Une partie des informations de ce site Web a été fournie par des sources externes. Le gouvernement du Canada n'assume aucune responsabilité concernant la précision, l'actualité ou la fiabilité des informations fournies par les sources externes. Les utilisateurs qui désirent employer cette information devraient consulter directement la source des informations. Le contenu fourni par les sources externes n'est pas assujetti aux exigences sur les langues officielles, la protection des renseignements personnels et l'accessibilité.
L'apparition de différences dans le texte et l'image des Revendications et de l'Abrégé dépend du moment auquel le document est publié. Les textes des Revendications et de l'Abrégé sont affichés :
| (12) Demande de brevet: | (11) CA 3014418 |
|---|---|
| (54) Titre français: | PROFILE POUR UN SYSTEME DE FIXATION ET D'ISOLATION THERMIQUE DE FENETRES, PORTES ET FACADES |
| (54) Titre anglais: | PROFILE FOR THE FASTENING AND THERMAL INSULATION SYSTEM OF WINDOWS, DOORS AND FACADES |
| Statut: | Réputée abandonnée et au-delà du délai pour le rétablissement - en attente de la réponse à l’avis de communication rejetée |
| (51) Classification internationale des brevets (CIB): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventeurs : |
|
| (73) Titulaires : |
|
| (71) Demandeurs : |
|
| (74) Agent: | AIRD & MCBURNEY LP |
| (74) Co-agent: | |
| (45) Délivré: | |
| (86) Date de dépôt PCT: | 2016-09-16 |
| (87) Mise à la disponibilité du public: | 2017-03-23 |
| Licence disponible: | S.O. |
| Cédé au domaine public: | S.O. |
| (25) Langue des documents déposés: | Anglais |
| Traité de coopération en matière de brevets (PCT): | Oui |
|---|---|
| (86) Numéro de la demande PCT: | PCT/PL2016/000104 |
| (87) Numéro de publication internationale PCT: | PL2016000104 |
| (85) Entrée nationale: | 2018-08-13 |
| (30) Données de priorité de la demande: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
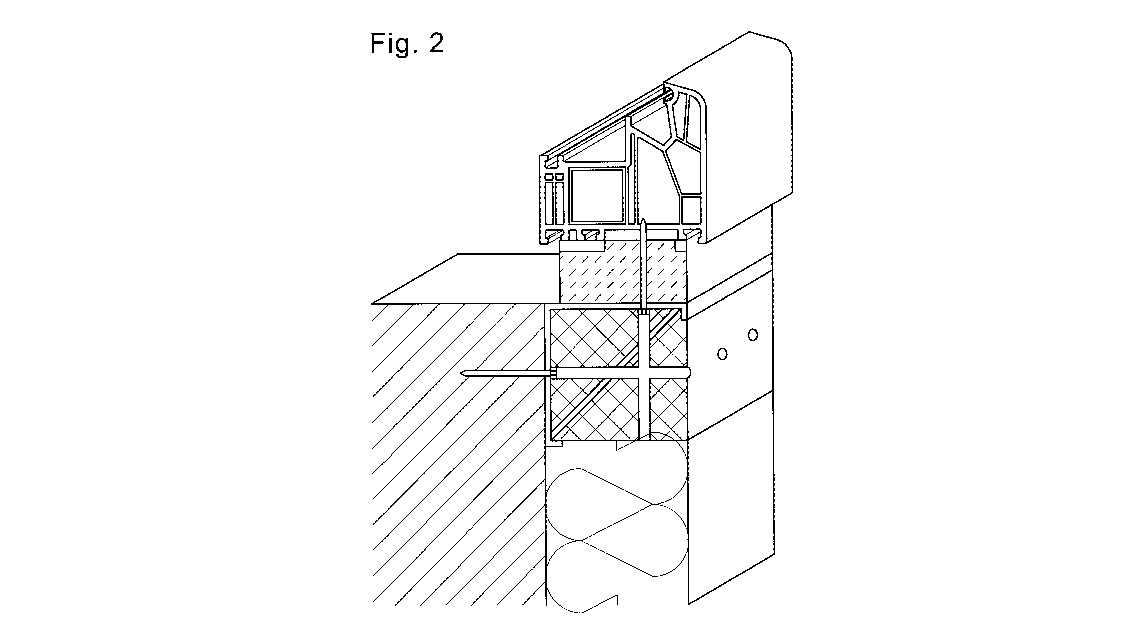
L'invention concerne un profilé pour un système de fixation et d'isolation thermique de fenêtres, portes et façades; un élément essentiel de celui-ci étant un fer d'angle (1), en un matériau quelconque, de préférence en acier, dont la section transversale ressemble à la lettre " L ", qui comporte des points d'inflexion longitudinaux (2) disposés le long des bords de ses deux bras, qui sont courbés vers l'intérieur du fer d'angle (1), de préférence à un angle de 90 °. Le fer d'angle (1) "L" est rempli d'un composé de remplissage (3). En outre, grâce au laminage des bords du fer d'angle (1) et à la présence de points d'inflexion longitudinaux (2) du fer d'angle (1) formé de cette manière, il est possible de placer l'entretoise (4) entre eux, laquelle dilate les bras du fer d'angle (1). L'entretoise (4) peut être sensiblement la barre plate longitudinale, et elle peut présenter des trous ou des saillies; éventuellement, l'entretoise (4) peut être constituée de petits panneaux disposés respectivement le long de la longueur du fer d'angle (1) "L". L'entretoise susmentionnée (4) forme toujours un angle aigu, avec le bras du fer d'angle (1) auquel elle est adjacente, et avec des points d'inflexion