Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 030103026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/US2018/066052
DIGITAL HIGH VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY
100011 The present application claims priority to and the benefit of co-
pending US
Provisional Patent Application Serial No. 62/608,016 filed on December 20,
2017,
entitled "DIGITAL CONTROLLED HIGH VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY" (our
reference 2296.004) and co-pending US Provisional Patent Application Serial
No.
62/608,018 filed on December 20, 2017, entitled "MULTI-CONTROLLABLE HIGH
VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY SYSTEM" (our reference 2296.005).
FIELD
[0002] The present embodiment generally relates to digital high voltage
power supply.
BACKGROUND
100031 A need exists for a digital power supply with improved performance
and reduced cost
compared to traditional analog counterparts.
100041 The present embodiments meet these needs
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
100051 The detailed description will be better understood in conjunction
with the
accompanying drawings as follows:
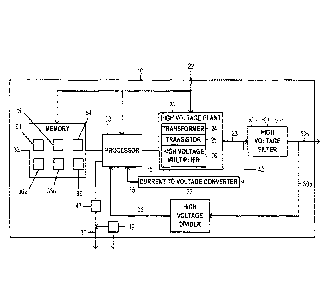
[0006] Figure 1 depicts an overview of the digital high voltage power
supply according to
one or more embodiments.
[0007] Figure 2 depicts a second power supply according to one or more
embodiments.
[0008] The present embodiments are detailed below with reference to the
listed Figures.
1
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE EMBODIMENTS
[0009] Before explaining the present apparatus in detail, it is to be
understood that the
apparatus is not limited to the particular embodiments and that it can be
practiced or
carried out in various ways.
1000101 The present invention related to a digital high voltage power supply.
1000111 The digital high voltage power supply has a high voltage plant
configured to receive a
low voltage and generate a high voltage signal containing unwanted sinusoidal
noise,
the high voltage plant comprising at least one of: a transformer, a
transistor, and a
high voltage multiplier.
1000121 The digital high voltage power supply has a plurality of filters,
wherein at least one
filter is connected to the high voltage plant. The at least one filter forms a
high
voltage output.
1000131 The digital high voltage power supply has a high voltage divider
to receive the high
voltage output and generate a scaled voltage feedback signal.
1000141 The digital high voltage power supply has a processor with memory
containing a
plurality of operating set points. The processor is connected to the low
voltage and
the high voltage plant.
[00015] The processor is configured to: receive the scaled voltage
feedback signal from the
high voltage divider; compare the scaled voltage feedback signal to the
plurality of
operating set points in the memory; compute, store, revised operating set
points using
the compared scaled voltage feedback signal; use the revised operating set
points to
simultaneously and automatically regulate output voltage to be within all
operating
set points; and generate an alert as output signals when output conditions
exceed any
operating set points.
[00016] The digital high voltage power supply can prevent injury and
casualties near a power
supply by preventing spikes in the power supply, exceeding human endurance.
2
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LI52018/066052
1000171 The digital high voltage power supply provides a clear feedback
signal that reduces
noise in the power supply. The digital high voltage power supply causes shut
down of
the power supply quickly and accurately to prevent fires and explosions in the
event
of a fault or explosive over-current condition due to high voltage.
[00018] In embodiments, the digital high voltage power supply has a digitally
compensated
circuit that can provide clean and accurate output. The digital high voltage
power
supply provides a stable power source for clear and accurate medical imaging
applications, which can allow for early diagnosis of illness and medical
conditions.
[00019] The digital high voltage power supply can provide a smaller sized
power supply. The
small size power supply enables the size and weight of medical equipment to be
reduced. The small size power supply can be used in the case of natural
disasters or
man-made disasters.
[00020] In embodiments, the digital high voltage power supply can provide a
stable power
source for equipment that detects contraband. This stable and reliable long
life power
source can be used by the TSA and the National Security Administration to
detect
threats to national security.
1000211 The digital high voltage power supply can allow for a wider
variable input voltage
range so that a single machine can be deployed and relocated into many
geographical
areas. The digital high voltage power supply provides many voltages with a
single
lightweight, portable, transportable digital high voltage power supply. For
instance,
the power supply can be from 0.5 pounds to 10 pounds. The digital high voltage
power supply enables multiple locations to be served sequentially without
needing
specially built machines for each location.
1000221 The digital high voltage power supply can be used for portable X-ray
units to provide
quick relief to devastated areas.
