Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
OBJECT POSITIONING METHOD AND APPARATUS, AND COMPUTER SYSTEM
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Technical Field
[0001] The present invention relates to the field of image recognition, and
more particularly to
an object positioning method, and corresponding device and computer system.
Description of Related Art
[0002] With the development of the internet technology, unmanned stores have
gradually been
in vogue in the field of novel retails. In the state of the art, anti-theft
monitoring of
commodities in unmanned stores mostly relies on the radio frequency
identification
(RFID) technology, whereby each commodity is required to be previously labeled
with
an anti-theft label, so the cost is high and use is inconvenient. Even if the
face
recognition technique is applied to recognize and confirm such behaviors of
consumers
as their going into and out of the stores, there is still a risk of violating
the privacy of
consumers due to the recognition of their faces.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0003] In order to deal with the deficiencies in prior-art technology, a main
objective of the
present invention it is to provide an object positioning method, so as to
realize
positioned detection of objects.
[0004] In order to achieve the above objective, according to the first aspect,
the present
invention provides an object positioning method that comprises:
[0005] receiving a color image and a depth image to which the color image
corresponds;
[0006] fusing the color image with the depth image to obtain a target image,
wherein the target
image is an RGBD image whose Alpha channel corresponds to the depth image and
whose RGB channels correspond to the color image; and
[0007] inputting the target image in a preset model for recognition, and
positioning a position
of a target object in the target image, wherein an input layer of the preset
model includes
1
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
RGB channels and an Alpha channel.
[0008] In some embodiments, before fusing the color image with the depth
image, the method
further comprises:
[0009] performing an image normalization operation on the depth image
according to a preset
method and a preset parameter.
[0010] In some embodiments, before fusing the color image with the depth
image, the method
further comprises:
[0011] performing image registration on the normalized depth image and the
color image.
[0012] In some embodiments, the color image is shot by a first camera, the
depth image is shot
by a second camera, and performing image registration on the color image and
the depth
image includes:
[0013] employing a checkerboard method to calibrate the first camera and the
second camera,
and obtaining corresponding transformation matrixes of the first camera and
the second
camera; and
[0014] performing image registration on the color image and the depth image
according to the
transformation matrixes.
[0015] In some embodiments, before inputting the target image in a preset
model for
recognition, the method further comprises:
[0016] performing data enhancement on the target image.
[0017] In some embodiments, a process of training the preset model includes:
[0018] obtaining a training image set, wherein the image set consists of a
color image
previously marked with a sample target and a depth image to which the color
image
corresponds;
[0019] performing an image normalization operation on the depth image, and
converting the
same to a preset format;
2
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
[0020] performing image registration on the color image and the corresponding
depth image;
[0021] fusing the depth image with the corresponding color image to obtain a
testing image,
wherein the testing image is an RGBD image whose Alpha channel corresponds to
the
depth image and whose RGB channels correspond to the color image; and
[0022] taking the testing image as input to a target model, correspondingly
taking the
previously marked sample target as expected output from the target model, and
continually training the target model until the target model satisfies a
preset condition.
[0023] In some embodiments, the target model is obtained by the following
mode:
[0024] modifying an input layer of a Yolov3 model as four channels, and
obtaining an
improved Yolov3 model, wherein the input layer includes RGB channels and an
Alpha
channel; and
[0025] clipping a backbone network of the improved Yolov3 model according to a
preset
clipping parameter, and obtaining the target model.
[0026] According to the second aspect, the present application provides an
object positioning
device that comprises:
[0027] a receiving module, for receiving a color image and a depth image to
which the color
image corresponds;
[0028] an image processing module, for fusing the color image with the depth
image to obtain
a target image, wherein the target image is an RGBD image whose Alpha channel
corresponds to the depth image and whose RGB channels correspond to the color
image;
and
[0029] a matching module, for inputting the target image in a preset model for
recognition, and
positioning a position of a target object in the target image, wherein an
input layer of
the preset model includes RGB channels and an Alpha channel.
[0030] In some embodiments, the image processing module is further usable for
performing
image registration on the color image and the depth image.
