Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
~~4;~~9~$
SYNTHETIC RESIN SURFACE FASTENER
INCLUDING INTEGRALLY MOLDED HOOKS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention:
This invention relates 1,o a synthetic resin sur-
face fastener including a base and hook elements which
are integrally molded, and more particularly to a
synthetic resin surface fastener member having hook
elements which can assure a very strong intermesh with
a companion surface fastener member.
2. Description of the Related Art:
There have been known a number of surface
fasteners in each of which a base and hook elements
protruding from the base are integrally molded. A
plurality of methods have been proposed to produce
such surface fasteners.
Japanese Patent Publication No. 53712/1982 dis-
closes one of such methods, for example. In this
method, a flat base and straight projections are
molded integrally first. Then tips of the straight
projections are pressed to and moved along semi-
circular grooves formed on a die so as to be in the
shape of hook. In this case, when the grooves have
random directions, the hooks will also have random
directions, thereby assuring a very strong grip with a
- 1 -
~:,(~~.:~L;:~3~
companion surface fastener member.
However since it is very difficult to mate with
the tips of the straight projections with the grooves,
and since the hooks are not produced in one step, not
only manufacturing processes are complicated but also
respective hooks are di.fficuli~ to face desired direc-
Lions. In addition, it is very difficult to shape the
hooks as predetermined. Therefore the hooks will not
be shaped uniformly, and cannot assure a strong grip
with the companion fastener member. For these rea-
sons, this method has not yet been in practical use.
With a method exemplified in Japanese Patent
Publication No. 22768/1973, both of a base and hook
elements are formed integrally by extrusion molding at
a time, and the hook elements are shaped in succes-
sion. In this method, a plurality of die discs and
spacer discs are piled one over another so as to ob-
tain a mold drum. Then melted thermoplastic resin is
extruded onto the surface of the mold drum, being
pushed into mold cavities on the die discs. The resin
on the surface of the mold drum is pressed to form a
base, being cooled. Then the spacer discs are
retracted inwardly so as to scrape a strip of molded
fastener member from the surface of the mold drum.
Each of the die discs has a number of hook-shaped
cavities which are spaced as predetermined and extend
- 2 -
toward the center from the circumferential edge of the
disc. The spacer discs have smooth surfaces. The
spacer discs are necessary because one die cannot have
cavities shaped in complete conformity with the con-
tour of the hooks. In addition, since the cavities on
each die discs face the circumferential direction of
the die disc, the hooks have the direction same as
that of the cavities. Therefore, all of the hooks
have the same direction. It is difficult to change
the direction of the hooks.
The existing surface fasteners have hooks which
usually face one direction, which means a fastening
force of the surface fasteners is directional, thereby
adversely affecting strong fastening and easy un-
fastening of the surface fasteners.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is therefore an object of this invention to
provide a surface fastener member which is integrally
molded and which can assure a very strong grip in any
direction by taking advantage of directionality of the
molded hooks.
According to this invention, there is provided a
synthetic resin surface fastener member comprising a
flat base and a plurality of hook elements bristling
from one surface of the flat base, both being molded
integrally, wherein the hook elements are arranged in
- 3 -
~~~~~9~
two or more sections, and the hook elements in one
section and those in sections adjacent thereto face
directions perpendicular to one another.
This invention is contemplated by taking ad-
vantage of the directionality o.f the hook elements
determined when the hook elements are molded. There-
fore, a number of hook elementa having the same direc-
tion compose one group while hook elements having a
direction perpendicular to that of the foregoing hook
elements compose another group. Groups of the hook
elements facing in the opposite directions are
alternately molded side by side on the same base.
When each row of hook elements facing the same
direction and each row of hooks facing the opposite
direction are alternately arranged side by side, when
each row has hook elements facing opposite directions,
or when adjacent groups of hook elements are per-
pendicular to each other in the direction of the hook
elements, the surface fastener member including the
foregoing hook elements can assure a very strong and
uniform intermesh with its companion surface fastener
member throughout the whole surface area.
BRIEF DESCRIPTTON OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a bottom plan view showing one typical
example of an integrally molded surface fastener ac-
cording to an embodiment of this invention:
- 4 -
FIG. 2 is a front elevation of the surface
fastener of FIG. 1;
FIG. 3 is a side elevation of hook elements, in
enlarged scale, of the surface fastener; and
FIGS. 4 and 5 are bottom plan views showing ar-
rangements of hook elements of circular surface
fastener members.
