Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
86769856
- 1 -
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR SUPPLEMENTING ON-DEMAND MEDIA
This application is a divisional of Canadian Patent
Application No. 2,758,292, which is a divisional of Canadian
Patent Application No. 2,425,472 filed October 9, 2001.
This application claims the benefit of U.S.
provisional patent application Nos. 60/239,521, filed October
11, 2000, 60/252,171, filed November 20, 2000, and 60/270,351,
filed February 21, 2001.
Background of the Invention
This invention relates to systems and methods for
providing on-demand media in interactive television
applications, and, more particularly, to systems and methods
for supplementing on-demand media in interactive television
applications.
Currently, digital versatile discs (DVDs) are used to
provide media users with various forms of media, typically
videos. DVDs are also used to store supplementary material,
such as actor interviews and theatrical trailers. However, such
supplementary material is limited by the amount of space
available on the disc. Furthermore, supplementary material
stored on DVDs is not updatable.
Therefore, it would be desirable to provide large
amounts of updatable media distribution systems which provide
supplemental content for on-demand media.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
86769856
- 2 -
Summary of the Invention
According to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method for providing on-demand media with
supplemental content, the method comprising: receiving a user
selection of on-demand media; receiving a user selection of
supplemental content; causing the selected on-demand media to
be displayed without displaying the selected supplemental
content; and during the display of the on-demand media, without
further user input, causing the selected supplemental content
to be simultaneously displayed with the on-demand media,
wherein the supplemental content is contextually related to a
currently displayed portion of the on-demand media displayed.
According to another aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a system for providing on-demand media with
supplemental content in an interactive application, comprising:
the interactive application implemented at least partially on
control circuitry configured to: receive a user selection of
on-demand media; receive a user selection of supplemental
content; cause the selected on-demand media to be displayed
without displaying the selected supplemental content; and
during the display of the on-demand media, without further user
input, cause the selected supplemental content to be
simultaneously displayed with the on-demand media, wherein the
supplemental content is contextually related to a currently
displayed portion of the on-demand media displayed.
According to still another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method for providing on-demand
media with supplemental content, the method comprising:
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
86769856
- 2a -
receiving a user selection of on-demand media; receiving a user
selection of at least one option related to supplemental
content that is contextually related to a portion of the on-
demand media and is not contextually related to a remainder of
the on-demand media; causing the selected on-demand media to be
displayed without displaying the supplemental content;
accessing metadata embedded within the on-demand media;
determining, based on content of the metadata embedded within
the on-demand media, that the metadata embedded within the on-
demand media includes a command to retrieve the supplemental
content; and during the display of the on-demand media, without
further user input, causing the supplemental content to be
simultaneously displayed with the portion of the on-demand
media when the supplemental content is contextually related to
the portion of the on-demand media displayed.
According to yet another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a system for providing on-demand
media with supplemental content, the system comprising: means
for receiving a user selection of on-demand media; means for
receiving a user selection of at least one option related to
supplemental content that is contextually related to a portion
of the on-demand media and is not contextually related to a
remainder of the on-demand media; means for causing the
selected on-demand media to be displayed without displaying the
supplemental content; means for accessing metadata embedded
within the on-demand media; means for determining, based on
content of the metadata embedded within the on-demand media,
that the metadata embedded within the on-demand media includes
a command to retrieve the supplemental content; and means for
causing, during the display of the on-demand media, without
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
86769856
- 2b -
further user input, the supplemental content to be
simultaneously displayed with the portion of the on-demand
media when the supplemental content is contextually related to
the portion of the on-demand media displayed.
Illustrative features of some embodiments of the
present invention are described, for example, in U.S.
provisional patent Application No. 60/239,521, filed October
11, 2000. Illustrative video-on-demand interface features for
use in accordance with some embodiments of the present
invention are described, for example, in U.S. provisional
patent Application Nos. 60/252,171, filed November 20, 2000 and
60/270,351, filed February 21, 2001.
On-demand media may include, for example, audio-on-
demand media, video-on-demand media, electronic publications
(e.g., books, magazines, newspapers, or any other suitable
electronic publications), electronic games, software
applications, or any other suitable on demand media.
Supplemental content for such on-demand media may be any
suitable passive or interactive text, graphics, animation,
video, audio, or suitable combination thereof such as, for
example, actor interviews, theatrical trailers, top-ten scenes
in a movie, music videos, web sites, third-party applications,
additional passive or interactive information associated with
the on-demand media, or any other suitable supplemental
content.
Some embodiments may display supplemental content
separate from on-demand media in, for example, separate
displays. Other embodiments may overlay supplemental content
onto a display. For example,
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 3 -
supplemental content may be overlaid over the on-demand
media that the user is watching, an application
display, or other suitable display. In some
embodiments, supplemental content may be displayed in
response to user actions. For example, supplemental
content may be displayed when a user selects a media
listing from a guidance application, as the user
browses through listings, or when a user selects on-
demand media. In some embodiments, supplemental
content may be displayed for a predefined period of
time when the user first accesses a segment of on-
demand media (e.g., a scene in a movie), and then the
supplemental content may disappear (e.g., fade away).
Some embodiments may provide supplemental content only
in response to the user's request (e.g., selecting an
on-screen button).
Supplementing on-demand media may be
performed by any suitable stand-alone, distributed, or
client-server based application. For example, a stand-
alone interactive television application, such as an
interactive television program guide or other suitable
guidance application, may receive supplemental content
and supplement on-demand media.
Supplemental content may be distributed using
any suitable approach. Supplemental content, or links
to supplemental content, may be provided as, for
example, synchronous metadata. Synchronous metadata is
data that is sent logically at the same time as the on-
demand media with which it is associated. The
synchronous metadata may be supplied contemporaneously
with the media, or prior to the media but with
information associating it with the media (e.g.,
identifiers, links, or any other suitable information).
Metadata may be provided in-band with or separate from
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
= 61009-630D
- 4 -
the media, out-of-band, using a carousel-based
approach, using a client-server based approach, using
localized caching, using a combination of these
approaches, or using any other suitable approach. One
or more of these approaches may require that a user's
in-home equipment include multiple tuners. Local
caching may be used to enhance the response time of the
system.
Brief Description of the Drawinas
The above and other features of some embodiments
of the invention will be apparent upon consideration of
the following detailed description, taken in
conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which
like reference characters refer to like parts
throughout, in which:
. FIG. 1 is a schematic block diagram of an
illustrative interactive television system, in
accordance with one embodiment of the present
invention.
FIG. 2A-2E show illustrative arrangements for
the interactive television application equipment of
FIG. 1, in accordance with various embodiments of the
present invention.
FIG. 3 is an illustrative schematic block
diagram of user television equipment of FIGS. 2A-2E, in
accordance with one embodiment of the present
invention.
FIG. 4 is a generalized schematic block
diagram of portions of the illustrative user television
equipment of FIG. 3, in accordance with one embodiment
of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is an illustrative main menu display
that may be displayed by an interactive television
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 5 -
application, in accordance with one embodiment of the
present invention.
FIG. 6 is an illustrative video-on-demand
menu display that may be displayed by an interactive
television application, in accordance with one
embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is an illustrative display that may be
displayed by an interactive television application when
a user browses through media listings, in accordance
with one embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 8 is an illustrative combined display
that may be displayed by an interactive television
application when a user browses through on-demand and
non-on-demand media listings, in accordance with one
embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 9 is an illustrative display that may be
displayed by an interactive television application in
response to a request to order on-demand media, in
accordance with one embodiment of the present
invention.
