Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
MULTI-STRAND BRAIDING DEVICE AND METHOD
Field
[0001] The present disclosure relates to a device and method for
intertwining flexible
strands of a material, and more particularly relates to a device and method
for braiding hair.
Background
[0002] Braiding is widely recognized as a form of hairstyling, and is
commonly used to
form ropes and other objects. Numerous devices have been developed to assist
in braiding or
intertwining hair and other materials. These devices are often directed to
braiding hair in a
flat, three-strand pattern. For example, U.S. Patent No. 4,369,690 discloses a
hand held, hand
operated device with a set of three elliptical gears, through which the user
places his or her
hair. By using a rack and pinion connected to a hand crank, two sector gears
move the
elliptical gears in an alternating pattern, thus forming the braid. Other hair-
braiding devices,
such as disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,988,181, use motors or actuators to
move strands about
in a set pattern to result in a three-strand braid.
[0003] Existing hair braiding devices, however, exhibit several drawbacks,
including
disorderly braids, inconsistent performance, and/or difficult operation.
Further, the existing
devices are limited to repeating a single braiding pattern using three
strands.
Summary
[0004] The present disclosure provides a device and method for intertwining
a filament,
or other flexible material in a variety of patterns. In particular, the device
comprises a
housing, which contains sector gears and elliptical gears, at least one motor,
and a controller
for controlling the motor. The hand-held braiding device may also comprise a
memory unit
and a user interface for selecting and storing different braiding patterns.
1
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
[0005] Another aspect of the present disclosure provides a method for
selecting a pattern
module for weaving strands. The pattern module may be selected using the user
interface of
the hand-held braiding device described above. This pattern module may be
stored in the
memory unit of the device or in a readable media device. The pattern module is
loaded into
the controller, for example, using the user interface, and the device is
operated using an
actuator.
[0006] Other systems, methods, features, and advantages of the present
disclosure will be
or become apparent to one with skill in the art upon examination of the
following drawings
and detailed description. The features, functions and advantages that have
been discussed
can be achieved independently in various embodiments of the present invention
or may be
combined in yet other embodiments further details of which can be seen with
reference to the
following description and drawings.
Brief Description of the Drawings
[0007] Many aspects of the invention can be better understood with
reference to the
following drawings. The components in the drawings are not necessarily to
scale, emphasis
instead being placed upon clearly illustrating the principles of the present
invention.
Moreover, in the drawings, like reference numerals designate corresponding
parts throughout
the several views.
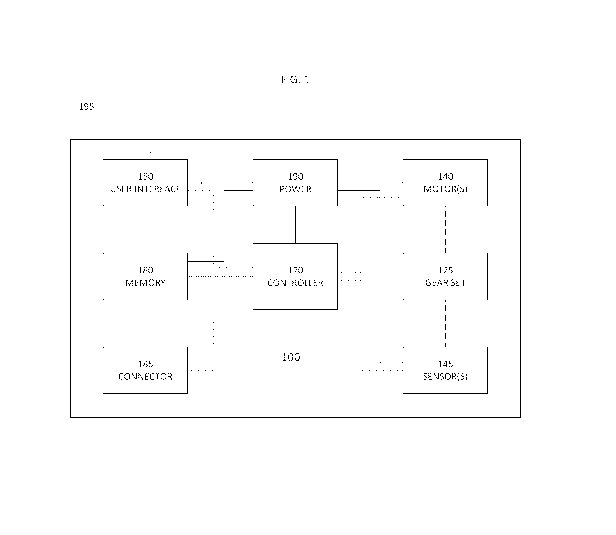
[0008] FIG. 1 is a schematic illustrating the relationship of the various
features according
to one embodiment of the present disclosure;
[0009] FIG. 2A is a top view one embodiment of a hair-braiding device in
accordance
with the present disclosure;
[0010] FIG. 2B is a side view of the device shown in FIG. 2A;
[0011] FIG. 2C is a partial top view, (without the housing), of the device
shown in FIG.
