Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
1
Aircraft Landina Gear Component
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The weight of an aircraft assembly can adversely affect fuel consumption of an
aircraft of which it forms a part.
The present inventor has devised a new type of an aircraft landing gear
component which can be of reduced weight in comparison to known
corresponding aircraft landing gear components and can be incorporated into an
aircraft landing gear assembly.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A first aspect of the invention provides an aircraft landing gear component
comprising: a first base member and a second base member, separated along a
first longitudinal axis, a plurality of first parallel hoops, each first hoop
lying along
the first longitudinal axis and aligned in a plane oriented at a first non-
zero angle
to the first longitudinal axis, and a plurality of second parallel hoops, each
second
hoop lying along the first longitudinal axis and aligned in a plane oriented
at a
second non-zero angle to the first longitudinal axis, the second non-zero
angle
being different from the first non-zero angle, wherein each of the first hoops
intersects with and is fixed to at least one of the second hoops, and wherein
each
of the second hoops intersects with and is fixed to at least one of the first
hoops,
such that the first and second hoops form a rigid structure extending between
the
first and second base members.
With such an arrangement, there is provided an aircraft landing gear component
having a geodetic shape and having a lower weight.
The aircraft landing gear component can further comprise at least one elongate
member aligned with the first longitudinal axis, the elongate member
intersecting
with and being fixed to one or more of the first hoops and one or more of the
second hoops. With such an arrangement, the component can have better
bending stiffness.
CA 3055592 2019-09-13
2
The first and second hoops can form a cylindrical part of the aircraft landing
gear
component.
The aircraft landing gear component can further comprise: a third base member,
separated from the second base member along a second longitudinal axis, a
plurality of third parallel hoops, each third hoop being distributed along the
second longitudinal axis and aligned in a plane oriented at a third non-zero
angle
to the second longitudinal axis, and a plurality of fourth parallel hoops,
each
fourth hoop being distributed along the second longitudinal axis and aligned
in a
plane oriented at a fourth non-zero angle to the second longitudinal axis, the
fourth non-zero angle being different from the third non-zero angle, wherein
each
of the third hoops intersects with and is fixed to at least one of the fourth
hoops,
and wherein each of the fourth hoops intersects with and is fixed to at least
one
of the third hoops, such that the third and fourth hoops form a rigid
structure
extending between the second and third base members.
With such an arrangement, the aircraft landing gear component can be suitable
for a greater range of applications.
The aircraft landing gear component can further comprise at least one second
elongate member aligned with the second longitudinal axis, the second elongate
member intersecting with and being fixed to one or more of the third hoops and
one or more of the fourth hoops. With such an arrangement, the component can
have better bending stiffness.
The third and fourth hoops can form a cylindrical part of the aircraft landing
gear
component.
The first and second longitudinal axes can lie along the same line. With such
an
arrangement, the component can provide a more simple linkage.
The aircraft landing gear component can further comprise a bearing for
coupling
to an airframe or to a second aircraft landing gear component. With such an
arrangement, the aircraft landing gear can be used as a bogie beam or a strut.
At least one of the base members can define the bearing.
CA 3055592 2019-09-13
3
The first, second and third base members can each define at least one bearing.
This might make the aircraft landing gear component particularly suited to use
as
a bogie beam.
The component can comprise a bogie beam.
The component can further comprise a covering, the covering surrounding the
first and second pluralities of hoops. Alternatively, the covering can cover
only a
single plurality of hoops. The covering can reduce aeroacoustic noise
generated
by the component.
The covering can comprise a structural part of the component. This can allow
the
overall component to be made more lightweight.
A second aspect of the invention provides a landing gear comprising: a first
part
arranged to connect to an aircraft, a second part arranged to contact the
ground,
and an aircraft landing gear component according to the first part.
A third aspect of the invention provides a method according to claim 15.
In a fourth aspect of the invention, the component can comprise an aircraft
assembly component arranged to form part of an aircraft assembly distinct from
a
landing gear assembly. Optional features of the first aspect can be applied to
the
aircraft assembly component of the fourth aspect in an analogous manner.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Embodiments of the invention will now be described with reference to the
accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a diagram of an aircraft;
Figures 2a to 2e are diagrams an aircraft landing gear assembly;
Figure 3 is a diagram of a landing gear component according to an embodiment
of
the invention; and
CA 3055592 2019-09-13
4
Figure 4 is a magnified view of part of the landing gear component of Figure
3.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENT(S)
Figure 1 is a diagram of an aircraft 10. The aircraft 10 includes assemblies
such
as a nose landing gear 12, main landing gear 14 and engines 16. Other aircraft
assemblies will be apparent to the skilled person. An aircraft assembly can be
a
group of interconnected parts which are arranged to be fitted to one or more
other aircraft assemblies as a unit. The term aircraft as used herein includes
aeroplanes, helicopters, UAVs and the like.