FIG. 10 is an illustrative setup display that
may be displayed by an interactive television
application, in accordance with one embodiment of the
present invention.
FIG. 11 is an illustrative display that may
be displayed by an interactive television application
for providing a user with options along with the on-
demand media, in accordance with one embodiment of the
present invention.
FIGS. 12 and 13 are illustrative displays
that may be displayed by an interactive television
application in response to a user indicating a desire
to view actor-related information, in accordance with
one embodiment of the present invention.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 6 -
FIG. 14 is an illustrative display that may
be displayed by an interactive television application
in response to a user indicating a desire to view
supplemental content related to an actor that the user
S is currently watching, in accordance with one
embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 15 is an illustrative display that may
be displayed by an interactive television application
in response to a user indicating a desire to view
additional information related to an actor that the
user is currently watching, in accordance with one
embodiment of the present invention.
FIGS. 16 and 17 are illustrative displays
that may be displayed by an interactive television
application in response to a user indicating a desire
to receive interactive media related to on-demand
media, in accordance with one embodiment of the present
invention.
FIGS. 18 and 19 are illustrative displays
that may be displayed by an interactive television
application in response to a user indicating a desire
to receive information related to the audio portion of
on-demand media, in accordance with one embodiment of
the present invention.
FIG. 20 is an illustrative display that may
be displayed by an interactive television application
in response to a user indicating a desire to receive
links related to on-demand media, in accordance with
one embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 21 is a flowchart of illustrative steps
involved in providing supplemental content for on-
demand media, in accordance with one embodiment of the
present invention.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
55604-33D
- 7 -
FIG. 22 is a flowchart of illustrative steps
involved in retrieving supplemental content for on-
demand media, in accordance with one embodiment of the
present invention.
FIG. 23 is a flowchart of illustrative steps
involved in providing the user with on-demand media, in
accordance with one embodiment of the present
invention.
FIG. 24 is a flowchart of illustrative steps
involved in presenting the user with supplemental
content for selected on-demand media, in accordance
with one embodiment of the present invention.
Detailed Description of the Invention
An interactive television application for
supplementing on-demand media may be based on any
suitable hardware platform or topology. Suitable
hardware that may be used in implementing such an
interactive television application includes hardware
such as satellite receivers, personal computer
televisions (PC/TVS), personal computers (e.g., with
television tuner cards), cable set-top boxes, or any
other suitable hardware. In some embodiments, the
interactive television application may be an
interactive television program guide. Illustrative
interactive television program guide systems are
described, for example, in Knee et al. U.S. patent
5,589,892 and Knudson et al. U.S. patent application
Serial No. 09/357,941, filed July 16, 1999. Client-
server program guide systems are described, for
example, in Ellis et al. U.S. patent application
= Serial No. 09/374,043, filed August 13, 1999.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
55604-33D
- 8 -
On-line program guide systems are
described, for example, in Boyer et al. U.S. patent
application Serial No. 08/938,028, filed September 18,
1997.
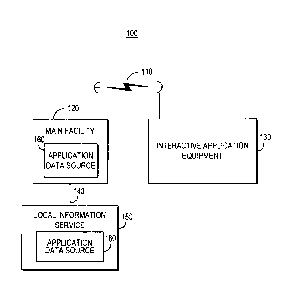
An illustrative system 100 in accordance with
one embodiment of the present invention is shown in
FIG. 1. Main facility 120 provides application data
from application data source 160 to interactive
application equipment 130 via communications link 110.
There may be multiple application data sources but only
one has been shown to avoid over-complicating the
drawing. If desired, application data sources may be
located at facilities separate from main facility 120,
such as at local information service 150, and have
their data provided to main facility 120 for
localization and distribution. Application data source
160 may be any suitable computer or computer-based
system for generating or obtaining data (e.g., manually
from an operator, electronically via a computer network
or other connection, or via storage media) and putting
the data into electronic form for distribution by main
facility 120. Link 110 may be a satellite link, a
telephone network link, a cable or fiber optic link, a
microwave link, an Internet link, a combination of such
links, or any other suitable communications link.
Video signals may also be transmitted over link 110 if
desired.
The application data distributed by main
facility 120 to interactive application equipment 130
may include any suitable application data. The
application data may include video-on-demand
information, audio-on-demand information, supplemental
content, or any other media-on-demand-related
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
55604-33D
- 9 -
information. In some embodiments, the application data
may include television programming data (e.g., program
identifiers, times, channels, titles, and descriptions)
and other data for services other than television
program listings (e.g., help text, pay-per-view
information, weather information, sports information,
music channel information, associated Internet web
links, associated software, etc.). There are
preferably numerous pieces or installations of
IC interactive application equipment 130, although only
one is shown in FIG. 1 to avoid over-complicating the
drawing.
Application data may be transmitted by main
facility 120 to interactive application equipment 130
using any suitable approach. For example, main
facility 120 may distribute application data
periodically, continuously, or with any other
frequency, as being files or as a stream. In some
approaches, data files may, for example, be
encapsulated as objects transmitted using a suitable
Internet based addressing scheme and protocol stack
(e.g., a stack which uses the user datagram protocol
(UDP) and Internet protocol (IF)). Systems in which
data is transmitted from a main facility to television
distribution facilities using such an approach are
described, for example, in Gollahon et al. U.S. patent
application Serial No. 09/332,624, filed June 11, 1999.
Supplementing on-demand media may be
performed by any suitable stand-alone, distributed, or
client-server based application. For example, a stand-
alone interactive television application, such as an
interactive television program guide or other suitable
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
¨ 10 -
guidance application, may receive supplemental content
and supplement on-demand media. Supplemental content
for such on-demand media may be any suitable passive or
interactive text, graphics, animation, video, audio, or
suitable combination thereof such as, for example,
actor interviews, theatrical trailers, top-ten scenes
in a movie, music videos, web sites, third-party
applications, additional passive or interactive
information associated with the on-demand media, or any
other suitable supplemental content.
In some embodiments; supplemental content may
be generated and transmitted at main facility 120 and
accumulated at distribution facility 180 (e.g., a cable
system headend). Supplemental content may be
transmitted concurrently with application data and
stored in user television equipment 200. Alternately,
supplemental content may be transmitted with on-demand
media. It is noted that distribution facility 180 may
distribute supplemental content periodically,
continuously, or with any other frequency, as being
files or as a stream.
In some embodiments, supplemental content may
be transmitted with on-demand media. The supplemental
content may be accumulated at distribution facility 180
and provided with on-demand media. In some approaches,
the supplemental content may be downloaded to user
television equipment 200 prior to the viewing of the
selected on-demand media. For example, when a user
indicates a desire to view an on-demand media selection
at a predetermined time (e.g., two hours from the
indication), the corresponding supplemental content may
be transmitted prior to viewing the selected on-demand
media.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
¨ 11 -
Local information service 150 may be any
facility suitable for obtaining data particular to a
localized region and providing the data to main
facility 120 over communications link 140. Local
information service 150 may be, for example, a local
weather station that measures weather data, a local
newspaper that obtains local high school and college
sporting information, or any other suitable provider of
information. Local information server 150 may be a
local business with a computer for providing main
facility 120 with, for example, local ski reports,
fishing conditions, menus, etc., or any other suitable
provider of information. Link 140 may be a satellite
link, a telephone network link, a cable or fiber optic
link, a microwave link, an Internet link, a combination
of such links, or any other suitable communications
link.
