Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
SEE-THROUGH BASED DISPLAY METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SIMULATORS
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to the field of simulators, and more
particularly to the field of
display methods and systems for simulators.
BACKGROUND
Flying an aircraft requires a good understanding, by the pilot, of his
position in space with
respect to the exterior environment and obstacles. Visually, this information
comes from
the pilot's perception of depth in the scene. This perception of depth is
naturally available in
real-world training thanks to human stereoscopic vision. However, the
perception of depth
is usually limited in a simulator environment used for training pilots.
In order to improve the situational awareness provided by a simulator
environment, visual
display technology offering a very wide field of view (FoV) are used to
provide an
immersive visual environment. IIowever such wide FoV displays usually cannot
provide a
true stereoscopic depth perception when the simulator is configured for
training two users
and can only render 2D images onto a flat surface. In addition, such displays
usually have a
large physical footprint.
Therefore, there is a need for an improved method and system for displaying
images in a
simulator.
SUMMARY
According to a first broad aspect, there is provided a display system for a
simulator
comprising: a first display for displaying a simulated scene, the first
display being
positionable away from a user; a second display for displaying a portion of
the simulated
scene, the second display being wearable by the user; at least one camera for
capturing
video images along a line of view of the user; a filter for filtering a
portion of a field of
view of the user; and a control unit configured for: receiving environment
images, the
environment images comprising a first set of images of the simulated scene, a
second set of
images of the simulated scene and at least a third set of images of a portion
of the simulated
- 1 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
scene; displaying the first and second set of images on the first display;
generating
augmented reality images based on the video images and the at least a third
set of images;
and displaying the augmented reality images on the second display.
In one embodiment, the first set of images comprises images of the simulated
scene
according to a first point of view and the second set of images comprises
images of the
simulated scene according to a second and different point of view.
In one embodiment, the control unit is further configured for receiving
simulation data and
generating the first and second sets of images using the received simulation
data.
In one embodiment, the augmented reality images comprise the video images to
which the
at least one third set of images is added.
In one embodiment, the control unit is further configured for generating the
at least one
third set of images using the line of view.
In one embodiment, the display system further comprises a tracking unit
configured for
tracking the line of view of the user.
In one embodiment, the tracking unit is configured for tracking a position and
an
orientation of a head of the user and the control unit is configured for
determining the line
of view using the position and the orientation of the head.
In one embodiment, the second display is configured for displaying
stereoscopic augmented
reality images.
In one embodiment, the second display comprises a binocular head-mounted
display.
In one embodiment, the first display is configured for displaying monoscopic
images.
In one embodiment, the first display comprises a rear projection screen and a
projector.
In one embodiment, the filter comprises a shutter device wearable by the user
adjacent to
the second display, the shutter device being configured for selectively
obstructing a portion
- 2 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
of a field of view of the user; and the control unit is configured for
sequentially displaying
the first and second set of images on the first display and synchronizing the
shutter device
with the sequential display of the first and second set of images to
selectively prevent the
user from seeing at least a section of the first display during display of the
second set of
.. images on the first display.
In one embodiment, the shutter device is configured for selectively blocking
at least a far
peripheral vision of the user.
In one embodiment, the shutter device and the second display are mounted on a
head-
mounted display.
In one embodiment, the shutter device comprises a liquid crystal shutter.
In one embodiment, the filter is a passive filter.
In one embodiment, the passive filter comprises a polarization glass device
for allowing the
user to see images having a given polarization, the images of the first set
having the given
polarization and the images of the second set having a polarization different
from the given
polarization for preventing the user from seeing the second images through the
polarization
glass device.
In one embodiment, the passive filter comprises a wavelength filter device for
allowing the
user to see images having a given wavelength range, the images of the first
set having the
given wavelength range and the images of the second set having a wavelength
range
different form the given wavelength range for preventing the user from seeing
the second
images through the wavelength filter device.
According to another broad aspect, there is provided a simulator comprising:
physical
elements mocking elements of a simulated system; and the above-described
display system.
According to a further broad aspect, there is provided a computer-implemented
method for
displaying images in a simulator, comprising: receiving scene images of a
simulated scene,
the scene images comprising a first set of images of the simulated scene, a
second set of
- 3 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
images of the simulated scene and at least one third set of images of a
portion of the
simulated scene; receiving video images captured by at least one camera along
a line of
view of a user; displaying the first and second set of images on a first
display positionable
away from a user; generating augmented reality images based on the video
images and the
at least one third set of images, the video images being captured by the at
least one camera
along a line of view of the user; displaying the augmented reality images on a
second
display, the second display being wearable by the user; and filtering a
portion of a field of
view of the user.
In one embodiment, the first set of images comprises images of the simulated
scene
according to a first point of view and the second set of images comprises
images of the
simulated scene according to a second and different point of view.
In one embodiment, the method further comprises receiving simulation data and
generating
the first and second sets of images using the received simulation data.
In one embodiment, the augmented reality images comprise the video images to
which the
at least one third set of images is added.
In one embodiment, the method further comprises generating the at least one
third set of
images using the line of view.
In one embodiment, the method further comprises tracking the line of view of
the user.
In one embodiment, the step of tracking the line of view of the user comprises
tracking a
position and an orientation of a head of the user, the method further
comprising
determining the line of view using the position and the orientation of the
head.
In one embodiment, the step of displaying the augmented reality images
comprises
displaying stereoscopically the augmented reality images.
In one embodiment, the step of displaying the augmented reality images
comprises
displaying the augmented reality images on a binocular head-mounted display.
- 4 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
In one embodiment, the step of displaying the first and second set of images
on the first
display displaying monoscopically the first and second set of images.
In one embodiment, the step of displaying monoscopically the first and second
set of
images comprises projecting the first and second sets of images on a rear
projection screen.
In one embodiment, the step of displaying the first and second set of images
on the first
display comprises sequentially displaying the first and second set of images
on the first
display; and the step of filtering the portion of the field of view of the
user comprises
selectively obstructing the portion of the field of view of the user in
synchronization with
the sequential display of the first and second sets of images, thereby
selectively preventing
the user from seeing at least a section of the first display during display of
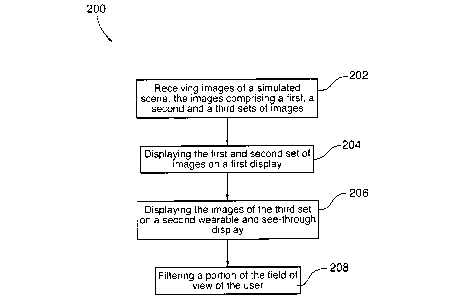
the second set of
images on the first display.
In one embodiment, the step of selectively obstructing a portion of a field of
view of the
user is performed by synchronizing a shutter device with the sequential
display of the first
and second sets of images, the shutter device being wearable by the user
adjacent to the
second display.
In one embodiment, the step of selectively obstructing a portion of a field of
view of the
user comprises selectively blocking at least a far peripheral vision of the
user.
In one embodiment, the images of the first set have a given polarization and
the images of
the second set have a polarization different from the given polarization, said
filtering
comprising allowing the user to see the first images having the given
polarization and
preventing the user from seeing the second images having the polarization
different from
the given polarization.
