Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
1
KINETIC ENERGY ABSORBING BARRIER STRUCTURE
BACKGROUND OF INVENTION
The present invention relates to a kinetic energy absorbing barrier
structure.
Terrorist attacks by means of vehicles driven at high speed in
crowded pedestrian areas, typically in city-centre streets and symbolic
locations, have generated the need for solutions capable of preventing or
at least limiting the scope of these acts.
Following numerous terrorist attacks, barriers such as Jersey
barriers or flower boxes have been installed in some cities to protect
pedestrian areas and other sensitive zones to prevent or limit further
terrorist attacks using motor vehicles to run into crowds.
However, Jersey barriers and other barriers in concrete or metal
materials currently used to prevent access to an area by unauthorised
vehicles have drawbacks and limitations of a technical and also aesthetic
nature.
From the technical viewpoint, Jersey barriers, and other barriers
constituted by solid forms resting on the ground, base their protective
capability on their weight, but are unable to ensure an adequate defence
unless they are connected to each other or to the ground, and can
therefore be crashed through with relative ease; instead, metal barriers
base their protection on the capability to provide an irremovable obstacle
and are much more resistant, but typically require major foundations and
deep ground anchorages that are difficult and expensive to implement,
especially in old town centres. The first are therefore used much more in
old towns and in urban centres, particularly due to the greater simplicity
and flexibility in installation.
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
2
A Jersey barrier roughly 3 m long, for example, weighs
approximately 1.5 - 2.0 t, while a concrete flower box can weigh from 150
kg to 900 kg depending on size.
When a barrier of this type is simply stood on the ground, unlike the
classic laying of Jersey walls in a road configuration with chain fastenings
connecting each Jersey barrier to the next, it can be easily moved or even
thrown by a vehicle hitting it.
In fact, by simulating, for example, a 3,000 kg vehicle travelling at 50
to 70 km/h, and assuming that the structure of the vehicle absorbs 30-40%
io of the energy through deformation during the impact, all of the remaining
energy is transmitted to the Jersey or concrete type barrier, which however
is rigid and non-deformable, and only stands on the ground. For this
reason, all of the remaining energy results in a violent movement of the
barrier for tens of metres, especially on smooth or slippery surfaces, such
is as sett for example. Perhaps the vehicle stops, but the barrier is
hurled,
like a curling stone on ice, and can therefore cause serious injury to
persons standing in the space affected by the barrier's movement.
Another drawback of Jersey barriers and other known types of
barriers is constituted by the negative landscaping impact, especially when
20 installed in old town centres, because they appear like some kind of bare
concrete wall in the middle of other areas of scenic interest, namely
historic, cultural or architectural.
Known types of barriers also provoke human feelings of "anxiety and
fear" due to their obvious function of protection, which contributes to a
25 feeling of being under continuous attack.
FR 2 710 229 Al describes a flower box for street furniture, actually
a large box for flowers comprising a container, arranged inside the box, a
mask arranged on the periphery, and a three-dimensional frame arranged
between the container and the mask. The mask comprises a facing
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
3
element mounted removably on the frame, which can constitute a modular
system such that the frame can be superimposed and/or juxtaposed with
another frame. FR 2 710 229 Al describes a flower box for street furniture
and not capable of acting as a safety barrier.
US 2009/001334 Al and US 2006/237913 Al describe structures
that can be filled with water used as ballast.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The aim of the present invention is to provide a barrier structure that,
first of all, is technically efficient, i.e. effectively capable of stopping a
vehicle and preventing the devastating effects of a possible attack.
Within the scope of this aim, one object of the invention is to provide
a barrier structure that has an extremely low landscaping impact.
Another object is to provide a barrier structure that can be a street
furniture component and that can be integrated with different functional
elements.
A further object of the present invention is to provide a structure that
can be produced using elements and materials that are commonly
available commercially and that is also competitive from an economic
standpoint.
This and other objects, which shall be described in greater detail
hereinafter, are attained by a barrier structure with a high capacity for
absorbing kinetic energy, achieved through the considerable deformability
of the system combined with minimum movement on the ground.
The above-mentioned structure is characterized in that it comprises
a shell designed to contain a frame in which multiple weights are suitably
positioned and which surrounds a tank; said tank being designed to
contain a volume of water, gel or other material and also defining one or
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
4
more compartments designed to contain soil for plants; said frame having
a high deformation capacity.