Referring now to Figures 2a to 2e, an aircraft assembly, namely an aircraft
landing gear assembly, is shown generally at 14. The landing gear assembly 14
includes a foldable stay 18, a lock link 20 and a down lock spring assembly 22
mounted to the stay 18 and arranged to urge the lock link 20 to assume a
locked
state. The landing gear assembly also includes a main shock absorber strut 24,
comprising a main fitting 26 and a sliding tube 28, as well as a pair of wheel
and
brake assemblies 30 pivotally coupled to a lower end of the sliding tube 28
via an
elongate bogie beam 29.
The aircraft landing gear assembly is movable between a deployed condition,
for
take-off and landing, and a stowed condition for flight. An actuator (not
shown) is
provided for moving the landing gear between the deployed condition and the
stowed condition. This actuator is known in the art as a retraction actuator,
and
more than one can be provided. A retraction actuator can have one end coupled
to the airframe and another end coupled to the main strut such that extension
and retraction of the actuator results in movement of the main strut between
deployed and stowed conditions.
The stay 18 serves to support the orientation of the main fitting 26 when the
landing gear is in the deployed condition. The stay 18 generally includes a
two
bar linkage that can be unfolded to assume a generally straight or aligned,
over
centre condition in which the stay 18 is locked to inhibit movement of the
main
fitting, as shown in Figures 2c and e. When the stay is broken, it no longer
prevents pivotal movement of the main fitting 26 and the main fitting 26 can
be
moved by the retraction actuator towards the stowed condition, as shown in
Figure 2a. During flight the stay 18 is arranged in the folded condition,
while
CA 3055592 2019-09-13
5
during take-off and landing the stay 18 is arranged in the generally straight
or
aligned condition. Some main landing gear assemblies include a pair of stays
coupled to a common shock absorbing strut.
The stay 18 has an elongate upper stay arm 18a having a lower end defining a
pair of lugs pivotally coupled via a pivot pin 32 to a pair of lugs defined at
an
upper end of an elongate lower stay arm 18b. The stay arms 18a and 18b can
therefore pivotally move relative to one another about the pivot pin 32. The
upper end of the upper stay arm 18a defines a pair of lugs that are pivotally
coupled to a lug of a connector 34 which in turn is pivotally coupled to the
airframe 11. The lower end of the lower stay arm 18b defines a pair of lugs
pivotally coupled to a lug of a connector 36 which in turn is pivotally
coupled to
the main fitting 26.
The lock link 20 has an elongate upper link arm 20a having a lower end
pivotally
coupled to an upper end of an elongate lower link arm 20b via a pivot pin 38.
The
link arms 20a, 20b can therefore pivotally move relative to one another about
the
pivot pin 38. An upper end of the upper link arm 20a defines a pair of lugs
that
are pivotally coupled to a lug of a connector 40 which in turn is pivotally
coupled
to the main strut 26. A lower end of the lower link arm 20b defines a lug that
is
pivotally coupled to lugs of the stay arms 18a, 18b via the pivot pin 32. Lugs
of
the upper stay arm 18a are disposed between the lugs of the lower stay arm 18b
and the lugs of the lower link arm 20b.
When the lock link 20 is in the locked condition, as illustrated in Figures 2d
and
2e, the upper and lower link arms 20a, 20b are generally longitudinally
aligned or
coaxial, and can be 'over-centre', such that the lock link 20 is arranged to
oppose
a force attempting to fold the stay 18, so as to move the landing gear
assembly
from the deployed condition towards the stowed condition. The lock link 20
must
be broken to enable the stay 18 to be folded, thereby permitting the main
fitting
26 to be moved by the retraction actuator towards the stowed condition.
One or more down lock springs 22 are generally provided to assist in moving
the
landing gear assembly to the deployed condition and locking it in that state
by
making the lock link. Down lock springs 22 also inhibit the lock link
accidentally
being unlocked. Down lock springs 22 are generally titanium alloy coil
springs,
CA 3055592 2019-09-13
6
which can be coupled between the lock link and another part of the landing
gear
assembly, such as an arm of the stay assembly, as shown in Figures 2b and 2e.
The spring assembly 22 is arranged to bias the lock link 20 towards the locked
condition by way of spring tension. A distal end of the spring 22a is coupled
to the
lower stay arm 18b via a lower engagement formation 22b which in turn is
coupled to an anchor point defined by the lower connector 22c.
The coil spring of the spring assembly 26 is at its shortest when the landing
gear
assembly is in the deployed condition, as shown in Figure 2e, and at its
longest
when the landing gear assembly approaches the stowed condition, as shown in
Figure 2b. As the landing gear assembly is retracted towards the stowed
condition, the spring of each spring assembly extends, resulting in increased
spring load and torsional stress.