1000231 The following definitions are used herein:
3
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
[00024] The term "alert" can refer to a signal that specifies when a
specific condition is met.
For example, an alert can be an LED emitting light when the input voltage
exceeds a
high output voltage limit.
[00025] The term "communication protocol or discrete I/O signals" can refer to
a signal or
group of signal that are used to interact with the high voltage power supply.
For
example, the communication protocol can be a signal received from a feedback
signal
from a voltage divider or communications from a computer to turn the high
voltage
output on or off.
[00026] The term "digital high voltage power supply" can refer to a high
voltage power
supply in which digital technology is used within the feedback loop for
control of the
high voltage power supply. For example, a digital high voltage power supply
can
increase or decrease the high voltage output using an analog set point and
prevent the
system from undesired voltage variations in excess of 1 percent,
[00027] The term "filters" can refer to a device or substance that passes
electric current of
certain frequencies or frequency ranges while preventing the passage of other
current
at different frequencies or different frequency ranges. For example, a filter
can be a
device that removes white noise from a signal or removes small voltage
variations
from a sine wave,
[00028] The term "high voltage" describes a variable voltage platform with
from 125 volts to
1 million volts allowing a user to select any of those voltages between 125
volts and 1
million volts on one platform, or have any one of those voltages in a separate
voltage
platform,
[00029] The term "high voltage divider" can refer to a passive linear
circuit that produces an
output voltage that is a fraction of the high voltage divider's input voltage.
For
example, a high voltage divider takes a high voltage and divides the high
voltage,
6000 volts to a low voltage 3.3 volts that can be used by the high voltage
power
supply based on an analog set point or on a digital set point.
4
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
100030] The term "high voltage multiplier" can refer to an arrangement of
capacitors and
rectifier diodes that is frequently used to generate high DC voltages. For
example,
high voltage multiplier can be a CockcroftWaltonTM three stage series
multiplier.
[00031] The term "high voltage output- is an electrical potential large
enough to cause injury
or damage to humans, wildlife, livestock or objects. Even though low voltage
is
incoming to the inventive power supply, the power supply can create a high
voltage
output. "High voltage output- can range from 100 Vdc up to 1,000,000 Vdc. The
output voltage can be provided through a pin, cable, or a connector.
1000321 The term -high voltage plant" can refer to an arrangement of
capacitors diodes and or
transformers which in combination, produce high voltage. One example could be
a
high voltage transformer with a diode and a capacitor that produces 500 Vdc.
[00033] The ten-n "low voltage" can refer to a voltage less then 100 Vdc. For
example, a low
voltage can be 24 Vdc for the input of the high voltage power supply or 3.3
Vdc for
the scaled voltage feedback signal_
[00034] The term "memory" non-transitory computer readable medium, such as a
solid state
memory, and the like in communication with the processor.
[00035] The term "non-transitory computer readable medium" excludes any
transitory signals
but includes any non-transitory data storage circuitry, e.g., buffers, and
cache, and
wherein the non-transitory computer readable medium does not erase when power
is
removed from the device or the device is shut down.
1000361 The term "operating set points" can refer to the point at which the
user wishes to
operate. For example, the operating high voltage set-point can be set to 3000
V by the
operator and the high voltage power supply will produce 3000 V.
[00037] The term "preset startup" can refer to a factory or user programmed
start up
condition. The power supply will power up and go to the exact factory
programed
voltage set point for the high voltage output. This high voltage output can be
5
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
anywhere from 0.001 percent to 100 percent of the power supply's capable
output
voltage.
[00038] The term "processor" refers to a computer, a field programmable gate
array (FPGA),
a complex programmable logic devices (CPLD) or a cloud based computing system.
For example the processor can be a microprocessor.
1000391 The term "revised operating set points" can refer to the operating
point that is set by
the power supply based on an error calculation. If the operating set-point is
set to
3000V but the power supply produces 3010 V the revised operating set-point
from
the power supply will then revise the operating set-point so that the output
voltage
will be 3000 V.
[00040] The term "scaled voltage feedback signal" can refer to the signal
coming from a high
voltage divider. The high voltage signal is scaled to a smaller workable
voltage like
3.3Vdc. The high voltage power supply can now use this signal to make
adjustments.
[00041] The term "transformer," can refer to an electrical device
consisting essentially of two
or more windings wound on a single core, which by electromagnetic induction
transforms electric energy from one set of one or more circuits, to another
set of one
or more circuits, such that the frequency of the energy remains unchanged and
constant, while the voltage and current usually change. For example, the
transformer
on the high voltage power supply can convert 24 Vac to 1200 Vac.