In one embodiment, the images of the first set have a first wavelength
bandwidth and the
images of the second set have a second wavelength bandwidth different from the
first
wavelength bandwidth, said filtering comprising allowing the user to see the
first images
having the first given wavelength range and preventing the user from seeing
the second
images having the second wavelength range.
- 5 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
According to still another broad aspect, there is provided a computer program
product for
displaying images in a simulator, the computer program product comprising a
computer
readable memory storing computer executable instructions thereon that when
executed by a
computer perform the steps of the above-described method.
.. According to still a further broad aspect, there is provided a display
system for a simulator
comprising: a main display for displaying a simulated scene, the main display
being
positionable away from a user; a see-through display for displaying a portion
of the
simulated scene, the see-through display being wearable by the user; a filter
for filtering a
portion of a field of view of the user; and a control unit configured for:
receiving
environment images, the environment images comprising a first set of images of
the
simulated scene, a second set of images of the simulated scene and a third set
of images of
at least a portion of the simulated scene; displaying the first and second set
of images on the
main display; and displaying the third set of images on the see-through
display.
In one embodiment, the first set of images comprises images of the simulated
scene
according to a first point of view and the second set of images comprises
images of the
simulated scene according to a second and different point of view.
In one embodiment, the control unit is further configured for receiving
simulation data and
generating the first and second sets of images using the received simulation
data.
In one embodiment, the control unit is further configured for generating the
third set of
images using the line of view.
In one embodiment, the display system further comprises a tracking unit
configured for
tracking the line of view of the user.
In one embodiment, the tracking unit is configured for tracking a position and
an
orientation of a head of the user and the control unit is configured for
determining the line
of view using the position and the orientation of the head.
- 6 -
CA 3018465 2019-03-18
=
In one embodiment, the see-through display is configured for displaying
stereoscopic
images.
In one embodiment, the second display comprises a binocular head-mounted see-
through
display.
In one embodiment, the main display is configured for displaying monoscopic
images.
In one embodiment, the main display comprises a rear projection screen and a
projector.
In one embodiment, the filter comprises a shutter device wearable by the user
adjacent to
the second display, the shutter device being configured for selectively
obstructing a portion
of a field of view of the user; and the control unit is configured for
sequentially displaying
the first and second set of images on the main display and synchronizing the
shutter device
with the sequential display of the first and second set of images to
selectively prevent the
user from seeing at least a section of the main display during display of the
second set of
images on the main display.
In one embodiment, the shutter device is configured for selectively blocking
at least a far
peripheral vision of the user.
In one embodiment, the shutter device and the see-through display are mounted
on a head-
mounted display.
In one embodiment, the shutter device comprises a liquid crystal shutter.
In one embodiment, the filter is a passive filter.
In one embodiment, the passive filter comprises a polarization glass device
for allowing the
user to see images having a given polarization, the images of the first set
having the given
polarization and the images of the second set having a polarization different
from the given
polarization for preventing the user from seeing the second images through the
polarization
glass device.
- 7 -
CA 3018465 2019-03-18
In one embodiment, the passive filter comprises a wavelength filter device for
allowing the
user to see images having a given wavelength range, the images of the first
set having the
given wavelength range and the images of the second set having a wavelength
range
different form the given wavelength range for preventing the user from seeing
the second
images through the wavelength filter device.
According to still another embodiment, there is provided a simulator
comprising: physical
mocking elements of a simulated system; and the above-described display
system.
According to still a further embodiment, there is provided a computer-
implemented method
for displaying images in a simulator, comprising: receiving scene images of a
simulated
scene, the scene images comprising a first set of images of the simulated
scene , a second
set of images of the simulated scene and a third set of images corresponding
to at least a
portion of the scene; displaying the first and second set of images on a main
display
positionable away from a user; displaying the third set of images on a see-
through display,
the see-through display being wearable by the user; and filtering a portion of
a field of view
of the user.
In one embodiment, the first set of images comprises images of the simulated
scene
according to a first point of view and the second set of images comprises
images of the
simulated scene according to a second and different point of view.
In one embodiment, the method further comprises receiving simulation data and
generating
the first and second sets of images using the received simulation data.
In one embodiment, the method further comprises generating the third set of
images using
the line of view.
In one embodiment, the method further comprises tracking the line of view of
the user.
In one embodiment, the step of tracking the line of view of the user comprises
tracking a
position and an orientation of a head of the user, the method further
comprising
determining the line of view using the position and the orientation of the
head.
- 8 -
CA 3018465 2019-03-18
In one embodiment, the step of displaying the third set of images comprises
displaying
stereoscopically the third set of images.
In one embodiment, the step of displaying the third set of images comprises
displaying the
third set of images on a binocular head-mounted see-through display.
In one embodiment, the step of displaying the first and second set of images
on the main
display comprises displaying monoscopically the first and second set of
images.
In one embodiment, the step of displaying monoscopically the first and second
set of
images comprises projecting the first and second sets of images on a rear
projection screen.
In one embodiment, the step of displaying the first and second set of images
on the main
.. display comprises sequentially displaying the first and second set of
images on the main
display; and the step of filtering the portion of the field of view of the
user comprises
selectively obstructing the portion of the field of view of the user in
synchronization with
the sequential display of the first and second sets of images, thereby
selectively preventing
the user from seeing at least a section of the main display during display of
the second set
of images on the main display.
In one embodiment, the step of selectively obstructing a portion of a field of
view of the
user is performed by synchronizing a shutter device with the sequential
display of the first
and second sets of images, the shutter device being wearable by the user
adjacent to the
see-through display.
In one embodiment, the step of selectively obstructing a portion of a field of
view of the
user comprises selectively blocking at least a far peripheral vision of the
user.
In one embodiment, the images of the first set have a given polarization and
the images of
the second set have a polarization different from the given polarization, said
filtering
comprising allowing the user to see the first images having the given
polarization and
preventing the user from seeing the second images having the polarization
different from
the given polarization.
- 9 -
CA 3018465 2019-03-18
In one embodiment, the images of the first set have a first wavelength
bandwidth and the
images of the second set have a second wavelength bandwidth different from the
first
wavelength bandwidth, said filtering comprising allowing the user to see the
first images
having the first given wavelength range and preventing the user from seeing
the second
images having the second wavelength range.
According to still another broad aspect, there is provided a computer program
product for
displaying images in a simulator, the computer program product comprising a
computer
readable memory storing computer executable instructions thereon that when
executed by a
computer perform the steps of the above-described method.
.. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Further features and advantages of the present invention will become apparent
from the
following detailed description, taken in combination with the appended
drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a flow chart of a method for displaying images in a simulator
comprising a
wearable display for displaying augmented reality images thereon, the reality
images being
generated using images recorded by a camera, in accordance with an embodiment;
Figure 2 is a block diagram of a simulator comprising a system for displaying
images to
two users, the system comprising two wearable displays for displaying thereon
augmented
reality images obtained using images captured by cameras, in accordance with
an
embodiment;
Figure 3 is an exemplary scene as seen by a user of the simulator of Figure 2,
in accordance
with an embodiment;
Figure 4 block diagram of a processing module adapted to execute at least some
of the steps
of the method of Figure 1, in accordance with an embodiment;
Figure 5 is a flow chart of a method for displaying images in a simulator
system comprising
a wearable see-through display, in accordance with an embodiment;
- 10 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
Figure 6 is a block diagram of a simulator comprising a system for displaying
images to
two users, the system comprising two wearable see-through displays, in
accordance with an
embodiment; and
Figure 7 block diagram of a processing module adapted to execute at least some
of the steps
of the method of Figure 5, in accordance with an embodiment.
