Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
The Mechanical Batterys
1. The Technical Field:
The technical field of the invention is the field of batteries storing
electric energy, which is considered the second kind of batteries until
now since all other batteries store electricity in the form of chemical
energy. Yet, this new battery, subject of the invention, stores
electricity in the form of mechanical energy. In some of its forms, it
does not need charging, wires or chargers. In other forms, it is
charged by wind or solar energy. It is used in the following fields:
1- Cell phones and smart devices in general.
2- Solar energy.
3- Wind energy.
4- Potential energy.
This is detailed in full in the explanation of the invention.
2. Background Art:
Chemical batteries, which were invented previously and are still in
use until now, whether dry or liquid, are among the things that
developed humans. These batteries have a lifetime not exceeding
four years for the good types. Some of them continue for days and
months. They depends in their manufacturing on materials harmful
to man and the environment in general with lots of machines
depending thereon to work, such as cars, phones, headlights ...etc.
To be charged, they need an electric source, chargers and cables of
wires. They need several hours for charging and in maintenance;
they need many things. Moreover, they are heavy and if they expire,
they are thrown to garbage boxes or in the streets or recycled, which
irreversibly harms the environment. Again, pollution with these
materials leads to chronic diseases that affect man, animal and even
fishes in the sea.
Therefore, the solution is now represented in this new invention that
I called "Mechanical Battery". May God grant us success!
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
Problem or Shortage in the Background Art:
Chemical batteries whether dry or liquid have the following
disadvantages:
1- Not long living, they expire in days to four years only.
2- Manufactured of poisonous materials harmful to man and
animal.
3- Heavy in weight.
4- Need an electric source for charging which is not available
away from electricity.
5- When thrown away, they are harmful to the environment.
6- They need a suitable fit charger and wires for charging.
7- Need a long time to be charged.
Disclosure of Invention:
The new invention, which I called "Mechanical Battery" which is
manufactured in four ways or more, is featuring many advantages to
make the dream that human dreamed long time ago come true. This
is represented in the following:
1- Long lasting for decades with no damage.
2- Not needing chargers or wires to be charged.
3- They do not need electric sources to be charged as they are
charged either manually or in conjunction with potential
energy or wind power etc.
4- They are not pollutant to the environment.
5- They provide an electrical source at any time anywhere.
6- They solve problems of smart equipments such as mobile
phones, electric cars.. .etc.
7- They adjust and utilize wind and solar energy very well.
8- They are used in manufacturing the batteries of satellites and
spaceships, which are charged with solar energy that increases
its longevity many times more than their current virtual
lifetime.
9- These batteries can generate direct and alternating current.
They can also generate one or three electric ends with one
negative end (3 phases). This depends on the way the dynamo
wires are coiled or according to their need to usage.
2
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
10- These
batteries are used with all machines and
equipment beginning with cell phones, ending with spaceships.
They provide man with an electric source wherever he goes.
Detailed Description:
This invention, called the "Mechanic Battery" has four ways or more
in its composition and components:
First Technique consists of the following parts:
1- An operating handle.
2- A spring wire.
3- A group of gears for accelerating speed.
4- A suitable electric generator.
5- An electricity unification circuit; when needed.
Parts Explanation
1- A handle to charge the battery. This handle is connected with the
column on which the spring is fixed. It becomes engaged when the
battery is charged by pulling the spring a little out. Then, after
complete filling, it is being returned to the inside so that it is being
separated from the column.
2- A spring wire; taking into account, thickness, strength and length
suitable for the machine work. The longer the spring, the longer time
the battery works. The thicker the spring, the higher the voltage
generated from the battery.
3- A group of gears for increasing speed. The gears should be
doubled; i.e. the big gear having a small gear to reduce the volume
of the Mechanic Battery and perform their purpose.
The first gear should spin in one direction and the spring should be
bearing on the first gear column, so that, when the first gear is turned
to fill in the spring, the movement is separated from the other gears
connected to the generator. The first or second gear is loaded on a
lining or a group of linings, permitting loading thereon and isolating
movement from other gears when filling in the spring (like the gear
3
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
in the back wheel of a bicycle). This is for the simplicity as when
filling in the spring in an easy way, not needing high effort.