Furthermore, the shape of the frame enables the connection of the
structures with one another in various "island" or "chain" configurations,
thus linking one element to the next, thereby considerably increasing the
containment capacity of energy originating from impacts and further limiting
movements of these structures on the ground.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Further characteristics and advantages of the subject of the present
invention will become clearer through an examination of the description of
a preferred, but not exclusive, embodiment of the present invention, shown
by way of non-limitative example in the accompanying drawings, in which:
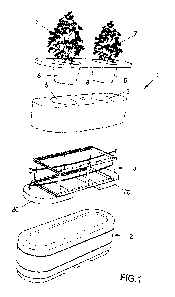
Figure 1 is an exploded perspective view of the kinetic energy
absorbing barrier structure, according to the present invention;
Figure 2 is an exploded front view of the structure;
Figure 3 is a perspective view showing an example of fitting out the
structure forming the subject of the present invention;
Figure 4 is a perspective view showing another example of fitting out
the structure;
Figure 5 is a perspective view showing a further example of fitting
out the structure;
Figure 6 is a perspective view showing a possible configuration of
multiple structures connected to each other;
Figure 7 shows an example of a wheeled device for handling the
structure;
Figure 8 is a side view, partially in section, showing the quick-
connection system in the working position;
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
Figure 9 is a perspective view of an example of quick-connection
system;
Figure 10 is a schematic plan view showing a series of structures to
be joined via the quick-connection system;
5 Figure 11 is a perspective view of the water tank;
Figures 12-15 show various possible configurations of multiple
structures connected to each other;
Figure 16 is a perspective view schematically showing the kinetic
energy absorbing barrier structure that, according to a further aspect of the
present invention, has a saw-toothed lateral edge;
Figure 17 is a perspective view that shows the structure with a saw-
toothed lateral edge and base with mechanical anchorage support;
Figure 18 is a partial view, in section, of the structure with a saw-
toothed edge;
Figure 19 is a perspective view that shows the structure with a saw-
toothed lateral edge and base with chemical support;
Figure 20 is an elevation view that shows the structure with a support
base with mechanical anchorage on turf or similar;
Figure 21 is an elevation view that shows the structure with a support
base with mechanical anchorage on an asphalt surface or similar;
Figure 22 is an elevation view that shows the structure with a support
base with a biadhesive gel base on a continuous smooth surface, such as
marble, or sett;
Figure 23 is an elevation view that shows the structure, according to
a further aspect of the invention, fitted with orthogonal teeth on one side;
Figure 24 is a view similar to the previous one showing the structure
in operation;
Figure 25 is an elevation view that shows the structure, according to
a further aspect of the invention, fitted with hidden props; and
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
6
Figure 26 is a view similar to the previous one showing the structure
in operation.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
With particular reference to the numeric symbols in the
aforementioned figures, the kinetic energy absorbing barrier structure
according to the present invention, indicated as a whole by reference
numeral 1, comprises a shell 2 designed to contain a frame 3 that
surrounds a tank 4.
The structure further comprises a plurality of suitably positioned
weights 20 made integral with the frame 3.
The tank 4 is designed to contain a volume of water or gel and
defines one or more compartments 5 designed to contain soil 6 for plants
7.
The shell 2 can be made of a plastic or metal material and is
characterized by a high deformation capacity.
The frame 3, which is preferably made of metal, for example of
aluminium or steel, also has a high deformation capacity.
The tank 4, which can be made of plastic for example, has at least
one filler plug 8 and one or more discharge plugs 9 arranged on the
bottom, for respectively introducing and discharging the water or gel 10.
The frame 3 and/or shell 2 have deformable rubber supports with a
high friction coefficient, indicated by reference numeral 11.
Two or more structures 1 can be rigidly connected to each other by
quick-connection means, thereby joining the various structures in a chain.
Figures 6 and 12-15 show some examples of possible
configurations.
The same connections, suitably configured, could also enable fixing
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
7
the structures to the ground.
Figures 8 and 9 show an example of quick-connection means,
indicated as a whole by reference numeral 12, constituted by T-couplings
13 inserted in guides 14 made in a wall 15 of the shell 2 and capable of
engaging a connection element 16 provided with suitable shaped slots 17.
A trolley system is provided to facilitate the handling of the structure.
Figure 7 shows an example of a trolley system, constituted by a
trolley 18 that can be associated with the shell 2 and is fitted with
retractable wheels 19.
According to the present invention, the barrier structure can be
assembled in situ or transported completely preassembled to the place of
installation.
At the place of installation, the tank 4 is filled with water, gel, or
another material suitable for giving a certain weight to the structure, which
shall be securely anchored to the paving due to the presence of
deformable rubber supports 11 with a high friction coefficient or shall be
fastened by suitable ironmongery.
The energy of a possible impact caused by a vehicle being driven
against the barrier is absorbed by the deformation of the frame 3 and by
the content of the tank 4, while the weight of the structure itself ensures
considerable resistance to movement.
