Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02960301 2017-03-06
WO 2016/023128 PCT/CA2015/050771
CHAIR
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001] This disclosure relates to the field of ergonomic chairs.
BACKGROUND
[0002] Ergonomic chairs for reducing various stresses on the body that
are
often related to sitting for long periods of time and/or due to incorrect
posture
when in the seated position are known and come in a variety of designs. Mesh
chairs that provide a mesh or material covering formed from a resilient
material
that is arranged over a chair frame for supporting the user in the seated
position
have gained popularity, at least in part for their modern aesthetics. Mesh
chairs
are also considered advantageous for allowing air flow through the mesh or
material covering enabling the user to remain cool when seated in the chair
for long
periods of time and for being more easily cleaned and/or sterilized than more
traditional chairs that include more fabric and cushioning.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0003] Fig. 1 is a perspective view of a chair frame with seat structure
according an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure;
[0004] Fig. 2 is a detail perspective view of the seat structure of the
chair
according to the exemplary embodiment of Fig. 1;
[0005] Fig. 3 is a perspective view of a chair frame with seat structure
according to a further exemplary embodiment; and
[0006] Fig. 4 is a matrix of test results.
1
CA 02960301 2017-03-06
WO 2016/023128 PCT/CA2015/050771
DESCRIPTION OF EXAMPLE EMBODIMENTS
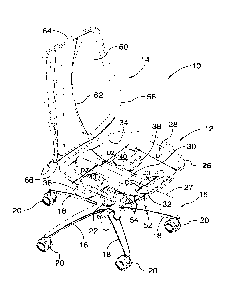
[0007] Referring now to Figures 1 and 2 there is shown a chair 10
according
to an example embodiment of the present disclosure. The chair 10 includes a
seat
structure 12, a back rest 14, and a base 16. The base 16 includes a plurality
of
radially spaced apart legs 18 each of which is provided with a caster or
roller 20,
the base 16 therefore providing rolling support to the chair 10. A support
post 22
extends upwardly from the center of the base 16 and typically includes a
height-
adjusting mechanism for allowing the overall height of the seat structure 12
to be
adjusted based on the needs of the individual user in accordance with
principles
known in the art.
[0008] The seat structure 12 is mounted at the upper end of the support
post
22. The seat structure 12 includes a frame member 26 that forms the periphery
of
the seat and defines a central opening 28 therethrough. A cross-beam member 30
having a generally concave or curved structure extends generally below the
central
opening 28 of the frame member 26 along the midline or centerline 27 of the
seat
structure 12 interconnecting the front and rear edges 32, 34 of the frame
member
26, the cross-beam member 30 serving to mount the seat structure 12 to the
upper
end of the support post 22. The frame member 26 and cross-beam member 30 may
be integrally formed or may be formed as separate components that are fixed
together forming the seat structure. The frame member 26 and cross-beam
member 30 are formed of molded plastic material.
[0009] A pair of cushion supports 38 extend laterally away from the cross-
beam member 30, one on either side of thereof. The cushion supports 38 are
rearwardly disposed by a distance D1 with respect to the front edge 32 of the
frame
member 26 and extend laterally away cross-beam member 30 by a distance D2
with respect to the midline or centerline 27 of the seat structure 12. The
distances
D1 and D2 are predetermined so as to generally correspond to and/or align with
the
position or general location of the ischicial tuberosity, or sitting bones, of
the
average user when in a seated position.
2
CA 02960301 2017-03-06
WO 2016/023128 PCT/CA2015/050771
[0010] The cushion supports 38 are formed as separate components that are
securely fixed to the cross-beam member 30. First and second support cushions
40
are secured to the upper surface 42 of the cushion supports 38 and are formed
from a suitable padded material to provide a cushioning effect. The cushion
supports 38 and support pads 40 are selected and/or together have a
predetermined overall thickness or height to ensure that the upper surface 44
of
the support cushions 40 lies at a level below the central opening 28 of the
frame
member 26 when arranged or mounted on the cushion supports 38.
[0011] As shown in Fig. 2, a thin, flexible membrane 50 is arranged so as
to
extend across the central opening 28 of the frame member 26. The membrane 50
is generally formed from a resilient mesh fabric that is stretched across the
central
opening 28 and affixed to the frame member 26.
