Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
STABLE GEL COMPOSITION HAVING HIGH OIL CONTENT, AND
PREPARATION METHOD THEREFOR AND APPLICATION THEREOF
Technical field
5
The present application generally relates
to a gel composition, and more specifically, to
a stable gel composition with a high oil content. The application also relates
to preparation
method and use of the gel composition.
Background of the Invention
10
Unsaturated fatty acid esters, especially
polyunsaturated fatty acid esters, are important
sources of essential fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acid esters (such as fish
oil, etc.) are
widely used as nutritional supplements at present. However, the taste and
nnouthfeel of
unsaturated fatty acid esters such as fish oil are often unbearable. Thus,
unsaturated fatty
acid esters usually are delivered as forms such as soft capsules. The shell of
such capsules
15
is often made of gelatin from a mammalian
(for example, derived from pigs or cattles).
However, in the prior art, in order to deliver an appropriate dose of oil, the
capsules of the
gel composition generally tend to be prepared in a larger volume, and such a
preparation
process will cause a problem that the capsules are difficult to be swallowed
by young
children and the elderly. In addition, the ingestion process of such capsules
is often
20
accompanied by the problem of the capsule
shell rupturing in the mouth, so that the
unpleasant taste of the capsule oil content is released in the oral cavity,
leaving a negative
impression on the consumers, thereby reducing the initiative to ingest the
capsule.
In recent years, an oil-in-water chewable gel composition has been used in the
fields of
food, medicine and health care products. The aqueous phase of the composition
is gelled
25
and the oil phase contains unsaturated
fatty acid esters or other oil-soluble active substances.
Such gel composition is usually called "oil gel", "gel oil", "structured oil"
or "lipid gel", etc.
1
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
The products on the market are mostly called "fish oil jelly" or "jelly fish
oil". For example,
CN101389310B discloses a chewable emulsion comprising physiologically
tolerable
unsaturated fatty acid esters, which contains 30 to 50wt% of the oil phase
ingredients.
However, the existing "oil gel" or "fish oil jelly" often has the problem of a
relatively
5 low oil content (for example, less than 50wt%), which makes the delivery
efficiency of an
active substance not high. In addition, since a composition with a high oil
content (for
example, an oil content higher than 50wt%) is prone to oil-water separation,
there is a
problem of oil precipitation on the surface of the product during storage.
This results in a
low storage stability of oil gel products and also causes problems such as a
loose texture and
10 a poor chewing feeling.
Therefore, how to increase the oil content in a composition and prepare a
stable gel
composition has become a common problem in this field.
Summary of the invention
15 The inventors have unexpectedly found that a significantly increased
oil content (for
example, to more than 50wt%) and stability of an oil gel product can be
achieved by using a
combination of two gelling agents and stabilizers at a specific ratio, and the
oil precipitation
on the surface caused by the oil-water separation along with the flavor of the
products can
be improved, and the greasy taste during consumption can be reduced. Also, the
texture (such
20 as hardness, elasticity, cohesiveness) of the products is improved, so
as to obtain a
composition with a higher delivery efficiency, an improved stability, and a
better mouthfeel.
In order to solve the above problems, the technical solution in this
application is as
follows: a gel composition, characterized in that, based on the total weight
of the gel
composition, the gel composition comprises: (1) 1 to 15wt% of a first gelling
agent, wherein
25 the first gelling agent is selected from a group consisting of gelatin,
carrageenan, pectin,
konjac gum, and guar gum; (2) 0.1 to 7wt% of a stabilizer, which is a mixture
of 2 to 5wt /0
2
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
of a hydrogenated palm oil, a palm stearin or a beeswax and 0.2 to lwt% of a
phospholipid;
and (3) 55 to 70wt% of an oil other than the hydrogenated palm oil and/or the
palm stearin.
Preferably, the gel composition is in a chewable and edible oil-in-water type.
In one embodiment, the gel composition further includes a second gelling
agent,
5 wherein the second gelling agent is selected from a group consisting of
xanthan gum, agar,
gel Ian gum, locust bean gum, arabic gum, and modified starch.
In one embodiment, the first gelling agent is gelatin, and the second gelling
agent is
xanthan gum.
In one embodiment, the melting point of the hydrogenated palm oil or palm
stearin
10 ranges from 39 C to 65 C.
In one embodiment, the oil is an unsaturated fatty acid or its esters.
In one embodiment, the oil is an animal oil, a vegetable oil, or a combination
thereof.
In one embodiment, the oil is a fish oil, an algae oil or a combination
thereof.
In one embodiment, the gel composition further comprises an additive useful in
15 medicines, foods, or health care products, wherein the additive is one
or more of a sweetener,
an acid regulator, a filler, a flavoring agent, a coloring agent, and an
antioxidant.
In one embodiment, the sweetener is xylitol, and/or sorbitol; the acid
regulator is citric
acid and its salts, and/or nnalic acid; the filler is resistant dextrin,
and/or inulin; the flavoring
agent is an oil-soluble essence, and/or a water-soluble essence; the coloring
agent is an oil-
20 soluble pigment and/or a water-soluble pigment; the antioxidant is
vitamin E, rosemary
extract, and/or polyphenols.
In one embodiment, the aqueous phase of the gel composition further comprises
a
water-soluble active ingredient, wherein the active ingredient is selected
from a group
consisting of a water-soluble vitamin, a water-soluble dietary fiber and a
mineral; and the oil
25 phase of the gel composition further includes an oil-soluble vitamin.
In another aspect, the present invention also provides a method for preparing
the above
3
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
gel composition, comprising:
(1) heating the first gelling agent in water at a temperature between 60 and
80 C until
the first gelling agent completely dissolves;
(2) adding the stabilizer to the oil and mixing them homogeneously;
5 (3) mixing the mixture obtained in the step (1) and the mixture
obtained in the step (2)
at a temperature between 60 C and 80 C homogeneously, and subjecting to
homogenization
and emulsification for 3 to 8 minutes; and
(4) shaping the mixture obtained in the step (3) to obtain the desired gel
composition,
wherein the shaping is achieved by one of the following methods:
10 (a) pouring the mixture obtained in the step (3) to a blister;
(b) filling the mixture obtained in the step (3) into a capsule; and
(c) packaging the mixture obtained in the step (3) in a packaging material,
wherein the
packaging material comprises one or more of an aluminum-plastic composite
pouch and a
packaging container made of a thernnoresistant material.