[00042] The term "transistor' can refer to a device that regulates current or
voltage flow and
acts as a switch or gate for electronic signals. For example, a transistor can
be a metal
oxide field effect transistor (MOSFET) that operates as an "on off' power
switch.
1000431 Now turning to the Figures, Figure 1 depicts an overview of the
digital high voltage
power supply 10.
[00044] The digital high voltage power supply 10 has a high voltage plant 20.
1000451 The high voltage plant 20 can be configured to receive a low voltage
22 and generate
6
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
a high voltage signal containing unwanted sinusoidal noise 23.
[00046] The voltage plant 20 can have at least one of: a transformer 24, a
transistor 25, and a
high voltage multiplier 26,
1000471 In embodiments, the voltage plant 20 can have one transformer 24
connected to a
transistor 25. In embodiments the voltage plant could have a plurality of
transformers
connected to a plurality of transistors, each pair connected in series and/or
in parallel.
[00048] In embodiments, the voltage plant 20 can have a transformer 24
connected to a high
voltage multiplier 26, In embodiments, the voltage plant can have a plurality
of
transformers connected to a plurality of high voltage multipliers, each pair
connected
in series and/or parallel.
[00049] In embodiments, the voltage plant 20 can have a transistor 25
connected to a
transformer 24 connected to a high voltage multiplier 26. The set of
transistor,
transformer and high voltage multiplier can be connected in series or in
parallel.
[00050] Multiples of transistors, transformers and high voltage
multipliers can be used in
embodiments. Each set of transistor, transformer and high voltage multiplier
can be
connected in series or in parallel to another set.
[00051] The digital high voltage power supply 10 has a plurality of
filters 60a-60c, wherein at
least one filter 60a-60c is connected to the high voltage plant 20.
[00052] In embodiments, at least one filter 60a can form a first high voltage
output 50a and a
second high voltage output 50b. In embodiments, a single high voltage output
can be
created.
[00053] In an embodiment, the first filter, 60a can be an inductive
resistance capacitor filter
-LRC filter" and connected in series to a second filter 60b that can be a
resistance
capacitor "RC" filter further connected in series to a third filter 60c, that
can be
another a RC resistance capacitance filter identical or different values from
the
second filter 60b.
7
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
1000541 The third filter, or last filter if only one, two or more than
three are used, provides the
high voltage output.
[00055] The high voltage output can be 4500 volts as the output.
1000561 A high voltage divider 33 can receive the high voltage output 50a and
50b and
generate a scaled voltage feedback signal 35.
1000571 For example, the high voltage divider can receive a high voltage
output of 1500 Vdc
and generate a scaled voltage feedback signal 35 of 2 Vdc.
[00058] The digital high voltage power supply 10 can contain a processor 30
for example a
microprocessor.
19 [00059] The processor 30 has memory 32 that can contain a plurality of
operating set points
36, such as 3000 bit operating set points.
[00060] In embodiments, the processor 30 can be connected to the low voltage
22 and the
high voltage plant 20.
[00061] The processor 30 can be configured to: receive the scaled voltage
feedback signal 35
from the high voltage divider 33, compare the scaled voltage feedback signal
35 to
the plurality of operating set points 36a-36b in the memory, compute and
store, at
least one revised operating set point 38 using the compared scaled voltage
feedback
signal 35, use the revised operating set point(s) 38 to simultaneously and
automatically regulate high voltage output 50 to be within all operating set
points;
and generate an alert 37 when output conditions exceed any operating set
points.
[00062] The operating set points are variable, based on user defined
parameters.
1000631 In embodiments, at least one of the preset set points and the
operating set points can
be analog, digital or both analog and digital set points.
[00064] In embodiments, simultaneously, the alert 37 can be automatically
transmitted
through a communication protocol 47 or discrete I/O signals 49.
8
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
[00065] As an example, a usable communication protocol can be RS-232.
[00066] In embodiments, a ripple and digital hunting mitigation 61 can be
located in the
memory 32. An example of a ripple and digital hunting mitigation 61 is a known
continuous frequency sine wave which needs to be removed from the output
signal.
[00067] In embodiments, the memory 32 can contain a first preset value 64 for
adjusting a
speed at which the output voltage reaches an operating set point after output
is
enabled of the high voltage power supply and a second preset value 66 in
memory for
adjusting a speed at which the output voltage is adjusted due to changing
current load
conditions.