4- A suitable generator in which the rotor element contains a magnet
either natural or artificial having two poles or four at most .This is to
adjust the gear speed and not to discharge the spring at once.
However, the dynamo shall have two poles magnet in its rotor and
two coils at its stator to complete this mission at best.
This mission is performed by the (pendulum) in old days' watches
and the mechanic timer.
Moreover, it shall be taken into consideration that the dynamo shall
directly be a direct current generator for devices that need alternating
current. Both ends of the dynamo shall be directed to the ends of the
device, which needs to be fed with electricity. All this shall be
adjusted in a suitable way.
5- An electric unification circuit; when needed.
Operating Technique
The Mechanical Battery is filled in this case that manually through a
handle outside, being turned in the direction compressing the spring
that turns easily in one direction. Then the handle is entered in the
device so that the spring springs back again to move the gears which
in turn operates the generator that generates electricity then the
alternating current produced by the dynamo turns into a direct
current by the unification circuit then the both ends are directed to
the device that needs to be fed with electricity.
All being with the power and will of God ............
Usages of this Technique
This Technique is used to work cell phones, laptops, computers,
headlights etc...
The Second Technique consists of following parts:
1- A half or one-third rounded flywheel.
2- A group of gears for reducing speed.
3- A spring.
4
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
4- A group of gears for accelerating speed.
5- A suitable generator.
6- A unification circuit; when needed.
7- A handle for manual operating.
Parts Explanation
1- A half or one-third rounded flywheel fixed on a column that
has a small gear fixed thereon to give a bigger gear with a
small gear fixed thereon connected to a bigger one and so on.
The column, the flywheel and gear fixed thereon shall work in one
direction so as when the flywheel moves up due to battery body
movement or any other movement the rises up easily due separating
movement from the other gears through a fiber or a metal slice fixed
for this purpose.
So, if the flywheel comes back to the resting situation due to earth
gravity, the gear fixed to the flywheel column engages to the group
of gears connected to the column the spring is fixed on.
2- A group of gears for reducing the speed begins with the gear
fixed on the flywheel column and ends with the gear that the
spring fixed on its column.
3- A spring, which is considered the backbone of the machine
that shall be suitable in length and thickness as, explained
before.
4- A group of gears for accelerating the speed begins with a big
gear fixed on the spring. This gear works in one direction as if
the flywheel moves, it leads to moving this gear to fill in the
spring and in the same time. The movement is being separated
from other groups of gears related to the generator.
5- A suitable generator with the rotor inside containing a magnet
either natural or artificial. It shall have two or four poles at
most. This is to adjust the gears' speed and not to discharge the
spring at once whereas the dynamo that contains two poles of
magnet at its rotor and two poles of the coils in the stator
complete this mission at best.
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
This is the mission the (pendulum) did in watches of the old days
and in the mechanical timer. All this shall be adjusted in a suitable
way.
6- A unification circuit makes the electric current generated from the
dynamo direct instead of being alternating. The two ends of the
circuit are being directly directed to the device.
(So the dynamo shall generate a direct current and then the
unification circuit is being dispensed).
7- A handle for manual switching. This is when there is no
movement or potential energy, the handle is being pulled to the
outside, so it is engaged with the column on which the spring is
fixed, so the spring contracts and then it is pushed to the inside to be
separated from the column of the spring.
Operating Technique
This technique is considered a manual-automatic so if the devise
body moves, the spring is charged by the movement. If there was no
movement, the spring is charged manually like the first operating
technique. This is through a handle connected to the column on
which the spring is fixed.
During filling by hand, the movement shall be isolated from the
group of gears that reduce the speed connected to the flywheel. In
the same time, the movement is separated from the other group
connected to the dynamo. During filling it in by movement, the
flywheel simply and easily swings back and forth so that the spring
gradually contract then it spreads making the dynamo turn and
generate electricity.
Usages of this Technique
This technique is used with cell phones, electric cars and any mobile
device.
The Third Technique: This works by wind power, consists of the
following parts:
1- A fan, or plastic or wood plate to face air.
2- A group of gears for reducing speed.
6
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
3- A spring.
4- A group of gears to accelerate speed.
5-A dynamo.
6- A unification circuit (when needed)
Parts Explanation
1- A wood plate or fan moved by air fixed on a high column. This
column has a small gear turning in one direction (i.e. instead of the
flywheel in the second technique above).