15 In one embodiment, the method comprises the following steps after
the homogenization
and emulsification in the step (3): adding a second gelling agent; then
subjecting to
homogenization and emulsification for 7 to 15 minutes; wherein the second
gelling agent is
one or more of xanthan gum, agar, gel Ian gum, locust bean gum, acacia gum,
and modified
starch.
20 In another aspect, the present invention also provides an edible
composition, which
comprises the above-mentioned gel composition.
In one embodiment, the edible composition is a food, medicine or health care
product.
In order to solve the above problems, the present application also provides a
stable
chewable gel composition with a high oil content, wherein an aqueous phase is
gelled and
25 may contain an active substance, and wherein an oil phase contains a
biologically active
ingredient such as an unsaturated fatty acid or its ester and/or an oil-
soluble active ingredient.
4
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
In one aspect, the active substance in the aqueous phase is a water-soluble
active ingredient,
and more preferably, the active ingredient is selected from a group consisting
of a water-
soluble vitamin, a water-soluble dietary fiber, a mineral or mixtures thereof.
In another aspect,
the oil-soluble active ingredient in the oil phase is selected from a group
consisting of oil-
5 soluble vitamins.
In one embodiment of the present application, a gel composition is provided.
Based on
the total weight of the gel composition, the gel composition contains: (1) 55
to 70wt% of an
oil; (2) 1 to 15wt% of a first gelling agent; (3) 0.1 to 2wt% of a second
gelling agent; and (4)
0.1 to 7wt% of a stabilizer; (5) optionally, other additives useful in a
medicinal, food and/or
10 health care product; and (6) wherein the balance is water.
In one aspect, the first gelling agent is selected from a group consisting of
gelatin,
carrageenan, pectin, konjac gum, guar gum and other gelling agents and the
combination
thereof. Preferably, the first gelling agent is
gelatin, gelatin and pectin, carrageenan and
konjac gum, or carrageenan. Preferably, the mass ratio of gelatin to pectin
ranges from 2:1
15 to 12:1. Preferably, the mass ratio of konjac gum to carrageenan ranges
from 1:4 to 3:1.
In another aspect, the second gelling agent is selected from a group
consisting of
xanthan gum, agar, gellan gum, locust bean gum, acacia gum, modified starch
and other
gel ing agents and any combination thereof. Preferably, the second gelling
agent is xanthan
gum, arabic gum, arabic gum and modified starch, locust bean gum, or gellan
gum.
20 Preferably, the mass ratio of arabic gum to modified starch ranges from
3:1 to 5:1.
In yet another aspect, the stabilizer is selected from a group consisting of
palm oil
(which is formed by a processing method selected from a group consisting of
hydrogenation,
refining, transesterification, and fractionation and is a palm oil product
having a melting
point of 39 to 65 C), phospholipid, phytosterol, edible waxes and other
substances with
25 similar effects and any combination thereof. Preferably, the stabilizer
is selected from a
group consisting of hydrogenated palm oil, palm stearin, beeswax, phospholipid
and a
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
mixture thereof. In one aspect, the stabilizer is a mixture of hydrogenated
palm oil, palm
stearin or beeswax and phospholipid, for example, a mixture of hydrogenated
palm oil and
phospholipid.
For example, the stabilizer
is a mixture of hydrogenated palm oil and
phospholipid at a mass ratio of 3 to 15:1. Preferably, based on the total
weight of the gel
5 composition, the phospholipid ranges from 0.2 to 1 wt %.
In still another aspect, the oil is selected from a group consisting of an oil
containing an
unsaturated fatty acid or esters thereof.
Preferably, the oil is
selected from a group
consisting of an animal oil, a vegetable oil and combinations thereof. More
preferably, the
oil is selected from a group consisting of a fish oil, an algae oil, and
combinations thereof.
10 In a further aspect, the oil may also optionally contain one or more
other additives useful in
a medicine, food, and health care product. Preferably, the biologically active
is the oil-
soluble vitamin E etc.
In still another aspect, the one or more other additives comprise one or more
components selected from a group consisting of a sweetener selected from a
group consisting
15 of xylitol, sorbitol and other alditols; an acid regulator selected from
a group consisting of
citric acid and its salts, nnalic acid and other acid regulators; a filler
selected from a group
consisting of resistant dextrin, inulin and other fillers; a flavoring agent
selected from a group
consisting of an oil-soluble essence, a water-soluble essence and other food
essences; a
coloring agent selected from a group consisting of a food grade pigment or a
coloring fruit
20 and vegetable juice such as an oil-soluble pigment and a water-soluble
pigment; and an
antioxidant selected from a group consisting of vitamin E, rosemary extract,
polyphenol and
other antioxidants.
In still another aspect, the gel composition is an oil-in-water gel emulsion,
wherein the
aqueous phase is gelled and contains an active ingredient and wherein the oil
phase contains
25 an unsaturated fatty acid or esters thereof and/or an oil-soluble active
ingredient.
Preferably, the active ingredient in the aqueous phase is a water-soluble
active ingredient,
6
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
for example selected from a water-soluble vitamin, a water-soluble dietary
fiber, a mineral
or a combination thereof. Preferably, the oil-soluble active ingredient in the
oil phase is
selected from an oil-soluble vitamin.
In still yet another aspect, the gel composition is in an oral form, such as a
chewable
5 form.
In another embodiment of the present application, a method for preparing the
gel
composition as described above is also provided.
In one aspect, the method includes: (1) heating the first gelling agent in
water at a
temperature between 60 and 80gC until the first gelling agent completely
dissolves; (2)
10 adding the stabilizer to the oil and mixing them homogeneously; (3)
mixing the mixture
obtained in the step (1) and the mixture obtained in the step (2) at a
temperature between
60 C and 80 C homogeneously, and subjecting to homogenization and
emulsification for 3-
8 minutes, adding the second gelling agent, then subjecting to homogenization
for 7 to 15
minutes; and (4) shaping the mixture obtained in the step (3) to obtain the
desired gel
15 composition. Preferably, the shaping comprises one of the following
methods:
(a) pouring the mixture obtained in the step (3) to a blister;
(b) filling the mixture obtained in the step (3) into a capsule; and/or
(c) packaging the mixture obtained in the step (3) in a packaging material,
preferably
wherein the packaging material comprises one or more of an aluminum-plastic
composite
20 pouch and a packaging container made of a thernnoresistant material.
In yet another embodiment of the present application, the use of the gel
composition as
described above in a food, medicine or health care product is also provided.