[00068] A second feedback loop 42 can be connected to a current to voltage
converter 75
providing another feedback signal 76 to the processor 30. The feedback signal
76 is
used to adjust a revised operating set point 38 in memory. The feedback signal
76
does not exceed one of the operating set points 36a-36b. As an example, a
current to
voltage converter can be a properly configured operational amplifier such as
those
available from Texas Instruments .
[00069] In embodiments, the alert 37 can contain a plurality of
communication signals, all
operating simultaneously to convey different commands and data.
[00070] In embodiments, a preset value can adjust the speed at which the
output voltage
reaches an operating set point after output is enabled of the high voltage
power supply
and a speed at which the output voltage is adjusted due to changing load
conditions.
[00071] Figure 2 depicts a second power supply 63 electrically connected
between the
processor 30 and the high voltage plant 20.
[00072] A temperature sensor 5 I can be connected to the processor. The
temperature sensor is
used to detect temperature around components of the power supply.
[00073] A voltage divider 65 can be configured to receive a second voltage
output 67 from the
high voltage plant, and generate a second scaled voltage feedback signal 69.
9
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
[00074] For example, if the first voltage output 67 is 2000 Vdc, the
second scaled voltage
feedback signal 69 can be 10 Vdc, as generated by the voltage divider 65.
[00075] In embodiments, a non-synchronous buck 101, a non-synchronous
boost 102, a
synchronous buck 103, or a synchronous boost 104 can each operate as the
second
power supply 63.
[00076] For example, a non-synchronous buck 101 in the power supply can be a
voltage
converter that converts a voltage from 24 Vdc to 19 Vdc.
[00077] For example a non-synchronous boost 102 in the power supply can be can
be a
voltage converter that converts a voltage from 24 Vdc to 36 Vdc.
[00078] For example a synchronous buck 103 usable in the power supply can be a
voltage
converter that converts a voltage from 29 Vdc to 15 Vdc.
[00079] For example, a synchronous boost 104 usable in the power system can be
a voltage
convert that converts a voltage from 12 Vdc to 28 Vdc,
[00080] Three different examples of the power system follow
[00081] Example 1. Digital high voltage power supply with a plastic case.
[00082] In embodiments, the digital high voltage power supply is contained in
a plastic case
that is sealed, The digital high voltage power can weigh 1/2 to 2 pounds.
1000831 A high voltage plant is in the case that can be attached to the
case, such as with
epoxy. The high voltage plant in this example receive a low voltage such as 12
volts
DC.
1000841 The high voltage plant converts the 12 volts to a high voltage signal
such as 1000 Vac
containing unwanted sinusoidal noise such as a 6 Vac signal which is like
static on a
phone call.
[000851 The high voltage plant can contain a transformer that converts the
12 volts to the
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
1000 volts or a voltage step up device, which does the same voltage
conversion, but
differently.
[00086] The high voltage plant contains a transistor such as a MOSFET
transistor which pulls
the low voltage 12 volts current through the transformer and creates a
magnetic field
that controls the passage of the voltage like a water valve connected to a
water pipe.
[00087] The high voltage plant contains a high voltage multiplier such as
a 6 times multiplier
which multiplies the voltage from the transformer to the high voltage signal
which is
6 times the transformer voltage. An example of a high voltage plant can be a
standard
series multiplier made by Dean Technology of Addison, Texas.
[00088] In this example, two filters are used. A first filter connects to
the high voltage plant
and the second filter connects to the high voltage plant in series with the
first filter.
[00089] The second filter forms a high voltage output.
1000991 The first filter in this example can be a combination of an
inductor, such as a 10
mierohenry inductor, and a capacitor such as a 1 microfarad capacitor
connected
together in parallel to each other with a ground.
[00091] The second filter can be a combination of a resistor in series
with the first filter and a
capacitor connected with a ground. The resistor can be a 10 kilo ohm resistor.
The
capacitor in the second filter can be a 2 microfarad capacitor.
[000921 The high voltage divider is in case and electrically connected
between the high
voltage signal and produces a scaled voltage feedback signal. The high voltage
divider is formed from a plurality of resistors connected in series The high
voltage
divider can use different size resistors, such as one 10 giga ohm resistor and
one 10
kilo ohm resistor.