It will be noted that throughout the appended drawings, like features are
identified by like
reference numerals.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
There is described a method and system for displaying images in a simulator.
The simulator
may be used for concurrently training two users such as a pilot and a copilot
of an aircraft.
The simulator comprises a main display on which images of a scene are
displayed to the
two users who each have a respective position relative to the main display.
Each user is
provided with a second display on which respective images are displayed. For
example, the
images displayed on a wearable display may correspond to a section of the
scene displayed
on the main display according to the point of view of the respective user.
Each user is
further provided with a respective filter adapted to partially filter the
field of view of the
user outside of the wearable display.
In one embodiment, the second display is wearable and comprises a non-
transparent or non-
translucent display. In this case, at least one camera captures images of what
the user would
see if he would not wear the wearable display, i.e. images of the physical
elements of the
simulator surrounding the user according to the line or point of view of the
user.
Augmented reality images are then created using the images captured by the
camera and at
least a portion of the images displayed on the main display. The created
images are then
displayed on the wearable display.
.. In another embodiment, the second or wearable display comprises a see-
through display. In
this case, the users are provided with no camera and at least a portion of the
images
displayed on the main display is displayed on the wearable display.
- 11 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
In one embodiment, the filters are active filters such as shutters. In this
case, two sets of
images are displayed on the main display. The first set of images comprises
images of a
scene suitable for being seen according to the point of view of the first
user. The second set
of images comprises images of the same scene suitable for being seen according
to the
.. point of view of the second user. The first and second sets of images are
displayed
sequentially on the first display, i.e. images of the first set and images of
the second set are
displayed on the first display in an alternating manner. The active filters
are used for
blocking at least a portion of the field of view of the users in a
synchronized manner with
the sequential display of the first and second sets of images. When an image
of the first set
.. is displayed on the first display, the shutter of the first user is open so
that the first user may
see the image displayed on the first display in addition to the image
displayed on its
wearable display while the shutter of the second user is closed so that the
second user
cannot see the image displayed on the first display and may only see the image
displayed
on its wearable display. Similarly, when an image of the second set is
displayed on the first
.. display, the shutter of the second user is open so that the second user may
see the image
displayed on the first display in addition to the image displayed on its
wearable display
while the shutter of the first user is closed so that the first user cannot
see the image
displayed on the first display and may only see the image displayed on its
wearable display.
In another embodiment, the filters are passive filters. For example, the
passive filters may
be polarized glasses. In this case, the polarized glasses of the first user
allows the first user
to see images having a first polarization while preventing the first user from
seeing images
having a second and different polarization. The polarized glasses of the
second user allows
the second user to see images having the second polarization while preventing
the second
user from seeing images having the first polarization. First images having the
first
.. polarization and second images having the second polarization are displayed
on the first
display. In one embodiment, the first and second images are displayed
concurrently on the
first display. In another embodiment, the first and second images are
displayed
sequentially. It should be understood that the first images having the first
polarization are
adequate for the first user, e.g. they may be suitable for being seen
according to the point of
view of the first user, while the second images having the second polarization
are adequate
- 12 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
for the second user, e.g. they may be suitable for being seen according to the
point of view
of the second user.
In another example, the passive filters may comprise wavelength filters. In
this case, the
wavelength filter of the first user is adapted to allow propagation of light
having a
wavelength comprised in a first range of wavelength, i.e. a first wavelength
bandwidth,
while the wavelength filter of the second user is adapted to allow propagation
of light
having a wavelength comprised in a second and different range of wavelength,
ie..e a
second wavelength bandwidth. First images having image data within the first
wavelength
bandwidth and second images having image data within the second wavelength
bandwidth
are concurrently displayed on the first display. While the first and second
images are
concurrently displayed on the first display, the first user only sees the
first images since his
wavelength filter cuts out the wavelengths corresponding to the second images
and the
second user only sees the second images displayed on the first display since
its wavelength
filter cuts out the wavelengths corresponding to the first images.
Figure 1 illustrates one embodiment of a method 10 for displaying images in a
simulator. In
this method, the users are provided with active filters and non-see-through
wearable
displays. As described in more detail below, the simulator is configured for
concurrently
training two users such as a pilot and a copilot. However, it should be
understood that the
simulator may be used by a single user or more than two users.
.. The method 10 is executed by a computer machine provided with at least one
processor or
processing unit, a memory and communication means.
At step 12, scene images, i.e. images of a scene to be displayed to a user,
are received. The
scene images offer a representation of the simulation environment to be
displayed to the
user (s) of the simulator. For example, the scene images may be simulated
images
representing what a pilot of an aircraft would see while flying.
- 13 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
The scene images comprise three sets of images. It should be understood that a
set of
images comprises images which are timely ordered so as to be displayed
according to a
temporal order to form a video.
In one embodiment, the three sets of images comprise images of a same scene.
For
example, the first set of images comprises images of a scene suitable for
being seen
according to a first point of view. The second set of images comprises images
of the same
scene suitable for being seen according to a second and different point of
view. For
example, when the simulator is configured for concurrently train two users
such as a pilot
and a copilot who are seated one next to the other, the first set of images
may comprise
images simulated for being seen according to the point of view of the pilot
while the second
set of images may comprise images simulated for being seen according to the
point of view
of the copilot. The third set of images comprises images of at least a portion
of the scene. It
should be understood that the third set of images may also comprise images
different from
the first and second sets of images.
In another embodiment, the third set of images may comprise two sets of
images, i.e. a set
of images according to the point of view of the left eye of the user and a
further set of
images according to the point of the right eye of the user.
In a further embodiment, the first and second sets of images may comprise
images of
different scenes. In this case, the third set of images comprise images of the
same scene as
that of the first or second set of images. For example, when the simulator is
configured for
concurrently train two users such as a pilot and a copilot, a different scene
could be
projected to the two users.
In one embodiment, an image of the third set is a portion of a corresponding
image of the
first or second set. For example, an image of the first set may represent a
scene and an
image of the third set may represent a portion or section of the same scene
according to a
given point of view. In an embodiment in which the third set of images
comprises images
for the left eye and the right eye, the third set of images comprises a set of
images of the
scene or a portion of the scene according to the point of view of the left eye
and a set of
- 14 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
corresponding images of the scene or a portion of the scene according to the
point of view
of the right eye.
In one embodiment, the first and second sets of images comprise monoscopic
images. In
the same or another embodiment, the third set of images comprises stereoscopic
images.
In an embodiment in which the simulator is configured for training two users,
the third set
of images comprises two sets of images each for a respective user.
