirably, liquid which does not
freeze in a cold district, such as propylene glycol, is used
as the liquid 4.
[0083]
Also, as shown in FIG. 4, both outer sides of the flat-
shaped blade elements 32 and 33 are shaped in such a manner
as to be gently curved from their upper ends to their bases
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
and are not connected to the inner peripheral surface of the
second partition 25. The reason for this is to allow the
flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33 to easily lean when
pressed, so as to exhibit a comfortable massaging effect.
Also, the reason is to allow the liquid 4 to easily flow in
the longitudinal direction through gaps 7 formed between the
inner peripheral surface of the second partition 25 and both
outer sides of the flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33, so
as to avoid increase in confinement pressure of the liquid 4.
[0084]
Desirably, as shown in FIG. 4, in a state in which the
liquid 4 is sealed in the closed space 5, the height of the
blade 3 is such that the upper end of the blade is in contact
with the lower surface of the second region 21; however, the
blade height may be higher or lower than the above contact
height. Also, desirably, the height of the first and second
partitions 15 and 25 is such that the distal ends of the
first and second partitions 15 and 25 are in contact with the
lower surface of the second region 21 and the upper surface
of the first region 11, respectively; however, the partition
height may be higher or lower than the above contact height.
[0085]
Next, referring to FIGS. 8 to 10, the dispositions of
the blades 3 and the flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33
according to other embodiments will be described. FIG. 8
shows the number and disposition of the flat-shaped blade
elements 32 and 33. Specifically, each of the blades 3 shown
31
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
in FIG. 8(A) is composed of three flat-shaped blade elements
32, 34, and 33 which are separated from one another by the
slits 31. The flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33 are
disposed in such a manner as to be divergent toward the heel
side, whereas the central flat-shaped blade element 34 is
disposed orthogonally to the longitudinal center line of the
first region 11.
[0086]
Each of the blades 3 shown in FIG. 8(B) is composed of
four flat-shaped blade elements 32, 35, 36, and 33 which are
separated from one another by the slits 31. The flat-shaped
blade elements 32 and 33 are disposed in such a manner as to
be divergent toward the heel side, and the central flat blade
elements 35 and 36 are also disposed in such a manner as to
be divergent toward the heel side. The central flat-shaped
blade elements 35 and 36 may be disposed orthogonally to the
longitudinal center line of the first region 11.
[0087]
Each of the blades 3 shown in FIG. 8(0) is composed of
five flat-shaped blade elements 32, 37, 38, 39, and 33 which
are separated from one another by the slits 31. The flat-
shaped blade elements 32 and 33 are disposed in such a manner
as to be divergent toward the heel side, and the inner flat-
shaped blade elements 37 and 39 are also disposed in such a
manner as to be divergent toward the heel side. The central
flat-shaped blade element 38 is disposed orthogonally to the
longitudinal center line of the first region 11. The inner
32
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
flat blade elements 37 and 39 may be disposed orthogonally to
the longitudinal center line of the first region 11.
[0088]
FIG. 9 shows embodiments in which the slits 31 of the
adjacent blades 3 are located at such positions as not to
overlap each other as viewed from a direction along the
center lines of the slits 31. The reason for this is that,
if the slits 31 of the adjacent blades 3 are located at such
positions as to overlap each other, the pressed liquid 4
flows excessively easily in the longitudinal direction,
therefore, the effect of reducing impact force of the liquid
4 is decreased.
[0089]
The divergent angle of the flat-shaped blade elements
32 and 33 is preferably 170 degrees to 120 degrees, more
preferably 160 degrees to 140 degrees. At a divergent angle
in excess of 170 degrees, the effect of reducing impact force
of the liquid 4 which flows out from the both sides of the
gaps between the blades 3 and impinges on the joint 6 between
the base plate 1 and the cover 2 is decreased, and, at a
divergent angle less than 120 degrees, when the foot sole or
the like touches down on the ground during walking or the
like, a feeling of lateral stability deteriorates. In the
present embodiment, the divergent angle is set at about 150
degrees.
[0090]
FIG. 10 shows embodiments in which the flat-shaped
33
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
blade elements 32 and 33 are divergent. Specifically, FIG.
10(A) shows an embodiment in which the flat-shaped blade
elements 32 and 33 of the toe-side blades 3a are disposed in
such a manner as to be divergent toward the toe side, whereas
the flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33 of the heel-side
blades 3b are disposed in such a manner as to be divergent
toward the heel side.