[0012] It is generally understood that a person in a seated position rests
on
the ischicial tuberosity, or sits bones, which extend from the lower, back
portion of
the pelvis or hip bones. When a person is standing, the ischicial tuberosity
is
generally covered by large muscle groups that generally provide cushioning or
padding to the otherwise bony protrusions of the ischicial tuberosity.
However,
when a person assumes a seated position, the muscles tend to shift leaving the
bony protrusions of the ischicial tuberosity to bear the majority of the
weight.
Bearing the majority of one's weight on the ischicial tuberosity can be quite
uncomfortable especially when one is in a seated position for a long duration
of
time, as is often typical of an office workplace situation. As well, depending
on the
size and overall weight of the user, when mesh is utilized, it has been
discovered
that pressure points may also be created against the backs of the user's legs
and/or
on their hips or thighs where the edges of the frame member may come into
contact with and impinge on the user's body.
3
CA 02960301 2017-03-06
WO 2016/023128 PCT/CA2015/050771
[0013] In the embodiment shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2, the cushion supports
38
and support pads 40 are strategically arranged in relation to the cross-beam
member 30 in order to reduce the pressure points associated with the membrane
50. In particular, the cushion supports 38 together with the support pads 40
provide support to the membrane 50 when the membrane 50 becomes stretched
under the weight of a user. The arrangement of the cushion supports 38 and
support pads 40 in relation to the cross-beam member 30 underneath the
membrane 50 also prevents the membrane 50 from bottoming-out under the
weight of a larger and/or heavier individual. Accordingly, should a larger
and/or
heavier individual assume a seated position on the chair 10, the user will end
up
resting on the support pads 40 and enjoy the comfort of the padded material
forming the support pads 40 as opposed to bottoming-out the seat structure 12
and
finding themselves resting on the cross-beam member 30. Accordingly, cushion
supports 38 and support pads 40 together provide additional support to the
membrane 50 which allows the seat structure 12 to provide the benefits
associated
with a mesh-style chair since the membrane 50 can stretch and conform to the
shape of the user when the user assumes a seated position bearing weight on
the
membrane 50 and allow for air-flow through the mesh-material forming the
membrane 50, but still offers the added benefit of support and cushioning to
the
sits bones or ischicial tuberosity of the user. The cushion supports 38 and
support
pads 40 also serve to reduce the overall amount of shear stress on the
membrane
50 which reduces the likelihood of the frame member 26 impinging on the user
and
creating uncomfortable pressure points that can have an adverse effect on the
overall comfort and ergonomic health of the user. It has also been found that
incorporating cushion supports 38 and support pads 40 underneath the membrane
50 prevents the user from sinking too low within the central opening 28 of the
frame member 26 and assuming a less-than-ideal sitting position. As a result,
the
user is less likely to be inclined to raise the overall height of the seat in
an effort to
compensate for sinking too low within the central opening 28 which raised seat
height would result in an even less ergonomic sitting position.
4
CA 02960301 2017-03-06
WO 2016/023128 PCT/CA2015/050771
[0014] A third support pad 52 is also provided at the front end 54 of the
cross-beam member 30 proximal to the front edge 32 of the frame member 26.
The third support pad 52 is arranged so as to generally lie between the user's
legs
when in the seated position on the chair 10. Accordingly, the third support
pad 52
provides additional support to membrane 50 in the area proximal the front edge
32
of the frame member 26 along the centreline or midline 27 of the seat
structure 12.
The third support pad 52 extends laterally on either side of the centreline or
midline
27 of the seat structure 12 by a distance D3 and is generally sized and
arranged
below the central opening 28 of the frame member 26 so as not to come into
contact with the user's legs when seated on the chair 10. The third support
pad 52,
therefore, provides support to only the membrane 50 at the front edge 32 of
the
seat structure 12. The third support pad 52 therefore works in combination
with
the first and second support pads 40 that are arranged within the central area
of
the seat structure 12 to provide a support triangle for providing additional
support
the membrane 50 under the weight of a user allowing the membrane 50 to adopt a
more comfortable position without undue shear stresses being created in the
material resulting in a more ergonomic and a more comfortable feel for users
of
various overall weights and/or sizes. Reducing the amount of shear stresses
created in the membrane 50 when under the weight of a user also tends to
increase
the life of the material forming the membrane 50 over time.
