Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
ADJUSTABLE FURNITURE
The present invention relates to an article of adjustable furniture such as a
chair or a bed, and
in particular concerns adjustable furniture having one or more adjustable
support sections
which can be moved to adjust the configuration of the furniture.
Known articles of adjustable furniture comprise complex mechanisms driven by
one or more
actuators between different configurations. US2002/0174487 discloses a
hospital bed having
adjustable back and thigh sections for supporting the occupant in various
positions, for
example in a flat horizontal position, in a recumbent or semi-recumbent
position or simply with
the backrest raised. The hospital bed of US2002/0174487 comprises a frame
having a pair of
parallel and spaced apart first and second side frame members; a mattress
support deck
including an adjustable back; a fixed seat section located adjacent to the
back section; and,
an adjustable thigh section located adjacent to the seat section. The thigh
section is movable
longitudinally relative to the seat section, to increase the length of the
thigh section as it is
raised relative to the frame. First and second curved tubes are coupled to
respective first and
second sides of the back section. A plurality of rollers are coupled to the
first and second side
frame members, with the rollers being configured to support the first and
second curved tubes
to permit movement of the curved tubes and the backrest section relative to
the frame. A linear
actuator is disposed beneath the back rest section and coupled to the first
and second tubes
to move the back rest section from a horizontal position to an elevated
position relative to the
frame. Two concentric arcuate tubes are provided on each side of the bed which
have a radius
of curvature centred on a location which emulates the natural hip pivot of a
person lying on
the mattress of the bed. The tubes are secured between three rollers on each
side of the bed.
Two rollers are located on a bottom side of the radially outer tube, that is
to say radially
outwards thereof, and the third roller is located on a top side of the
radially inner tube. Cross-
members extend between the tubes. The arrangement provides a so called shear-
less pivot
mechanism in which the adjustable back section pivots about 30 the natural hip
point of the
person on the bed.
The arrangement disclosed in US2002/0174487 may be considered heavy, robust
and
mechanically complex.
In a modern domestic setting, where mattress thicknesses of 12 to 18 inches
are common,
and more typically 14 to18 inches in the United States, the overall weight,
stiffness and rigidity
of the mattress can place an unacceptable load on the operating mechanism of
the bed, for
example thicker, heavier mattresses can cause the motor (actuator) to struggle
and reduce
the longevity of the motor and mechanism. This is becoming increasingly
relevant as the
1
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
market place is driven by customer demand for thicker mattresses. Motorised
adjustable beds
have been known to fail after a short number of cycles using mattresses of the
afore-
mentioned thickness. One way to overcome this has been to use special, more
flexible,
"ribbed" mattress. However, this is not a practical solution for most
applications.
A further problem associated with known designs is the requirement for the
operating
mechanism to be as compact as possible to free up space underneath the bed. In
domestic
beds, this space is often used to house drawers for storage, and therefore the
more compact,
or thinner the mechanism, the greater the storage capability.
There is therefore a requirement for an adjustable article of furniture which
addresses the
aforementioned problems associated with known designs, which is at least as
easy to
manufacture, store, transport, deliver and assemble as non-adjustable
furniture of known
designs.
Thus according to one aspect of the present invention, there is provided an
article of adjustable
furniture comprising at least one support section and a drive mechanism
operable to effect
pivotal movement of the at least one support section, the drive mechanism
including at least
a first and a second component pivotally joined by a bearing assembly, such
that operation of
the drive mechanism causes pivotal movement between the first and second
components so
as to effect pivotal movement of the at least one support section.
The provision of a bearing assembly for pivotal components of a drive
mechanism enables
more efficient use of the actuator. A result of more efficient actuator use is
the ability of the
actuator to drive the support sections from a shallower angle, which enables
more compact
mechanisms to be used, freeing up space within the furniture.