In this regard, it should be noted that the structure can be rigidly
associated with other similar structures, as schematically shown in Figures
6 and 10, via quick-connection means, to form a modular barrier that is
substantially unmovable.
The possible removal or shifting of the structure is facilitated by the
possibility of emptying the tank, via the discharge plugs 9 and also by the
possible presence of the trolley system.
According to the present invention, the barrier structure can be
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
8
integrated with various functional elements, of which Figures 3-5 show just
a few examples.
The structure can also be integrated with autonomous day and night
signs, for example, via LEDs powered by solar panels.
The structure forming the subject of the present invention can be
used to make a modular barrier, even one with complex configurations and
connecting different types of functional elements, such as seats, folding
seats, tables, lamps, shelters, bike racks, etc.
Two examples of barrier modules are shown in the figures: a straight
io module and a circular module.
According to a further aspect of the present invention, the structure
is advantageously provided with a saw-toothed lateral edge 21, which
extends along the lower outer perimeter of the base of the shell 2.
The saw-toothed edge 21 is configured to puncture the tyres of a
is vehicle that hits the structure.
In fact, at the moment of impact, it is foreseen that the structure
deforms and the vehicle tends to run up onto the first edge.
It is found to be advantageous to stop the vehicle's directionality, and
sometimes its traction, by making the vehicle straddle the structure.
20 In this way, a single block is created that increases the performance
of the structure, as the weight of the vehicle is effectively added to that of
the flower box itself.
According to a further aspect of the present invention, the structure
is advantageously provided with a support base with mechanical
25 anchorage specifically studied for open agglomerate surfaces, such as
asphalt for example.
The mechanical anchoring is obtained via saw-toothed elements 22
fixed beneath the shell 2.
The mechanical anchorage system enables to significantly increase
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
9
the performance of the structure when the flower box stands on asphalt.
In practice, in addition to just friction, the saw-toothed elements 22
constitute a kind of crampon that, by biting into the asphalt, tends to block
any movement of the structure.
According to a further aspect of the present invention, the structure
is advantageously provided with a chemical type of support base,
specifically studied for continuous smooth surfaces, such as marble, sett,
etc.
The chemical type support base is advantageously constituted by a
io biadhesive gel 23 applied on the bottom of the shell 2.
In practice, in addition to just friction, a kind of chemical gripper is
formed that tends to block any movement of the structure.
The locking system using a biadhesive offers the advantage of being
easily reversible when the structure is mechanically detached by removing
is it with hoisting means.
A further advantage of the locking system using a biadhesive is
constituted in that, unlike glues, it leaves no residues and does not
damage the surfaces.
Figures 23 and 24 show a further embodiment of the structure 1 that
20 comprises an orthogonal saw-toothed lateral edge 24 on the side of the
shell 2 opposite to the side provided with the saw-toothed lateral edge 21,
i.e. the side opposite to the side against which the possible vehicular
impact is expected.
As schematically shown in Figure 24, if the vehicle impact should
25 cause an inclination of the structure, the orthogonal saw-toothed lateral
edge 24, which is on the side opposite to the side of impact, would bite the
ground, stopping the translational movement of the structure 1.
Figures 25 and 26 show a further embodiment of the structure 1 that
comprises hidden props 25.
CA 03082971 2020-05-19
WO 2019/116200 PCT/IB2018/059829
Each prop 25 is inserted within and hinged to the structure 1 at a
hinge point 26.
As schematically shown in Figure 26, a possible impact of a vehicle
causes deformation of the structure and, as a consequence, the props 25
5 that have the hinge point on the side of impact burst through the opposite
side of the structure and are driven into the ground, blocking translational
movement of the structure 1.
In practice, it has been found that the invention achieves the
intended aim and objects.
10 A kinetic energy absorbing barrier structure has been produced that
performs the task of ensuring an adequate protection from vehicles and, at
the same time, constitutes an effective element of street furniture that is
functional and aesthetically pleasing.
In fact, the device forming subject of the present invention, which
is can be aesthetically disguised as a flower box or something else, is
essentially an energy absorber that uses the water/gel not just as simple
ballast, as in devices of the prior art, but rather as a means to transform,
at
the moment of impact, the kinetic energy of the vehicle into kinetic and
potential energy of the mass of water or gel.
Basically, in the present invention, the water absorbs the energy
through column dissipation and/or water choking-atomization, in practice
rendering the distribution of the energy on impact harmless.
This is made possible because the frame and the tank are highly
deformable and able to instantaneously transfer the energy (instantaneous
pressure increase in tank).
The structure forming the subject of the present invention can
advantageously be made with recycled materials.
Naturally, the materials used, as well as the dimensions, can vary
according to needs.