longitudinaux (2) sortant de ce bras, lequel angle est normalement de 45 °. L'entretoise (4) est ensuite la bissectrice de l'angle défini par le bras du fer d'angle (1) et du point d'inflexion longitudinal (2) . Dans la solution basique, le profil est fixé à la face de paroi au moyen d'éléments de fixation, des broches ou des vis (7). La vis (7) passant à travers le bras horizontal du fer d'angle (1) fixe le cadre de la fenêtre, de la porte porte ou d'autres éléments de façade au fer d'angle (1) "L". L'installation peut être également effectuée avec l'utilisation d'ancrages de fixation (6), directement connectés au profil et supportant relativement le profil, puis être également reliée à la paroi du bâtiment. Des ancrages de fixation (6) peuvent comprendre un ou plusieurs pivots (8). Ils peuvent également être constitués de plusieurs éléments coulissants (9), permettant la séparation, et ainsi l'allongement des ancrages de fixation (6). L'utilisation de pivots (8), qui peuvent avoir la forme de charnières, est améliorée par la résistance des ancrages de fixation (6).
The subject of the invention is the profile for the fastening and thermal insulation system of windows, doors and facades, an essential element of which is the angle iron (1), made of any material, preferably of steel, with the cross section resembling the letter "L", which has longitudinal inflection points (2) arranged along the edges of its both arms, which are bent towards the inside of the angle iron (1), preferably at an angle of 90°. The angle iron (1) "L" is filled with the filling compound (3). In addition, thanks to rolling of the edges of the angle iron (1) and the presence of longitudinal inflection points (2) of the iron angle (1) formed this way, it is possible to place the brace (4) between them, which expands the arms of the angle iron (1). The brace (4) may be substantially the longitudinal flat bar, whereby it can have holes or protrusions; optionally the brace (4) can be made of small boards arranged respectively along the length of the angle iron (1) "L". The aforementioned brace (4) always forms an acute angle - with the arm of the angle iron (1), which it is adjacent to and with longitudinal inflection points (2) going out of this arm - which angle is typically 45°. The brace (4) is then the bisector of the angle defined by the arm of the angle iron (1) and of the longitudinal inflection point (2). In the basic solution - the profile is fixed to the wall face by means of fasteners, pins or screws (7). The screw (7) passing through the horizontal arm of the angle iron (1) fixes the frame of the window, door or other facade elements to the angle iron (1) "L". The installation may be also performed with the use of fixing anchors (6), directly connected to the profile, relatively supporting the profile, and then also connected to the building wall. Fixing anchors (6) may be equipped with one or several swivels (8). They may also be made of several sliding elements (9), enabling the separation, and thus the elongation of fixing anchors (6). The use of swivels (8), which may have the form of hinges, is improved by the strength of fixing anchors (6).