DETAINED DEBCItI~~TION
A typical example of a surface fastener accord-
ing to this invention will now be described with
reference to the accompanying drawings.
In the drawings, reference numeral 11 stands for
a base which has hook elements 15 extending from a
surface thereof and a clamp 13 protruding from the
other surface thereof. The clamp 13 is adapted to be
attached to a non-illustrated mounting base on which
an interior finish material is to be installed in an
automobile, for example. The base 11, hooks 15 and
clamp 13 are integrally produced by extrusion or in-
jection molding so as to serve a surface fastener mem-
ber 1. The surface fastener member 1 is installed on
a ceiling reinforcement 2, for example on an
automobile ceiling, as follows. The clamp 13 of the
surface fastener member 1 is inserted through an open-
ing 131 of the ceiling reinforcement 2 so that the
ceiling reinforcement 2 is sandwiched by the clamp 13
_ 5 _
and the base 11 of the surface fastener member 1.
Then a pile-like surface on the rear surface of an in-
terior finish material is made to intermesh with hook
heads 12 of the surface fastener member l, so that the
interior finish material is installed on the ceiling
reinforcement 2.
As-described above, the hook elements 15 are ar-
ranged in two or more section;. The hook elements 15
in the respective sections are arranged so that their
directions are perpendicular one another. In the em-
bodiment shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the hook elements 15
are arranged in four sections by quartering the square
base 11. However, the number of the sections is not
limited to four. Tn addition, the number of the sec-
tions depends upon the shape of the base 11. When the
base is circular, the hook elements 15 will be ar-
ranged in sections as shown in FIGS. 4 and 5.
Arrangement and typical shapes of the hook ele-
ments will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to
3. As shown in FIG. 3, each hook element 15 looks
like the crest of a wave in cross sectional outline.
The lateral crass sectional area of the hook element
15 is decreased gradually from a bottom toward a
tip 17. Specifically a portion 18 at which the hook
element 15 extends straight from the base 11 is
slightly and gently sloped toward the tip 17. The
- 6 -
~~~~9~
front of the hook element 15 is substantially upright.
Reinforcing ribs 19 extend from opposite sides of the
hook element 15. The shape of the hooks shown in
these drawing figures is given as an example, and is
not limited to the example.
A plurality of the hook elements 15 having tips
facing.the same direction and/or those facing the op-
posite direction according to the structure of mold
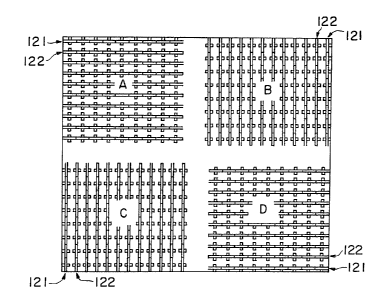
dies are arranged in rows on the base 11. In this em-
bodiment, rows 121 of the hook elements facing the
same direction and rows 122 of the hook elements
facing the opposite direction are alternately arranged
so as to form a section A. In sections B and C ad-
jacent to the section A, the rows 121 and 122 are ar-
ranged so as to be perpendicular to those of the sec-
tion A. In the section D adjacent to the sections B
and D, the arrangement of the rows 121 and 122 are the
same as that in the section A. The surface fastener
member 1 of this embodiment has four hook groups in
the sections A, B, C and D. The rows of the hook ele-
ments, i.e. the directions of the hook elements 15, in
adjacent two sections, are perpendicular to one anoth-
er. Each section is equal in the area, i.e. the sec-
tions A and D are equal in size while the sections B
and C are equal in size.
With the foregoing arrangement, the hook heads
~~~ ~.~.~9~3
1~ of the hook elements 15 of the surface fastener
member 1 face at least four directions. Therefore the
surface fastener member 1 can grip completely with a
flexible pile-like surface of the companion surface
fastener member, providing a strong fastening force
throughout the intermeshing areas.
The surface fastener member having the integral-
ly molded hook elements can ds:monstrate a uniform
fastening force throughout it:: whole surface area.
g -