The present invention will now be described by way of example only with
reference to the
accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a perspective view from above of a frame and operating mechanism
of an
adjustable bed according to one embodiment of the present invention, with the
bed in a semi-
upright configuration for supporting an occupant in a seated position,
Figure 2 is a perspective view from above and the rear, left hand side rear
quarter, of the
frame and operating mechanism of the adjustable bed of Figure 1,
Figure 3 is a perspective view of the bed of Figure 1 with the bed viewed from
below,
2
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
Figure 4 a side elevation view of the bed of Figure 1, with the bed in the
semi-upright adjusted
position of Figure 1,
Figure 5 is a perspective view similar to Figure 2 with the bed in a fully
upright adjusted
position,
Figure 6 a side elevation view of the bed similar to Figure 4, with the bed in
the fully upright
adjusted position of Figure 5,
Figure 6a is a side elevation view of the bed of Figure 6 with a mattress
supported thereon,
Figure 7 is a perspective view similar to Figure 2 with the bed in a fully
lowered position, with
part of the mattress support deck shown in ghost outline,
io Figure 8 a side elevation view of the bed, with the bed in the fully
lowered position of Figure
7,
Figure 9 is a perspective view of the bed of Figure 1 with the bed viewed from
below in plan,
Figure 10 is a side elevation view of the bed of Figure 1 in a semi-upright
configuration,
Figure 11 is perspective view of the bed of Figure 1 in a fully upright
adjusted position,
Figures 12 to 16 are enlarged perspective views of components of the bed of
Figure 1,
Figure 17 is a side elevation view of an alternative bed with the foot support
in a fully raised
position,
Figure 18 is a perspective view of the bed of Figure 17 with the foot support
in a fully raised
position,
Figure 19 is a perspective view of the bed of Figure 17with the support panels
removed,
Figures 20 to 25 are enlarged perspective views of components of the bed of
Figure 17, and
Figure 26 is a side elevation view of an alternative bed with the back support
in a semi-upright
configuration.
With reference to Figures 1 to 16, an article of adjustable furniture in the
form of a bed 10
comprises a mattress support platform or deck 11 having a plurality of
adjacent planar
mattress support panels, including an adjustable back, neck and head (upper
body) support
section panel 12, a lumbar support section panel 13, a non- adjustable
intermediate support
3
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
section panel 14, a non-adjustable lower body support section panel 16, an
adjustable thigh
section panel 17 and a lower limb and foot support section panel 18.
Throughout the drawings
of Figures 2,5, and 7 the panels 12-18 are shown in ghost outline in order to
reveal the detailed
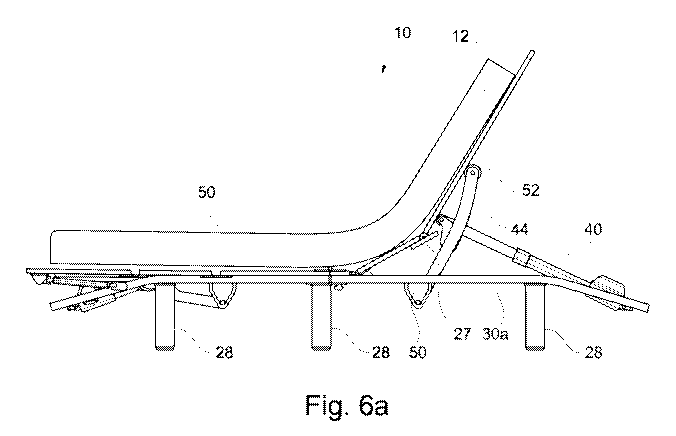
construction of the adjustable bed 10. Figure 6a shows a bed assembly
including the
adjustable bed 10 in the position of Figure 6 with a mattress 50 supported on
the deck 11. The
mattress 50 is shown slightly elevated above the deck 11 for clarity, although
it will be
appreciated that the mattress 50 is in direct physical contact with the deck
11 in use. It will be
appreciated that references to a mattress include both a separate mattress and
a mattress
integrated with the support sections or panels.
The panels 12-18 are mounted on a support frame 20. The upper body support
panel 12 and
lumbar support panel 13 are adjustably mounted on the support frame 20. The
intermediate
support panel 14 and lower body support section panel 16 are fixed in relation
to the frame
20. The thigh support panel 17 and lower limb/foot support panel 18 are
adjustably mounted
on the support frame 20. The lumbar support section 13 has an upper surface
19, and the
backrest support section 14 has an upper surface 21. An interior angle B, is
defined between
upper surfaces 19,21, the interior angle B always being less then 180 degrees
when the bed
moves towards the fully raised configuration such that the backrest section 14
is always tilted
towards (anti-clockwise when viewing Figure 4 such that a head of the occupant
(not shown)
is supported by the backrest support section.