At step 14, video images captured by a camera are received. The video images
are captured
along the line of sight or line of view of the user, i.e. the camera
substantially captures what
the user sees. The line of view may be defined by a vector of which the
direction
corresponds to the direction along which the user looks at, and an origin
point located such
as a point located between the two eyes of the user or a point located on an
eye of the user
for example.
In one embodiment, the video images may be captured by two cameras, each
recording
respective images of the same scene according to a different point of view.
For example,
the first camera may capture images as seen by the left eye of the user and
the second
camera may capture images as seen by the right eye of the user.
In an embodiment in which the simulator is configured for training two users,
two different
sets of video images are received at step 14. The first set of images
comprises video images
captured along the line of view of the first user while the second set of
images comprises
video images captured along the line of view of the second user.
At step 16, augmented reality images are generated using the third set of
images and the
video images. An augmented reality image corresponds to a video image in which
a
simulated scene image is inserted.
In one embodiment, an augmented reality image corresponds to its respective
video image
captured by a camera, in which an image of the third set is inserted. The
image of the third
set replaces the representation of the first display within the video image,
i.e. the first
- 15 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
display within the video image is replaced by an image of the third set
representing a
portion of the simulated scene.
In an embodiment in which the simulator is configured for training two users,
two sets of
augmented reality images are generated at step 16, each one for a respective
user.
At step 18, the first and second sets of images are displayed on a first
display. In one
embodiment, the first and second sets of images are concurrently displayed on
the first
display. In another embodiment, the first and second sets of images are
sequentially
displayed on the first display, i.e. images of the first set and images of the
second set are
displayed on the first display in an alternating manner. For example, at least
a first image of
the first set may be displayed during a first period of time, then at least a
first image of the
second set is displayed during a second period of time, etc. In one
embodiment, the period
of time during which an image of the first set is displayed is equal to the
period of time
during which an image of the second set is displayed.
For example, images of the first set may be displayed 30 times per second and
images of
the second set may also be displayed 30 times per second when the display rate
is 60 Hz,
each image being displayed during 16.67 ms. In another example, images of the
first set
may be displayed 60 times per second and images of the second set may also be
displayed
60 times per second when the display rate is 120 Hz, each image being
displayed during
8.33 ms.
At step 20, the augmented reality images are displayed on a second display
concurrently to
the sequential display of the first and second sets of images on the first
display. As
described below, the second display is wearable so as to be adjacent to the
eyes of the user.
In an embodiment in which the simulator is configured for training two users,
two sets of
augmented reality images are generated and each set of augmented reality
images is
displayed on a respective second display for a respective user.
- 16 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
At step 22, a portion of the field of view of the user is filtered using an
optical filter. The
optical filter may be an active filter such as a shutter device.
Alternatively, the optical filter
may be a passive filter such as a polarization filter or a wavelength filter.
In an embodiment in which an active filter such as a shutter device is used,
the portion of
the field of view of the user is selectively blocked and the step 18 comprises
sequentially
displaying the first and second sets of images on the first display. The
blocking of the
portion of the field of view of the user is synchronized with the sequential
display of the
first and second sets of images. In one embodiment, the blocking of the field
of view is
synchronized with the display of the second set of images so that the field of
view of the
user is partially blocked while images of the second set are displayed. As a
result, the whole
field of view of the user is clear/unblocked when images of the first set are
displayed. In
another embodiment, the blocking of the field of view is synchronized with the
display of
the first set of images so that the field of view of the user is partially
blocked when images
of the first set are displayed. As a result, the whole field of view of the
user is
clear/unblocked when images of the second set are displayed.
In an embodiment in which the simulator is configured for training two users,
the field of
view of the users is partially blocked in an alternating manner. For example,
the partial
blocking of the field of view of the first user may be synchronized with the
second set of
images so that only the first images when displayed on the first display are
within the field
.. of view of the first user. The partial blocking of the field of view of the
second user is
synchronized with the display of the images of the first set so that only the
images of the
second set when displayed are within the field of view of the second user.
Therefore, when an image of the first set is displayed on the first display,
the field of view
of the first user is clear and the first user may see the augmented reality
image displayed on
his second display and at least a section of the first image displayed on the
first display. On
the other end, when an image of the first set is displayed, the field of view
of the second
user is partially blocked so that the second user may only see the augmented
reality image
displayed on his second display.
- 17 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
Similarly, when an image of the second set is displayed on the first display,
the field of
view of the second user is clear and the second user may see the augmented
reality image
displayed on his second display and at least a section of the second image
displayed on the
first display. On the other end, when an image of the second set is displayed,
the field of
view of the first user is partially blocked so that the first user may only
see the augmented
reality image displayed on his second display.
In an embodiment in which passive filtering is performed at step 22, the first
and second
sets of images are concurrently displayed on the first display at step 18. In
one
embodiment, polarization is filtered. In this case, the images of the first
set have a first
polarization while the images of the second set have a second and different
polarization.
The light coming from the portion of the field of view of the user is filtered
so that only the
light having the first polarization may reach the user's eyes and only the
images of the first
set may be seen by the user.
When the simulator is used for training two users, the light coming from the
portion of the
field of view of the first user is filtered so that only the light having the
first polarization
may reach the first user's eyes and only the images of the first set may be
seen by the first
user. Similarly, the light coming from the portion of the field of view of the
second user is
filtered so that only the light having the second polarization may reach the
second user's
eyes and only the images of the second set may be seen by the second user.
In another embodiment, wavelength is filtered. In this case, the images of the
first set have
a first range of wavelength associated thereto while the images of the second
set have a
second and different range of wavelength associated thereto. The light coming
from the
portion of the field of view of the user is filtered so that only light having
a wavelength
contained in the first range of wavelength may reach the user's eyes and only
the images of
the first set may be seen by the user.
When the simulator is used for training two users, the light coming from the
portion of the
field of view of the first user is filtered so that only light having a
wavelength contained in
the first range of wavelength may reach the first user's eyes and only the
images of the first
- 18 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
set may be seen by the first user. Similarly, the light coming from the
portion of the field of
view of the second user is filtered so that only light having a wavelength
contained in the
second range of wavelength may reach the second user's eyes and only the
images of the
second set may be seen by the second user.
In one embodiment, the first set of images comprises images of the simulated
scene
according to the point of view of the first user such as a pilot and the
second set of images
comprises images of the simulated scene according to a second and different
point of view,
i.e. the point of view of the second user such as a copilot.
In one embodiment, the method 10 further comprises receiving simulation data
and
generating the first and second sets of images using the simulation data. In
one
embodiment, the simulation data comprises at least visual information such as
the
information about the geometry of the elements in the world and position
information such
as the position or coordinates of the elements within the world. In one
embodiment, the
generation of the first and second sets of images is performed as a function
of a position of
the users relative to that of the first display while using the simulator. For
example, the first
set of images may be generated to suit the point of view of the first user,
i.e. the first set of
images is generated as a function the position of the head of the first user,
while the second
set of images may be generated to suit the point of view of the second user,
i.e. the second
set of images is generated as a function the position of the head of the
second user.
In one embodiment, the generation of the first and second sets of images may
be static, i.e.
the position of the user is predefined or determined once, and the first and
second sets of
images are generated as a function of the respective unique position for their
respective
user.
