Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
129754~
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
Control of Welding Robot
BACKGROUND OF T~E INVENTION
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a control of an
industrial robot, and more particularly, to a control of a
welding robot.
Description of the Prior Art
A conventional welding robot for performing a welding
such as spot welding automatically in accordance with a
programmed sequence includes a working section including a
welding gun which is adapted to be placed against a work to
be welded. In one type of the welding robot, the working
section includes an arm having a hand at one end and a
welding gun is carried by the hand. The arm and the hand are
designed so that the gun can be moved with respect to the
work and located against a spot on the work where the welding
is to be carried out. In another type, the working section
may be stationary and the work to be welded is carried to a
location where the welding operation is made by the welding
gun in the working section of the robot. The working section
is controlled by means of a timer controlled operating unit
so that the welding is carried out in accordance with welding
controlling parameters, such as the pre-pressing time, the
pressing force and pressing force holding time, the welding
time and the welding current.
According to the conventional robots, a memory is
~J~
lZ~754~l
provided to store informations concerning the welding
controlling parameters which are specific to respective ones
of the works to be welded. A control unit is also provided
for selecting welding controlling parameters which are
specific to the particular work to be welded.
In the conventional welding robot, inconveniencies have
been experienced in that the operator is required to
determine and memorize in the memory the welding controlling
parameters in advance of the operation of the robot.
Usually, the welding controlling parameters are determined in
accordance with the properties of the work to be welded, such
as the thickness and the type of the sheets constituting the
work, the number of the sheets in the work. Further, such
welding controlling parameters must be determined for each
position where the welding is to be carried out. Therefore,
time and labor are consumed in determining the parameters in
starting the welding. It should further be noted that it is
very difficult to determine the welding controlling
parameters in a precise manner for various different works.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is therefore an object of the present invention to
provide a control system for a welding robot in which welding
controlling parameters can be determined relatively easily in
a precise manner for each welding position.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a
control system for a welding robot in which the welding
controlling parameters can be determined with less time and
less labor.
lZ9754~
A further object of the present invention is to provide
a control system for a welding robot with which the quality
of the welding can be improved.
According to the present invention, the above and other
5objects can be accomplished by a control system for a welding
robot including a working section having welding gun means
and actuating means for moving the gun means toward a work to
be welded, a timer controlled operating unit for controlling
operations of the welding gun means and the actuating means.
10A sequencer may be provided for determining the sequence of
welding operation. There is provided control means for
producing a welding initiating command signal and welding
control signals representing welding controlling parameters
for a specific position where a welding is being carried
15out. The welding initiating signal is applied to the
sequencer to initiate the welding operation and the welding
controlling parameters are applied to the operating unit so
that the welding is carried out in accordance with the
conditions as determined by the parameters.
20The control unit may be embodied by a microprocessor
and a processing unit may be provided to apply informations
concerning the work to be welded, such as the type of sheets
in the work, the thickness and the number of the sheets. The
processing unit may have memories of informations concerning
the positions to be welded, and the welding conditions such
as the type of the sheets to be welded and the thickness and
the number of the sheets. The control unit receives from the
lZ9'~S4~
processing unit signals representing the informations
concerning the welding conditions and carries out
calculations to determine the welding controlling parameters.
In another form of the present invention, the processing unit
may be omitted and the informations concerning the welding
conditions may be applied to the control unit as manual
inputs.
As described above, the control unit functions to
calculate in accordance with the input applied thereto
welding control parameters which are appropriate to the
specific position where the welding is to be carried out and
send welding initiating signal to the sequencer and the
welding controlling parameters to the timer controlled
operating unit. The sequencer functions, when the welding
initiating signal is received from the control means, to
transmit the welding initiating signal to the timer
controlled operating unit. The operating unit then functions
to control the working section of the robot so that the
welding is performed with the required welding parameters
such as the pre-pressing time, the pressing force, the
welding current and voltage, etc. After the welding
operation is finished, the sequencer produces a welding
finish signal which is applied to the control unit to finish
the welding operation in the particular position. Then, the
control unit produces a signal, when appropriate, for moving
the working section to another position where the welding is
to be carried out next. The control unit further produces a
further welding initiating signal so that a further step of
~Z~7S41
welding is carried out at the aforementioned another
position.
The timer controlled operating unit functions to
operate the welding gun means and the actuating means in
accordance with the welding controlling parameters which are
applied by the control unit. Thus, the pressure and the time
for the pre-pressing, the pressure and the time for pressing
in the welding step, the durati~n for the current supply and
the intensity of the welding current are determined by the
timer controlled operating unit in accordance with the
signals as received from the control unit.