In another aspect, the present invention also provides an edible composition,
which
comprises the above-mentioned gel composition.
25 In one embodiment, the edible composition is a food, medicine or
health care product.
7
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Description of the drawings
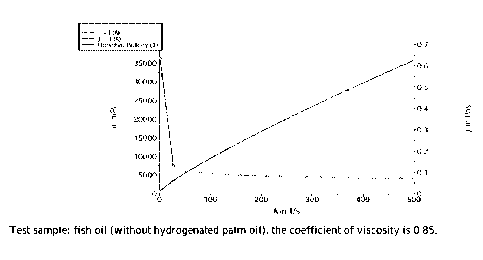
Fig. 1 shows a test sample of a fish oil (no hydrogenated palm oil) with a
viscosity
coefficient of 0.85.
Fig. 2 shows a test sample of fish oil + hydrogenated palm oil with a
viscosity
5 coefficient of 1.03.
Detailed description of the invention
For the purpose of the detailed description below, it is to be understood that
various
alternative changes to a component and sequences of steps may be adopted in
this application,
10 unless indicated to the contary. In addition, unless in any working
examples, or where
otherwise indicated, all numbers representing quantities of ingredients used
in, for example,
the specification and claims should be understood as being modified by the
term "about" in
all cases. Therefore, unless indicated to the contrary, the numerical
parameters set forth in
the following specification and claims are approximate values that vary
according to the
15 desired performance to be obtained in this application and at least is
not intended to limit the
application of the principle of equivalence to the scope of the claims. Each
numerical
parameter should at least be interpreted based on the number of significant
figures reported
and through the application of ordinary rounding techniques.
Although the numerical ranges and parameters set forth in the broad range of
this
20 application are approximate values, the numerical values listed in the
specific examples are
reported as accurately as possible. However, any numerical value inherently
contains certain
errors that inevitably result from the standard deviation found in its
respective test
measurement.
In addition, it is to be understood that any numerical range described herein
is intended
25 to include all sub-ranges subsumed therein. For example, the range of "1
to 10" is intended
to include all sub-ranges between (and including) the minimum value of 1 and
the maximum
8
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
value of 10, that is, having a minimum value equal to or greater than 1 and a
maximum value
equal to or less than 10.
In this application, unless expressly stated otherwise, the use of the
singular includes
the plural and the plural includes the singular. In addition, in this
application, unless
5 expressly stated otherwise, the use of "or" means "and/or", even if
"and/or" can be used
explicitly in some cases. In addition, in this application, unless expressly
stated otherwise,
the use of "a" or "an" means "at least one."For example, "a" polymer, "a"
composition, etc.
refer to any one or more of these items.
In one embodiment of the present application, a chewable and edible oil-in-
water gel
10 composition is provided. In another embodiment of the present
application, a stable
chewable gel composition with a high oil content is provided.
As used herein, the term "oil" has the conventional meaning in the
pharmaceutical, food,
and health care product industries, namely, fatty acid triglycerides. The oils
that can be used
in the gel composition of the present application can be various oils commonly
used in the
15 fields of medicine, food and health care products, such as vegetable oil
or animal oil or a
mixture thereof. In one aspect, the oil used in the gel composition of the
present application
is an oil rich in an unsaturated fatty acid or its esters, and more
preferably, a fish oil and/or
an algae oil. In a further aspect, the oil may also contain one or more
biologically active
ingredients that can be used in foods, medicines and/or health care products.
As used herein,
20 the term "biologically active ingredient" refers to an ingredient
capable of exerting a certain
effect on an organism. The biologically active ingredient that can be used in
the gel
composition of the present application include, but are not limited to an oil-
soluble vitamin
and the like.
As used herein, the term "high oil content" refers to a product having an oil
content of
25 50Wt% or more. For example, the high oil content can refer to a product
having 55wt% or
more, 60wt% or more, 65wt% or more up to 70wt% or less, 75wt% or less, 80wt%
or less,
9
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
85wt% or less, 90wt% or less, 95wt% or less, or even 100wt% or less of oil
content. In the
embodiment of the present application, preferably, the gel composition has an
oil content of
50wt% to 80wt%. More preferably, the gel composition has an oil content of
55wt% to
70wt%. The above weight percentages are based on the total weight of the gel
composition.
5 In one embodiment of the present application, the oil-in-water gel
composition contains an
oil other than hydrogenated palm oil and/or palm stearin. Preferably, the oil
content ranges
from 55to 70wt%.
As used herein, the term "stable" means that a product will not undergo oil-
water
separation during a relatively long storage time (for example, 1 year or more,
preferably 2
10 years or more). The "stable" gel composition as described in this
application will not exhibit
oil-water separation within the specified shelf life or more of a medicine,
food or health care
product, for example, and there will be notoil precipitation on the surface.
Greasy taste
may not be felt when such a gel composition is taken, and therefore the
product flavor is
improved. In addition, such a gel composition can also have an improved
texture (such as
15 hardness, elasticity, and cohesiveness, etc.) over a long period of
tinne, thereby providing a
better mouthfeel.
As used herein, the term "chewable" has its conventional meaning in the
pharmaceutical,
food, and health care product industries. In the embodiment of the present
application, the
gel composition exists in a form that can be broken or disrupted by chewing.
The chewable
20 gel composition as described in this application can be used in a
nutritional supplement, for
example, as or used in a medicine, food or health care product. Preferably,
the gel
composition described in the present application is the so-called "fish oil
jelly" or "jelly fish
oil".
As used herein, the term "gel" refers to a special semi-solid state
transformed from a
25 solution or sol under a certain condition (such as by the use of a
gelling agent), in which a
network structure filled with liquid as a dispersion medium in the structural
voids is formed
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
spatially by the use of a gelling agent. As used herein, the term "gelling
agent" refers to an
agent capable of gelling a solution or sol. In the embodiment of the present
application, the
gel composition is an "oil-in-water" type gel emulsion formed by using a
specially selected
gelling agent, in which the aqueous phase is gelled as the continuous phase
and the oil phase
5
as the discontinuous phase dispersed in
the structural voids of the continuous phase. Suitable
gelling agents are well known in the food, pharmaceutical and nutraceutical
industries and
are capable of solution/sol-gel conversion, including but not limited to
gelatin, xanthan gum,
carrageenan, pectin, konjac, acacia gum, locust bean gum, agar, gellan gum or
a mixture of
gelling agents, etc.