In some embodiments, local information
service 150 may be any suitable facility for providing
supplementary content particular to a localized region.
Local information service 150 may provide supplemental
content to main facility 120 over communications link
140 for accumulation at distribution facility 180
(e.g., a cable system headend). Local information
service 150 may be used to provide, for example,
national and local advertisements relating to the
selected on-demand media.
An interactive television application may be
implemented on interactive application equipment 130.
Five illustrative arrangements for interactive
application equipment 130 are shown in FIGS. 2A-2E. As
shown, interactive application equipment 130 may
include distribution facility 180, distribution
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 12 -
equipment 170 located at distribution facility 180, and
user television equipment 200.
The interactive television application, such
as an interactive television program guide or other
guidance application, web browser, or other suitable
interactive television application, may run totally on
user television equipment 200 using the arrangements of
FIGS. 2A and 2C, or may run partially on user
television equipment 200 and partially on interactive
application equipment 130 using a suitable
client-server or distributed processing arrangement
such as those shown in FIGS. 25 and 25. Distribution
facility 180 may be any suitable distribution facility
(e.g., a cable system headend, a broadcast distribution
facility, or any other suitable type of distribution
facility), and may have distribution equipment 170.
Distribution equipment 170 of FIGS. 2A, 2B,
2C, and 25 is equipment suitable for providing
application data to user television equipment 200 over
communications path 190. In FIG. 2E, distribution
equipment 170 may provide application data, such as
program guide data, to Internet service system 220 via,
for example, a suitable computer network or Internet
link.
Supplemental content, or links to content,
may be distributed to user television equipment 200 by
distribution equipment 170 as, for example, synchronous
metadata. Synchronous metadata is data that is sent
logically at the same time as the media with which it
is associated. The metadata may be provided in-band
with or separate from the media, out-of-band, using a
carousel-based approach, using a client-server based
approach, using localized caching, using a combination
of these approaches, or using any other suitable
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 13 -
approach. The synchronous metadata may be supplied
contemporaneously with the media, or prior to the media
but with information associating it with media (e.g.,
identifiers, links, or any other suitable information).
One or more of these approaches may require that a
user's in-home equipment include multiple tuners.
Localized caching may be used to enhance the response
time of the system.
The metadata may include other types of data.
The metadata may include, for example, commands that
indicate to the users' in-home equipment (or client
applications running on the equipment) that a
particular action is to be performed (e.g., overlaying
a visual indicator onto the on-demand media). The
metadata may include, for example, a directory that
indicates segments of on-demand media, a directory of
supplemental content that is available for the on-
demand media, or any other suitable information. In
some approaches, the metadata may be used as markers
within the on-demand media. For example, supplemental
content may include a number of segments (e.g., actor
interviews, trailers, top-ten scenes in the movie,
music videos, or any other suitable segment). The
segments may be provided along with the actual movie or
separately from the actual movie. The system may
provide a menu that indicates the segments and allows
the user to jump directly to the segment based on the
metadata.
Distribution equipment 170 may include, for
example, suitable transmission hardware for
distributing application data on a television channel
sideband, in the vertical blanking interval of a
television channel, using an in-band digital signal,
using an out-of-band digital signal, or by any other
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 14 -
suitable data transmission technique. Analog or
digital signals for on-demand media (e.g., television
programs, on-demand movies, on-demand music, etc.) may
also be distributed by distribution equipment 170 to
user television equipment 200 over communications
paths 190 on multiple television channels.
Alternatively, on-demand media may be distributed to
user television equipment 200 from some other suitable
distribution facility, such as a cable system headend,
a broadcast distribution facility, a satellite
television distribution facility, or any other suitable
type of television distribution facility. In another
suitable approach, on-demand media may be distributed
from an in-home server. In yet another suitable
approach, the media may be a media segment or program
that the use has previously selected to be recorded.
Communications paths 190 may be any
communications paths suitable for distributing
application data. Communications paths 190 may
include, for example, a satellite link, a telephone
network link, a cable or fiber optic link, a microwave
link, an Internet link, a data-over-cable service
interface specification (DOCSIS) link, a radio
frequency link, a combination of such links, or any
other suitable communications link. Communications
paths 190 preferably have sufficient bandwidth to allow
distribution facility 180 or another distribution
facility to distribute television programming to user
television equipment 200. There are typically multiple
pieces of user television equipment 200 and multiple
associated communications paths 190, although only one
piece of user television equipment 200 and
communications path 190 are shown in FIGS. 2A-2D to
avoid over-complicating the drawings. If desired,
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 15 -
television programming, application data, supplemental
content, and on-demand media may be provided over
separate communications paths.
FIG. 25 shows an illustrative arrangement for
interactive application equipment 130 in a
client-server based or distributed interactive
application system. As shown in FIG. 2B, distribution
equipment 170 may include server 210. Server 210 may
use any suitable combination of hardware and software
to provide a client-server based application.
Server 210 may, for example, run a suitable database
engine (e.g., SQL Server by Microsoft) and provide
application data and supplemental content in response
to queries generated by an application client
implemented on user television equipment 200. If
desired, server 210 may be located at main facility
120, or other location, such as a cable system headend,
a broadcast distribution facility, a satellite
television distribution facility, or any other suitable
type of television distribution facility.
The application client may retrieve
application data and supplemental content from server
210 using any suitable client-server based approach.
The client may, for example, pass SQL requests as
messages to server 210. In another suitable approach,
the application client may invoke remote procedures
that reside on server 210 using one or more remote
procedure calls. Server 210 may execute SQL statements
for such invoked remote procedures. In still another
suitable approach, client objects executed by the
application may communicate with server objects
executed by server 210 using, for example, an object
request broker (ORB). This may involve using, for
example, Microsoft's Distributed Component Object Model
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 16 -
(DCOM) approach. In another suitable approach, the
application client may also retrieve supplemental
content from server 205 over communications path 190.
The application client may communicate with
server 210 over communications path 190 using any
suitable network and transport layer protocols, if
desired. They may communicate, for example, using a
protocol stack which includes Sequenced Packet
Exchange/Internetwork Packet Exchange (SPX/IPX) layers,
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) layers, Appletalk Transaction
Protocol/Datagram Delivery Protocol (ATP/DDP) layers,
DOCSIS or any other suitable network and transport
layer protocols.
FIGS. 2C and 2D show illustrative
Internet-based interactive television application
systems. Distribution facility 180 may, for example,
include Internet service system 220. Internet service
system 220 may use any suitable combination of hardware
and software capable of providing application data to
the application using an Internet based approach (e.g.,
the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)). If desired,
Internet service system 220 may be located at a
facility that is separate from distribution
facility 180.
If the application is implemented on user
television equipment 200 of interactive application
equipment 130 as shown in FIG. 20, Internet service
system 220 (or other suitable equipment at distribution
facility 180 that is connected to Internet service
system 220) may provide application data and
supplemental content to user television equipment 200
via the Internet, or via distribution equipment 170
using any suitable Internet-based approach (e.g., using
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
55604-33D
- 17 -
the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) over a
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) type link). If the interactive television
application implemented on interactive application
equipment 130 is a client-server based application as
shown in FIG. 2D, server 210 may obtain application
data and supplemental content from Internet service
= system 220. The application may also, however, obtain
application data from Internet service system 220 via
an Internet connection.