In another embodiment, the generation of the first and second sets of images
may be
dynamic, i.e. the position of the user is tracked in real-time, and the first
and second sets of
images are generated as a function of the respective tracked position for
their respective
user.
- 19 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
Similarly, the method 10 may comprise a step of generating the third set of
images for the
user or each user when the simulator is configured for training more than one
user. In this
case, the third set of images is generated using the simulation data and the
line of view of
the user.
In one embodiment, the third set of images comprises stereoscopic images. In
this case, the
third set of images may comprise a first series of images for the left eye of
the user and a
second series of images for the right eye of the user. Each image of the first
series and the
second series may represent a section or portion of a scene displayed on the
first display. In
this case, the second display comprises a left display for displaying the
series of images to
the left eye and a right display for displaying the second series of images to
the right eye. In
this case, a line of view may be determined for each eye of the user and the
first and second
series of images are generated as a function of the line of view of the
respective eye to
which they are associated.
It should be understood that when the third set of images comprise
stereoscopic images, the
augmented reality images are also stereoscopic. In this case, the video images
may
comprise a first set of video images corresponding to what is being seen by
the left eye of
the user and a second set of video images corresponding to what is being seen
by the right
eye of the user. In another example, a single camera may be used to generate a
single set of
video images and the video images for the left and right eyes may be obtained
by a
extracting a respective portion of the video images contained in the single
set.
In one embodiment, the method 10 further comprises tracking the line of view
of the user
or the users if the simulator is configured for training more than one user.
In one
embodiment, the position and orientation of the head of the user is tracked
and the line of
view is determined using the position and orientation of the head of the user.
In one embodiment, the step 22 of selectively and partially obstructing the
field of view of
the user is performed by synchronizing a shutter device with the sequential
display of the
first and second sets of images, as described in more detail below. In one
embodiment, only
the far peripheral vision of the user is selectively blocked at step 22.
- 20 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
Figure 2 illustrates one embodiment of a simulator 50 for concurrently
training two users
such as a pilot and a copilot of an aircraft for example. The simulator 50
comprises a first
or main display 52, a wearable display 54, 56 for each user, a wearable
shutter device 58,
60 for each user, a tracking system 62, a video camera 64, 66 for each user
and a control
unit 68. The simulator 50 further comprises physical elements (not shown) such
as a frame,
walls, a control panel, control instruments, etc.
In the illustrated embodiment, the main display 52 comprises a curved rear
projection
screen and at least one projector (not shown) for projecting monoscopic images
on the rear
projection screen. However, it should be understood that any adequate display
for
displaying monoscopic images may be used. For example, the main display 52 may
be a
dome for front projection, an LED screen or the like.
As illustrated in Figure 2, the display 52 is positioned away from the users
for filling the
monocular field of views (peripheral vision) for the two users having a
different point of
view when looking at the display 52.
In the illustrated embodiment, the wearable display 54, 56 is integrated on a
head
mountable device to form a head mounted display, Each wearable device 54, 56
comprises
a left display 70 positionable adjacent and in front of a left eye of the user
and a right
display 72 positionable adjacent and in front of a right eye of the user. The
two displays 70
and 72 allow displaying stereoscopic images to the user. While the present
description
refers to a wearable display provided with a left and a right displays, it
should be
understood that any adequate wearable display configured for displaying
stereoscopic
images may be used.
It should be understood that the wearable displays 54 and 56 may be replaced
by a single
wearable display of which the screen is divided into two sections, each for
displaying a
respective image in front of a respective eye.
The shutter device 58, 60 is configured for at least partially selectively
blocking the field of
view of the user that is outside of the wearable display 54, 56. For example,
the wearable
-21 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
display 54, 56 may be positioned to cover the central portion of the field of
view of the user
such as a 114 field of view while the shutter device 58, 60 may comprise two
shutters 74
and 76 each positioned on a respective side of the user head and adjacent to a
respective
display 70, 72. The two shutters 74 and 76 allow selectively blocking the
portion of the
field of view of the user that is located outside of the central portion of
the field of view and
covered by the display 70, 72.
In an embodiment in which the displays 70 and 72 are part of a head mounted
display, the
shutter device 58, 60 may be mounted on the head mounted display.
In one embodiment, the shutter devices 58, 60 and/or the shutters 74 and 76
may comprise
a liquid crystal shutter (LCS). The LCS can be operated so as to be
substantially transparent
to allow the user to see the display 52 or substantially opaque so as to
prevent the user from
seeing the display 52. However, it should be understood that any device
adapted to
selectively and partially block the field of view of a user so as selectively
allow the user to
see the main display 52 and prevent the user from seeing the display 52 may be
used.
In one embodiment, the shutter devices 58 and 60 may be replaced by passive
filters such
as polarized glasses. In this case, the images of the first set have a first
polarization and the
images of the second set have a second and different polarization. The
polarization of the
polarized glasses of each user is different and determined according to the
polarization of
the respective images that they allow seeing. The polarization of the images
of the first set
is chosen as a function of the polarization of the polarized glasses for the
first user (who
will look at the display 52 according to the first point of view) and the
polarization of the
polarized glasses for the second user so that when the images of the first set
are displayed
on the main display 52, the first user may see the images of the first set
displayed on the
main display 52 through his polarized glasses while the second user cannot see
the images
.. of the first set displayed on the main display 52 through his polarized
glasses. Similarly, the
polarization of the images of the second set is chosen as a function of the
polarization of the
polarized glasses for the second point of view and the polarization of the
polarized glasses
for the second user (who will look at the main display according to the second
point of
view) so that when the images of the second set are displayed on the main
display 52, the
- 22 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
second user may see the images of the second set displayed on the main display
52 through
his polarized glasses while the first user cannot see the images of the second
set displayed
on the main display 52 through his polarized glasses. In one embodiment, the
first and
second sets of images are displayed sequentially on the main display 52
similarly to when
shutters devices 58 and 60 are used. In another embodiment, the first and
second sets of
images having different polarization are displayed concurrently on the main
display 52
As described above, the simulator 50 comprises a tracking system 62 for
tracking the line
of view of each user. In the illustrated embodiment, the tracking system 62
comprises a
tracking camera 80 and a head tracker 82, 84 positionable on the head the
user. The
tracking camera 80 along with the head tracker 82, 84 allows determining the
position and
the orientation of the head of the user, from which the line of view of the
user may be
determined. When the display 54, 56 is part of a head mounted display, the
head tracker 82,
84 can be mounted on the head mounted display.
It should be understood that any adequate tracking system or device adapted to
track the
line of view of a user or the position and orientation of the head of a user
may be used. For
example, AC magnetic tracking system, DC magnetic tracking system, ultrasonic
tracking
system, inertial sensors tracking system, texture-based, infrared camera
tracking system,
inside-out camera tracking, system mechanical linkage tracking system or the
like can be
used
The camera 64, 66 is mountable on the head of the user so as to capture video
images of
what the user is seeing. For example, the camera 64, 66 may be mounted on a
head
mounted display, if any. In one embodiment, the camera 64, 66 is a dual
camera, i.e. it
comprises a left camera positioned so as to capture the images as seen by the
left eye of the
user and a right camera positioned so as to capture the images as seen by the
right eye of
the user.
