Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
20141 ~3
Field of the Invention
The invention refers to an apparatus for treating
gases, in particular flue gases, said apparatus comprising a
hollow casing which extends mainly vertically, said casing
holding various built-in components, in particular floors,
column separators or gas washers.
Prior Art
Known apparatuses comprise a casing which is
dimensioned to cater for the whole amount of gases to be
treated, said casing including built-in components arranged in
such a manner that they extend across the whole clear opening
of said casing.
The above leads to the disadvantage that mostly very
large cross-sections are necessary. This causes problems in
dimensioning and constructing the components to be built in.
Furthermore, large cross-sections, which can be found in known
apparatuses of the above mentioned kind, cause the flow
through the built-in components to vary across the cross-
section, whereupon their effectiveness is reduced
accordingly.These difficulties cause planning of such
apparatuses to be very expensive and time-consuming and,
furthermore, require extensive model tests. This consequently
leads to long periods of construction which constitute a
considerable disadvantage in a time when regulations on
environmental protection are made more and more stringent.
SummarY of the Invention
It is the object of the invention to avoid these
disadvantages and to propose an invention of the above
mentioned kind which, on the one hand, enables a mostly
consistent flow across the whole cross-section of the built-in
components and, on the other hand, requires only relatively
simple supporting structures for the built-in components.
According to the invention this is achieved in that
the casing is subdivided by at least two crossing partitioning
walls, whereby fixing devices are attached both to said
partitioning walls and the interior walls of said casing, said
fixing devices being arranged for placing on to it floors,
column separators, demisters or spraying devices and that said
casing comprises connections or openings for feed pipes and
2 2~141 ~3
that guiding plates are arranged for separating the gas flow
and directing it towards the subdivisions of the cross-
sections of the casing.
Thereby the above results in correspondingly small
cross-sections and simple fixing devices for the components to
be built in, whereby said components, with regard to their
statics, may be dimensioned considerably smaller than those
which would be necessary ior the same gas flow in prior
solutions. Furthermore, this measure leads to a more even
distribution of the gas flow to be treated, said distribution
occurring across the whole cross-section of the casing.
A further feature of the invention may comprise the
exterior wall of the casing having fixing devices, said fixing
devices being intended for mounting auxiliary units such as
pumps or accumulators.
These measures enable the arrangement of an
accumulator behind each built-in component operating in a wet
manner, such as gas washers, column separators and such-like,
and to place said accumulator only slightly lower versus the
respective built-in components. Consequently less pumping
power is required within circulations, as the lifting heights
for pumps are very small.
It is a further object of the invention to propose an
arrangement with apparatuses in accordance with the invention,
said arrangement being easily adjustable to the gas flow to be
treated and not requiring extensive planning therefor.
In accordance with the invention this is achieved in
that prefabricated casings in various predefined sizes are
erected at a distance from each other and that said casings
comprise built-in components according to the respective
requirements, whereby a separate, if necessary~controllable,
supply of the gas to be treated is arranged for each of the
parallelly fed casings.
This measure allows modular prefabrication of both
casings and fixing devices for various components to be built
in, whereby it would suffice, for the various plants, to place
the number of casings which are required for treating the
developing gases next to each other.
There is an additional advantage in that in the case
of part-load operation even the apparatus for treating the
developing gas flow may be adjusted to the respective amount
3 2~4~
of developing gases, so that the part of the apparatus for
treating the gas flow which remains in operation can be
operated at a capacity of around 100 percent, e.g. within a
range of 80 to 120 percent, thereby causing optimal conditions
even in the case of part-load operation. If this is applied to
the whole apparatus one can start out from the fact that even
in the case of minute part-loads, efficiency is very high.
It may be further intended that each casing consists
of several components, said components being connected to each
other and being arranged in a stack-like manner, which
simplifies production of prefabricated modules. Furthermore,
this enables adjustment to the respective requirements, in
particular to the number of stages of treatment which are
required for the gas flow.
It is a further object of the invention to propose an
arrangement comprising apparatuses according to the invention
for treating larger amounts of gases, said apparatuses being
easily adju6table to the amount of gases to be treated.
In accordance with the invention this is achieved in
that prefabricated casings in various predefined sizes are
erected at a distance from each other and that said casings
comprise built-in components according to the respective
requirements, whereby a separate, if necessary controllable,
supply of the gas to be treated is arranged for each of the
parallelly fed casings.
Depending on the amount of gases to be treated, this
measure allows the arrangement of a number of apparatuses
according to the invention, said apparatuses being designed
for relatively small amounts of gases, thereby causing low
planning requirements. By placing the apparatuses at a
di~tance, mutual influence, in particular thermal coupling, is
avoided. Furthermore, arrangements constructed in such a
manner may also effectively be operated at part-load
operation, as in this case a pertinent number of apparatuses
can be turned off or excluded from utilization.