In another suitable arrangement, distribution
= equipment 170 may include computer equipment or other
suitable hardware on which a first portion or version
of the interactive television application is
implemented. A second portion or version of the
application may be implemented on user television
equipment 200. The two versions or portions of the
interactive television application may communicate
= using any suitable peer-to-peer communications scheme
(e.g., messaging, remote procedure calls, etc.) and
perform interactive application functions
distributively between distribution facility 180 and
user television equipment 200.
Another suitable arrangement in which an
on-line application, such as an on-line program guide,
is implemented on interactive application equipment 130
is shown in FIG. 2E. On-line program guide systems are
described, for example, in Boyer et al. U.S. patent
application Serial No. 08/938,028, filed September 18,
1997. The user may have personal computer
(PC) 240 on which a web-enabled application client or
web browser is implemented. Personal computer 240 may
be connected to Internet service system 220 via
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 18 -
Internet link 230. Internet service system 220 may use
any suitable combination of computer hardware and
software capable of providing an on-line server
application or web site. Internet service system 220
is shown as obtaining application data from
distribution facility 180. In other suitable
approaches, Internet service system 220 may obtain
information from other systems such as, for example,
main facility 120, local information service 150, or
any other suitable source of application data.
In the examples of FIGS. 2A-2E, on-demand
media may be provided using remote servers such as a
media server 205, server 210, or using any other
suitable video-on-demand equipment. Servers such as
media server 205, server 210, or other video-on-demand
equipment may be located at network nodes associated
with a distribution facility or any other suitable
location. Although shown as separate, server 205 and
server 210 may also be combined as a single server.
Media server 205 may communicate with a distribution
facility over communications path 190. The
distribution facility may be a cable system headend, a
satellite television distribution facility, a
television broadcast facility, or any other suitable
facility for distributing video-on-demand content,
television, and music programming to users.
Supplemental content may be provided to user
television equipment 200 with on-demand media according
to the given approaches shown in FIGS. 2A-2E. In one
suitable approach, supplemental content may be
generated at main facility 120. Main facility 120 may
transmit supplemental content to be stored at
distribution facility 180. Distribution facility 180
may distribute supplemental content to user television
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 19 -
equipment 200 via communications link 190. In another
suitable approach, supplemental content may be created
by main facility 160. Main facility 160 may distribute
the supplemental content to user television equipment
200. In yet another suitable approach, when metadata
is embedded within on-demand media, supplemental
content may be retrieved from media server 205.
An illustrative arrangement for user
television equipment 200 is shown in FIG. 3. In some
embodiments, user television equipment 200 of FIG. 3
may receive video or a digital video stream and data
from distribution facility 180 (FIG. 2a), such as a
program distribution facility or some other suitable
distribution facility, at input 250. In some
embodiments, user television equipment 200 may receive
video or a digital video stream and data directly from
main facility 160. During normal television viewing, a
user tunes set-top box 260 to a desired television
channel. The signal for that television channel is
then provided at video output 270. The signal supplied
at output 270 is typically either a radio-frequency
(RF) signal on a predefined channel (e.g., channel 3 or
4), or an analog demodulated video signal, but may also
be a digital signal provided to television 280 on an
appropriate digital bus (e.g., a bus using the
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
(IEEE) 1394 standard, (not shown)). The video signal
at output 270 is received by optional secondary storage
device 290.
The interactive television application may
run on set-top box 260, on television 280 (if
television 280 has suitable processing circuitry and
memory), on a suitable analog or digital receiver
connected to television 280, or on digital storage
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
55604-33D
- 20 -
device 300 if digital storage device 300 has suitable
processing circuitry and memory. The interactive
television application may also run cooperatively on a
suitable combination of these devices. Interactive
television application systems in which a cooperative
interactive television program guide application runs
on multiple devices are described, for example, in
Ellis U.S. patent application Serial No. 09/186,598,
filed November 5, 1998.
Secondary storage device 290 can be any
suitable type of analog or digital program storage
device or player (e.g., a videocassette recorder (VCR),
a personal video recorder (PVR), a digital versatile
disc (DVD) player, etc.). Program recording and other
features may be controlled by set-top box 260 using
control path 310. If secondary storage device 290 is a
videocassette recorder or a personal video recorder,
for example, a typical control path 310 may involve the
use of an infrared transmitter coupled to the infrared
receiver in the recorder that normally accepts commands
from a remote control such as remote control 320.
Remote control 320 may be used to control set-top box
260, secondary storage device 290, and television 280.
In some embodiments, on-demand media may be
stored on digital storage device 300. Distribution
equipment 170 may stream on-demand media to be stored
on digital storage device 300.
If desired, a user may record programs,
application data, or a combination thereof in digital
form on optional digital storage device 300. Digital
storage device 300 may be a writeable optical storage
device (such as a DVD player capable of handling
recordable DVD discs), a magnetic storage device (such
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
55604-33D
- 21 -
as a disk drive or digital tape), or any other digital
storage device. Interactive television program guide
systems that have digital storage devices are
described, for example, in Hassell et al. U.S. patent
application Serial No. 09/157,256, filed September 17,
1998.
=
Digital storage device 300 can be contained
in set-top box 260 or it can be an external device
connected to set-top box 260 via an output port and
appropriate interface. If necessary, processing
circuitry in set-top box 260 formats the received
video, audio and data signals into a digital file
format. Preferably, the file format is an open file
format such as the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG)
MPEG-2 standard or the Moving Joint Photographic
Experts Group (MJPEG) standard. The resulting data is
streamed to digital storage device 300 via an
appropriate bus (e.g., a bus using the Institute
Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 1394
standard), and is stored on digital storage device 300.
In another suitable approach, an MPEG-2 data stream or
series of files may be received from distribution
equipment 170 and stored.
Television 280 receives video signals from
secondary storage device 290 via communications path
330. The video signals on communications path 330 may
either be generated by secondary storage device 290
when playing back a prerecorded storage medium (e.g., a
videocassette or a recordable digital video disc), by
digital storage device 300 when playing back a
pre-recorded digital medium, may be passed through from
set-top box 260, may be provided directly to television
280 from set-top box 260 if secondary storage device
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 22 -
290 is not included in user television equipment 200,
or may be received directly by television 280. During
normal television viewing, the video signals provided
to television 280 correspond to the desired channel to
which a user, has tuned with set-top box 260. Video
signals may also be provided to television 280 by
set-top box 260 when set-top box 260 is used to play
back information stored on digital storage device 300.
Set-top box 260 may have memory 340. Memory
340 may be any memory or other storage device, such as
a random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM),
flash memory, a hard disk drive, a combination of such
devices, etc., that is suitable for storing application
instructions and application data for use by the
interactive application.
Set-top box 260 may have communications
device 350 for communicating directly with distribution
equipment 170, server 210 or Internet service system
220 over communications path 190. Communications
device 350 may be a modem (e.g., any suitable analog or
digital standard, cellular, or cable modem), network
interface card (e.g., an Ethernet card, Token ring
card, etc.), or other suitable communications device.
Communications device 350 may also be a personal
computer with an Internet connection in, for example,
the arrangement shown in FIGS. 2C and 2D. Television
280 may also have such a suitable communications device
if desired. In an alternative approach, user
television equipment 200 may communicate with Internet
service system 220 via distribution equipment 170 using
a suitable return path.