The control unit 68 comprises at least one processor or processing unit, a
memory or
storing unit and a communication unit for transmitting and/or receiving data.
is configured
for executing the steps of the method 10.
- 23 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
The control unit 68 receives a first set of images to be displayed on the main
display 52 for
the first user and a second set of images to be displayed for the second user
also on the
main display 52. In one embodiment, the images of the first set represents a
scene
according to the point of view of the first user while the images of the first
set represents
the same scene according to the point of view of the second user. For example,
the scene
may correspond to the outside of a vehicle to be simulated as seen through a
window of the
vehicle. In another embodiment, the images of the first and second sets may
represent
different scenes so different scenes be displayed to the two users on the same
display 52.
In one embodiment, the control unit 68 is configured for receiving simulation
data and
generate the first and second sets of images. The images of the first set may
be generated
according to the point of view of the first user and the images of the second
set may be
generated according to the point of view of the second user. The point of view
of each user
may be predefined. Alternatively, the point of view of each user may be
determined
according to the position of the head of each user as detected by the tracking
unit XX and
any other adequate position tracking device. In this case, the point of view
may be
determined only once at the beginning of the simulation and all of the images
of the first
and second sets are generated according to the determined points of view. In
another
example, the point of view of each user may change during the simulation and
the
generation of the images of the first and second sets is performed using the
changing points
of view.
The control unit 68 further receives a third set of images for the first user
and a fourth set of
images for the second user. Each image of the third set corresponds to a
section or portion
of a corresponding image in the first set, which is determined as a function
of the line of
view of the first user. Similarly, each image of the fourth set corresponds to
a section or
portion of a corresponding image in the second set which is determined as a
function of the
line of view of the first user. The line of view is tracked substantially
continuously.
As described above, the third set of images may comprises images generated
according to
the line of view of the left eye of the first user and images generated
according to the line of
view of the right eye of the first user. Similarly, the fourth set of images
may comprises
- 24 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
images generated according to the line of view of the left eye of the second
user and images
generated according to the line of view of the right eye of the second user
In one embodiment, the control unit 68 is further configured for generating
the third set of
images and the fourth set of images. In this case, the images of the third set
may be
.. generated from the images of the first set and the images of the fourth set
may be generated
from the images of the second set. Alternatively, the images of the third and
fourth sets may
be generated from the simulation data.
The control unit 68 is further configured for generating the augmented reality
images to be
displayed on the display 54 of the first user and the display 56 of the second
user.
Regarding the first user, the control unit 68 combines together in real time
the video images
coming from the camera 64 and the images of the third set to obtain augmented
reality
images which are transmitted to the display 54 to be displayed thereon.
Similarly, regarding
the second user, the control unit 68 combines together in real time the video
images coming
from the camera 66 and the images of the fourth set to obtain augmented
reality images
which are transmitted to the display 56 to be displayed thereon.
In an embodiment in which the display 54, 56 comprises a left display 70 and a
right
display 72, it should be understood that augmented reality images are received
or generated
for both the left display 70 and the right display 72, for each display 54,
56.
The control unit 68 is further configured for sequentially displaying the
first and second
sets of images on the display 52 concurrently to displaying the augmented
reality images on
the displays 54 and 56. The control unit 68 is further adapted to control the
wearable shutter
device 58 and 60 synchronously with the sequential display of the images of
the first and
second sets. As described above, the images of the first and second sets are
sequentially
displayed on the display 52. During the display of images of the first set on
the display 52,
the control unit 68 opens the shutter device 58 while closing the shutter
device 60 of the
second user. During the display of images of the second set on the display 52,
the control
unit 68 closes the shutter device 58 while opening the shutter device 60 of
the second user.
As a result, when images of the first set are displayed on the display 52, the
second user is
- 25 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
prevented from seeing the images displayed on the display 52 and may only see
the
augmented reality images displayed on the display 56 while the first user may
see both the
images displayed on the display 52 and the augmented reality images displayed
on the
display 54. When images of the second set are displayed on the display 52, the
first user is
prevented from seeing the images displayed on the display 52 and may only see
the
augmented reality images displayed on the display 54 while the second user may
see both
the images displayed on the display 52 and the augmented reality images
displayed on the
display 54.
Figure 3 illustrates an exemplary of what a user sees while using a display
system such as
the display system 50. A 2D image 100 is a scene is displayed on a main
display located
away from the user. The user is provided with a left wearable display 102
positioned in
front of his left eye and a right wearable display 104 positioned in front of
his right eye. A
respective augmented reality image 106, 108 is displayed on the left and right
displays 104
and 106 to provide a 3D image to the user. Each augmented reality image
corresponds to
what the respective eye would see if the respective display 102, 104 would not
be
positioned in front of the respective eye. For example, the image 106
corresponds to the
portion of the image 100 that the left eye of the user would see if the
display 102 would not
be present. The image 108 corresponds to the combination of a portion of the
image 100
and a portion of a video image captured by a camera. More precisely, the
section of the
video image which corresponds to the main display is replaced by an image
representing
the portion of the image 100 that the right eye of the user would see if the
display 104
would not be present.
In the exemplary embodiment illustrated in Figure 3, the image 100 is
generated according
to the point of view of the user and the shutter device (not shown) is open
when the image
100 is displayed on the main display so that the user wearing the displays 102
and 104 may
see his environment outside of the displays 102 and 104 including the image
100 displayed
on the main display, It should be understood that the shutter device of the
other user is
closed when the image 100 is displayed on the main display so that the second
user may
only see the augmented reality images displayed on his left and right displays
when the
- 26 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
image 100 is displayed on the main display. On the contrary, when an image
generated
according to the point of view of the second user is displayed on the main
display, the
shutter device of the first user is closed and the shutter device of the
second user is open so
that only the second user may see the main display.
In one embodiment, the simulated images used for generating the augmented
images 106
and 108 have a resolution or a quality as perceived by the user which is
greater than the
resolution or quality as perceived by the user of the 2D image 100 displayed
on the main
display.
In one embodiment, the images of the first and second sets are 2D images and
the display
52 is a large field of view display to fill the peripheral vision for two
different points of
view. The images of the first set are generated according to the point of view
of the first
user while the images of the second set are generated according to the point
of view of the
second user.
In one embodiment, the display 52 comprises a rear projection screen and at
least one
projector for projecting images on the rear face of the rear projection screen
to reduce the
physical footprint of the display 52.