2- A group of gears for reducing speed starting with the gear fixed
on the fan or the plate column. This ends with the gear on which
column the spring is fixed.
3- A spring that is considered the spring of the machine. And it shall
be suitable in length and thickness as explained before.
4- A group of gears for accelerating speed starting with a big gear in
which the spring is fixed. This gear works in one direction. If the
plate or fan moves, it ends to moving this gear to fill in the spring
and at the same time; the movement is separated from the rest group
of gears that are connected to the generator.
5- A suitable generator. Its roller shall contain a magnet whether
natural or artificial and to have two poles or four at most. In
addition, this is to adjust the speed of gears and not to discharge the
spring at once. Whereas the dynamo that has magnetic two poles at
its rotor and on two poles of coils at its stator completes this mission
in the best way.
This is the mission the (pendulum) did in watches of the old days
and in the mechanical timer.
Taking into consideration that the dynamo shall directly be a direct
current generator. This is in devices needing direct current. The
dynamo shall generate be an alternating current with devices that
need alternating current and the ends of the dynamo are directed to
the ends of the device that needs electricity.
In addition, the dynamo shall be a generator for three positive ends
(3 phases) and this is according to usage needs.
7
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
6- A unification circuit that makes the electricity generated from the
dynamo a direct current instead of alternating and the ends of the
circuit are being directly directed to the device or the machine. (The
circuit shall be used when needed).
Operating Technique
When the plate is moved by the wind, it simply and easily rises up
due separating movement from the other gears. So when it is back to
the rest position because of earth gravity, the gear is engaged to the
column, which leads to connecting the movement with the spring
column and through continuous movement by the wind the spring is
compressed and so the dynamo works and generates electricity.
However, when the fan moves by the wind, its movement passes
through the gears that reduce speed to the spring column and so the
column coils to compress the spring.
Usages of this Technique
This technique is suitable for the fields to run irrigation machines
and provide houses with electricity as the wind contracts the spring
in the period when electricity is not in use. So, when it is needed
when there is no wind, the spring is so filled with charging.
This is considered a new opening in this realm as it can enter the
domain of generating electricity by wind power in which the
generated energy ranges among lacking, few and plenty according to
wind strength and weakness. Therefore, when energy is saved in a
strong spring, it becomes practical, continuous and permanent
energy. This is due to the existence of power saved for many hours
that makes it a perfect energy for human usage.
The Fourth Technique: It is a mechanical battery filled or charged
by an electric motor consisting of the following parts:
1- An overload.
2- A suitable electric motor.
3- A group of gears for reducing the speed.
4- A suitable spring.
5- A group of gears for accelerating the speed.
6- A suitable generator.
8
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
7- An electric brake.
8- Relay or cut-out for cutting and connecting electricity
automatically.
Parts Explanation
1- An overload in the junction coming from home electricity going
to the electric motor. When filling the spring and being completely
charged, its mission is to pull out high electricity which makes the
overload cut electricity from the motor.
2- An electric motor that shall be suitable in its power to fill the
spring.
3- A group of gears to reduce speed that connected to the motor from
an end and to the column that the spring is on from the other end.
4- A spring that is fit in length and strength.
5- Gera group for accelerating speed connected to the motor on one
side and to the column with the spring on the other side.
6- A suitable electric generator as explained before. (It can produce
one or three phases).
7- An electric brake containing an electric coil so as to press on the
column connected to the dynamo to stop it from turning when there
is electricity, so that when electricity is cut, it separates from the
dynamo column then the dynamo becomes free to move.
8- Relay or cut-out with the following functions:
A. Connects electricity coming from outside the house with
the two ends feeding the house. This is when electricity is
present.
B. When electricity cuts off, the coil of the relay stops from
pulling the chip connecting electricity into the house. In this
case, when the chip separates from the coil, it connects
electricity coming from the generator and the house is directly
fed with electricity.
(All this happens in a fraction of a second)
9
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
Operating Technique
The electric motor is connected to the house electricity and existing
in the electricity junction connected to the motor. The overload cuts
electricity from the motor when the spring is completely charged. So
if electricity is connected to the motor, the motor turns the gears
which reduce, connected to the column with the spring which so
contracts. When it contracts, the motor stops from whirling and the
dynamo does not work after the spring is full in presence of the
original electricity of the house. That is because of the electric brake
that stops it in presence of electric current. So, when it cuts off, the
following happens:
The brake is released so the dynamo becomes free and at the same
time the spring opens so that the gears and dynamo turn, then
electricity is generated.