Application data may be stored inset-top box
for use by the application. For example, two weeks of
television program listings data may be stored by the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 23 -
application. All or part of the application data may
be provided on-demand or in a continuous or periodic
data stream, or using any other suitable approach. The
application data may include universal identifiers for
programs. The identifiers may be used by the
application on playback or recording to indicate to the
system provider what programs are being played back or
recorded. The application data may include identifiers
for commercials, scenes within programs, or any other
media, or portions of media to attempt to maximize the
granularity of the feedback. The system provider may
be a program guide provider, a television service
provider, Internet service providers, application
providers, cable system operators, broadcast or
satellite television operators, etc.
Supplemental content may also be stored in
set-top box for use by the application. For example,
supplemental content for upcoming on-demand media
selections may be stored by the application. All or
part of the supplemental content may be provided
on-demand or in a continuous or periodic data stream,
or using any other suitable approach. The selected on-
demand media may include metadata, which may include a
directory of supplemental content that is available for
the on-demand media and markers for the on-demand
media. Such markers may be used by the application on
playback to indicate to the system provider what
supplemental content should be pre-cached. Pre-caching
supplemental content may attempt to maximize the
granularity of the feedback.
A more generalized embodiment of user
television equipment 200 of FIG. 3 is shown in FIG. 4.
As shown in FIG. 4, application data from distribution
facility 180 (FIG. 2a) is received by control circuitry
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 24 -
360 of user television equipment 200. The functions of
control circuitry 360 may be provided using the set-top
box arrangement of FIGS. 2a and 2b. Alternatively,
these functions may be integrated into an advanced
television receiver, personal computer television
(PC/TV), or any other suitable arrangement. If
desired, a combination of such arrangements may be
used.
User television equipment 200 may also have
secondary storage device 370 and digital storage device
380 for recording media. Secondary storage device 370
can be any suitable type of analog or digital program
storage device (e.g., a videocassette recorder (VCR), a
personal video recorder (PVR), a digital versatile disc
(DVD), etc.). Program recording and other features may
be controlled by control circuitry 360. Digital
storage device 380 may be, for example, a writeable
optical storage device (such as a DVD player capable of
handling recordable DVD discs), a magnetic storage
device (such as a disk drive or digital tape), or any
other digital storage device.
User television equipment 200 may also have
memory 390. Memory 390 may be any memory or other
storage device, such as a random access memory (RAM).
read only memory (ROM), flash memory, a hard disk
drive, a combination of such devices, etc., that is
suitable for storing application instructions and
application data for use by control circuitry 360.
User television equipment 200 of FIG. 4 may
also have communications device 400 for supporting
communications between the application and distribution
equipment 170, server 210, or Internet service system
220 via communications path 190. Communications device
400 may be a modem (e.g., any suitable analog or
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 25 -
digital standard, cellular, or cable modem), network
interface card (e.g., an Ethernet card, Token ring
card, etc.), or other suitable communications device.
A user may control the operation of user
television equipment 200 with user input device 410.
User input device 410 may be a pointing device,
wireless remote control, keyboard, touch-pad, voice
recognition system, or any other suitable user input
device. To watch television, a user instructs control
circuitry 360 to display a desired television channel
on display device 420. Display device 420 may be any
suitable television, monitor, or other suitable display
device. To access the functions of the application, a
user may instruct the application implemented on
interactive application equipment 130 to generate a
main menu or other desired display for display on
display device 420. To access sound, a user may
instruct control circuitry 360 to provide audio media
on audio device 425. Audio device 425 may be part of
display device 420, or may be separate.
The interactive television application may
provide access to information and media that are
available on-demand (e.g., video-on-demand, personal
video recorders, etc.), and may supplement such on-
demand media with any suitable passive or interactive
content. On-demand media is media that a user may
request for access (e.g., immediate or future playback)
or distribution to the user's home equipment over a
cable or other suitable path. On-demand media may
include, for example, audio selections, video
selections, electronic publications, electronic games,
software applications, third-party applications, or
other types of media.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 26 -
FIGS. 5-20 show illustrative displays for
providing users with access to on-demand media and
associated supplemental content. For purposes of
illustration, the examples of FIGS. 5-20 are described
primarily in the context of an interactive guidance
application and, more particularly, an interactive
television program guide system which provides video-
on-demand media information. In other embodiments, the
interactive guidance application may be an audio
guidance application, a video-on-demand guide
application, or any other suitable guidance
application.
An illustrative interactive television main
menu display 450 is shown in FIG. 5. Displays 450 and
program guide displays generally may include mail
icon 502, clock 504, provider logo 506, one or more
interactive advertisements 508, and any other suitable
display element. They may, for example, include other
graphics, animations, selectable advertisements, video
windows, or other suitable content.
Display 450 may contain selectable
advertisements such as advertisements 508. Display 450
may also contain viewer services options 452. Suitable
viewer services options 452 include, for example, an
option to access features or information of a personal
video recorder, an option to access messages (either
e-mail messages or messages provided from television
system service provider), an option to adjust parental
control settings (e.g., blocked channels or ratings,
etc.), an option to set favorites (e.g., favorite
channels, etc.), an option to set up the interactive
television application or user equipment, and an option
to exit menu display 450.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 27 -
Display 450 may also contain program listings
options 454. Options 454 may include an option to view
program listings organized by time, organized by
channel, or organized by genre (e.g., sports, children,
etc.). Options 454 may also include an option to
search for programs of interest (e.g., using keywords,
based on a title search, based on an actor search,
etc.).
Cable showcase options 456 may be selected to
access video-on-demand program listings, pay-per-view
program listings, pay-per-view event listings, premium
channel listings, music channel listings, or adult
program listings.
Users may select a desired option by, for
example, positioning highlight region 458 on top of
options 452, 454, and 456 using remote control 320
(FIG. 3). The user may select the highlighted option
by, for example, pressing a select or enter or OK key.
In response to a user selecting the "VOD"
option of FIG. 5, the interactive television
application may present the user with a display such as
display 500 of FIG. 6. When the user selects an
interactive advertisement 508 from an interactive
television application display, the interactive
television application may provide the user with
additional information, with an opportunity to order a
program or product, with an opportunity to set a
reminder, or any other suitable feature that is related
to the advertised on-demand media.
Display 500 may also contain various options
that allow the user to view video-on-demand program
listings organized by different genres (e.g., family,
action, drama, comedy, kids, thrillers, classics,
etc.). When the user selects one of these options, the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 28 -
interactive television application may provide a
display in which all of the displayed program listings
are video-on-demand program listings in the genre
associated with the selected option. These selections
for on-demand media are merely illustrative. In other
embodiments, display 500 may include, for example,
selections for audio-on-demand media, electronic
publications, electronic games, software applications,
or any other suitable on-demand media.
Display 500 of FIG. 6 shows illustrative
video-on-demand options 510. Such options 510 may
include various options that allow a user to view
video-on-demand program listings organized by different
genres (e.g., family, action, drama, comedy, kids,
thrillers, classics, etc.). When the user selects one
of these options 510, the interactive television
application may provide the user with a display in
which all of the displayed program listings are
video-on-demand program listings in the genre
associated with the selected option.
In response to, for example, the user
selecting Movies A-Z option 512, the interactive
application may provide listing displays, such as
illustrative listing display 700 of FIG. 7.