3
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
[0031] According to the third aspect, the present application provides a
computer system that
comprises:
[0032] one or more processor(s); and
[0033] a memory, associated with the one or more processor(s), for storing a
program
instruction that performs the following operations when it is read and
executed by the
one or more processor(s):
[0034] receiving a color image and a depth image to which the color image
corresponds;
[0035] fusing the color image with the depth image to obtain a target image,
wherein the target
image is an RGBD image whose Alpha channel corresponds to the depth image and
whose RGB channels correspond to the color image; and
[0036] inputting the target image in a preset model for recognition, and
positioning a position
of a target object in the target image.
[0037] The present invention achieves the following advantageous effects.
[0038] The present invention discloses receiving a color image and a depth
image to which the
color image corresponds, fusing the color image with the depth image to obtain
a target
image, wherein the target image is an RGBD image whose Alpha channel
corresponds
to the depth image and whose RGB channels correspond to the color image,
inputting
the target image in a preset model for recognition, and positioning a position
of a target
object in the target image; by recognizing the image fused by the color image
and the
depth image, relative to recognition performed merely on the basis of the
color image
or the depth image, efficiency of and precision in positioning the target
object in the
target image are greatly enhanced, tracking of the shifting path of the target
object can
be realized according to the position of the positioned target object,
purchasing paths
of consumers can be tracked when applied to unmanned stores, application can
also be
found in the analysis of purchasing behaviors of consumers at the same time of
guaranteeing safety of goods, and purchasing experiences of consumers are
enhanced.
[0039] The present application further discloses performing such image
processing operations
4
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
as image normalization on the depth image and image registration on the color
image
and the depth image before fusing the color image and the depth image, whereby
precision in positioning the target object is further enhanced.
[0040] The present application proposes inputting the target image in a preset
model for
recognition after performing data enhancement on the target image, whereby
positioning efficiency is ensured.
[0041] Not all products of the present invention are necessarily required to
simultaneously
possess all the aforementioned effects.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0042] In order to more clearly describe the technical solutions in the
embodiments of the
present invention, drawings required for the illustration of the embodiments
will be
briefly introduced below. Apparently, the drawings described below are merely
directed
to some embodiments of the present invention, and it is possible for persons
ordinarily
skilled in the art to base on these drawings to acquire other drawings without
spending
creative effort in the process.
[0043] Fig. 1 is a flowchart illustrating people detection in an unmanned
store provided by the
embodiments of the present application;
[0044] Fig. 2 is a view schematically illustrating the framework of a Yolov3-
4channel network
structure provided by an embodiment of the present application;
[0045] Fig. 3 is a flowchart illustrating the method provided by an embodiment
of the present
application;
[0046] Fig. 4 is a view illustrating the structure of the device provided by
an embodiment of
the present application; and
[0047] Fig. 5 is a view illustrating the structure of the computer system
provided by an
embodiment of the present application.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
[0048] In order to make more lucid and clear the objectives, technical
solutions and advantages
of the present invention, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the
present
invention will be clearly and comprehensively described below with reference
to the
accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Apparently,
the
embodiments as described are merely partial embodiments, rather than the
entire
embodiments, of the present invention. All other embodiments obtainable by
persons
ordinarily skilled in the art on the basis of the embodiments in the present
invention
without spending any creative effort shall all be covered by the protection
scope of the
present invention.
[0049] As noted in the Description of Related Art, in order to ensure safety
of commodities in
an unmanned store, it is possible to install cameras in the unmanned store, to
analyze
moving tracks of customers according to images shot by the cameras, to
recognize
suspicious customers according to the moving tracks, to also analyze
purchasing
behaviors of customers according to the moving tracks, and to enhance
purchasing
experiences of customers.
[0050] In order to achieve the above objectives, the present application
discloses inputting a
target image in a preset model, and determining the position of a target
object according
to the output result of the model, whereby is realized real-time recognition
of customers'
positions and moving tracks.
[0051] Embodiment 1
[0052] An example is taken by the use of a Yolov3 model to detect images shot
in an unmanned
store and to recognize the position of a customer, as shown in Fig. 1, the
method can be
realized through the following steps.
[0053] The Yolov3 model is a general target detection model usable for
processing images, and
extracting such target objects in the images as people and commodities, etc.
[0054] However, this model can only be used to detect 3-channel RGB color
images, but
cannot fuse depth images with color images, and also cannot detect RGBD images
6
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
obtained after such fusing.