10
In one aspect of the present application,
a chewable and edible oil-in-water gel
composition is provided, which comprises a first gelling agent. In one
embodiment, the
chewable and edible oil-in-water gel composition further comprises a second
gelling agent
selected from xanthan gum, agar, gellan gum, locust bean gum, arabic gum, and
modified
starch.
15
In one aspect of the present application,
a gel composition is provided, which includes
a gelling agent, and the gelling agent may be a combination of the first
gelling agent and the
second gelling agent.
In various aspects of the present invention, the first gelling agent may be
selected from
gelatin, carrageenan, pectin, konjac gum, guar gum, and other gelling agents
and mixtures
20
thereof. Preferably, the first gelling
agent may be gelatin, for example, gelatin that can be
prepared from collagen of any mammal or collagen of any aquatic species.
Preferably, the
first gelling agent is gelatin and pectin, carrageenan and konjac gum, or
carrageenan.
Preferably, the mass ratio of gelatin to pectin ranges from 2:1 to 12:1.
Preferably, the mass
ratio of konjac gum to carrageenan ranges from 1:4 to 3:1. Based on the total
weight of the
25
gel composition, the first gelling agent
may be 1 to 15wt%, preferably 2 to 12wt%. The
second gelling agent may be selected from xanthan gum, agar, gellan gum,
locust bean gum,
11
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
arabic gum, modified starch and other gelling agents, and mixtures thereof.
Preferably, the
second gelling agent may be xanthan gum, arabic gum, arabic gum and modified
starch,
locust bean gum, or gellan gum. Preferably, the mass ratio of arabic gum to
modified starch
ranges from 3:1 to 5:1. Based on the total weight of the gel composition, the
second gelling
5 agent may be 0.1 to 2wW0, preferably 0.2 to 1.0wW0. Preferably, the
gelling agent used in
the gel composition of the present application is a combination of gelatin and
xanthan gum,
a combination of gelatin, gum acacia and modified starch, a combination of
gelatin, pectin
and gum acacia, a combination of carrageenan, konjac gum and locust bean gum,
and the
combination of carrageenan and gellan gum. Such a combination of gelling
agents has the
10 effects of significantly improving the water holding capacity of the
composition and
stabilizing the oil-water interface, thereby improving oil-water separation.
As used herein, the term "stabilizer" refers to an additive that has been
found
experimentally to be used in a formulation to improve the stability of the
composition (such
as light stability, thermal stability, storage stability), etc. For example,
it has been found
15 experimentally that hydrogenated palm oil has the effect of curing oils,
and its effect can be
tested by viscosity testing with a rotary rheometer. The results show that
hydrogenated palm
oil may increase the viscosity of the oil, thereby improving the stability of
the oil in the
system. The viscosity coefficient of a fish oil
(without adding hydrogenated oil) is
determined to be 0.85, and the viscosity coefficient of a fish oil plus
hydrogenated palm oil
20 is 1.03 (the test spectrum is shown in Figs 1 and 2). Specifically, the
Hack Rotational
Rheometer is used for viscosity measurement, in which the temperature is set
to 25 C and
CR mode (controlling shear rate) is used. The test sample is placed on the
test platform. The
viscosity is measured according to the set parameters. The test sample is
sheared by rotating
using a test probe. The value is determined by a force-sensing element and
transmitted to a
25 software to display a shear stress corresponding to the shear rate in a
quantified form. The
sample used in Fig. 1 is a pure fish oil, and the sample used in Fig. 2 is a
homogeneous
12
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
mixture of a fish oil + 5% hydrogenated palm oil heated and dissolved at a
temperature
between 60 C and 80 C and cooled. Viscosity is measured by the above method.
The X axis
represents the shear rate, the Y1 axis represents the shear stress, and the Y2
axis represents
the viscosity. The viscosity coefficients of the two samples are obtained by
fitting a curve.
5 The larger the value, the higher the corresponding viscosity.
In the embodiment of the present application, the stabilizer that can be used
in the gel
composition of the present application can be selected from palm oil (which is
formed by a
processing method selected from a group consisting of hydrogenation, refining,
transesterification, and fractionation and is a palm oil product having a
melting point of 39
10 to 65 C), phospholipid, phytosterol, edible waxes and other substances
with similar effects
and any combination thereof. Preferably, the stabilizer is selected from
hydrogenated palm
oil, palm stearin, phospholipid, beeswax and mixtures thereof. More
preferably, the stabilizer
is a mixture of hydrogenated palm oil, palm stearin, or beeswax and
phospholipid. For
example, the stabilizer may be a mixture of hydrogenated palm oil and
phospholipid. In one
15 aspect, the stabilizer may be a mixture of hydrogenated palm oil, palm
stearin, or beeswax
and phospholipid in a mass ratio of 3 to 15:1. Preferably, the stabilizer used
in the present
application is a mixture of (hydrogenated palm oil or palm stearin or
beeswax):phospholipid
in a mass ratio of (5 to 10):1. For example, without limitation, the
phospholipid is in the
range of 0.2 to 1wt% based on the total weight of the gel composition.
Alternatively, based
20 on the total weight of the gel composition, hydrogenated palm oil, palm
stearin or beeswax
is in the range of 2 to 5wt%, for example, 2wt%, 2.5wt%, 3wt%, 3.5wt%, 4wt% ,
4.5wt%.
The effect of solidifying the oil may be achieved by such a stablizer which
may have a
significant role in the stability of the oil, thereby improving the stability
of the gel
composition. In addition, the use of phospholipid in the gel composition can
also improve
25 the fluidity of the composition.
In one embodiment, the oil-in-water gel composition contains 0.1 to 7wt% of a
13
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
stabilizer. In one embodiment, the stabilizer is a mixture of 2 to 5wt% of
hydrogenated palm
oil, palm stearin or beeswax and 0.2 to 1wt% of phospholipid.
The gel composition of the present application may optionally contain other
additives
that can be used in a medicine, food and/or health care product, including but
not limited to
5 a sweetener, an acid regulator, a filler, a flavoring agent, a coloring
agent, and an antioxidants,
etc.
In one aspect, the sweetener may be selected from xylitol, sorbitol, and other
alditols.
Preferably, the sweetener may make up 10 to 30wt% of the total weight of the
gel
composition.
10 In another aspect, the acid regulator may be one or more of citric
acid and its salts, malic
acid, and other acid regulators. Preferably, the acid regulator may make up
0.05-0.5wt% of
the total weight of the gel composition.