In one embodiment, the above described method and system allow reducing or
eliminating
parallax error for both users, and providing the two users with motion
parallax cues. This
may be achieved by combining the high resolution of a head-tracked helmet
mounted
display (HMD) to display 3D high resolution augmented reality images and cover
the
binocular field of view of the users, e.g. the central vision of the users,
with the wide field
of view of an electronically collimated display:
Figure 4 is a block diagram illustrating an exemplary processing module 120
for executing
the steps 12 to 22 of the method 10, in accordance with some embodiments. The
processing
module 120 typically includes one or more Computer Processing Units (CPUs)
and/or
Graphic Processing Units (GPUs) 122 for executing modules or programs and/or
instructions stored in memory 124 and thereby performing processing
operations, memory
- 27 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
124, and one or more communication buses 126 for interconnecting these
components. The
communication buses 126 optionally include circuitry (sometimes called a
chipset) that
interconnects and controls communications between system components. The
memory 124
includes high-speed random access memory, such as DRAM, SRAM, DDR RAM or other
random access solid state memory devices, and may include non-volatile memory,
such as
one or more magnetic disk storage devices, optical disk storage devices, flash
memory
devices, or other non-volatile solid state storage devices. The memory 124
optionally
includes one or more storage devices remotely located from the CPU(s) 122. The
memory
124, or alternately the non-volatile memory device(s) within the memory 124,
comprises a
non-transitory computer readable storage medium. In some embodiments, the
memory 124,
or the computer readable storage medium of the memory 124 stores the following
programs, modules, and data structures, or a subset thereof:
an augmented reality image generator module 130 for generating augmented
reality images and displaying the generated augmented reality images on the
respective
wearable display of each user;
a sequential display module 132 for sequentially sequentially displaying the
first and second sets of images on a main display located away from the users;
and
a shutter control module 134 for synchronizing the shutters of the users with
the sequential display of the images on the main display.
Each of the above identified elements may be stored in one or more of the
previously
mentioned memory devices, and corresponds to a set of instructions for
performing a
function described above. The above identified modules or programs (i.e., sets
of
instructions) need not be implemented as separate software programs,
procedures or
modules, and thus various subsets of these modules may be combined or
otherwise re-
arranged in various embodiments. In some embodiments, the memory 124 may store
a
subset of the modules and data structures identified above. Furthermore, the
memory 124
may store additional modules and data structures not described above.
- 28 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
Although it shows a processing module 120, Figure 4 is intended more as
functional
description of the various features which may be present in a management
module than as a
structural schematic of the embodiments described herein. In practice, and as
recognized by
those of ordinary skill in the art, items shown separately could be combined
and some items
.. could be separated.
While the above description refers to a method and system in which at least
one camera is
used for capturing images of the environment surrounding the main display 52
present
within the field of view of the user. Figure 5 illustrates one embodiment of a
method 200
for displaying images on a main display such as display 52 while using no
camera. In this
case, the user wears a see-through display which allows him to see the
environment
surrounding the main display 52 through the see-through display 52.
The method 200 is executed by a computer machine provided with at least one
processor or
processing unit, a memory and communication means.
At step 202, scene images, i.e. images of a scene to be displayed to a user,
are received. The
scene images offer a representation of the simulation environment to be
displayed to the
user (s) of the simulator. For example, the scene images may be simulated
images
representing what a pilot of an aircraft would see while flying.
The scene images comprise three sets of images. As described above, it should
be
understood that a set of images comprises images which are timely ordered so
as to be
displayed according to a temporal order to form a video.
In one embodiment, the three sets of images comprise images of a same scene.
For
example, the first set of images comprises images of a scene suitable for
being seen
according to a first point of view, e.g. the point of view of a pilot. The
second set of images
comprises images of the same scene suitable for being seen according to a
second and
different point of view, e.g. the point of view of a copilot. The third set of
images
comprises images of at least a portion or section of the scene.
- 29 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
It should be understood that the third set of images may also comprise images
different
from the first and second sets of images.
In another embodiment, the third set of images may comprise two sets of
images, i.e. a set
of images according to the line of view of the left eye of the user and a
further set of images
according to the line of the right eye of the user.
As described above, the first and second sets of images may comprise images of
different
scenes.
In one embodiment, an image of the third set is a portion of a corresponding
image of the
first or second set. For example, an image of the first set may represent a
scene and an
image of the third set may represent a portion or section of the same scene as
it would be
seen through the see-through display and according to a given point of view.
In an
embodiment in which the third set of images comprises images for the left eye
and the right
eye, the third set of images comprises a set of images of the scene or a
portion of the scene
according to the point of view of the left eye and a set of corresponding
images of the scene
or a portion of the scene according to the point of view of the right eye.
In one embodiment, the first and second sets of images comprise monoseopic
images. In
the same or another embodiment, the third set of images comprises stereoscopic
images.
In an embodiment in which the simulator is configured for training two users,
the third set
of images comprises two sets of images each for a respective user.
At step 204, the first and second sets of images are displayed on a first or
main display. In
one embodiment, the first and second sets of images are concurrently displayed
on the first
display. In another embodiment, the first and second sets of images are
sequentially
displayed on the first display, i.e. images of the first set and images of the
second set are
displayed on the first display in an alternating manner, as described above.
For example, at
least a first image of the first set may be displayed during a first period of
time, then at least
a first image of the second set is displayed during a second period of time,
then at least a
second image of the first set is displayed during a third period of time, at
least a second
- 30 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
image of the second set is subsequently displayed during a fourth period of
time, etc. In one
embodiment, the period of time during which an image of the first set is
displayed is equal
to the period of time during which an image of the second set is displayed.
At step 206, the third set of images is displayed on a second see-through
display
concurrently to the sequential display of the first and second sets of images
on the first
display. As described below, the see-through display is wearable so as to be
adjacent to the
eyes of the user. the images of the third set represent the portion of the
scene displayed on
the main display as seen through the see-through display.
In an embodiment in which the simulator is configured for training two users,
two sets of
third sets of images are generated and each third set of images is displayed
on a respective
see-through display for a respective user.
At step 208, a portion of the field of view of the user is filtered using an
optical filter. The
optical filter may be an active filter such as a shutter device.
Alternatively, the optical filter
may be a passive filter such as a polarization filter or a wavelength filter.
In an embodiment in which an active filter such as a shutter device is used,
the portion of
the field of view of the user is selectively blocked and the step 204
comprises sequentially
displaying the first and second sets of images on the first display. The
blocking of the
portion of the field of view of the user is synchronized with the sequential
display of the
first and second sets of images. In one embodiment, the blocking of the field
of view is
synchronized with the display of the second set of images so that the field of
view of the
user is partially blocked while images of the second set are displayed. As a
result, the whole
field of view of the user is clear/unblocked when images of the first set are
displayed. In
another embodiment, the blocking of the field of view is synchronized with the
display of
the first set of images so that the field of view of the user is partially
blocked when images
of the first set are displayed. As a result, the whole field of view of the
user is
clear/unblocked when images of the second set are displayed. It should be
understood that
the images of the third set may be continuously displayed independently of the
type of
images displayed on the main display.
- 31 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
In an embodiment in which passive filtering is performed at step 208, the
first and second
sets of images are concurrently displayed on the first display at step 204. In
one
embodiment, polarization is filtered. In this case, the images of the first
set have a first
polarization while the images of the second set have a second and different
polarization.
The light coming from the portion of the field of view of the user is filtered
so that only the
light having the first polarization may reach the user's eyes and only the
images of the first
set may be seen by the user.
When the simulator is used for training two users, the light coming from the
portion of the
field of view of the first user is filtered so that only the light having the
first polarization
may reach the first user's eyes and only the images of the first set may be
seen by the first
user. Similarly, the light coming from the portion of the field of view of the
second user is
filtered so that only the light having the second polarization may reach the
second user's
eyes and only the images of the second set may be seen by the second user.