Thus, according to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided in a welding robot including a working
section having welding gun means and actuating means for
moving ~he gun means toward a work to be welded to carry out
a welding, a timer controlled operating unit for controlling
operations of the welding gun means and the actuating means
and a sequencer connected with the operating unit for
initiating the welding operation, by a control system
including control means for producing a welding initiating
command signal and welding control signals, said control
means being adapted to receive informations concerning the
work to be welded and calculating based on the informations
welding controlling parameters for a specific position where
the welding is to be carried out, the control means being
connected with said sequencing means and said timer
controlled operating unit to apply the welding initiating
1~97S41
signal to the sequencing means to initiate the welding
operation and the welding controlling parameters to the
operating unit so that the welding is carried out in
accordance with conditions as determined by the parameters.
S According to a specific aspect of the present
invention, driving means is provided for driving the working
section of the robot so that the working section is
sequentially aligned to positior.s where welding operations
are to be carried out in accordance with the sequence as
determined by the control unit. There may be provided
processing means which has memory means memorizing the
sequence of the positions where the welding is to be carried
out. The control unit may then receive signals representing
the sequence of welding positions from the processing means
and control the driving means in accordance with the
signals. The processing means may further have memories of
the informations of the work to be welded which are applied
to the control means so that the control means can perform
the calculations for obtaining the welding controlling
parameters.
In another aspect of the present invention, the robot
is of a type wherein the working section is stationary and
the work is moved to the position where the welding position
is aligned to the welding gun means. In this type, manual
input means may be provided to apply the informations of the
work to be welded to the control means. Further, there may
be provided manual means to produce the welding initiating
signal so that the welding is started after the welding
~Zg7S41
position is aligned with the welding gun means of the working
section.
According to the features of the present invention, the
preparation for the welding operation is very simple as
compared with the conventional control system for the welding
robot. It is only required to select the type of welding
which is in advance memorized in the processing means or to
apply informations on the work to be welded directly to the
control means.
The above and other objects and features of the present
invention will become apparent from the following
descriptions of a preferred embodiment taking reference to
the accompanying drawing.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
The drawing is a schematic illustration of the control
system for a welding robot in accordance with one embodiment
of the present invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
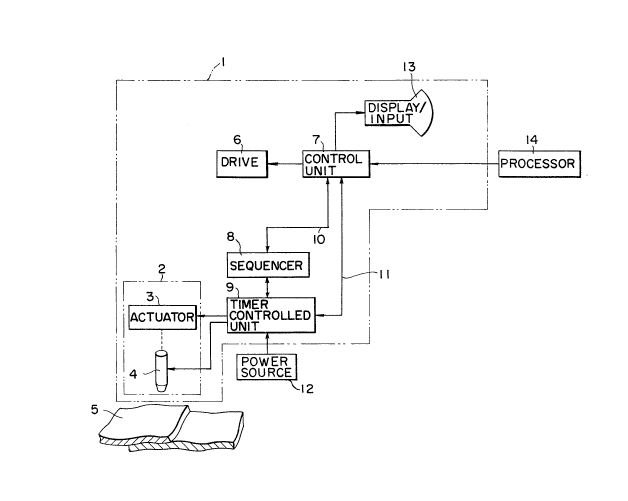
Referring to the drawing, there is schematically shown
a spot welding robot 1 which includes a working section 2
having a welding gun 4 which is adapted to be located against
a work 5 to be welded and an actuating cylinder 3 for
actuating the gun 4 toward the work 5. As shown in the
drawing, the work 5 is comprised of two or more metal sheets
which are laid one over the other. The welding gun 4
includes an electrode 4a which is forced onto the work 5 by
means of the cylinder 3. Although not shown in the drawing,
~Z97S41
an opposing electrode is provided at the side of the work 5
opposite to the electrode 4 so that the work is held between
the electrode 4a and the opposing electrode. The cylinder 3
forces the electrode 4 so that the work 5 is gripped between
the opposing electrodes under a pressure which is
appropritate to the specific welding condition.
The welding robot 1 is further provided with a driving
unit 6 whic~ may include electric motors or other driving
devices. The driving unit functions to move the working
section 2 with respect to the work 5 so that the welding gun
4 is aligned to the position on the work 5 where the welding
is to be carried out. There is further provided a timer
controlled operating unit 9 which is connected with the
cylinder 3 and the electrode 4a of the welding gun 4. A
control unit 7 is provided and connected on one hand through
a line 10 with a sequencer 8 which is in turn connected with
the operating unit 9 and on the other hand through a line 11
with the operating unit 9. The control unit 7 is also
connected with the driving unit 6 to control the operation of
the driving unit ~. A display/input unit 13 is provided and
connected with the control unit 7. In the illustrated
embodiment, the control unit 7 is further connected with a
processing unit 14.
The processing unit 14 may be embodied by a computer
and has memories of informations concerning welding positions
on the work 5, sequence of welding carried out at the welding
positions and welding conditions such as the number of metal
sheets in the work 5, the thickness and the type of the metal
lZ975~1
sheets in the work 5. The display/input unit 13 has an input
section provided with input key switches so that the operator
can initiate the welding operation by actuating the key
switches which are appropriate to the welding conditions.
Further, the unit 13 can display informations concerning the
welding welding operations which has been and is being
carried out.