The frame 20 comprises two half sections 20a, 20b hinged together at their
respective
adjacent ends. The two half sections include a head end sub-assembly 20a and a
toe end
sub-assembly 20b. The two half sections 20a, 20b are hinged together at their
respective
adjacent ends by hinges 24 fixed to the upward facing surface of the panels14
and 16 at their
respective adjacent edges, as can best be seen in Figures 1 and 10. The hinge
arrangement
is such that the two half sub-assemblies provide a full length structural
support frame when
hinged apart and locked into position, as shown in the drawings of Figures 1
to 8. The hinged
sub¨assemblies 20a, 20b allow the upper and lower halves of bed to be folded
onto one
another, as will be described in greater details below, for transportation,
storage, distribution
and delivery purposes.
The upper body support panel 12 and the lumbar support section panel 13 are
adjustably
mounted on the head end support frame sub-assembly 20a. The intermediate
support panel
14 is fixedly mounted on the head end support frame subassembly 20a, adjacent
to the lumbar
support panel 13. The lower body panel 16 is fixed in relation to the toe end
support frame
sub-assembly 20b adjacent to the intermediate panel 14. The thigh support
panel 17 and
4
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
lower limb / foot support panel 18 are adjustably mounted on the toe end
support frame sub-
assembly 20b adjacent to the fixed lower body support section panel 16.
The lumbar support panel 13 is pivotally connected to the fixed intermediate
support by means
of a hinged joint 22 extending along the respective adjacent edges of the
panels. As can best
be seen in Figure 9, the hinged joint 22 comprises a plurality of hinges 22'
spaced along the
edges of the adjacent edges of panels 13 and 14 within the region of the frame
20. The
adjacent edges of the panels 13 and 14 are provided with respective elongate
hinge mounting
brackets 23a, 23b, preferably of metal construction, which extend on the
underside of the
panels 13 and 14 between the sides of the frame 20a, as can best be seen in
Figure 8. Three
hinges 22' are provided, including a centrally located hinge and a pair at the
respective ends
of the elongate mounting brackets 23a, 23b. In the illustrated embodiment, the
hinges 22' are
conventional design and construction and are fixedly secured to the respective
mounting
brackets to pivotally mount the lumbar support panel to the fixed intermediate
support panel
about the pivot axis of the hinge 22.
The upper body support panel 12 is similarly pivotally connected to the lumbar
support panel
by means of a hinged joint 25 extending along the respective adjacent edges of
the panels.
The hinged joint 25 comprises a plurality of hinges 25' spaced along the edges
of the adjacent
edges of panels 12 and 13 within the region of the frame 20. The adjacent
edges of the panels
12 and 13 are provided with respective elongate hinge mounting brackets 26a,
26b, preferably
of metal construction, which extend on the underside of the panels 12 and 13
between the
sides of the frame 20a, as can best be seen in Figure 8. Three hinges 25' are
provided,
including a centrally located hinge and a pair at the respective ends of the
elongate mounting
brackets 26a, 26b. In the illustrated embodiment, the hinges 25' are
conventional design and
construction and are fixedly secured to the respective mounting brackets to
pivotally mount
the upper body support panel 12 to the lumbar support panel about the pivot
axis of the hinge
25.
Hinges 22' and 25' may be conventional pin bracket type hinges or, in other
embodiments,
constructed of a fatigue resistant plastics material, for example as a so
called "living hinge".
Other types of hinge are also contemplated including extruded metal tubes, for
example
.. extruded aluminium or aluminium alloy, having a d or p shape cross-section,
including a
longitudinal mounting flange as an integral part of the extrusion, where a
hinge pin passes
through the extruded tube in a known manner and optionally mounted on bearings
(ball
bearing type) located at the respective ends of the tube to support the hinge
pin in a low friction
manner. In preferred embodiments, at least hinges 25' are provided with
limited angular
adjustment so that the adjustable panel 12 has a limited downward angular
adjustment with
5
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
respect to the lumbar support panel 13. In the illustrated embodiment, the
hinge 25 is provided
with an abutment stop in the form of a rectangular, preferably metal, plates
27 that are fixedly
secured or connected to the hinge mounting bracket 26a in the region of the
hinges 25'. The
plates 27 are positioned on the underside of the hinge 25 and prevent panel 12
being lowered
beyond the plane of panel 13 by mutual abutment of the plates 27 and the
underside of the
mounting brackets 26b. Thus, when the panels 12 and 13 are lowered flat they
remain 180
degrees apart.
Hinges 22' and 25' are also limited upwards so each platform section 12. 13
cannot go beyond
this angle relative to the previous panel section it is hinged to (typically
30 degrees, or the total
combined angel of angular adjustment divided by the number of intermediary
platform
sections). Hinges 22' and 25' are also limited downwards so each platform
section cannot fall
below parallel to the previous section it is hinged to.