In yet another aspect, the filler may be selected from resistant dextrin, inul
in, and other
fillers. Preferably, the filler may make up 0 to 5% of the total weight of the
gel composition.
15 In yet another aspect, the flavoring agent may be a flavor, for
example selected from an
oil-soluble essence, a water-soluble essence, and other food essences.
Preferably, the
flavoring agent may make up 0 to 5wt% of the total weight of the gel
composition.
In still another aspect, the colorant may be a food-grade pigment or a colored
fruit and
vegetable juice, for example, selected from a food-grade pigment such as oil-
soluble
20 pigments and water-soluble pigments. Preferably, the colorant may make
up 0 to 0.5wt% of
the total weight of the gel composition.
In yet another aspect, the antioxidant may be selected from vitamin E,
rosemary extract,
polyphenol, and other antioxidants. Preferably, the antioxidant may make up 0
to 0.5wt% of
the total weight of the gel composition.
25 In the embodiment of the present application, the gel composition
further includes water
to make up the gel composition to 100wt%, that is, the balance is water. In
one aspect, for
14
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
example without limitation, water makes up10 to 30wt% of the total weight of
the gel
composition.
In another embodiment of the present application, a method for preparing the
above-
mentioned chewable and edible oil-in-water gel composition is also provided.
The gel
5 composition can be prepared by a method in which the first gelling agent,
stabilizer and oil
are mixed homogeneously and the resulting mixture is shaped.
In one aspect, the preparation method includes:
(1) heating the first gelling agent in water at a temperature between 60 and
80gC until
the first gelling agent completely dissolves;
10 (2) adding the stabilizer to the oil and mixing them homogeneously;
(3) mixing the mixture obtained in the step (1) and the mixture obtained in
the step (2)
at a temperature between 60 C and 80 C homogeneously, and subjecting to
homogenization
and emulsification for 3 to 8 minutes; and
(4) shaping the mixture obtained in the step (3) to obtain the desired gel
composition,
15 wherein the shaping is one of the following methods:
(a) pouring the mixture obtained in the step (3) to a blister;
(b) filling the mixture obtained in the step (3) into a capsule; and
(c) packaging the mixture obtained in the step (3) in a packaging material,
wherein the
packaging material comprises one or more of an aluminum-plastic composite
pouch and a
20 packaging container made of a thernnoresistant material.
The preparation method may further include the following operations after
homogeneous emulsification in step (3): adding a second gelling agent; then
subjecting to
homogenization and emulsification for 7 to 15 minutes; wherein the second
gelling agent is
selected from xanthan gum, agar, gellan gum, locust bean gum, arabic gum, and
modified
25 starch.
In another embodiment of the present application, a method for preparing the
gel
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
composition as described above is also provided. The gel composition can be
prepared by a
method in which the first gelling agent, stabilizer and oil are mixed
homogeneously, the
second gelling agent is then added and mixed homogeneously and the resulting
mixture is
shaped.
5 In one aspect, the preparation method includes:
(1) heating the first gelling agent in a suitable amount of water to
completely dissolve
the first gelling agent which is kept warm for use;
(2) adding the stabilizer to the oil and mixing them homogeneously which are
kept
warm for use;
10 (3) mixing the mixtures obtained in the step (1) and the step (2)
at a temperature between
60 C and 80 C homogeneously, and subjecting to homogenization and
emulsification with
a homogenizer for about 5 to 10 minutes; adding the second gelling agent and
subjecting to
homogenization and emulsification for about 10 to 15 minutes; and
(4) shaping the mixture obtained in the step (3) to obtain the desired gel
composition.
15 In a further aspect, the preparation method includes:
(1) heating the first gelling agent and optionally a sweetener, an acid
regulator, a
colorant, a water-soluble flavoring agent in a suitable amount of water at a
temperature
between 60 and 80 C until the first gelling agent completely dissolves and
keeping the
mixture warm for use;
20 (2) adding the stabilizer and optionally an antioxidant and an oil-
soluble flavoring agent
to the oil and mixing them homogeneously which are kept warm for use;
(3) adding the mixture obtained in the step (2) to the mixture obtained in the
step (1)
and mixing them at a temperature between 60 C and 80 C homogeneously, and
subjecting
to homogenization and emulsification with a homogenizer for 5 to 10 minutes;
adding the
25 second gelling agent and subjecting to homogenization for 10 to 15
minutes;
(4) shaping the mixture obtained in the step (3) to obtain the desired gel
composition,
16
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
wherein the shaping in the step (4) may comprise one of the following methods:
(a) pouring the mixture obtained in the step (3) to a blister;
(b) filling the mixture obtained in the step (3) into a capsule; and/or
(c) packaging the mixture obtained in the step (3) in a packaging material.
5
Preferably, the packaging material
comprises one or more of an aluminum-plastic
composite pouch and a packaging container made of a thermoresistant material.
In another embodiment of the present application, the use of the gel
composition as
described above in a food, medicine or health care product is also provided.
The food,
medicine or health care product may be in a chewable form.
10
The application will be further explained
in detail below with reference to the examples.
However, those skilled in the art should understand that these examples are
provided for
illustrative purposes only, and are not intended to limit the application.
Examples
15
The embodiments of the present application
will be described in detail below in
conjunction with examples, but those skilled in the art will understand that
the following
examples are only used to illustrate the present application, and should not
be regarded as
limiting the scope of the present application. If specific conditions are not
indicated in the
examples, it shall be carried out in accordance with the conventional
conditions or the
20
conditions recommended by the manufacturer.
When the manufacturer is not indicated in the
examples, the reagents or instruments used are all conventional products that
can be
purchased commercially. Unless otherwise indicated, all amounts listed are
described in
parts by weight based on the total weight. This application should not be
interpreted as being
limited to the working examples described.
Preparation method:
17
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
1. Aqueous phase: heating xylitol, sorbitol, potassium citrate, resistant
dextrin, and the
first gelling agent (e.g., gelatin, carrageenan) with an appropriate amount of
water at 60 C
until the first gelling agent completely dissolves;
2. Oil phase: adding mixed tocopherol, lemon essence, hydrogenated palm oil,
and
5
phospholipid to an oil (for example, fish
oil), mixing themhomogeneously and keeping them
warm at 60 C for use;
3. Adding the oil phase to the aqueous phase, stiring them homogeneously,
homogenizing them at 60 C in a homogenizer for 10 minutes, and pouring the
resulting
composition onto a blister for shaping; or after homogenization, further
adding a second
10
gelling agent (for example, xanthan gum,
arabic gum), homogenizing for 10 minutes, and
pouring the resulting composition onto a blister for shaping.