Referring to Figure 2e, a lock stay actuator 42 is coupled between the upper
stay
arm 18a and lower link arm 20b and is arranged to pivotally move the link arms
20a, 20b so as to 'lock' and 'unlock' the lock link 20, as illustrated in
Figure 2c.
The actuator 42 can break the lock link 20 against the down lock spring bias,
allowing the landing gear assembly to be folded and stowed as described
previously.
As will be appreciated from the above, various aircraft assemblies include a
structural element which, in use, is arranged to directly or indirectly react
load
applied to it by another assembly of the aircraft; for example, an outer
cylinder
(main fitting) or inner cylinder (sliding tube) of an aircraft assembly shock
absorbing strut, a bogie or truck beam, side stays or lock stays, axles and
wheel
levers.
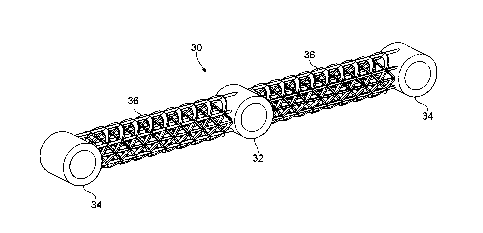
Referring now to Figure 3, a landing gear component according to an embodiment
of the invention is shown generally at 30.
In this example, the assembly 30 is a bogie beam 30.
The bogie beam 30 comprises a centrally located primary bearing 32. The
primary bearing 32 is in the form of a cylinder which extends transversely
across
the bogie beam 30 and is open at both ends to define a bore for receiving a
bogie
CA 3055592 2019-09-13
7
hinge pin, via which the bogie beam 30 can be pivotally coupled to a sliding
tube
of a shock absorbing strut.
The bogie beam 30 further comprises a pair of axle bearings 34. Each axle
bearing 34 is in the form of a cylinder which extends transversely across the
bogie beam 30 and is open at both ends to define a bore for receiving an axle,
on
which wheel and brake assemblies can be mounted.
The primary bearing 32 is connected to the axle bearings 34 by elongate beam
sections 36.
While the above-described embodiment refers to a bogie beam, the present
disclosure is adaptable to be used in relation to other landing gear
components
such as the structural elements described above. When used with other landing
gear components, the number of bearings can be different from 3, the elongate
beam sections 36 can number either greater or fewer than two and any elongate
beam sections need not be aligned as shown in figure 3, but can be
perpendicular
for example.
Referring additionally to Figure 4, each elongate beam section 36 is formed by
a
plurality of intersecting hoops to generally define a generally cylindrical
shape.
Each elongate beam section 36 has a longitudinal axis L.
More specifically, a plurality of first hoops 38 are orientated at 45 to the
longitudinal axis L of the bogie beam 30. A plurality of second hoops 40 are
orientated at 135 to the longitudinal axis L of the bogie beam 30 so as to be
orientated at 90 to the first hoops 38. The first hoops 38 are axially
separated
from one another by a first distance Dl. The second hoops 40 are axially
separated from one another by a second distance D2, which in this embodiment
is
equal to the first distance Dl.
The elongate beam section 36 also has a stringer 42, which is a straight
member
that intersects both the first hoops 38 and the second hoops 40. In the
embodiment shown in figures 3 and 4, there are 8 stringers 42. However,
different numbers of stringers 42 can be used.
CA 3055592 2019-09-13
8
In an alternative embodiment, the first hoops 38, the second hoops 40 and the
stringers 42 can be arranged so as to define, in negative space between the
features, approximately equilateral triangles on the surface of the generally
cylindrical shape.
The elongate beam section 36 can be covered with a covering (not shown). Such
a covering can be a structural, plated surface which increases the structural
rigidity of the elongate beam section 36. The covering can also be non-
structural
and can improve the aerodynamic properties of the landing gear component 30.
It will be understood that the first hoops 38, the second hoops 40 and the
stringers 42 can all be formed simultaneously using an additive layer
manufacturing process. Such a process would have the effect that the first
hoops
38, the second hoops 40 and the stringers 42 can intersect without any join
lines,
and can form a continuous structure.
It should be noted that the above-mentioned embodiments illustrate rather than
limit the invention, and that those skilled in the art will be capable of
designing
many alternative embodiments without departing from the scope of the invention
as defined by the appended claims. In the claims, any reference signs placed
in
parenthesis shall not be construed as limiting the claims. The word
"comprising"
does not exclude the presence of elements or steps other than those listed in
any
claim or the specification as a whole. The singular reference of an element
does
not exclude the plural reference of such elements and vice-versa. Parts of the
invention can be implemented by means of hardware comprising several distinct
elements. In a device claim enumerating several parts, several of these parts
can
be embodied by one and the same item of hardware. The mere fact that certain
measures are recited in mutually different dependent claims does not indicate
that a combination of these measures cannot be used to advantage.
CA 3055592 2019-09-13