[0055] RGB stands for the common color standards in the field of industry,
whereby various
colors are obtained by changing the values of the three color channels as red,
green and
blue and through mutual superpositions amongst them, and the standards can
almost
subsume all colors perceptible to the human vision.
[0056] RGBD stands for the addition of an Alpha channel based on the 3-channel
RGB, and
adds additional information originating from a depth image to the RGB image.
Pixel
values of the depth image represent the actual distance between the camera and
the shot
object, and an RGBD image fused by the depth image and a color image can more
clearly express the actual status of the shot object than a single color
image, so the result
obtained on the basis of recognition of an RGBD image is more precise than on
the
basis of recognition of the color image.
[0057] In order to enable the Yolov3 model to support recognition of the RGBD
image, the
model should be improved, and the improving process includes:
[0058] modifying the input layer of the Yolov3 model to change it from being
able to be input
only with a 3-channel RGB image to being able to be input with the RGBD image
that
includes RGB channels and an Alpha channel, and the model thusly modified can
be
renamed as a Yolov3-4channe1 network model.
[0059] In order to accelerate the reasoning speed of the model and to enhance
the output
efficiency of the model, the Yolov3-4channe1 Backbone network layer can be
clipped
according to a preset clipping parameter, to reduce the number of model layers
of the
model to accelerate computation.
[0060] Fig. 2 is a view schematically illustrating the framework of a Yolov3-
4channel network
structure that includes an input layer, a Res layer, a convolutional layer
(cony), an upper
sampling layer (upSample), a Yolo layer, and a concat layer.
[0061] In order to obtain the color image and the depth image, it is possible
to install a color
camera and a depth camera respectively in the unmanned store to collect color
images
7
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
and depth images, the installation height is 3 to 4 meters above ground, and
the
installation angle is perpendicular to the ground.
[0062] After image collection and model improvement have been completed, it
can be started
to train the model to obtain the preset model, and the specific training
process includes
the following steps.
[0063] Step A ¨ collecting an image dataset.
[0064] The dataset contains color images and corresponding depth images, 85%
of the dataset
can be used for training the model, while the remaining 15% is used for
testing the
model.
[0065] Step B ¨ marking people contained in the color image with a VOC format,
and
converting the color image from a BGR pattern to an RGB pattern.
[0066] BGR is a color standard that is inverse to the RGB sequence, and
represents the
sequence of blue, green, red.
[0067] VOC is an image marking rule usable for marking target objects in
images.
[0068] Step C ¨ preprocessing the depth image.
[0069] The preprocessing process can include:
[0070] performing an image normalization operation on the depth image;
[0071] the image normalization can include:
[0072] suppose significant bits of the depth image are 16 bit, the camera is
distanced from the
ground at a height of 4000 mm, then the following formula is used to normalize
the
depth image within the interval of [0, 2551.
[0073] ndepth = depth/4000 * 255, depth represents the depth read from this
depth image.
[0074] The normalized depth image is converted to a unit8 format, which is a
data type of
pictures.
[0075] Step D ¨ performing image registration on the color image and the
corresponding depth
8
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
image.
[0076] The specific process of image registration includes:
[0077] with respect to a first camera that shots color images and a second
camera that shots
depth images, employing a checkerboard calibration method to calculate
internal
reference matrixes of the first camera and the second camera respectively, and
to
calculate external reference matrixes of the first camera and the second
camera relative
to a preset checkerboard, and calculating corresponding transformation
matrixes of the
first camera and the second camera according to the internal reference
matrixes and the
external reference matrixes; and
[0078] performing image registration on the color image and the corresponding
depth image
according to the transformation matrixes.
[0079] Step E ¨ taking the depth image as an Alpha channel of a target image,
and taking the
color image as RGB channels of the target image to perform image fusion, and
obtaining a 4-channel RGBD target image.
[0080] Step F ¨ performing data enhancement on the target image.
[0081] The data enhancement method includes such image processing methods as
image
clipping, image size adjusting, image rotational angle adjusting, image
luminance and
contrast adjusting, etc.
[0082] Step G ¨ taking the target image as input to the improved model,
correspondingly taking
marked people as expected output from the model, and training the model.