According to the above preparation method, the gel compositions 1 to 25 were
prepared,
and the specific components are listed in Table 1 below.
Test Method:
Texture test:
The texture test was performed on the prepared gel composition using a texture
analyzer
according to the TPA method. 20 parallel samples of each gel composition were
taken, and
20
the average of the measured values was
taken as the measurement result. The results are
reported in Table 1 below.
The texture test was performed as described below.
1. A texture analyzer was used to perform the texture test by the TPA method
(texture
profile analysis), which is a general method for testing texture
characteristics in the industry,
25
also known as the secondary chewing test,
using the test probe to secondary compress
samples. The index was quantified by a force sensing element.
2. Testing process: The sample was placed in the middle of the test bench. The
TPA
method was selected and the test button was started to perform the test. The
parallel test was
repeated with 20 samples.
30
3. Data processing: The test results of
each sample were recorded by the force sensing
element of the instrument and then processed by software and finally presented
as specific
values. The average value of indicators for 20 parallel samples was taken as
the result output,
which was scored and evaluated.
18
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Oil precipitation test:
A centrifuge was used to test the degree of oil precipitation of the obtained
gel
composition. The emulsion of the same amount was taken and centrifuged at a
high speed
for layering. The precipitated oil layer was separated and weighed. 3 parallel
samples of
5 each gel composition were taken and the average of the measured values
was used as the
measurement result. The results were reported in Table 1 below.
The oil precipitation test was carried out as follows:
1. Test conditions. The instrument was a centrifuge which was hold at a
temperature of
55 C. The speed was set to 8000rpm, and the centrifugation time was 5min;
10 2. Measurement process. A certain amount of emulsion before shaping
was weighted
and into a centrifuge tube, and the total weight of the emulsion and the
centrifuge tube was
recorded. Then, the same amount of water was added to the centrifuge tube
which was
placed symmetrically in the centrifuge. The centrifugation was performed under
the above
test condition. After centrifugation, the upper layer of oil was taken using a
pipette and then
15 the centrifuge tube and the remaining emulsion were weighted. The weight
was determined
in triplicate.
3. Data processing: The amount of oil precipitation was the difference between
the total
weight before centrifugation and the total weight after centrifugation. The
amount of oil
precipitation was converted to a value in g/10g of the gel composition. The
data of 3 parallel
20 samples were used as the result outputs which were used to perform
scoring test.
The test data of the texture test and the oil precipitation test of the tested
gel composition
were scored and were all represented as a score. Finally, the scores were
summed to
comprehensively evaluate the effects of each composition in the Examples with
the total
score.
25 Hardness (g): <6500 was counted as 1 point; 6500 to 6999 as 2
points; 7000 to 7499 as
3 points; 7500 to 7999 as 4 points; 8000 to 8499 as 5 points; 8500 to 8999 as
4 Points; 9000
to 9499 as 3 points; 9500 to 9999 as 2 points; and >10000 as 1 point.
Elasticity: <0.60 was counted as 1 point; 0.60 to 0.69 as 2 points; 0.70 to
0.79 as 3
points; 0.80 to 0.89 as 4 points; 0.90 to 0.99 as 5 points; 1.00 to 1.09 as 4
points; 1.10 to 1.19
30 as 3 points; 1.20 to 1.29 as 2 points; and 1.30 to 1.39 as 1 point.
Cohesiveness: <0.50 was counted as 1 point; 0.50 to 0.59 as 2 points; 0.60 to
0.69 as 3
points; 0.70 to 0.79 as 4 points; 0.80 to 0.89 as 5 points; 0.90 to 0.99 as 4
points; 1.00 to 1.09
as 3 points; 1.10 to 1.19 as 2 points; 1.20 to 1.29 as 1 point.
19
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Oil precipitation (g/10g): >0.90 was counted as 1 point; 0.80 to 0.89 as 2
points; 0.70
to 0.79 as 3 points; 0.6 to 0.69 as 4 points; <0.6 as 5 points.
Table 1: The contents of the components and test results of the gel
compositions and the
comparative composition according to the application
Composition
1 2 3
4 5 6 7
No.
gelatin 4 4 4
4 4 4 4
xyl itol 8 8 8
8 8 8 8
sorbitol 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
fish oil 55 55 55
55 55 55 55
vitamin E 0.3 0.3 0.3
0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3
citric acid
0.05 0.05 0.05
0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
monohydrate
lemon essence 0.2 0.2 0.2
0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2
resistant
0.5 0.5 0.5
0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5
dextrin
water 29.75 28.95 29.95
27.95 23.95 26.15 29.75
xanthan gum 0.2 1.0 0
0 0 0.4 0
hydrogenated
0 0 0
2 6 3 0
palm oil
phosphol ipid 0 0 0
0 0 0.4 0.2
beeswax 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
palm stearin 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
Glyceryl
0 0 0
0 0 0 0
M onostea rate
Hardness 3 3 3
3 3 5 3
Elasticity 4 3 2
3 3 5 3
Cohesiveness 3 4 2
3 3 5 2
Oil 2 2 1
3 4 5 3
precipitation
composite 12 12 8
12 13 20 11
score
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Table 1 (continued): The contents of the components and test results of the
gel compositions
and the comparative composition according to the application
Composition
8 9 10
11 12 13 14
No.
gelatin 4 4 4
4 4 4 4
xylitol 8 8 8
8 8 8 8
sorbitol 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
fish oil 55 55 55
55 60 70 55
vitamin E 0.3 0.3 0.3
0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3
citric acid
0.05 0.05 0.05
0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
monohydrate
lemon essence 0.2 0.2 0.2
0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2
resistant dextrin 0.5 0.5 0.5
0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5
water 28.95 26.55 29.15
26.55 21.15 11.15 27.55
xanthan gum 0 0 0.4
0.4 0.4 0.4 0
hydrogenated
2
0 3 0
3 3 3
palm oil
beeswax 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
palm stearin 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
phospholipid 1.0 0.4 0.4
0 0.4 0.4 0.4
Glyceryl
0
0 0 0
0 0 0
Monostearate
Hardness 3 4 4
4 5 5 4
Elasticity 2 4 4
3 5 5 4
Cohesiveness 3 4 4
4 5 5 3
Oil precipitation 3 4 3
4 4 4 4
composite score 11 16 15
15 19 19 15
Table 1 (continued): The contents of the components and test results of the
gel compositions
and the comparative composition according to the application
21
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Composition 15 16 17
18 19 20 21
No.