2A;
2
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
[0012] FIGS. 3A ¨ 3D are illustrations depicting the motion of the gears of
a hair-
braiding device in accordance with the present disclosure;
[0013] FIG. 4 is an illustration of a gear set in accordance with another
embodiment of a
hair-braiding device in accordance with the present disclosure;
[0014] FIG. 5 is an illustration of a sleeve according to one embodiment of
the hair-
braiding device of the present disclosure;
[0015] FIGS. 6A ¨ 6E are illustrations of various steps of a method for
forming a four-
strand braid according to the present disclosure; and
[0016] FIG. 7 is a schematic of one embodiment of a system for selecting a
hair-braiding
style according to another aspect of the present disclosure.
Detailed Description
[0017] In the following description, reference is made to the accompanying
drawings,
which form a part hereof, and in which is shown, by way of illustration,
various embodiments
of the present disclosure. It is understood that other embodiments may be
utilized and
changes may be made without departing from the scope of the present invention.
[0018] FIG. 1 illustrates one embodiment of the present disclosure, wherein
the various
features of the device 100 are represented schematically. In this figure, the
features of the
device are not represented to scale, but are arranged for convenience in
explaining the device.
The solid lines between the elements represent the electrical connections from
power source
190. The dotted lines represent data or command connections between the
various elements
and a controller 170. The dashed lines represent the physical connections
between the gear
set 125 and the at least one motor 140, and between the gear set and the at
least one sensor
145. The gear set, which may comprise a conventional set of toothed gears or
other
strategically shaped items, is driven by at least one motor 140, which is
controlled by the
controller 170. A plurality of sensors 145 monitor the movement of the gear
set 125 and
3
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
provide data to the controller 170, which is used in the execution of a set of
instructions. The
instructions are provided to the controller through the memory unit 180 by
using a user
interface 150. The sectioned line 195 is drawn around the memory unit 180 and
the user
interface 150 to show that these two features in particular may be separate
from the physical
hand-held device.
[0019] FIGS. 2A and 2C illustrate another embodiment of a device 100
according to the
present disclosure. The hair-braiding device 100 comprises a housing 101 with
a handle 102
attached thereto. The hair-braiding device 100 also comprises three sector
gears 110 and four
elliptical gears 120. The sector gears 110 and the elliptical gears 120 are
arranged in the
housing 101 and are accessible at each of the top and bottom sides of the
housing 101
through an opening 105. Each of the elliptical gears 120 is hollow and
contains a respective
sleeve 130. The various gears are turned by the motors 140, each of which is
shown
connecting to one of the sector gears 110. Each of the sector gears 110
rotates about a
corresponding pivot 115. The illustrated embodiment also shows three sensors
145, each of
which is paired with a respective motor 140. The hair-braiding device also
comprises an
actuator 160.
[0020] FIG. 2B illustrates another embodiment of a hair-braiding device 100
in
accordance with the present disclosure, comprising a housing 101 and a handle
102. A user
interface 150 is visible on the side of the housing 101. Connector 185 is also
visible on the
side of the hair-braiding device 100.
[0021] In some embodiments, the housing 101 of the hair-braiding device 100
is
comprised of two pieces, an upper housing and a lower housing, which fit
together to form
the housing 101 having a cavity therein to contain many of the elements of the
hair-braiding
device 100. Alternatively, the housing 101 may comprise a unitary structure,
wherein, for
example, the housing comprised two halves that are brought together using a
thermoplastic
4
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
weld. The opening 105 of the housing allows access to the moving parts of the
hair-braiding
device 100, namely, The material of the housing structure may be comprised of
any suitable
material, including plastics, metals, and any other material commonly used in
the
manufacture of household beauty products. The opening 105 may be provided on
the top and
the bottom of the housing 101, thereby allowing the user to access the gears
from either side.
Further, the housing 101may be provided with a protective or decorative cover,
which may be
used for aesthetic purposes or to cover seams or other parts of the housing
101 in which hair
may potentially become caught.
[0022] In various embodiments, the handle 102 may be formed with the
housing 101 or
as a separate element which is attached to the housing 101 at a later time. In
some
embodiments, the shape of the handle 102 comprises an ergonomic shape. The
handle 102
may also comprise an outer surface formed of foam or another suitable
substance for creating
a comfortable grip, as may be found commonly in the art.
[0023] In the embodiment shown in FIGS. 2A and 2C, three sector gears 110
and four
elliptical gears 120 are visible through the opening 105 in the housing 101.