[0091]
FIG. 10(B) shows an embodiment in which the flat-shaped
blade elements 32 and 33 of the toe-side blades 3a and the
heel-side blades 3b are both disposed in such a manner as to
be divergent toward the heel side. Furthermore, FIG. 10(0)
shows an embodiment in which the flat-shaped blade elements
32 and 33 of the toe-side blades 3a and the heel-side blades
3b are both disposed in such a manner as to be divergent
toward the toe side.
[0092]
FIGS. 11 and 12 show relations between the divergent
direction of the flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33, and
the tilting direction of the flat-shaped blade elements 32
and 33. FIG. 11(B) and FIG. 12(B) show a case where the
divergent direction and tilting direction of the flat-shaped
blade elements 32 and 33 are the same. Specifically, in FIG.
11(B), the divergent direction and the tilting direction of
the flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33 are toward the toe
side. In FIG. 12(B), the divergent direction and the tilting
direction of the flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33 are
34
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
toward the heel side.
[0093]
By contrast, FIGS. 11(0) and 12(0) show a case where
the divergent direction and the tilting direction of the
flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33 are reversed.
Specifically, in FIG. 11(C), the flat-shaped blade elements
32 and 33 are divergent toward the toe side, but are tilted
toward the heel side. In FIG. 12(C), the flat-shaped blade
elements 32 and 33 are divergent toward the heel side, but
are tilted toward the toe side.
[0094]
Desirably, the blade 3c located nearest to the toe-side
blades 3a shown in FIG. 10 is tilted toward the heel side,
and the blade 3d located nearest to the heel-side blades 3b
is tilted toward the toe side; however, their tilting
directions may be reversed.
[0095]
The tilting angle of the flat-shaped blade elements 32
and 33, etc., is desirably 30 degrees to 60 degrees, more
desirably 40 degrees to 50 degrees, with respect to a
vertical plane. At an tilting angle less than 30 degrees,
the flat-shaped blade elements 32 and 33, etc., become
unlikely to fall when pressed by the foot sole, so that
stimulation to the foot sole becomes excessively strong, and,
at an tilting angle in excess of 60 degrees, the flat-shaped
blade elements 32 and 33 easily fall, so that stimulation to
the foot sole becomes excessively weak. In the present
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
embodiment, the tilting angle is set to about 45 degrees.
[0096]
Desirably, the upper ends of the flat-shaped blade
elements 32 and 33, etc., have a cross-sectional shape
outlined by an arc-shaped curve or the like. The reason for
this is that stimulation to the foot sole becomes soft,
thereby yielding a comfortable massaging effect.
[0097]
FIG. 13 shows examples of cross-sectional shapes of the
first partition 15 and the second partition 25. Specifically,
FIG. 13(A) shows a cross-sectional shape composed of a
rectangular base portion and a semicircular distal end. FIG.
13(B) shows a rectangular cross-sectional shape whose distal
end has radiused corners. Furthermore, FIG. 13(C) shows a
trapezoidal cross-sectional shape whose distal end has
radiused corners. Notably, the cross-sectional shapes of the
first partition 15 and the second partition 25 are not
limited to the above-mentioned cross-sectional shapes.
[0098]
Five positions marked with letter C in FIG. 14 indicate
those positions at which, in the conventional shoe midsole A,
the liquid 4 is likely to leak from the joint 6 between the
base plate 1 and the cover 2. Therefore, desirably, the
grooves or cuts 151 of the first partition 15 and the grooves
or cuts 251 of the second partition 25 shown in FIGS. 6 and 7
are provided at positions other than the five positions
marked with letter C. The reason for this is to prevent the
36
CA 02873158 2014-10-16
quickly moving liquid 4 from directly hitting the joint 6 at
the five positions marked with letter C.
[0099]
FIG. 15 shows a case where the sole member of footwear
according to the present invention is applied as the shoe
midsole A mentioned above. FIG. 16 shows a case where the
sole member of footwear according to the present invention is
applied as a shoe outsole B.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
[0100]
The present invention can be utilized widely in the
footwear industry, since, during walking or the like, the
sole member of footwear of the present invention absorbs
impact while providing a feeling of stability, exhibits a
massaging effect through stimulation of the foot sole, and
can prevent leakage of sealed-in liquid.
37