As will be described in greater detail below, panels 12 and 13 may be raised
by a
predetermined maximum amount about their respective pivot axis during
adjustment of the
bed, for example 65 degrees, combined, from the horizontal plane as defined by
the flat
orientation of fixed intermediate support panels 14 and 16 of the bed. Hinges
22 and 25 are
provided with stop means to limit the degree of relative angular adjustment of
the panels 12
and 13. Typically the maximum combined angular adjustment of the panels is 65
degrees with
respect to the plane of the fixed non-adjustable panel 14. The hinges 22 and
25 may thus be
adapted so that they contribute to the maximum angular adjustment of the
panels 12 and 13
by equal amounts or substantially equal amounts, for example, 50/50 or 40/60
depending on
the particular application and maximum angel of adjustment required.
As previously described, in embodiments of the present invention, the maximum
combined
angle of adjustment of the backrest and lumbar support sections is typically
50-65 degrees. In
the illustrated embodiment, the angle of adjustment is shared between hinges
22 and 25
connecting each side of the lumbar support platform. The hinge axes are
preferably 200 ¨
300mm apart in the longitudinal direction of the bed, as best seen from the
view of Figure 9.
In the illustrated embodiment, a single lumbar support platform having a
length dimension of
250mm is preferred.
In Figures 5 and 6 the bed 10 is shown in a fully articulated configuration,
adjusted for
supporting an occupant in a raised upright seated position. In this position,
the upper body
support section panel 12 and the lumbar support section panel 13 are raised,
and inclined with
respect to, the fixed intermediate support section panel 14. The upper body
support section
6
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
panel 12 is raised about its pivot axis defined by hinge 25 and the lumbar
support panel 13 is
raised about its pivot axis defined by hinge 22.
Referring to Figure 6, it can be seen that the combined angle ASB is defined
between a plane
PS defined by the seat section 16 and a plane PB defined by the backrest
support section 12,
the combined angle ASB being shared between a first angle ASM defined between
the seat
section plane PS and a plane PM defined by the lumbar support section 13, and
a second
angle AMB defined between the plane PM defined by the mattress support section
13 and the
plane PB defined by the backrest support section 12.
In the lowered position (Figures 7 and 8) the adjustable support panels 12, 13
combine with
the fixed panel 14 and fixed panel or seat section 16 and adjustable panels 17
and 18 to define
a substantially flat planar horizontal mattress support platform or deck. The
various support
panels 12-18 may each have a mattress support cushion (not shown) of pre-
determined
thickness, which combine to provide a mattress foundation for supporting a
suitable mattress.
Alternatively, a mattress may be positioned directly on top of the panels 12-
16. The panels
12-16 may be upholstered, with or without support cushions. The present
invention also
contemplates arrangements where the frame 20 is configured to be placed within
the internal
space of a bed surround, for example of the type common in North America, or
integrated in
a divan type bed foundation structure, more typically found in the United
Kingdom. In the
illustrated embodiment, the bed frame 20 is provided with floor standing legs
28 and is thus
self-supporting. Thus, the present invention also contemplates arrangements
where the frame
20 is arranged to be positioned within a separate surrounding structure, for
example a
decorative wood or upholstered surround including head and toe boards and
lateral side
panels between the head and toe boards. The dimensions of the bed are such
that the bed
has the size of a double bed, but the present invention contemplates beds of
many different
widths including standard single size beds to much larger doubles.
The half frame sub-assemblies 20a and 20b each comprises a generally
rectangular structural
support frame, preferably constructed of metal but other materials may be used
for various
component parts, in addition to or instead of metal, including board type
material, for example
engineering plastic, MDF, timber or other fibre type board for example.
The two half sections 20a and 20b each comprise a pair of elongate parallel
lateral side frame
members in the form of respective side rails 30a, 30b. The side frame members
extend
longitudinally along the length of the bed on both sides thereof and are
joined together at their
respective ends by metal, preferably steel, cross-members 31a, 31b, 32a, 32b
to form
rectangular box type structural support frames 20a, 20b.