The sector gears
110 are in a shape similar to the profile of a symmetrical apple core in
appearance and the
elliptical gears are in the approximate shape of an ellipse with two pointed
ends. The shape
of the sector gears 110 and elliptical gears 120 are complementary, such that
by adding the
pointed "elliptical" shape of an elliptical gear to each side of the sector
gears 110, the objects
collectively take the approximate shape of a circle. By arranging the gears in
an alternating
fashion (elliptical, sector, elliptical, sector, etc.), with the center of
each gear forming a
straight line, (in a vertical direction looking at FIGS. 2A or 2C), the gear
arrangement takes
the shape of a series of intersecting circles. See also FIG. 3A.
[0024] The motions of the gears rotate about each of the three pivots 115.
Each of the
sector gears 110 corresponds to one of the pivots 115, which is located at the
center of each
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
of the sector gears 110. In some embodiments the pivot 115 may comprise a pin
or other
physical feature at the center of the sector gears 110. Alternatively, the
pivots 115 may be
formed integral to the sector gears 110. In other embodiments, a pivot 115 is
merely defined
as the location about which the rotation takes place, wherein the motion of
the gears is
guided, for example, by outer constraints on the movement of the gears, such
as a channel
defining the outer bounds of the gear set 125.
[0025] The elliptical gears 120 also rotate about one of the pivots 115,
but may rotate
about any one of the pivots, depending on the relative position of the
elliptical gear. The
elliptical gears 120 also rotate about one of the pivots 115, but may rotate
about any one of
the pivots, depending on the relative position of the elliptical gear. For
example, FIGS. 3A-
3D demonstrate the relative motion of the gears wherein the gears are rotated
about one of the
pivots 115 at a time, wherein the arrows show the direction of rotation. FIG.
3A shows the
gears in a default position, wherein the gear arrangement takes the shape of a
set of
intersecting circles, as explained above. FIG. 3B shows a first motion of the
gears wherein
sector gear 111 is rotated about pivot 116; FIG. 3C shows a second motion
wherein sector
gear 112 is rotated about pivot 117; and FIG. 3D shows a third motion wherein
sector gear
113 is rotated about pivot 118. In some embodiments sector gears 111 and 113
may be
rotated simultaneously. By performing these motions in the desired order, the
relative
position of elliptical gears 120 may be changed. Note, for example, open space
135 (shaded),
which changes position through each of FIGS. 3A-3D, as these motions are
performed in
succession. In some embodiments, the sector gears 110 may be rotated in either
direction
about the corresponding pivot 115.
[0026] In the embodiment illustrated in FIG. 2C, the motion of the sector
gears 110 and
elliptical gears 120 is manipulated by three separate motors 140. As shown in
FIG. 2C, the
motors 140 may be in contact with the sector gears when the gears are in the
default position
6
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
(FIG. 3A). The outlying portions of the sector gears 110 and the perimeter of
each of the
elliptical gears may include a plurality of teeth. These teeth may then be
manipulated by one
or more of the motors 140, which may be a worm drive or similar actuator to
rotate the gears
about any one of the pivots 115 as desired. The teeth of the sector gears 110
of one
embodiment of a gear set 125 are visible in FIG. 3E.
[0027] Other motors and arrangements of motors relative to the gears are
further
contemplated by this disclosure, as may be apparent to one of ordinary skill
in the art. For
example, in some embodiments, the motors 140 may be rotary in nature and
connected to one
of the pivots 115, either directly or by some other mechanical device such as
a drive belt,
thereby turning the respective gears. In this alternative example, the sector
gears 110 and
elliptical gears 120 may be toothless. In this respect, the use of the term
"gear" within the
present disclosure may be construed to include a plurality of moving parts
which may result
in a similar motion.
[0028] In one alternative embodiment, the device 100 of the present
disclosure may
comprise one motor 140 which provides power to drive each of the sector gears
independently. This alternative arrangement may be achieved using, for
example, a clutch
for each of the rotating sector gears, wherein the controller operates the
engagement of each
clutch.
[0029] The present disclosure further includes alternative embodiments
comprising
expanded gear sets with the ability to handle more than four strands of hair
or filaments. One
alternative embodiment is shown in FIG. 4A, wherein the gear set 225 comprises
five sector
gears 210 and six elliptical gears 220, in a linear arrangement. Similarly,
other linear
arrangements may be devised comprising "n" sector gears and "n+1" elliptical
gears. FIG.