Display 700 shows a portion of a list 702 of
alphabetized video-on-demand movies that the
interactive television application may display. Users
may select listings by, for example, pressing the arrow
keys of remote control 320 to position the highlight
region 704 (as shown in FIG. 3), and pressing the "OK"
key of the remote control. Listing indicator 706 may
allow the user to view the video-on-demand movies
available in selected subsets of the alphabet. Arrow
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 29 -
indicators 708 may allow the user to advance through
the alphabetized listing of video-on-demand movies.
In some embodiments, the interactive
television application may provide listings for on-
demand and non-on-demand media in a single display,
such as, for example, illustrative combined listings
display 750 of FIG. 8. Display 750 includes program
listings region 752 having listings 754 for non-on-
demand media and listings 756 for on-demand media. One
or more listings 754 may provide the user with
information about programs on specific channels showing
at a particular time. Listings 754 includes the names
of programs showing at 8:00 PM on channel 98 through
channel 102. Listings 756 may include the names of
programs, the cost of each program, and other suitable
information. Listings 754 and listings 756 may include
other media-related information, such as program
descriptions, ratings, any other suitable information.
Display 750 may provide listings 756 such that users
may access listings of video-on-demand media. The
listings shown are merely illustrative. Any other
suitable approach may also be used.
FIG. 9 shows an illustrative ordering
display 800 that may be provided by the interactive
television application in response to a user indicating
a desire to access or download on-demand media, such as
by, for example, selecting a movie listing from either
FIG. 7 or FIG. 8. In this example, the user has
selected "Meet the Parents." Display 800 may present
one or more options to a user relating to ordering the
selected video-on-demand media. Display 800 may
include, for example, the title of the movie selection
and a description of the selection. Description area
804 may include a detailed description of the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 30 -
selection, information on the actors, the running time,
the year of release, the rating for the selection, and
any other suitable information. As shown, display 800
may also include mail icon 502, current time 504,
provider logo 506, and one or more interactive
advertisements 508.
Display 800 may also include ordering
information 806, a PIN entry region 808, and a "Last"
button 810. Ordering information 806 may include the
cost to purchase the selection. When the user desires
to purchase the on-demand media, display 800 may allow
the user to enter a purchase code or personal
identification number (PIN) into PIN entry region 808.
The user may enter the code or numbers using the remote
control. If the user selects "Last" button 810, the
user may be returned to a previous display, such as
display 700 of FIG. 7.
When a valid purchase code or PIN is received
by the interactive television application, the
interactive television application may authorize the
distribution of the selected on-demand media to the
user. The selected media may be distributed by main
facility 120 (FIG. 1) or any other suitable
distribution source to the user television equipment.
In some embodiments, display 500 of FIG. 6
may also include "Setup" option 514. In response to a
user selecting "Setup" option 514, the interactive
television application may provide setup options for,
in this example, video-on-demand media. An
illustrative video-on-demand setup display 600 is shown
in FIG. 10. Display 600 may include one or more
features relating to on-demand media (e.g., on-demand
videos), such as "Pop-up Feature" option 602, "Provide
Supplemental Content" option 604, "Overlaid onto the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 31 -
Media" option 606, "Without the Media" option 608,
"Full Screen" option 610, and "Letterbox (Widescreen)"
option 612. In this example, display 600 includes
checkboxes 614-624 adjacent to the plurality of
options. However, any other suitable user interface
element may be used. For example, radio buttons,
character fields, or on-screen buttons may be used. In
some embodiments, a user may indicate his or her
selection by placing a checkmark into one of checkboxes
614-624 adjacent to each option. For example,
checkmarks may be placed into checkboxes 614-624 by
highlighting one of the checkboxes with the remote
control and pressing the "OK" key. The interactive
television application may indicate the selection by
displaying a checkmark in the checkbox.
When "Pop-up Feature" option 602 is selected,
the interactive television application may provide
supplemental content in windows that wholly or
partially obscure the on-demand media while the media
is being watched by the user. Alternatively, the
window may be resized so as not to be obscured.
When "Provide Supplemental Content" option
604 is selected, the interactive television application
may supplement the video-on-demand media with suitable
passive or interactive content. For example, video-on-
demand media may be supplemented with text, graphics,
video, audio, animations, software applications, or any
other suitable type of passive or interactive content.
The supplemental content may be concurrently or non-
concurrently displayed with the requested video-on-
demand media. When "Overlaid onto the Media" option
606 is selected, the interactive television application
may overlay supplemental content onto on-demand media.
When "Without the Media" option 606 is selected, the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139
PCT/US01/31516
- 32 -
interactive television application may display
supplemental content outside of the on-demand video
window. For example, supplemental content may be
displayed in the black space that appears when the
video-on-demand media is displayed in letterbox
(widescreen) format. Alternatively, the window may be
resized so as not to be obscured.
When "Full Screen" option 610 and "Letterbox
(Widescreen)" option 612 are selected, the interactive
television application may display on-demand media in
full screen, and letterbox format, respectively.
In some embodiments, video-on-demand setup
options 602-612 as shown in display 600 may be included
with viewer services options 452 as shown in main menu
display 450 (FIG. 5). For example, a user may select
the "Setup" button of display 600. In response to the
user selecting the "Setup" button, the user may be
provided with options similar to those shown in display
600 of FIG. 10.
During playback, the interactive application
may provide supplemental content for the on-demand
media. As shown in FIGS. 12-19, for example, an
interactive guidance application may superimpose
supplemental content onto the on-demand media. In FIG.
11, display 900 shows the selected on-demand media in
letterbox format. Letterbox format may include
darkened regions 902 and 904. Darkened regions 902 and
904 may include buttons 906-914. In response to the
user selecting a button 906-914, the interactive
television application may present the user with
supplemental content related to the on-demand media.
Regions 902 and 904 may also include other content,
such as interactive advertisement 916, logos, mail,
current time, or any other suitable information.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 33 -
The interactive television application may
also display interactive advertisement 916 as part of
display 900. If desired, advertisement 916 may be
passive. Display 900 may also provide a status bar
918. Status bar 918 may include, for ample, the
provider logo, the title of the selected on-demand
media, the time remaining of the media, or any other
suitable information.
In some embodiments, the interactive
television application may provide a non-letterbox
display (not shown). Such a display may include a
video or application window which is superimposed onto
the display. In these embodiments, interactive
advertisements, status bars, supplemental content, or
any other suitable content may be overlaid onto the
video or application window. For example, the
interactive television application may automatically
provide supplemental content based on the user-selected
on-demand media. The supplemental content may be
overlaid onto a window displaying the on-demand media.
Alternatively, the window displaying the on-demand
media ma be resized such that the advertisements,
status bars, supplemental content, or any other
suitable content, do not obscure the on-demand media.
On-screen interface elements, such as buttons
906-914, may provide users with access to supplemental
content. For example, a visual indicator, such as an
icon or any other suitable text or graphic, may appear
on the screen. The visual indicator may represent
interactivity that is available to the user. In
response to the user selecting the visual indicator,
supplemental content may be provided. In some
embodiments, however, the interactive television
application may automatically provide supplemental
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139
PCT/US01/31516
- 34 -
content. The interactive television application may
provide supplemental content based on, for example,
user-defined settings (e.g., setup display), the user-
selected on-demand media, user favorites, or any other
suitable information.
In the example of FIG. 11, display 900
includes "Actor Interviews" button 906, "Cast Info"
button 908, "Play 'Meet the Parents' Trivia" button
910, "Music Videos" button 912, and "Links" button 914.