7
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
The side frame members 30a, 30b are constructed of suitably dimensioned box
section metal
tube, preferably steel, and the cross-members 31a and 32b of similar
rectangular box section
metal tube. The frame 20 is provided with legs 28 towards each of the corners
of the
rectangular frame structure and at an intermediate position at the end of the
toe end sub-
assembly 20b. The side members 30a, 30b and respective cross members 31a, 31b
and 32a,
32b are joined together by welding or alternatively by fixing means such as
screws, bolts,
fasteners or the like. In preferred embodiments, the legs are
attachably/detachably fixed to
the frame by suitable reversible fixing means as are well known in the art,
for example screw
thread fittings.
The two half sub-assemblies 20a and 20b are provided with locking means for
locking the
frame members 30a, 30b together when the frame 20 is unfolded. The locking
means
comprises a metal plate 33 secured on the underside of the respective side
frame members
30b in the region of the hinged connection 24. The metal plate 33 extends over
the underside
of the adjacent side frame member 30a and is attachably/detachably fixed
thereto by suitable
reversible fixing means, as are well known in the art, for example screw
thread fittings, such
as a butterfly or winged 5 nut/bolt connection 35 as in the illustrated
embodiment.
The unfolded and locked support frame 20 constitutes a floor standing base of
the bed 10.
The frame 20 may stand directly on legs 28 or alternatively be provided with
castors, feet or
the like at the end of the legs, as is well known in the art. Alternatively,
the legs may be
removed and the frame adapted to be mounted within a bed surround, for example
with the
side frame members sitting on a suitable mounting on the inside of a suitably
adapted bed
surround. As previously indicated, the frame 20 can be manually folded and
unfolded about
the traverse hinge axis defined by the hinge elements 24. Either the head end
or toe end frame
is moved so that the two half sections of the frame are brought together by 10
relative
movement about the hinge axis as shown in Figures 9 and 10 where the panels 12
and 14 lie
flat on top of the panel 16. As can be seen in Figures 9 and 10 when the legs
28 are unattached
the adjustable bed 10 has a very small space envelope, with half the length
dimension of the
unfolded bed in exchange for a modest increase in depth, approximately the
additional depth
of the toe end half frame.
Movement of the adjustable panels 12 and 13 is effected by means of a powered
actuation
mechanism comprising a linear actuator 40 and a first connecting means in the
form of a
pivotal "H-frame" 42. The H-frame 42 comprises a pair of arms 44 and a cross-
member 46
extending between and connecting the arms 44 approximately midway along their
length. The
arms 44 have a first distal end 65 and a second distal end 67 with an aperture
69 positioned
towards the second distal end 67. Each arm 44 has a feature in the form of a
raised portion
8
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
71 co-axial with the aperture 69. The arms 44 are generally straight but curve
upwards at their
first distal end 65 where a roller in the form of a bearing 52 is rotatably
mounted. The bearings
52 contact the underside of the panel 12 along wear resistant strips 54 which
may be of metal,
nylon or the like, along which the bearings 52 run when the panel 12 is
lowered and raised.
The H-frame is pivotally mounted at the second distal end of arms 44 on a
second component
in the form of a bracket 50 which is fixed to the underside of the head end
sub-assembly frame
20a at pivot points 48. The brackets 50 depend from the underside of the frame
20a in the
region of hinges 25. The bracket 50 includes an integral bearing housing 51
which is
configured as described below to house and retain a bearing assembly 53.
In Figures 12 to 16, the bearing assembly 53 comprises an inner race 55 having
an inner race
internal diameter DI R, and an outer race 57 having an outer race external
diameter DOR. The
inner 55 and outer 57 races are rotationally moveable relative to each other.
The bearing
housing 51 has an external wall 57 which includes a part-circular section 59
and a crimped
section 61 extending from the part-circular section 59. The crimped section 59
is formed after
the bearing assembly 53 is located within the bearing housing 51 such that the
bearing
assembly 53 is both retained in, and is rotationally fixed with respect to the
bearing housing
51. The arms 44 are pivotally attached to the bracket 50 by engagement of the
raised portion
71 with an outer face 73 of the inner race 55, and are secured to the bracket
50 using a nut,
bolt and washer arrangement 75 such that the arms 44 rotate with the inner
race 55 relative
to the outer race 57 which is rotationally fast with the bracket 50 which is
fixed to the frame
20.
The actuator 40 is a linear actuator of the Delta-drive type as produced by
Dewert-Okin GmbH,
having a first end (motor and gear box end) pivotally mounted to the cross
member 32b and
a second end (rod) pivotally connected to a bracket 56 secured to the cross-
member 46. The
bracket 56 is configured such that the connection between the output rod of
the actuator and
the bracket 56 is in the plane of the panel 12. This is achieved by means of a
cut-out slot 58
in the panel 12 through which the bracket 56 and end of the output rod of the
actuator extend.