[0083] The training process includes: modifying the training parameter of the
model,
employing a stochastic gradient descent algorithm to persistently observe
descending
circumstance of a loss function Loss of the model until the value of the loss
function
Loss no longer descends can then be regarded that the model has completed
training,
and outputting the preset model of the target.
[0084] After the preset model of the target has been obtained, the preset
model can then be
9
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
used to recognize images, and the recognizing process includes:
[0085] Step A ¨ receiving the color image and a depth image to which the color
image
corresponds;
[0086] Step B ¨ performing an image normalization operation on the depth image
according
to a preset method and a preset parameter, and converting the same to a unit8
format;
[0087] Step C ¨ performing image registration on the depth image obtained in
step B and the
color image;
[0088] the image registration process includes:
[0089] with respect to a first camera that shots color images and a second
camera that shots
depth images, employing a checkerboard calibration method to calculate
internal
reference matrixes of the first camera and the second camera respectively, and
to
calculate external reference matrixes of the first camera and the second
camera relative
to a preset checkerboard, and calculating corresponding transformation
matrixes of the
first camera and the second camera according to the internal reference
matrixes and the
external reference matrixes; and
[0090] performing image registration on the color image and the corresponding
depth image
according to the transformation matrixes.
[0091] Step D ¨ fusing the color image with the depth image to generate a
target image whose
Alpha channel corresponds to the depth image and whose RGB channels correspond
to
the color image, and performing data enhancement on the target image;
[0092] the data enhancement includes, but is not limited to, such image
processing methods as
image clipping, image size adjusting, image rotational angle adjusting, image
luminance and contrast adjusting, etc.
[0093] Step E ¨ inputting the target image in the preset model for
recognition, and positioning
a position of the target object in the target image.
[0094] Through the above method it is made possible to recognize such a target
object as
lo
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
people in the target image, precision and efficiency in people recognition are
enhanced,
and such subsequent operations as tracking, poi ________________________ tiait
recognition, and duplicate-
removing from plural objects according to the recognition result are
facilitated.
[0095] Embodiment 2
[0096] Corresponding to the above method, the present application provides an
object
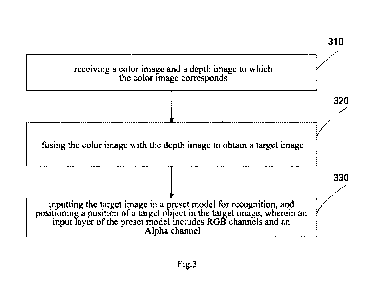
positioning method, as shown in Fig. 3, the method comprises:
[0097] 310 - receiving a color image and a depth image to which the color
image corresponds;
[0098] 320 - fusing the color image with the depth image to obtain a target
image, wherein the
target image is an RGBD image whose Alpha channel corresponds to the depth
image
and whose RGB channels correspond to the color image;
[0099] preferably, before fusing the color image with the depth image, the
method further
comprises:
[0100] 321 - performing an image normalization operation on the depth image
according to a
preset method and a preset parameter.
[0101] Preferably, before fusing the color image with the depth image, the
method further
comprises:
[0102] 322 - performing image registration on the normalized depth image and
the color image.
[0103] Preferably, the color image is shot by a first camera, the depth image
is shot by a second
camera, and performing image registration on the color image and the depth
image
includes:
[0104] employing a checkerboard method to calibrate the first camera and the
second camera,
and obtaining corresponding transformation matrixes of the first camera and
the second
camera; and
[0105] performing image registration on the color image and the depth image
according to the
transformation matrixes.
11
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
[0106] 330 - inputting the target image in a preset model for recognition, and
positioning a
position of a target object in the target image, wherein an input layer of the
preset model
includes RGB channels and an Alpha channel.
[0107] Preferably, before inputting the target image in a preset model for
recognition, the
method further comprises:
[0108] 331 - performing data enhancement on the target image.
[0109] Preferably, a process of training the preset model includes:
[0110] 340 - obtaining a training image set, wherein the image set consists of
the color image
previously marked with a sample target and the depth image to which the color
image
corresponds;
[0111] performing an image normalization operation on the depth image, and
converting the
same to a preset format;
[0112] performing image registration on the color image and the corresponding
depth image;
[0113] fusing the depth image with the corresponding color image to obtain a
testing image,
wherein the testing image is theRGBD image whose Alpha channel corresponds to
the
depth image and whose RGB channels correspond to the color image; and
[0114] taking the testing image as input to a target model, correspondingly
taking the
previously marked sample target as expected output from the target model, and
continually training the target model until the target model satisfies a
preset condition.