4B illustrates another embodiment of the present disclosure, wherein gear set
325 has 12
elliptical gears arranged around four sector gears. This embodiment is
therefore able to
7
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
weave up to 12 strands of hair or filament at one time. FIG. 4C illustrates
another
embodiment comprising a gear set 425 arranged in a triangular formation,
having seven
elliptical gears and three sector gears. Further embodiments with numerous
potential
arrangements are also contemplated by the present disclosure, as may be
apparent to one
having ordinary skill in the art.
[0030] As discussed above, the elliptical gears 120 comprise a hollow
center for carrying
strands of a flexible material. In some embodiments, the hair-braiding device
of the present
disclosure comprises a plurality of sleeves 130, which fit into the hollow
center of the
corresponding elliptical gears 120. The sleeves 130 are formed from a flexible
material that
may be removed from the elliptical gears and replaced. The sleeves 130 may be
used to
assist in bundling the flexible material into strands (including bundles of
individual strands).
The sleeves 130 may also be configured to preserve tension on the strands
without requiring
additional work from a user. This may be accomplished by selecting a tactile
material for the
sleeves 130.
[0031] FIG. 5 illustrates another embodiment of the present disclosure,
wherein the
sleeves 530 may be constructed with a surface 535 that substantially fills the
hollow space
within the elliptical gears. In the embodiment shown in FIG. 5, the sleeve 530
further
includes a slot 536, through which the strands may be inserted. The sleeve 530
should be
formed of a flexible material, wherein slot 536 exhibits some elastic
properties, thereby
accommodating various sizes of strands. The elastic properties of sleeve 530
also help to
create tension on the strands when in use.
[0032] The present disclosure may be implemented using a variety of
mechanisms to hold
the strands in place while operating the device 100. In a further embodiment,
for example,
the sleeves 130 may be replaced by individual clasps that hold the individual
strands in the
8
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
hollow center portion of the elliptical gears 120. Alternatively, the clasps
may be provided at
the free end of the strands.
[0033] Referring again to FIG. 2C, the controller 170 sends signals to each
of the motors
140, which turn the sector gears 110, thereby rearranging the elliptical gears
120 and the
respective strands which pass through the elliptical gears, resulting in the
formation of the
desired braid. In some embodiments the motors 140 can be controlled to operate
in a number
of different sequences, each one forming a unique braid. Further, the
operation of the motors
may be changed from one pattern to another after a specified number of turns,
thereby
forming a series of alternating braid patterns in the strands of hair or
filaments. The hair-
braiding device 100 may also comprise a number of sensors 145, which allow the
controller
to sense the rotation of the gears. In some embodiments, the controller
comprises a
processor.
[0034] The various braiding patterns discussed above may be stored, for
example, as a
pattern module comprising a set of instructions. For example, the memory unit
180 may be
provided with free space thereon, whereby additional or new patterns may be
loaded onto the
memory unit 180 and stored therein. The controller 170 may recall any of the
stored braiding
patterns via user input. Referring again to FIG. 2B, the user input may be
provided via the
user interface 150. The user interface 150 may be a simple switch or dial or
may be provided
as a graphical user interface (GUI), as shown, wherein the GUI comprises a
touchscreen. In
alternative embodiments, the functions of the user interface may be fulfilled
using an external
computing device, such as a smart phone, or a computer.
[0035] In some embodiments, the pattern modules may be stored in the memory
unit
using a number of different methods. For example, the user may provide new
patterns for the
hair-braiding device 100 by uploading them into the device or by using the
GUI. Patterns
may be uploaded, for example, using connector 185, which may be configured to
receive a
9
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
communications cable, such as a USB interface. Alternatively, the patterns may
be uploaded
wirelessly, using a suitable communication protocol, such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi,
infrared
transmission, or some other type of communication.
[0036] The actuator 160 allows the user to control the starting and
stopping of the motor
without disrupting the overall set of instructions being executed by the
controller 170. The
actuator 160, which may alternatively comprise a trigger, button, lever, or
switch, allows the
user to have direct control over the device. The actuator 160 may further
include a spring. In
some embodiments, the actuator 160 comprises multiple settings to control the
speed of the
gears. This may be controlled, for example, based on the amount of force
placed on the
actuator 160. Also, the actuator 160 may comprise a sliding selector, which
may be moved
laterally to control the speed of the output.