Note : Les revendications sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
2024-08-01 : Dans le cadre de la transition vers les Brevets de nouvelle génération (BNG), la base de données sur les brevets canadiens (BDBC) contient désormais un Historique d'événement plus détaillé, qui reproduit le Journal des événements de notre nouvelle solution interne.
Veuillez noter que les événements débutant par « Inactive : » se réfèrent à des événements qui ne sont plus utilisés dans notre nouvelle solution interne.
Pour une meilleure compréhension de l'état de la demande ou brevet qui figure sur cette page, la rubrique Mise en garde , et les descriptions de Brevet , Historique d'événement , Taxes périodiques et Historique des paiements devraient être consultées.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Demande non rétablie avant l'échéance | 2022-03-16 |
| Le délai pour l'annulation est expiré | 2022-03-16 |
| Réputée abandonnée - omission de répondre à un avis relatif à une requête d'examen | 2021-12-07 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2021-09-16 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2021-09-16 |
| Réputée abandonnée - omission de répondre à un avis sur les taxes pour le maintien en état | 2021-03-16 |
| Représentant commun nommé | 2020-11-07 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2020-09-16 |
| Représentant commun nommé | 2019-10-30 |
| Représentant commun nommé | 2019-10-30 |
| Inactive : Réponse à l'art.37 Règles - PCT | 2018-11-14 |
| Inactive : Page couverture publiée | 2018-08-29 |
| Inactive : CIB en 1re position | 2018-08-28 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2018-08-28 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2018-08-28 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2018-08-28 |
| Inactive : Demande sous art.37 Règles - PCT | 2018-08-23 |
| Inactive : Notice - Entrée phase nat. - Pas de RE | 2018-08-22 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2018-08-20 |
| Demande reçue - PCT | 2018-08-20 |
| Exigences pour l'entrée dans la phase nationale - jugée conforme | 2018-08-13 |
| Demande publiée (accessible au public) | 2017-03-23 |
| Date d'abandonnement | Raison | Date de rétablissement |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-12-07 | ||
| 2021-03-16 |
Le dernier paiement a été reçu le 2019-09-13
Avis : Si le paiement en totalité n'a pas été reçu au plus tard à la date indiquée, une taxe supplémentaire peut être imposée, soit une des taxes suivantes :
Les taxes sur les brevets sont ajustées au 1er janvier de chaque année. Les montants ci-dessus sont les montants actuels s'ils sont reçus au plus tard le 31 décembre de l'année en cours.
Veuillez vous référer à la page web des
taxes sur les brevets
de l'OPIC pour voir tous les montants actuels des taxes.
| Type de taxes | Anniversaire | Échéance | Date payée |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taxe nationale de base - générale | 2018-08-13 | ||
| Rétablissement (phase nationale) | 2018-08-13 | ||
| TM (demande, 2e anniv.) - générale | 02 | 2018-09-17 | 2018-08-13 |
| TM (demande, 3e anniv.) - générale | 03 | 2019-09-16 | 2019-09-13 |
Les titulaires actuels et antérieures au dossier sont affichés en ordre alphabétique.
| Titulaires actuels au dossier |
|---|
| "ERGO PLUS" SP. Z.O.O. |
| Titulaires antérieures au dossier |
|---|
| ARTUR BORUSZEWSKI |