[0115] Preferably, the target model is obtained by the following mode:
[0116] 341 - modifying an input layer of a Yolov3 model as four channels, and
obtaining an
improved Yolov3 model, wherein the input layer includes RGB channels and an
Alpha
channel; and
[0117] clipping a backbone network of the improved Yolov3 model according to a
preset
clipping parameter, and obtaining the target model.
12
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
[0118] Embodiment 3
[0119] Corresponding to the above method, the present application provides an
object
positioning device, as shown in Fig. 4, the device comprises:
[0120] a receiving module 410, for receiving a color image and a depth image
to which the
color image corresponds;
[0121] an image processing module 420, for fusing the color image with the
depth image to
obtain a target image, wherein the target image is an RGBD image whose Alpha
channel
corresponds to the depth image and whose RGB channels correspond to the color
image;
and
[0122] a matching module 430, for inputting the target image in a preset model
for recognition,
and positioning a position of a target object in the target image, wherein an
input layer
of the preset model includes RGB channels and an Alpha channel.
[0123] Preferably, the image processing module 420 is further usable for
performing image
registration on the color image and the depth image.
[0124] Preferably, the image processing module 420 is further usable for
performing an image
normalization process on the depth image according to a preset method and a
preset
parameter.
[0125] Preferably, the image processing module 420 is further usable for
performing image
registration on the normalized depth image and the color image.
[0126] Preferably, the color image is shot by a first camera, the depth image
is shot by a second
camera, and the image processing module 420 is further usable for employing a
checkerboard method to calibrate the first camera and the second camera, and
obtaining
corresponding transformation matrixes of the first camera and the second
camera; and
for
[0127] performing image registration on the color image and the depth image
according to the
transformation matrixes.
13
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
[0128] Preferably, the image processing module 420 is further useable for
performing data
enhancement on the target image.
[0129] Preferably, the device further comprises a model training module 430
for obtaining a
training image set, wherein the image set consists of the color image
previously marked
with a sample target and the depth image to which the color image corresponds;
for
[0130] performing an image normalization operation on the depth image, and
converting the
same to a preset format; for
[0131] performing image registration on the color image and the corresponding
depth image;
for
[0132] fusing the depth image with the corresponding color image to obtain a
testing image,
wherein the testing image is the RGBD image whose Alpha channel corresponds to
the
depth image and whose RGB channels correspond to the color image; and for
[0133] taking the testing image as input to a target model, correspondingly
taking the
previously marked sample target as expected output from the target model, and
continually training the target model until the target model satisfies a
preset condition.
[0134] Preferably, the model training module 430 is further usable for
modifying an input layer
of a Yolov3 model as four channels, and obtaining an improved Yolov3 model,
wherein
the input layer includes RGB channels and an Alpha channel; and for clipping a
backbone network of the improved Yolov3 model according to a preset clipping
parameter, and obtaining the target model.
[0135] Embodiment 4
[0136] Corresponding to the above method and device, Embodiment 4 of the
present
application provides a computer system that comprises: one or more
processor(s); and
a memory, associated with the one or more processor(s), for storing a program
instruction that performs the following operations when it is read and
executed by the
one or more processor(s):
14
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
[0137] receiving a color image and a depth image to which the color image
corresponds;
[0138] fusing the color image with the depth image to obtain a target image,
wherein the target
image is an RGBD image whose Alpha channel corresponds to the depth image and
whose RGB channels correspond to the color image; and
[0139] inputting the target image in a preset model for recognition, and
positioning a position
of a target object in the target image.
[0140] Fig. 5 exemplarily illustrates the framework of a computer system that
can specifically
include a processor 1510, a video display adapter 1511, a magnetic disk driver
1512,
an input/output interface 1513, a network interface 1514, and a memory 1520.
The
processor 1510, the video display adapter 1511, the magnetic disk driver 1512,
the
input/output interface 1513, the network interface 1514, and the memory 1520
can be
communicably connected with one another via a communication bus 1530.