The gearbox and motor end of the actuator 40 is connected to the cross-member
32b at a
position midway along its length. The cross-member 32b is located in a plane
lower than the
general or notional plane of the frame 20 due to the downwardly canted end of
the frame 20a.
The side members 30a are inclined downwards along the final third of their
length from a
position immediately rearward of the legs 28 attached to the frame 20a. The
side members
are inclined downwards approximately 20 degrees or so, so that the connection
point between
the actuator 40 and the frame 20a is below and offset from the notional plane
of the frame 20.
This arrangement ensures the actuator is also inclined with respect to the
notional plane of
9
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
the frame and the plane of the panel 12 when the panel 12 is in its lowered
position (Figures
7 and 8). In combination with the other end of the actuator being in the plane
of the panel 12,
by means of the bracket 56 and cut out 58, the actuator is able to apply a
significant initial
force to the panel 12 when the panel is to be raised from is lowered position
of Figures 7 and
8. It is to be understood that the force component acting on the panel 12 when
movement is
initiated from its lowered position is dependent on the angular orientation of
the actuator force
vector with respect to the panel 12.
Rotational movement of the panel 12 is thus effected by activation of linear
electrical actuator
40 positioned on the underside of the bed within the space envelope of the
frame. Thus, panel
12 is raised and lowered by respective extension and retraction of actuator
40. In operation,
in the fully lowered configuration of the bed, the adjustable panels 12 and 13
lie flat on the
side rails 30a, with the output rod of actuator 40 fully retracted towards the
respective gearbox
end of the actuator. This position is shown in Figures 7 and 8. In order to
raise the panels 12
and 13, the output rod of the actuator 40 is extended away from the gearbox
end of the
actuator. Rotational movement of lumbar support panel 13 is thus
simultaneously effected by
activation of linear electrical actuator 40. Panels 12 and 13 are this raised
and lowered by
extension and retraction of actuator 40.
The provision of a bearing assembly and housing at the pivotal connection of
the arm 44 and
the bracket 50 results in a significantly lower initial actuator force being
required to move the
panel when compared to using a conventional nut, bolt and washer arrangement.
In alternative
embodiments, a bearing assembly and housing arrangement can be provided at
other pivotal
connections to further reduce the initial actuator force requirement. For
example, the bearing
assembly and housing arrangement can be provided between the cross-member 46
of the H-
bar 42 and the actuator 40 to provide a pivotal connection. An identical
bracket to the bracket
50 of the embodiment of Figures 1 to 16 can replace the bracket 56 used to
pivotally connect
the cross-member 46 of the H-bar 42 and the actuator 40.
In preferred embodiments, the maximum combined angular adjustment of the
panels 12 and
13 is 65 degrees, that is to say the maximum raised inclined angle of the
backrest panel 12
with respect to the notional flat horizontal plane of the bed is limited to 65
degrees. This angle
of adjustment includes the combined angle of adjustment of the lumbar support
panel 13 with
respect to the fixed panel 14 and the angle of adjustment of the backrest
panel 12 with respect
to the lumbar support panel 13. The combined angular adjustment may be less,
for example,
a maximum of 60, 55, 50 degrees or less, and may be contributed by equal
amounts of angular
adjustment by the panels 13 and 14. The maximum angular adjustment is
determined by the
geometry of the actuation mechanism including the mounting arrangement and the
operation
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
stroke of the actuator as well as the relative length dimensions of the
respective adjustable
panels.
It is to be understood that a mattress of appropriate thickness, say in the
range of 25 to 50cm
(10 to 20 inches), is to be positioned on the mattress support platform of the
bed 10.