gelatin 4 4 4
4 4 4 4
xyl itol 8 8 8
8 8 8 8
sorbitol 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
fish oil 55 55 55
55 55 55 55
vitamin E 0.3 0.3 0.3
0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3
citric acid
0.05 0.05 0.05
0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
monohydrate
lemon essence 0.2 0.2 0.2
0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2
resistant 0.5 0.5 0.5
0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5
dextrin
water 25.65 27.25 29.55
26.95 29.55 27.75 27.95
xanthan gum 0 0 0.4
0 0 0 0
hydrogenated 4 2 0
3 0 2 0
palm oil
phosphol ipid 0.3 0.7 0
0 0.4 0.2 0
beeswax 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
palm stearin 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
Glyceryl 0 0 0
0 0 0 2
M onostea rate
Hardness 3 3 3
3 3 4 2
Elasticity 4 3 4
3 3 3 2
Cohesiveness 2 2 3
3 3 4 2
Oil 4 4 3
4 3 4 1
precipitation
composite 13 13 13
13 12 15 7
score
Table 1 (continued): The contents of the components and test results of the
gel compositions
and the comparative composition according to the application
22
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Composition 22 23 24
25 26 27 28
No.
gelatin 4 4 4
4 4 4 4
xyl itol 8 8 8
8 8 8 8
sorbitol 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
fish oil 55 55 55
55 55 60 70
vitamin E 0.3 0.3 0.3
0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3
citric acid
0.05 0.05 0.05
0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
monohydrate
lemon essence 0.2 0.2 0.2
0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2
resistant 0.5 0.5 0.5
0.5 0.5
0.5
0.5
dextrin
water 24.55 26.15 22.35
24.75 25.15 20.15 10.15
xanthan gum 0.4 0.4 0.4
0.6 0.4 0.4 0.4
hydrogenated 3 0 6
4 0 0 0
palm oil
phosphol ipid 2 0.4 1.2
0.6 0.4 0.4 0.4
beeswax 0 0 0
0 4 4 4
palm stearin 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
Glyceryl 0 3 0
0 0 0 0
M onostea rate
Hardness 2 4 2
4 4 4 4
Elasticity 3 4 2
5 5 5 5
Cohesiveness 2 4 3
5 4 4 4
Oil 3
5 4 4
2 2
5
precipitation
composite 9 15 9
19 18 17 17
score
Table 1 (continued): The contents of the components and test results of the
gel compositions
and the comparative composition according to the application
23
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Composition 29
30 31
No.
gelatin 4
4 4
xylitol 8
8 8
sorbitol 2
2 2
fish oil 55
60 70
vitamin E 0.3
0.3 0.3
citric acid 0.05
0.05 0.05
monohydrate
lemon essence 0.2
0.2 0.2
resistant 0.5
0.5 0.5
dextrin
water 26.15
21.15 11.15
xanthan gum 0.4
0.4 0.4
hydrogenated 0
0 0
palm oil
phospholipid 0.4
0.4 0.4
beeswax 0
0 0
palm stearin 3
3 3
Glyceryl 0
0 0
M onostea rate
Hardness 5
5 4
Elasticity 5
5 5
Cohesiveness 4
4 4
Oil
4
4
4
precipitation
composite 18
18 17
score
Table 1 (continued): The contents of the components and test results of the
gel compositions
and the comparative composition according to the application
24
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Composition 32 33 34
35 36 37 38
No.
gelatin 1 15 8
2 2 6 0
carrageenin 0 0 0
0 0 0 0.5
acacia gum 0 0 0.5
1.5 2 0.5 0
modified 0 0 0.1
0.5 0
0
0
starch
gellan gunn 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
locust bean 0 0 0
0 0
0
2
gum
pectin 0 0 0
0 1 0.5 0
konjak gum 0 0 0
0 0 0 1.5
xylitol 8 8 8
8 8 8 8
sorbitol 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
fish oil 60
60 60
60 60 60 60
vitamin E 0.3 0.3 0.3
0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3
citric acid
0.05 0.05 0.05
0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
monohydrate
lemon essence 0.2 0.2 0.2
0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2
resistant 0.5 0.5 0.5
0.5 0.5
0.5
0.5
dextrin
water 18.95 12.65 16.95
21.55 20.55 18.55 21.55
xanthan gum 2 0.1 0
0 0 0 0
hydrogenated 6
1 3
3 3 3 3
palm oil
phospholipid 1 0.2 0.4
0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4
beeswax 0 0 0
0
0
0 0
palm stearin 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
Glyceryl 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
Monostearate
Hardness 4 5 5
4 4 5 4
Elasticity 5 4 4
5 4 4 4
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
Cohesiveness 4 5 4
4 4 4 4
Oil 5 4 4
4 5
4
4
precipitation
composite 18 18 17
17 17
17
16
score
Composition 39 40 41
No.
gelatin 0 0 0
carrageenin 2 1.0 2.5
acacia gum 0 0 0
modified 0 0 0
starch
gellan gum 0 2 0.2
locust bean 0.2 0 0
gum
pectin 0 0 0
konjak gum 0.5 0 0
xylitol 8 8 8
sorbitol 2 2 2
fish oil 60
60 60
vitamin E 0.3 0.3 0.3
citric acid
0.05 0.05 0.05
monohydrate
lemon essence 0.2 0.2 0.2
resistant 0.5 0.5 0.5
dextrin
water 22.85 23.05 22.85
xanthan gum 0 0 0
hydrogenated 3 3 3
palm oil
phospholipid 0.4 0.4 0.4
26
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
beeswax 0 0 0
palm stearin 0 0 0
Glyceryl 0 0 0
M onostea rate
Hardness 5 4 5
Elasticity 3 5 3
Cohesiveness 4 3 4
Oil 4 4 4
precipitation
composite 16 16 16
score
As can be seen from the above table, the gel compositions of the present
application
(including the combination of the first gelling agent (gelatin) and the second
gelling agent
(xanthan gum) and the stabilizers (hydrogenated palm oil or palm stearin or
beeswax +
5 phospholipid)) have a superior performance (5 points) in terms of the
most indicators of the
textures (hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and oil precipitation, and
achieve 4 points in
terms of only a few indicators, showing an excellent comprehensive performance
(a
comprehensive score is close to or equal to full marks, 20 points). In
addition, the oil content
contained in the gel composition according to the present application can be
up to 70 wt%
10 of the total weight of the compositions.