[0141] The processor 1510 can be embodied as a general CPU (Central Processing
Unit), a
microprocessor, an ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit), or one or
more
integrated circuit(s) for executing relevant program(s) to realize the
technical solutions
provided by the present application.
[0142] The memory 1520 can be embodied in such a form as an ROM (Read Only
Memory),
an RAM (Random Access Memory), a static storage device, or a dynamic storage
device. The memory 1520 can store an operating system 1521 for controlling the
running of a computer system 1500, and a basic input/output system (BIOS) for
controlling lower-level operations of the computer system 1500. In addition,
the
memory 1520 can also store a web browser 1523, a data storage administration
system
1524, and an icon font processing system 1525, etc. The icon font processing
system
1525 can be an application program that specifically realizes the
aforementioned
various step operations in the embodiments of the present application. To sum
it up,
when the technical solutions provided by the present application are to be
realized via
software or firmware, the relevant program codes are stored in the memory
1520, and
invoked and executed by the processor 1510.
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
[0143] The input/output interface 1513 is employed to connect with an
input/output module to
realize input and output of information. The input/output module can be
equipped in
the device as a component part (not shown in the drawings), and can also be
externally
connected with the device to provide corresponding functions. The input means
can
include a keyboard, a mouse, a touch screen, a microphone, and various sensors
etc.,
and the output means can include a display screen, a loudspeaker, a vibrator,
an
indicator light etc.
[0144] The network interface 1514 is employed to connect to a communication
module (not
shown in the drawings) to realize intercommunication between the current
device and
other devices. The communication module can realize communication in a wired
mode
(via USB, network cable, for example) or in a wireless mode (via mobile
network, WIFI,
Bluetooth, etc.).
[0145] The bus 1530 includes a passageway transmitting information between
various
component parts of the device (such as the processor 1510, the video display
adapter
1511, the magnetic disk driver 1512, the input/output interface 1513, the
network
interface 1514, and the memory 1520).
[0146] Additionally, the computer system 1500 may further obtain information
of specific
collection conditions from a virtual resource object collection condition
information
database 1541 for judgment on conditions, and so on.
[0147] As should be noted, although merely the processor 1510, the video
display adapter 1511,
the magnetic disk driver 1512, the input/output interface 1513, the network
interface
1514, the memory 1520, and the bus 1530 are illustrated for the aforementioned
device,
the device may further include other component parts prerequisite for
realizing normal
running during specific implementation. In addition, as can be understood by
persons
skilled in the art, the aforementioned device may as well only include
component parts
necessary for realizing the solutions of the present application, without
including the
entire component parts as illustrated.
[0148] As can be known through the description to the aforementioned
embodiments, it is
16
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29
CA 03166338 2022-06-29
clearly learnt by person skilled in the art that the present application can
be realized
through software plus a general hardware platform. Based on such
understanding, the
technical solutions of the present application, or the contributions made
thereby over
the state of the art, can be essentially embodied in the form of a software
product, and
such a computer software product can be stored in a storage medium, such as an
ROM/RAM, a magnetic disk, an optical disk etc., and includes plural
instructions
enabling a computer equipment (such as a personal computer, a server, or a
network
device etc.) to execute the methods described in various embodiments or some
sections
of the embodiments of the present application.
[0149] The various embodiments are progressively described in the Description,
identical or
similar sections among the various embodiments can be inferred from one
another, and
each embodiment stresses what is different from other embodiments.
Particularly, with
respect to the system or system embodiment, since it is essentially similar to
the method
embodiment, its description is relatively simple, and the relevant sections
thereof can
be inferred from the corresponding sections of the method embodiment. The
system or
system embodiment as described above is merely exemplary in nature, units
therein
described as separate parts can be or may not be physically separate, parts
displayed as
units can be or may not be physical units, that is to say, they can be located
in a single
site, or distributed over a plurality of network units. It is possible to base
on practical
requirements to select partial modules or the entire modules to realize the
objectives of
the embodied solutions. It is understandable and implementable by persons
ordinarily
skilled in the art without spending creative effort in the process.
[0150] What the above describes is merely directed to preferred embodiments of
the present
invention, and is not meant to restrict the present invention. Any
modification,
equivalent substitution and improvement makeable within the spirit and scope
of the
present invention shall all be covered by the protection scope of the present
invention.
17
Date Regue/Date Received 2022-06-29