Movement of the adjustable panels 17 and 18 is effected by means of a powered
actuation
mechanism comprising a linear actuator 40a identical to the actuator 40
driving panel 12, and
a first connecting means in the form of a pivotal frame 42a. The frame 42a
comprises a pair
of arms 44a and a cross-member 46a extending between and connecting the arms
44a. The
arms have a first distal end 65a which is connected to the underside of the
panel 17, and a
second distal end 67a which is pivotally mounted on a second component in the
form of a
bracket 50a which is fixed to the frame 20 at pivot points 48a. The brackets
50a depend from
the underside of the frame 20 in the region of hinges 41'. In contrast to the
pivotal connection
between arms 44 and bracket 50 via a bearing assembly and housing arrangement,
the arms
44a are pivotally attached to the bracket 50a using a simple nut, bolt and
washer arrangement
75a such that the arms 44a rotate relative to the bracket 50a which is fixed
to the frame 20. In
an alternative embodiment, the bearing assembly 53 and bearing housing 51
described in
relation to the movement of the panel 13 can be used to provide a pivotal
connection between
the arms 44a and the bracket 50 instead of the nut, bolt and washer
arrangement. Similarly,
the pivotal connection between the actuator 40a and the cross-member 46a can
be provided
by a bearing assembly and housing arrangement as described in relation to the
pivotal
connection between actuator 40 and cross-member 46.
The actuator 40a has a first end (motor and gear box end) pivotally mounted to
the cross
member 31a and a second end (rod) pivotally connected to a bracket 56a secured
to the
cross-member 46a. Rotational movement of the panel 17 is thus effected by
activation of linear
electrical actuator 40a which causes the cross-member 46a and arms 44a to
rotate. Thus,
panel 17 is raised and lowered by respective extension and retraction of
actuator 40a. Panel
18, by virtue of being connected to panel 17 via hinge 43' is also raised and
lowered as panel
17 is raised and lowered. A brace 81 is fixed to the underside of panel 18 and
the frame 20 to
provide additional rigidity and support when panel 18 is under load (Figure
3).
In the above described embodiments, panels 12 and 13 are rotated by an
actuator 40 acting
on panel 12 via arms 44, and panels 17 and 18 are rotated by actuator 40a
acting on panel
17, that is to say, a first connecting means 44,44a acts on and engages with
the respective
panels 12,17. It is the fact that panels 17 and 18, and panels 12 and 13 are
connected by
11
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
respective hinges 43' and 25' which causes panel 18 to rotate as panel 17 is
rotated, and
panel 13 to rotate as panel 12 is rotated.
With reference to Figures 17 to 25, an alternative bed 110 is identical to the
bed described in
Figures 1 to 16 except that instead of a single connecting means acting on
panel 17, a first
connecting means or component in the form of a pair of arms 144a acts and
engages with
panel 118 and a second connecting means or component in the form of a pair of
arms 190
which act on and engage with panel 117 such that an actuator 140a, which is
identical to
actuator 40a, simultaneously drives both panels 117,118.
Actuator 140a is connected to the frame 120 and to the cross-member 146a in
the same way
as actuator 40 is connected to the frame 20 and to the cross-member 46 of the
embodiment
of Figures 1 to 16.
Arms 144 extend from cross-member 146 and have a roller bearing 152 at one end
which is
identical to bearing 52, and is pivotally connected to the frame 120 at the
other end at pivot
point 148 by an integral bearing housing 151 identical to the bearing housing
51, and a raised
portion 171 located on bracket 150, the raised portion 171 being identical to
the raised portion
71 (Figure 20). A corner brace 199 is provided between the arms 144 and cross-
member 46
to provide rigidity. The bracket 150 is fixed to and depends from the frame
120. The bearing
housing 151 retains a bearing assembly (not shown) in the same way as
described in relation
to bearing housing 51 and bearing assembly 53. The pivotal connection between
the bracket
150 and arm 144 is provided in the same was as described in relation to the
bracket 50 and
arm 44.
The bearing housing 151 and the bearing assembly is located on the arms 144a
(first
component) and the raised portion 171 is located on bracket 150 (second
component) which
is in contrast to the pivotal connection between bracket 50 and arm 44 where
the raised portion
71 is provided on the arm 44 and the bearing housing 51 and bearing assembly
53 is provided
on the bracket 50. It will be appreciated therefore that the bearing housing
and assembly can
be provided on one of the first or second components, and the feature, such as
the bracket
with the raised portion can be provided on the other of the first and second
components to
provide the pivotal connection.
Arms 190 are pivotally connected to the arms 144 at pivot point 191, which is
positioned
approximately mid-way along the length of arms 144, via a raised portion 171a
which engages
with a bearing assembly (not shown) identical to bearing assembly 53, housed
within an
integral bearing housing 151a on one end of the arm 190. Raised portion 171a
(Figure 21) is
12
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
identical to raised portion 171, and the integral bearing housing 151a is
identical to the integral
bearing housing 151. The pivotal connection between the raised portion 171a of
arm 144 and
arm 190 is provided in the same was as described in relation to the bracket 50
and arm 44.