The relay or the cut-out at the same time disconnect the original
electricity ends and connects the dynamo electricity. That is because
when the original electricity exists, the relay coil attracts a metal
chip that conducts electricity to the house; so that if electricity cuts
off, it cuts from the relay coil and the metal chip comes back to its
normal position making positive and negative ends coming from the
dynamo touch the house electricity wires made for lighting lamps or
the house in general when the mechanic battery size is big.
Usages of this Technique
It can be used with houses, shops, doctors' clinics... etc. (when
electricity is cut off).
The fifth Technique: it works in combination with light energy.
It is the same as the fourth technique in components, except that it
replaces house electricity with electricity of photoelectric panels
(known as light or solar energy) as when there is light the electric
motor runs and contracts the spring. At the same time the dynamo
does not run because of the electric brake. So, if light stops and it is
dark; the relay or cut-out cuts out the electricity ends coming from
the solar panels and conducts electricity generated by the dynamo to
the house after the electric brake stops. (And all this happens in a
fraction of one second).
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
Usages of this Technique
1- This technique is used with absolute success with solar
energy. This is instead of using mechanic batteries with lots of
disadvantages. This leads to reducing the cost of one kilowatt
generated by solar energy.
Also using this technique with solar energy, the battery is charged
very quickly not like the case in mechanical batteries.
2- This technique can be used with absolute success with
satellites of short lives because of the mechanical batteries
therein.
So, if this technique is used with satellites it shall double its life
more and more. All this saves money and energy wasted in
manufacturing such satellites.
Method of Use:
1- Cell phones and smart mobile devices in general.
2- Indicator lights and insect zappers
3- Computer sets.
4- Wind power plants.
5- Wireless devices used by police officers and others.
6- Electric cars.
7- Radio and telephone devices.
8- Running watering machines in fields and lighting houses far
from electricity sources.
9- It is used in generating electricity to operate satellites and
space ship.
10- It is used in combination with solar energy and wind power.
11- It is used when electricity cuts off from houses, doctor clinics
and hospitals.
11
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
12- It is used to light lamp posts without need to electricity.
IN conclusion this it is used for everything that needs energy to work
12
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
Brief description of the drawing
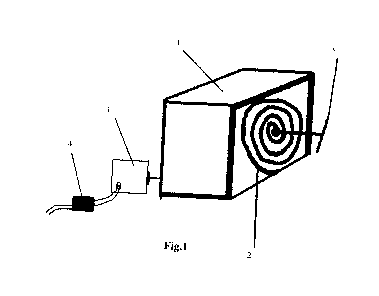
Explanation of the Drawing of the First Technique
1- A group of gears to accelerate the speed.
2- A spring.
3- A suitable electric generator.
4- A unification circuit (when needed).
5- A handle to switch.
Explanation of the Drawing of the Second Technique
1- A half or one-third rounded flywheel.
2- A group of gears to reduce the speed.
3- A group of gears to accelerate the speed.
4- A spring.
5- A suitable generator.
6- A unification circuit (when needed).
7- A handle for manual operating.
Explanation of the Drawing of the Third Technique
1- A fan, plate or a plastic plate to repel air.
2- A group of gears to reduce the speed.
3- A group of gears to accelerate the speed.
4- A spring.
5-A dynamo.
6- A unification circuit (when needed).
13
CA 02940780 2016-08-25
Explanation of the Drawing of the Fourth Technique
1- An overload.
2- A suitable electric motor.
3- A group of gears to reduce the speed.
4- A group of gears to accelerate the speed.
5- A suitable spring.
6- A suitable generator.
7- An electric brake.
8- A relay or cut-out to automatically cut and conduct electricity.
Explanation of the Drawing of the Fifth Technique
1- An overload.
2- A suitable electric motor.
3- A group of gears to reduce the speed.
4- A group of gears to accelerate the speed.
5- A suitable spring.
6- A suitable generator.
7- An electric brake.
8- A relay or cut-out to automatically cut and conduct electricity.
9- Photoelectric panels.
14