"Actor Interviews" button 906 may allow the
user to access actor interviews for actors featuring in
the on-demand media that the user is currently
watching. In response to a user selecting button 906,
the interactive television application may present the
user with illustrative display 1000 as shown in FIG.
12. Display 1000 may provide a pop-up window 1002
overlaid onto the video or application. Pop-up window
1002 may be any suitable video or application window.
In other approaches, the supplemental content in pop-up
window 1002 may be displayed in region 902, region 904,
or any other suitable location. Pop-up window 1002 may
also be concurrently or non-concurrently displayed with
the selected on-demand media. For example, the
interactive television application may provide
supplemental content in a pop-up window when a user has
completed viewing the selected on-demand media.
In some embodiments, pop-up window 1002 may
be activated upon user selection. In response to a
user selecting button 906 with the remote control, for
example, pop-up window 1002 may become active, and
provide the user with the actor interview. In the
example of FIG. 12, the user has selected to view the
actor interview with Ben Stiller. The interactive
television application may remove pop-up window 1002 in
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 35 -
response to, for example, a user selecting button 906.
In another approach, pop-up window 1002 may
automatically disappear after the completion of the
actor interview.
In some embodiments, the actor interview
shown in pop-up window 1002 may correspond with the
actor that the user is currently watching. For
example, in a particular scene, Ben Stiller may have a
monologue. In response to a user selecting button 906,
the actor interview displayed in pop-up window 1002 may
be an interview with Ben Stiller. In this example, the
interactive television application is context sensitive
such that it relates the supplemental content to the
current portion of the on-demand media.
In other embodiments, the interactive
television application may provide supplemental content
without pop-up windows. As shown in FIG. 13, for
example, the actor interview alternatively shown in
pop-up window 1002 may instead replace the on-demand
media. The interactive television application may
pause the on-demand media when the actor interview is
provided to allow the user to continue watching the on-
demand media when the actor interview is over. In
other embodiments, the interactive television
application may provide actor interviews or other
supplemental content within regions 902 and 904.
Another type of illustrative supplemental
content is actor information. In response to a user
selecting "Cast Info" button 908 of FIG. 14, for
example, the interactive television application may
provide supplemental content regarding actor
information. In some embodiments, the interactive
television application may provide supplemental content
in pop-up windows 1102. The supplemental content may
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139
PCT/US01/31516
- 36 -
be context sensitive. For example, the interactive
television application may provide information relating
to each actor that the user is currently watching. In
this example, when two characters, such as Ben Stiller
and Teri Polo are shown in a particular scene, pop-up
windows 1102 may provide the names of the characters or
actors. For example, when Ben Stiller enters a scene,
a pop-up window may appear to indicate that the actor
that the user is currently watching is Ben Stiller.
However, any other suitable information may also be
included in pop-up windows 1102. For example, the
interactive television application may also present the
user with actor interviews, such as, for example, the
interview shown in FIGS. 12 and 13, along with other
actor information.
In this example and displays, generally, the
interactive application presents supplemental content
in pop-up windows 1102. In other approaches, the
interactive application may also present supplemental
content in region 902, region 904, or any other
suitable location. The interactive television
application may also concurrently or non-concurrently
display pop-up windows 1102 with the selected on-demand
media.
In some embodiments, pop-up window 1102 may
be activated upon user selection. In response to a
user selecting pop-up window 1002 with the remote
control, for example, pop-up window 1102 may become
active, and provide the user with supplemental content.
The interactive television application may remove pop-
up window 1102 in response to, for example, a user
selecting button 908. In another approach, pop-up
window 1102 may automatically disappear after the
completion of the supplemental content (e.g., the actor
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 37 -
that the user is currently watching exits the
particular scene of on-demand media).
In some embodiments, when the user selects
button 908, the interactive television application may
enter a mode in which pop-up windows 1102 appear and
disappear automatically as scenes change and as actors
enter or exit in the on-demand media. This mode may be
exited and pop-up windows 1102 may be removed when the
user selects button 908.
In some embodiments, when a user selects one
of pop-up windows 1102, the interactive application may
transfer the user to an illustrative display 1200 as
shown in FIG. 15. Display 1200 may include detailed
actor information window 1202, which may include actor
information, such as, for example, character
information, biographical information on the actor,
others movies with that actor, etc. Any other suitable
information relating to the character or the actor may
also be displayed.
In response to a user unhighlighting button
908 by, for example, selecting button 908 with the
remote control, the interactive television application
may transfer the user back to the on-demand media
window and the on-demand media may continue to be
played.
In other embodiments, the interactive
television application may provide supplemental content
without pop-up windows. For example, the interactive
television application may pause the on-demand media
when the supplemental content is provided to allow the
user to continue watching the on-demand media when the
user has completed viewing the supplemental content.
Another suitable type of supplemental content
is interactive media related to the user-selected on-
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 38 -
demand media. Interactive media may include a trivia
game, an interactive quiz, an interactive purchase
opportunity, a survey, or any other suitable media. As
shown in FIG. 16, the interactive television
application provides the user with "Play 'Meet the
Parents' Trivia" button 910. In response to a user
selecting button 910, the interactive television
application may provide the user with interactive
window 1302. As shown, during the viewing of "Meet the
Parents," interactive window 1302 may be provided
within region 904. In this example, interactive window
1302 provides the user with a "Meet the Parents" trivia
game. However, the interactive television application
may provide the user with any other suitable
supplemental content in interactive window 1302. For
example, the interactive television application may
provide the user with a survey relating to the user's
enjoyment of the selected media.
As shown in display 1400 of FIG. 17, the
interactive television application may provide the user
with interactive window 1402 showing the results of the
trivia. Such results may include, for example, the
correct answer, the number of participants, the
distribution of user responses, or any other suitable
information.
Another illustrative type of supplemental
content is music information. As shown in FIG. 18, the
interactive application provides the user with "Music
Videos" button 912. In response to a user indicating a
desire to access music information by, for example,
selecting button 912, the interactive television
application may provide the user with an interactive
window of music information. An illustrative
interactive window of music information 1502 is shown
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 39 -
in FIG. 18. The music information may be context
sensitive. For example, interactive window 1502 may
display media that relates to the music played within
the on-demand media when the user indicates a desire to
access the music information. For example, when
viewing the on-demand media, the user may indicate a
desire to obtain information relating to the song
playing in the background of the selected media by
selecting button 912. The interactive television
application may provide the title of the song, the
artist, a clip of the music video, a picture of the
artist, or any other suitable media in interactive
window 1502.
In response to a user selecting interactive
window 1502, the interactive application may be provide
the user with additional music information in an
interactive window 1602 as shown in FIG. 19.
Interactive window 1602 may display, for example, links
corresponding to the music information in interactive
window 1502. For example, window 1502 may display a
music video of a song by an artist. Window 1602 may
display a link to that artist's official website, a
link to purchase merchandise relating to that artist, a
link to purchase that artist's compact disc, or any
other suitable link.
Supplemental content may include links which
are related to on-demand media. As shown in FIG. 20,
for example, the interactive television application may
provide the user with "Links" button 914. In response
to a user selecting button 914, the interactive
television application may provide interactive window
1702 having one or more selectable links. Selectable
links may include, for example, a link to purchase the
selected media, a link to the official website of the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 40 -
selected media, a link to an actor's homepage, a link
to a website selling merchandise relating to the
selected media, or any other suitable link related to
the selected media. In response to the user selecting
a link, the interactive television application may
transfer the user to, for example, a web site, a third-
party application (e.g., a game, an information
service, etc.), additional passive or interactive
information associated with the media, or any other
suitable supplemental content.