Arms 190 have another integral bearing housing 151b identical to integral
bearing housing
151a, at their other end which is pivotally connected to a bracket 195 which
is fixed to the
underside of the thigh support panel 117 using fixing means such as screws
196. The bracket
195 includes a raised portion 171b (Figure 24) which is identical to raised
portions 71,171a.
The integral bearing housing 151 retains a bearing assembly (not shown)
identical to bearing
assembly 53. The pivotal connection between the raised portion 171b of arm 190
and bracket
195 is provided in the same was as described in relation to the bracket 50 and
arm 44. The
bracket 195 is positioned on the thigh support panel 117 such that the pivotal
connection is
about an axis which is close to the hinge point 143 between panels 117 and
118. It will be
appreciated that the bracket 195 can be positioned anywhere on the length of
the panel 117
providing that position enables pivotal movement of panels 117 and 118 between
the lowered
and the raised positions.
In operation, activation of the linear electrical actuator 140a causes the
cross-member 146a
and arms 44a to rotate about pivot point 148. As arms 144a rotate, the bearing
152 acts on
the underside of panel 118 causing it to be raised relative to the frame 120.
Simultaneously,
rotation of arms 144 causes the pivotally connected arms 190 to rotate and act
against the
underside of panel 117 causing panel 17 to rotate relative to the frame 120
about hinge 122'
(Figure 17). Thus, operation of the actuator 140a drives both panels 117 and
118 at the same
time by virtue of the first (arm 144) and second (arm 190) connecting means.
With reference to Figure 26, an alternative bed 210 is identical to the bed
described in Figures
1 to 16 except that instead of a single connecting means in the form of arm 44
acting on panel
12, a first and second connecting means is used to drive panels 212 and 213 in
the same way
as actuator 40a drives panels 117 and 118 in the embodiment of Figures 17 to
25. The first
connecting means in the form of arm 244 is identical to arm 44 except it
further includes and
additional raised portion 263 which is identical to the raised portion 63 on
arm 44. The raised
portion 263 enables a pivotal connection to be made with a second connecting
means in the
form of arm 290 which is identical to arm 190. Bracket 250 is identical to
bracket 50 and is
pivotally connected to arm 244 in the same way as bracket 50 is connected to
arm 44. The
raised portion 263 is positioned approximately three-quarters of the way along
the length of
the arm 244 towards the bracket 250. The raised portion 263 is positioned
along the length of
arm 244 to provide the required relative rotation between panels 213 and 212
as they are
moved between lowered and raised configurations relative to the frame 220.
13
CA 03071465 2020-01-28
WO 2019/021026
PCT/GB2018/052151
Operation is similar to the way actuator 40a drives panels 117 and 118 in the
embodiment of
Figures 17 to 25 Activation of the linear electrical actuator (not shown but
identical to actuator
40) causes the arms 244 to rotate about pivot point 248. As arms 244 rotate,
the bearing 252
acts on the underside of panel 212 causing it rotate relative to the frame
220. Simultaneously,
rotation of arms 244 causes the pivotally connected arms 290 to rotate and act
against the
underside of panel 213 causing panel 213 to rotate relative to the frame 220
about hinge 222'.
Thus, operation of the actuator drives both panels 212 and 213 at the same
time by virtue of
the first (arm 244) and second (arm 290) connecting means.
It will be understood that in the embodiments of Figures 1 to 26, at least two
concepts have
been described. One concept relates to the provision of first and second
connecting means
which act on panels of an adjustable bed to enable coordinated pivotal
movement of the
panels. A second concept relates to providing a bearing assembly to allow
pivotal movement
between components of an adjustable bed. Furthermore, the two concepts have
been
described in relation to pivotal movement between lumbar and back support
panels and to
pivotal movement between foot and thigh support panels. It will be appreciated
that the two
concepts can be used independently of each other, and that each of the
concepts can be used
to provide pivotal movement between lumbar and back support panels and/or to
pivotal
movement between foot and thigh support panels.
It will also be understood that whilst the above embodiments have been
described in relation
to an adjustable bed, the concepts also can be applied to an adjustable chair.
For example, a
bearing assembly and housing can be used to provide a pivotal connection
between moving
components of the chair such as an actuator supported on a fixed based section
and a
moveable seat section which is pivotally connected to the actuator. Similarly,
first and second
connecting means can be used to simultaneously move support panels on a chair.
14