The control unit 7 is connected with the processir.a
unit 14 for receiving the aforementioned informacions
concerning the work 5 to be welded. The control unit may be
constituted by a microprocessor which includes a CPU, a
memory and an input/output I/O. The aforementioned
informations may be temporarily memorized in the memory.
Further, the control unit 7 has memories on various data
concerning the welding gun which is being used in the robot
and informations such as formulae required for carrying out
calculations which will bedescribed later. Further, the
memory can store the data concerning the step up
condition, the result of the inspections on the cable break
down and internal leakage, and the output of counters for
indicating the time for the replacement of cables.
The data in the memory can be displayed on the
display/input unit 13. Through actuations of the input
section of the display/input section 13, it is possible to
modify the stored data in the memory of the control unit 7 or
it is possible to apply new or additional data to the memory.
The control unit 7 functions to read informations
lZ9754~
concerning the welding gun 4 used in the robot 1 on the basis
of the data stored in the memory and performs calculations
based on the informations concerning the work to be welded
to obtain welding controlling parameters which are most
appropriate to the welding position where the welding
operation is being made. The welding controlling parameters
thus obtained are then transmitted through the line 11 to the
timer controlled operating unit 9.
The timer controlled operating unit 9 functions to
control the cylinder 3 and the welding gun 4 in the working
section 2 so that the welding operations are carried out
under welding conditions such as the pre-pressing time, the
pressing pressure and the welding current and voltage as
determined by the welding control parameters. An electric
power source 12 is provided for supplying the welding current
through the operating unit 9 to the welding gun 4. When a
malfunction is detected, the control unit 9 analyzes the
malfunction and transmit the informations concerning the
malfunction.
The operating unit 9 transmits informations concerning
the results of the welding operation to the control unit 7
and the informations are stored in the memory of the control
unit 7 as already described. When required, the informations
of the results of welding may be displayed on the
display/input unit 13. The results of the welding may be
represented for example in terms of the power factor of the
load, the secondary current, the trigger timing, the margin
factor and the current supply time period.
1 0
~Z975~1
The control unit 7 further produces a welding
initiating signal when the working section 2 i5 aligned with
the position on the work 5 where the welding is to be made.
The welding initiating signal is applied through the linelO
to the sequencer 8 which then transmit the welding initiating
signal to the timer controlled operating unit 9 so that the
welding step is started. When the welding is finished in one
position on the work 5, the sequencer produces a welding end
signal which is applied to the control unit 7.
The control unit 7 further produces a driving signal
which is applied to the driving unit 6. The driving unit 6
functions to drive the working section 2 to a location where
the welding gun 4 is aligned with the position where the
welding is to be carried out.
Thus, in operation of the robot 1, the control unit 7
sends the driving signal to the driving unit 6 to have the
welding gun 4 in the working section 2 aligned with the
position on the work where the welding is to be made. The
control`unit 7 further performs calculations based on the
informations concerning the work to be welded as received
from the processing unit 14 to obtain the welding control
parameters. The control unit 7 produces a welding initiating
signal which is applied to the sequencer 8. The sequencer 8
then transmits the welding initiating signal to the timer
controlled operating unit 9 so that the welding step is
started. During the welding step, the control unit 7 applies
the welding controlling parameters which are appropriate to
lZ9 ~541
the position on the work where the welding is being carried
out.
When the welding in the particular position on the work
S is completed, the sequencer produces a welding end signal
which is applied to the controller 7. The controller 7 then
produces a further driving signal based on the informations
concerning the sequence of welding positions as received from
the processing unit 14. The driving unit 6 is thus actuated
to have the welding gun 4 in the working section 2 aligned
with the position on the work where the welding is to be
carried out next. As soon as the alignment is made, a
further welding step is carried out. The display/input unit
13 displays informations on the welding controlling
parameters of the position where the welding is being carried
out as well as informations concerning the results of welding
made in the positions where the welding has already been
made. The input keys on the unit 13 may be actuated as
necessary to modify the informations on the work as stored in
the memory of the control unit 7.
The processing unit 14 may be omitted when appropriate.
Then, the informations concerning the work 5 may be applied
to the control unit 7 by actuating the input keys on the
display/input unit 13. The control unit then performs
calculations to determine the welding controlling parameters.
In other respects, the operations may be made in a manner
similar to that previously described.
The present invention can be embodied in a welding
robot in which the working section having a welding gun and
lZ975~
an actuating cylinder is not movable. In such a case, the
work S is moved with respect to the welding gun 4 to a
position where the location to be welded is aligned with the
welding gun. The welding operations may be carried out in a
manner similar to that previously described.
In case of a spot welding robot as described, the
informations on the work to be welded are given in the form
of the type and the thickness of the sheets and the number of
the sheets in the work. In a robot for another type of
welding, the informations may be given in different forms.
The invention has thus been shown and described with
reference to a specific embodiment. however, it should be
noted that the invention is in no way limited to the details
of the illustrated arrangements but changes and modifications
may be made without departing from the scope of the appended
claims.