In another embodiment, wavelength is filtered. In this case, the images of the
first set have
a first range of wavelength associated thereto while the images of the second
set have a
second and different range of wavelength associated thereto. The light coming
from the
portion of the field of view of the user is filtered so that only light having
a wavelength
contained in the first range of wavelength may reach the user's eyes and only
the images of
the first set may be seen by the user.
When the simulator is used for training two users, the light coming from the
portion of the
field of view of the first user is filtered so that only light having a
wavelength contained in
the first range of wavelength may reach the first user's eyes and only the
images of the first
set may be seen by the first user. Similarly, the light coming from the
portion of the field of
view of the second user is filtered so that only light having a wavelength
contained in the
second range of wavelength may reach the second user's eyes and only the
images of the
second set may be seen by the second user.
In one embodiment, the method 200 further comprises receiving simulation data
and
generating the first and second sets of images using the simulation data, as
described above.
- 32 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
Similarly, the method 200 may comprise a step of generating the third set of
images for the
user or each user when the simulator is configured for training more than one
user. In this
case, the third set of images is generated using the simulation data and the
line of view of
the user. In one embodiment, the images of the third set are generated by
determining the
line of view of the user and determining which portion of the main display is
viewed by the
user through the see-through display. The determination of the portion of the
main display
that is seen through the see-through display may be determined based on the
position of the
user head or the position of the see-through display, the orientation of the
head of the user
and the dimensions of the see-through display. The images of the third set
then corresponds
to the portion of the scene that is to be concurrently displayed on the
determined portion of
the main display and the images are generated as a function of the point of
view of the
user.. Therefore, when the user cannot see any portion of the main display, no
image is
displayed on the see-through display.
In one embodiment, the third set of images comprises stereoscopic images. In
this case, the
.. third set of images may comprise a first series of images for the left eye
of the user and a
second series of images for the right eye of the user. Each image of the first
series and the
second series may represent a section or portion of a scene displayed on the
first display. In
this case, the second display comprises a left display for displaying the
series of images to
the left eye and a right display for displaying the second series of images to
the right eye. In
.. this case, a line of view may be determined for each eye of the user and
the first and second
series of images are generated as a function of the line of view of the
respective eye to
which they are associated.
It should be understood that the first, second and third sets of images used
in the method
200 may be the same as those used for the method 10.
In one embodiment, the method 200 further comprises tracking the line of view
of the user
or the users if the simulator is configured for training more than one user.
In one
embodiment, the position and orientation of the head of the user is tracked
and the line of
view is determined using the position and orientation of the head of the user.
- 33 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
In one embodiment, the step 208 of selectively and partially obstructing the
field of view of
the user is performed by synchronizing a shutter device with the sequential
display of the
first and second sets of images, as described in more detail below. In one
embodiment, only
the far peripheral vision of the user is selectively blocked at step 208. In
another
embodiment, at least the far peripheral vision of the user is selectively
blocked at step 208.
Figure 6 illustrates one embodiment of a simulator system 300 for executing
the method
200. In this case, the simulator system 300 comprises no camera such as
cameras 64, 66 for
recording he field of view of the users. The simulator system 300 comprises a
main display
302, a wearable display 304, 306 which is see-through for each user, a
wearable filter 308,
310 for each user, a tracking system 312 and a control unit 314. The simulator
system 3200
further comprises physical elements (not shown) such as a frame, walls, a
control panel,
control instruments, etc.
The see-through display device 304, 306 may be integrated on a head mountable
device to
form a head mounted display. Each see-through device 304, 306 may comprise a
single
display sized and shaped for covering both eyes of a user, as illustrated in
Figure 6. In this
case, a single image may be displayed on the single see-through screen 304,
306.
Alternatively, the see-through screen 304, 306 may be divided into two
sections, i.e. a left
section and a right section. In this case, a corresponding image of the third
set is displayed
on each one of the left and right sections of the see-through display 304,
306.
In another embodiment, the see-through display 304, 306 may comprise a left
see-through
screen positionable adjacent and in front of a left eye of the user and a
right see-through
screen positionable adjacent and in front of a right eye of the user. The two
see-through
screens allow displaying stereoscopic images to the user.
As described above, each wearable filter 308, 310 is adapted to at least
partially filter the
field of view of the respective user outside of the respective see-through
display device
304, 306. In one embodiment, the filters 308 and 310 are active filters such
as shutters. In
another embodiment, the filters 308 and 310 are passive filters. For example,
the passive
- 34 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
filters may be polarized glasses. In another example, the passive filters may
be wavelength
filters.
In an embodiment in which the see-through display device 304 and 306 are part
of a head
mounted display, the filter 308, 310 may be mounted on the head mounted
display.
The control unit 314 is configured for receiving the first, second and third
sets of images
and displaying the first and second sets of images on the main display 302
while displaying
the third set of images on the see-through display device 304. 306, as
described above.
In an embodiment in which the filters 308 and 310 are passive filters, the
control unit 314
may be adapted to concurrently display the first and second sets of images on
the main
display 302. In an embodiment in which the filters 308 and 310 are active
filters, the
control unit 314 may be adapted to sequentially display the first and second
sets of images
on the main display 302.
In one embodiment, the control unit 314 may be configured for generating the
first and
second sets of images and/or generating the third set of images, as described
above.
It should be understood that when the wearable display 304, 306 is see-
through, the control
unit 314 is not configured for generating augmented reality images since the
simulator
comprises no camera. The control unit 314 simply displays the images of the
third set on
the see-through display 304, 306 without combining them with images captured
by a
camera.
In one embodiment such as an embodiment in which the filters 308 and 310 are
shutters, it
should be understood that the control unit 314 is configured for sequentially
displaying the
first and second sets of images on the display 302 concurrently to displaying
the images of
the third set on the see-through displays 304 and 306. The control unit 314 is
further
adapted to control the wearable shutter devices 308 and 310 synchronously with
the
sequential display of the images of the first and second sets. As described
above, the
images of the first and second sets are sequentially displayed on the display
302. During the
display of images of the first set on the display 302, the control unit 314
opens the shutter
-35 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24
device 308 while closing the shutter device 310 of the second user. During the
display of
images of the second set on the display 302, the control unit 314 closes the
shutter
device 308 while opening the shutter device 310 of the second user. As a
result, when
images of the first set are displayed on the display 302, the second user is
prevented from
seeing the images displayed on the display 302 and may only see the augmented
reality
images displayed on the display 306 while the first user may see both the
images displayed
on the display 302 and the augmented reality images displayed on the display
304. When
images of the second set are displayed on the display 302, the first user is
prevented from
seeing the images displayed on the display 302 and may only see the augmented
reality
images displayed on the display 304 while the second user may see both the
images
displayed on the display 302 and the augmented reality images displayed on the
display 304.
The embodiments of the invention described above are intended to be exemplary
only. The
scope of the invention is therefore intended to be limited solely by the scope
of the
appended claims.
- 36 -
CA 3018465 2018-09-24