[000931 The high voltage divider is configured to receive the high voltage
output of 1000
volts and generate a scaled voltage feedback signal of 3 volts DC.
11
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
[00094] A processor, such as a microprocessor with programmable peripherals,
and various
hardware features and memory.
1000951 The memory for this example contains 40% operating set points. Some of
the step
points are a specific voltage or current that the power supply can be set to
for
operation. Other set points are time intervals, or restart intervals, shut
down lengths of
time. For example, a specific voltage can be changed from 2000 volts to 5000
volts
by entering a user defined value into the memory of the processor.
[00096] An example of a time interval set point can be stay on for 5
minutes.
[00097] An example of a restart interval can be attempt to restart every
one second.
[000981 An example of shutdown lengths of time can be stay off for 5 seconds.
[00099] The processor is connected to the low voltage and the high voltage
plant.
[000100] The processor is configured to: receive the scaled voltage feedback
signal from the
high voltage divider; compare the scaled voltage feedback signal to the
plurality of
operating set points in memory; compute and store in memory, at least one
revised
operating set point using the compared scaled voltage feedback signa].
[000101] For example, the processor computes at least one revised operating
set point of a
higher or lower voltage depending on the needs of the customer, such as a
computation of 4000 volts or 1000 volts, like and A-D value of 2000 or 4096.
[000102] The processor uses the revised operating set point to simultaneously
and
automatically regulate high output voltage within all operating set points.
[000103] Example 2: Digital high voltage power supply with open board.
[000104] In an embodiment the digital high voltage power supply is contained
in an open board
that is sealed. The digital high voltage power can weigh 11/2 to 2 pounds.
[000105] In the case is a high voltage plant that can be attached to the case,
such as with epoxy.
12
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
The high voltage plant in this example, receives a low voltage such as 12
volts DC.
[000106] The high voltage plant converts the 12 volts to a high voltage signal
such as 1000
volts DC containing unwanted sinusoidal noise, such as a 6 volt AC signal
which is
like static on a phone call.
.. 10001071 The high voltage plant contains a transformer such as transform
that converts the 12
volts to the 1000 volts or a voltage step up device can be used which does the
same
voltage conversion, but differently.
10001081 The high voltage plant contains a transistor such as a MOSFET
transistor which pulls
the low voltage 12 volts current through the transformer and creates a
magnetic field
that controls the passage of the voltage like a water valve connected to a
water pipe.
10001091 The high voltage plant contains a high voltage multiplier such as a 6
times multiplier
which multiplies the voltage from the transformer to the high voltage signal
which is
6 times the transformer voltage. An example of a high voltage plant can be a
standard
series multiplier made by Dean Technology of Addison, Texas.
.. [000110] In this example, two filters are used. A first filter connects to
the high voltage plant
and the second filter connects to the high voltage plant in series with the
first filter.
[000111] The second filter forms a high voltage output.
[0001121 The -first filter in this example can be a combination of an
inductor, such as a 10
rnicrohenry inductor, and a capacitor such as a 1 microfarad capacitor
connected
together in parallel to each other with a ground.
10001131 The second filter can be a combination of a resistor in series with
the first filter and a
capacitor connected with a ground. The resistor can be a 10 kilo ohm resistor.
The
capacitor in the second filter can be a 2 microfarad capacitor.
10001141 The high voltage divider is in case and electrically connected
between the high
voltage signal and produces a scaled voltage feedback signal. The high voltage
13
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
divider is formed from a plurality of resistors connected in series The high
voltage
divider can use different size resistors, such as one 10 giga ohm resistor and
one 10
kilo ohm resistor.
10001151 The high voltage divider is configured to receive the high voltage
output of 1000
volts and generate a scaled voltage feedback signal of 3 Vdc.
10001161 A processor, such as a microprocessor with programmable peripherals,
and various
hardware features and memory.
10001171 The memory for this example contains 4096 operating set points;. Some
of the set
points are a specific voltage or current that the power supply can be set to
for
operation. Other set points are time intervals, or restart intervals, shut
down lengths
of time. For example, a specific voltage can be changed from 2000 volts to
5000 volts
by entering a user defined value into the memory of the processor.
10001181 An example of a time interval set point can be stay on for 5 minutes.
10001191 An example of restart intervals can be attempt to restart every one
second.
10001201 An example of a shut down lengths of time can be stay off for 5
seconds.
10001211 The processor is connected to the low voltage and the high voltage
plant.