Brief De~criPtion of the drawinas
Based on the drawing the details of the drawing are
outlined as follows:
Fig. 1 shows a diagrammatic top view of an
arrangement with apparatuses in accordance with the invention.
4 2~14~3
Fig. 2 shows a vertical section through an
arrangement with apparatuses in accordance with the invention.
Detailed Description of Preferred Embodvment
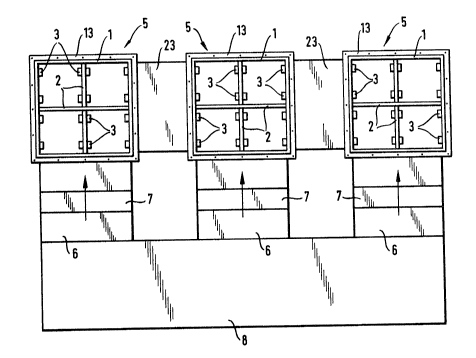
As is diagrammatically outlined in fig. 1, each of
the apparatuses consists of casing 1 with a more or less
square profile. Said casing is subdivided by two crossing
partitioning walls 2. Fixing devices 3 are attached to these,
as well as to the interior walls of casing 1, whereby said
fixing devices 3 are intended for accepting or supporting
various components to be built in, such as floors, demisters,
column separators, spraying devices and such-like.
The arrangement in accordance with fig. 1 shows
several such apparatuses 5 which are connected to accumulator
8 via corresponding feed pipes 6, said feed pipes preferably
comprising independently controllable ventilators 7.
As can be seen from fig. 1, the subdivision of the
clear opening of casing 1 results in relatively small sizes
for each component to be built in, so that said components are
subjected to very low mechanical stresses during operation and
thus need only be dimensioned very weakly.
The subdivision of the cross-section also causes the
gas flow to be treated to pass through said components more
evenly.
Fig. 2 diagrammatically shows a vertical section
through an arrangement with inventive apparatuses 5.
Therein casings 1 of apparatuses 5 consist of several
parts 9 to 12, said parts being arranged in a stack-like
manner and connected to each other and having on their facing
ends flanges 13.
The lowermost part 9 of casing 1, said part also
comprising feed opening 14 for the gases to be treated, in
partlcular flue gases, comprises guide plates 15, said plates
ensuring even distribution of the inflowing gases to the four
divisions across the clear opening of casing 1, said divisions
being brought about by partitioning walls 2.
Parts 10, 11 and 12 of casing 1 comprise, as was
already outlined based on fig. 1, fixing devices on
partitioning walls 2 and the interior walls of casing 1.
Various components to be built in, such as floors 16,
demisters 17, spraying devices 18, column separators 19,
distribution devices 20 for e.g. injecting oxygen, ozone, or a
2~1~183
mixture of such gases for a denitration device for removing
nitrogen oxides from flue gases, or dust collectors 21 are
either supported by or attached to said fixing devices.
Furthermore, casing 1 comprises openings 22 for
various pipes, said openings allowing compact guiding of the
pipes through said casing.
Apparatuses 5 are arranged at a distance from each
other, but are connected via stages 23. Accumulators 24 are
attached to said stages, whereby said accumulators are
connected on the one side with collecting pipes of column
separators 19 and on the suction side with pumps 2~, said
pumps being intended for upholding circulations, in particular
for lime milk for desulphurization or for ammonia for
discharging nitrates from a denitration device.
Both casings 1 and the components to be built in may
be prefabricated in various predefined sizes for various
plants. Depending on the amount of gas to be treated, a
pertinent number of apparatuses 5 according to the invention
may be erected and may parallely be fed with the gas to be
treated.
Cross-section sizes of 2m x 2m, 2.5m x 2.5m and 3m x
3m have proved to be preferable for casings 1. Each
subdivision results in a relatively small area of cross-
section. In the case of such small areas of cross-section, it
is relatively simple to determine the reactions which will
take place and the flow of the gases to be treated through the
built-in components. This makes model tests unnecessary which
otherwise have to be performed for large areas of cross-
sections of e.g. lOm x lOm, whereby the results of said tests
are not always satisfactory.
Due to the inventive measures it is very easy to
erect plants for treating large amounts of gas with the lowest
possible planning efforts, because one only has to erect the
pertinent number of subdivided casings. Thus it is also
po8sible to adjust the apparatus for treating the gas flow to
the amount of gas to be treated, as the supply of gas to the
respective casings, said casings comprising the respective
20~4~3
built-in components, may either be interrupted or opened. It
may further be intended to arrange respective control devices
in separate feed pipes, said pipes leading to each partial
cross-section of each casing, thus causing the partial cross-
sections of the casings fed by the gas flow to practically
operate at their normal rating.