When only the first gelling agent (gelatin) and the second gelling agent
(xanthan gum)
are used without the stabilizers and when the compositions have the same oil
content of 55
wt%, the resulting gel compositions can only reach low scores or moderate
scores (between
1 and 3 points) in terms of the most indicators of the textures (hardness,
elasticity and
15 cohesiveness) and oil precipitation, and only can achieve 4 points in
terms of a few
indicators. The comprehensive scores are ordinary or even not good (between 8
and 12
points).
When only the first gelling agent (gelatin) and a stabilizer (hydrogenated
palm oil or
palm stearin or beeswax) are used without the second gelling agent (xanthan
gum) and a
20 component of the stabilizers (phospholipid) and when the compositions
have the same oil
content of 55 wt%, the resulting gel compositions can only achieve moderate
scores (between
27
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
3 and 4 points) in terms of the texture (hardness, elasticity and
cohesiveness) and oil
precipitation. The comprehensive scores are ordinary (between 12 and 13
points).
When only the first gelling agent (gelatin) and a component of the stabilizers
(phospholipid) are used without the second gelling agent (xanthan gum) and
another
5
component of the stabilizers (hydrogenated
palm oil or palm stearin or beeswax) and when
the compositions have the same oil content of 55 wt%, the resulting gel
compositions can
only achieve low or moderate scores (between 2 and 3 points) in terms of the
texture
(hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and oil precipitation. The
comprehensive scores are
average (between 11 and 12 points).
10
When only the first gelling agent (gelatin)
and the stabilizer (hydrogenated palm oil or
palm stearin or beeswax + phospholipid, and the mass ratio of hydrogenated
palm oil:
phospholipid ranges from 5:1 to 10:1) are used without the second gelling
agent (xanthan
gum) and when the compositions have the same oil content of 55 wt%, the
resulting gel
compositions achieve moderate scores (4 points) in terms of the most
indicators of the texture
15
(hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and
oil precipitation and achieve 3 points in terms of
a few indicators. The comprehensive score are above average (between 15 and 16
points),
but still lower than those achieved by the gel compositions of the present
application.
When only the first gelling agent (gelatin) is used without the second gelling
agent
(xanthan gum) and the stabilizer (hydrogenated palm oil or palm stearin or
beeswax +
20
phospholipid) and when the compositions
have the same oil content of 55 wt%, the resulting
gel compositions perform poorly in terms of the texture (hardness, elasticity
and
cohesiveness) and oil precipitation, or only reach moderate scores (between 1
and 3 points)
in terms of a few indicators. The comprehensive scores are poor (only 8
points).
When a monoglyceride with similar properties is substituted for hydrogenated
palm oil
25
or palm stearin or beeswax as a component
of the stabilizers and added to the gel composition
together with the first gelling agent (gelatin), the second gelling agent
(xanthan gum) and a
component of the stabilizers (phospholipid) and when the compositions have the
same oil
content of 55 wt%, the resulting gel compositions perform poorly in terms of
the texture
(hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and oil precipitation, or only reach
moderate scores
30
(between 1 and 4 points). The comprehensive
scores are low or moderate (7 points and 15
points).
When beeswax is substituted for hydrogenated palm oil as a component of the
stabilizers and added to the gel composition together with the first gelling
agent (gelatin),
28
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
the second gelling agent (xanthan gum) and a component of the stabilizers
(phospholipid)
and when the compositions have the same oil content of 55 wt%, the resulting
gel
compositions can achieve excellent or moderate scores (between 4 and 5 points)
in terms of
the texture (hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and oil precipitation. The
comprehensive
5 scores are above average (between 17 and 18 points).
When palm stearin is substituted for hydrogenated palm oil as a component of
the
stabilizers and added to the gel composition together with the first gelling
agent (gelatin),
the second gelling agent (xanthan gum) and a component of the stabilizers
(phospholipid)
and when the compositions have the same oil content of 55 wt%, the resulting
gel
10 compositions can achieve excellent or moderate scores (between 4 and 5
points) in terms of
the texture (hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and oil precipitation. The
comprehensive
scores are above average (between 17 and 18 points).
When the first gelling agent (gelatin), the second gelling agent (arabic gum
and
modified starch) and the stabilizers (hydrogenated palm oil or palm stearin or
beeswax +
15 phospholipid) are used and when the compositions have the same oil
content of 60 wt%, the
resulting gel compositions can achieve excellent or moderate scores (between 4
and 5 points)
in terms of the texture (hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and oil
precipitation. The
comprehensive scores are above average (17 points).
When the first gelling agent (gelatin and pectin), the second gelling agent
(arabic gum)
20 and the stabilizers (hydrogenated palm oil or palm stearin or beeswax +
phospholipid) are
used and when the compositions have the same oil content of 60 wt%, the
resulting gel
compositions can achieve excellent or moderate scores (between 4 and 5 points)
in terms of
the texture (hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and oil precipitation.
The
comprehensive scores are above average (17 points).
25
When the first gelling agent (carrageenan
and konjac gum), the second gelling agent
(locust bean gum) and the stabilizers (hydrogenated palm oil or palm stearin
or beeswax +
phospholipid) are used and when the compositions have the same oil content of
60 wt%, the
resulting gel compositions can achieve moderate scores (between 4 and 5
points) in terms of
the most indicators of the texture (hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and
oil precipitation
30 and can achieve 5 and 3 points in terms of a few indicators. The
comprehensive scores are
above average (16 points).
When the first gelling agent (carrageenan), the second gelling agent (gellan
gum) and
the stabilizers (hydrogenated palm oil or palm stearin or beeswax +
phospholipid) are used
29
CA 03146688 2022-2-2
and the compositions have the same oil content of 60 wt%, the resulting gel
compositions
can achieve average scores or more (between 3 and 5 points) in terms of the
texture
(hardness, elasticity and cohesiveness) and oil precipitation. The
comprehensive scores are
above average (16 points).
5 It can be seen that this application has achieved the effects of
improving oil stability
and improving the texture of the compositions by using a specially selected
combination of
gelling agents and stabilizers. In particular, the stability of the
composition is improved by
addition of the specially selected stabilizers at a ratio. When the second
gelling agent is added
in a specific ratio, the water holding capacity of the composition is better,
thereby improving
10 oil-water separation and obtaining a composition with a better oil
content.
CA 03146688 2022-2-2