10001221 The processor is configured to: receive the scaled voltage feedback
signal from the
high voltage divider; compare the scaled voltage feedback signal to the
plurality of
operating set points in memory; compute and store in memory, at least one
revised
operating set point using the compared scaled voltage feedback signal.
10001231 For example, the processor computes at least one revised operating
set point of a
higher or lower voltage depending on the needs of the customer, such as a
computation of 4000 volts or 1000 volts, like anti A-D value of 2000 or 4096.
10001241 The processor uses the revised operating set point to simultaneously
and
automatically regulate high output voltage within all operating set points.
14
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
10001251 Example 3: Digital high voltage power supply with metal case.
[0001261 In an embodiment the digital high voltage power supply is contained
in a metal case
that is sealed The digital high voltage power can weigh 2 pounds to 3 pounds.
10001271 In the case is a high voltage plant that can be attached to the case,
such as with epoxy,
The high voltage plant, in this example, receives a low voltage such as 12
Vdc.
10001281 The high voltage plant converts the 12 volts to a high voltage signal
such as 1000
volts DC containing unwanted sinusoidal noise such as a 6 Vac signal which is
like
static on a phone call.
10001291 The high voltage plant contains a transformer such as transform that
converts the 12
volts to the 1000 volts or a voltage step up device can be used which does the
same
voltage conversion, but differently,
[0001301 The high voltage plant contains a transistor such as a MOSFET
transistor which pulls
the low voltage 12 volts current through the transfoimer and creates a
magnetic field
that controls the passage of the voltage like a water valve connected to a
water pipe.
[000131] The high voltage plant contains a high voltage multiplier such as a 6
times multiplier
which multiplies the voltage from the transformer to the high voltage signal
which is
6 times the transformer voltage. An example of a high voltage plant can be a
standard
series multiplier made by Dean Technology of Addison, Texas.
[000132] In this example, 2 filters are used. A first filter connects to the
high voltage plant and
the second filter connects to the high voltage plant in series with the first
filter.
[000133] The second filter forms a high voltage output.
10001341 The first filter in this example can be a combination of an inductor,
such as a 10
microhenry inductor, and a capacitor such as a 1 microfarad capacitor
connected
together in parallel to each other with a ground.
10001351 The second filter can be a combination of a resistor in series with
the first filter and a
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
capacitor connected with a ground. The resistor can be a 10 kilo ohm resistor.
The
capacitor in the second filter can be a 2 microfarad capacitor.
10001361 The high voltage divider is in case and electrically connected
between the high
voltage signal and produces a scaled voltage feedback signal. The high voltage
divider is formed from a plurality of resistors connected in series. The high
voltage
divider can use different size resistors, such as one 10 Giga-Ohm resistor and
one 10
Kilo ohm resistor.
[000137] The high voltage divider is configured to receive the high voltage
output of 1000
volts and generate a scaled voltage feedback signal of 3 Vdc.
[000138] A processor, such as a microprocessor with programmable peripherals,
and various
hardware features and memory.
[000139] The memory for this example contains 4096 operating set points. Some
of the step
points are a specific voltage or current that the power supply can be set to
for
operation. Other set points are time intervals, or restart intervals, shut
down lengths
of time. For example, a specific voltage can be changed from 2000 volts to
5000 volts
by entering a user defined value into the memory of the processor.
[000140] An example of a time interval set point can be stay on for 5 minutes.
[000141] An example or a restart interval can be attempt to restart every one
second.
[000142] An example of shutdown lengths of time can be stay off for 5 seconds.
[000143] The processor is connected to the low voltage and the high voltage
plant.
19001441 The processor is configured to: receive the scaled voltage feedback
signal from the
high voltage divider; compare the scaled voltage feedback signal to the
plurality of
operating set points in memory; compute and store in memory, at least one
revised
operating set point using the compared scaled voltage feedback signal.
10001451 For example, the processor computes at least one revised operating
set point of a
16
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20
CA 030110026 2020-04-22
WO 2019/126062 PCT/LIS2018/066052
higher or lower voltage depending on the needs of the customer, such as a
computation of 4000 volts or 1000 volts, like and A-D value of 2000 or 4096.
10001461 The processor uses the revised operating set point to simultaneously
and
automatically regulate high output voltage within all operating set points.
10001471 While these embodiments have been described with emphasis on the
embodiments, it
should be understood that within the scope of the appended claims, the
embodiments
might be practiced other than as specifically described herein.
17
Date Regue/Date Received 2023-01-20