[0015] In the embodiment shown, the back rest 14 is similar in structure
to
the seat structure 12 in that it comprises a frame member 58 that forms the
periphery of the back rest 14 and defines a generally elongated, central
opening 60.
A back support member 62 extends generally along the centerline or midline of
the
back rest 14 interconnecting the top and bottom edges 64, 66 of the back frame
member 58. A second membrane (not shown) is generally arranged across the top
of the frame member 58 so as to extend across the central opening 60 defined
by
the frame member 58. Similar to the membrane 50 used on the seat structure 12,
the membrane for the back rest is formed by a mesh material that can stretch
and
conform to the shape of the user's back when the user rests against the back
rest
14 of the chair. The back rest 14 is mounted to the base 16 by tilt mechanism
in
CA 02960301 2017-03-06
WO 2016/023128 PCT/CA2015/050771
order to permit limited, pre-determined movement of the back rest 14 (e.g.
forward
tilt, backwards tilt) with respect to the base independent of the seat
structure 12.
The back rest 14 may also be provided with additional features such as an
adjustable lumbar support mechanism and/or a head rest (not shown) positioned
at
the upper edge 64 of the back rest 14.
[0016] By providing both a back rest 14 and a seat structure 12 formed by
frame members 26, 58 fitted with a resilient mesh membrane 50, 62 arranged
across the central openings 28, 60 of the frame members 26, 58 allows for air-
circulation around and through both the seat structure 12 and back rest 14. As
well, since membranes used for both the seat structure 12 and the back rest 14
are
generally spaced apart from the supporting structures (e.g. frame members 26,
58
and cross-beam members 30, 62) forming both the seat structure 12 and back
rest
14, the chair 10 can be relatively easily cleaned since the components of the
seat
structure 12 and back rest 14 are accessible, which is advantageous in
environments requiring a degree of cleanliness. Furthermore, by providing a
seat
structure 12 having a combination membrane and support cushion structure as
described above, a comfortable and durable chair 10 is provided that is suited
to a
wide range of individual users.
[0017] A further exemplary embodiment is shown in Fig. 3 and designated
with general reference 10A. This embodiment is substantially identical to the
embodiment of FIG. 1 and 2, differing only in that first and second support
pads 40
are connected by a bridge 40A.
[0018] Without intending to be bound by theory, it has been found that an
advantageous arrangement of the cushion provided by pads 40 (and 52, when
present) is associated with support pads providing the maximum amount of
support
possible without the user feeling the pads in use. Accordingly, the technology
can
advantageously be deployed with removable pads of differing densities (to
enable
users to customize the chair by substitution of pads) or with pads having
adjustable
air bladders.
6
CA 02960301 2017-03-06
WO 2016/023128 PCT/CA2015/050771
[0019] Fig. 4 is a matrix of images showing localized pressure
experienced by
a user of a leading mesh-only seat [left column], a leading foam-only seat
[right
column] and a foam-mesh seat according an embodiment of the present invention
[central column]. In each column: the uppermost image is a plan view showing
localized pressures; the middle image is a side view, which assists in
understanding
quantum of the pressure differential; and the bottom image is a perspective
view.
With reference to the left column, it will be seen that, in the leading mesh
chair,
areas of high pressure exist adjacent the sit bones (the light areas at the
top of the
uppermost image) and also adjacent under the thighs near the front edge of the
chair (the light areas at the bottom of the uppermost image). The leading foam-
only seat shows much better distribution, as no areas of very high pressure
appear
in the images. In the mesh-foam chair tests, the pressure to which the sit
bones
are exposed has been improved relative to the leading mesh-only chair, and the
pressure to which the thighs are exposed at the chair leading edge has been
vastly
improved relative to the leading mesh-only chair. From the above, it will
be
evident that significant advantage in pressure distribution can be attained by
practising the present invention, but the images shown should be understood to
be
representative of single samples, only, and are merely included by way of
example.
[0020] While but two embodiments of the chair and seat structure have
been
illustrated and described, it will be understood that certain adaptations and
modifications can be made. Therefore, the above discussed embodiments are
considered to be illustrative and not restrictive.
7