As another example, the interactive
television application may provide the user with access
to a list of titles for on-demand media. In response
to a user selecting a title, the interactive television
application may provide links to other information,
applications, stores of information such as web sites,
or other suitable resource destinations.
FIGS. 21-24 are flowcharts of illustrative
steps involved in providing supplemental content for
on-demand media in accordance with various embodiments
of the present invention. In practice, the steps shown
in FIGS. 21-24 may be performed in any suitable order,
some may be deleted, and others added.
FIG. 21 shows a flow chart of illustrative
steps involved in providing supplemental content with
on-demand media in an interactive television
application system. At step 2105, indications of user-
identified on-demand media are received. On-demand
media may include, for example, audio-on-demand, video-
on-demand, electronic publications (e.g., books,
magazines, newspapers, or any other suitable electronic
publications), electronic games, software applications,
or any other suitable on-demand media. Selecting on-
demand media may include browsing through media
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 41 -
listings. Media listings may include current media,
upcoming media, or any other suitable media.
In response to the user's indication, the
interactive television application may rtrieve
supplemental content related to the selected on-demand
media. For example, a user may be provided with a
media listing. When the user selects a particular on-
demand media selection from the listing, the
interactive television application may provide the user
with an ordering display, as shown in FIG. 9. When the
interactive television application receives an
indication of the user-selected on-demand media, the
interactive television application may retrieve
supplemental content. The steps involved in providing
supplemental content for on-demand media are discussed
below in FIG. 22.
At step 2115, upon the interactive television
application retrieving the supplemental content, the
interactive television application may provide the user
with the selected on-demand media. The steps involved
in providing on-demand media are discussed below in
FIG. 23.
Some embodiments may allow users to watch or
listen to supplemental content while simultaneously
watching on-demand media. At step 2120, the
interactive television application may provide the user
with supplemental content for on-demand media. For
example, in response to the interactive television
application providing the user with on-demand media,
the interactive television application may read the
metadata embedded within the selected on-demand media.
The metadata may direct the interactive television
application to retrieve and locally cache supplemental
content. Such supplemental content may be context
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139
PCT/US01/31516
- 42 -
sensitive. For example, the supplemental content may
relate to a portion of the on-demand media. The steps
involved in providing users with supplemental content
for on-demand media are discussed below in FIG. 24.
It is noted that although the user is shown
as viewing supplemental content and on-demand media
simultaneously, the user may view supplemental content,
view on-demand media, or both.
FIG. 22 is a flowchart of illustrative steps
involved in retrieving supplemental content related to
on-demand media, in accordance with one embodiment of
the present invention. In response to receiving
indications that the user has selected on-demand media,
the interactive television application may retrieve
supplemental content related to on-demand media. At
step 2210, the interactive television application may
determine if the user selected to view the on-demand
media at a predetermined time. For example, the
interactive television application may determine the
scheduled time for the selected on-demand media (e.g.,
immediate playback, playback in two hours, etc.).
At step 2215, if the user has scheduled on-
demand media for immediate viewing, the interactive
television application may download the supplemental
content along with the selected on-demand media (e.g.,
synchronous metadata). Supplemental content, or links
to content, may be provided as, for example,
synchronous metadata. Synchronous metadata is data
that is sent logically at the same time as the media
with which it is associated.
Alternately, at step 2220, the interactive
television application may download supplemental
content prior to viewing the on-demand media. For
example, supplemental content may be provided in-band
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139
PCT/US01/31516
- 43 -
with or separate from the media, out-of-band, using a
carousel-based approach, using a client-server based
approach, using localized caching, using a combination
of these approaches, or using any other suitable
approach. In response to the interactive television
application retrieving supplemental content prior to
viewing the on-demand media, the interactive television
application may store supplemental content in the user
equipment at step 2225. At step 2230, when the
interactive television application retrieves
supplemental content, the interactive television
application may also retrieve information associating
supplemental content with the media (e.g., identifiers,
links, or any other suitable information).
Alternatively, at step 2235, in response to
receiving indications that the user has selected on-
demand media, the interactive television application
may retrieve supplemental content related to on-demand
media from the main facility. The supplemental content
may be downloaded along with the application data.
FIG. 23 is a flowchart of illustrative steps
involved in providing a user with on-demand media, in
accordance with one embodiment of the present
invention. In response to a user request and in
conjunction with retrieving supplemental content
related to the selected on-demand media, the
interactive television application may provide the user
with on-demand media. At step 2310, the interactive
television application may provide the user with
options relating to on-demand media. For example, the
interactive television application may provide the user
with media listings organized by time, organized by
channel, organized by genre, or organized using any
suitable listings feature. The interactive television
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 44 -
application may provide the user with options that
allow the user to direct the interactive television
application to provide displays containing only
on-demand media listings, to provide displays
containing only non-on-demand media listings, or to
provide displays containing both on-demand media
listings and non-on-demand media listings. These
arrangements are merely illustrative examples.
At step 2315, indications of user-selected
options are received. For example, if the users has
selected one of the on-demand media listings from the
list or display as shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, the
interactive television application may provide the user
with ordering displays (as shown in FIG. 9). Ordering
displays may allow the user to view pricing information
for the on-demand media, and may allow the user to
provide a personal identification number (PIN) or other
information that allows the interactive television
application to process the order. In response to the
user purchasing on-demand media, the interactive
television application may provide the user with on-
demand media at step 2320. For example, the
interactive television application may direct media
server 205 to provide a digital video stream of the
selected on-demand media to user television equipment
200.
FIG. 24 is a flowchart of illustrative steps
involved in providing a user with supplemental content
relating to on-demand media, in accordance with one
embodiment of the present invention. In response to
providing the selected on-demand media, the interactive
television application may provide the user with the
corresponding supplemental content. At step 2410, the
interactive television application may provide the user
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139 PCT/US01/31516
- 45 -
with options relating to supplemental content. For
example, the interactive television application may
provide the user with setup displays as shown in FIG.
10. The interactive television application may provide
the user with options relating to the presentation of
supplemental content (e.g., overlaid onto the on-demand
media, displayed in a separate display, etc.).
Upon receiving indications of user-selected
options relating to supplemental content at step 2415,
the interactive television application may determine if
supplemental content is provided as metadata at step
2420. If the metadata contains information associating
supplemental content with on-demand media (e.g.,
identifiers, tags, links, or any other suitable
information), the interactive television application
may read the metadata at step 2425. For example, the
metadata may contain links to supplemental content that
may be context sensitive. At step 2430, the
interactive television application may determine when
the user desires to view the media. For example, the
interactive television application may retrieve a
schedule and determine the playback time associated
with the selected on-demand media. If the user
indicates a desire to view the on-demand media at a
later time, the interactive television application may
locally cache supplemental content to enhance the
response time of the interactive television application
at step 2435. At step 2440, the interactive television
application may display the supplemental content to the
user.
Thus, systems and methods for supplementing
on-demand media are provided. One skilled in the art
will realize that the present invention can be
practiced by other than the described embodiments,
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26
WO 02/32139
PCT/US01/31516
- 46 -
which are presented for purposes of illustration and
not of limitation, and that the present invention is
limited only by the claims which follow.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-06-26