[0037] The hair-braiding device 100 further comprises a power source 190,
which
provides electrical power to the various parts of the device. The power source
may comprise
a battery, an AC connection, and/or the connector 185. The power source may
comprise a
rechargeable battery in connection with an AC connection and/or power from the
connector
185. In FIG. 2C, the embodiment is shown with the power source 190 residing
inside the
handle 102. In other embodiments, the power source 190 may be located within
the housing
101 or external to the device 100.
[0038] In operation, the hair-braiding device 100 of the present disclosure
may be used as
part of a method for intertwining multiple strands of a flexible material in
various braid
patterns. In one embodiment, shown in FIG. 6A, the method comprises separating
four
strands 601 (wherein a strand may be a bundle of individual hairs, filaments,
or other flexible
material). This flexible material may include flexible metallic elements,
fibrous elements,
human or animal hair (such as a horse's tail), animal skins, textiles, or any
other flexible
material that the user may desire to weave. Alternatively, where the strands
comprise a
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
bundle of flexible material, the bundle may be temporarily held together with
a rubber band
or a small strip of paper, as is commonly known in the art.
[0039] In FIG. 6B, the strands 601 are shown being inserted into the
sleeves 130.
Referring to FIG. 6C, once each of the strands are placed into the sleeves,
the sleeves 130 are
placed in the hair-braiding device 100 at the center of the elliptical gears
120 (not shown).
Alternatively, the strands may be placed directly into the elliptical gears
without the sleeves
130 or the sleeves may be left in the elliptical gears 120 while the strands
are inserted.
[0040] Next, the user selects the desired pattern and begins operating the
hair-braiding
device 100 using actuator 160. FIG. 6D illustrates the weaving action of the
hair-braiding
device 100 when in use. The resulting braid will have a more aesthetic
appearance where the
correct amount of tension is placed on each strand 601. In some embodiments,
this tension is
provided by the sleeves 130, as discussed above. Finally, once the weaving
action is
complete, the hair-braiding device 100, including the sleeves 130, is removed
from the ends
of the strands.
[0041] Referring to FIG. 6E, the resulting weave or braid is then secured.
In some
embodiments, the woven strands may be secured by using a tie 602, which may be
a ribbon
or an elastic band. Alternatively, the woven strands may be secured by
singeing, by use of an
adhesive, or by another known method.
[0042] Referring to FIG. 7, another aspect of the present disclosure
provides a method
700 for selecting a desired pattern module 701 for use with a hair-braiding
device in
accordance with the present disclosure. As with the various embodiments
discussed above,
the hair-braiding device 100 may be employed in connection with many other
flexible
materials in addition to hair. A pattern 701 may be located on an internet
server 705, on a
computing device 710, (such as a smart phone, tablet, or computer), or on a
readable media
device 755, (such as, for example, a flash drive, a memory card, a cartridge,
or some other
11
CA 02882236 2015-02-16
WO 2014/028761
PCT/US2013/055182
proprietary or commonly used design). The pattern module 701 may be downloaded
from
the internet server 705 to the computing device 710, or from the computing
device 710 to the
readable media device 755. The pattern module 701 may be stored in the memory
unit 735 of
the hand-held device 720, or it may be loaded directly into the controller
730. The storing or
loading of the pattern module 701 may be accomplished using wireless
communication, as
described above, or through a connector, such as cable connector 740 or
readable media
connector 750. Where a plurality of pattern modules 701 are stored on the
memory unit 735,
the desired pattern module 701 may be selected using the user interface 725.
Alternatively,
the function of the user interface 725 may be performed using the computing
device 710.
[0043] It should be emphasized that the above-described embodiments of the
present
device and method are merely possible examples of implementations and merely
set forth for
a clear understanding of the principles of the disclosure. Many different
embodiments of the
disclosure described herein may be designed and/or fabricated without
departing from the
spirit and scope of the disclosure. All these and other such modifications and
variations are
intended to be included herein within the scope of this disclosure and
protected by the
following claims. Therefore the scope of the disclosure is not intended to be
limited except
as indicated in the appended claims.
12