Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02119456 2002-10-31
-1-
Load Cell Mount for Hospital Weigh Bed
Brief Summary of the Invention
This invention relates to a weigh bed and is
particularly related to a fluidized patient support
system weighing of the order of 1,500 pounds. The
fluidized patient support system is disclosed in U.S.
Patent No. 4,672,699. The patient support system
includes a tub filled with a mass of granular material
and covered with a loose-fitting flexible patient contact
sheet. Air is forced into the granular material to
fluidize it, thus supporting the patient on a fluidized
system. The tub, the granular materials and patient
weigh in excess of 1,000 pounds, usually in the range of
1200 - 1600 pounds. The tub is mounted on a base which
is trapezoidal in cross section.
An objective of the present invention has been to
provide a scale for continuously weighing the patient,
the scale including a transducer formed by load cell
beams generally of the type disclosed in U.S. patent No.
4, 974, 692 .
CA 02119456 2002-10-31
-2-
In the '692 patent, a patient support structure is
mounted on a base by means of four load cells, one
mounted at each corner of the bed. Each load cell has a
load cell beam that is cantilever-mounted at one end and
engages a steel ball at the other end. The steel ball is
engaged by upper and lower flat seats that provide a
rolling contact between the ball and the seats. The ball
and flat seat combination provides assurance that only
vertical components of force are imposed on the load cell
and hence measured by the scale. A system of rods
connected between the base of the bed and the patient
support prevents the patient support structure from
rolling off the balls.
A further objective of the present invention has
been to provide an improvement on the rolling ball
support of the '692 patent.
The obj ectives of the present invention are attained
by substituting for the flat seats of the '692 patent
cup-shaped upper and lower surfaces. The cup-shaped
upper and lower surfaces are generally hemispherical and
of a substantially greater diameter than the ball
captured between the surfaces. Any tendency of the
patient support to move in a lateral direction is
therefore resisted by the ball having to
wo 93ia6sa-r Pc:rius~zias3z9
_3_
roll uphill, so to speak, with respect to the cup-
shaped seats which confine it. The heavier the load,
' that is the patient support, the harder it is to ride
uphill to dislodge the cups from the steel ball
disposed between them.
The combination of cups and steel ball
connecting the load cells to the heavy patient support
assures that only vertical forces will be measured by
the load cells and will confine the patient support
against lateral movement with respect to its base.
Another feature of the invention has been to
provide retainers cooperating with bolts depending
from the patient support tub, the retainers providing
further assurance that lateral movement of the tub
with respect to the base will be resisted.
Further, the bolts themselves pass through
holes in the base to provide added insurance against
lateral movement. The bolts are maintained out of
contact with the retainers or the base itself in
normal operation so that there is no frictional force
between tub and base that would influence the weighing
of the patient.
As another feature of the invention, the
base has two trapezoidal structures each having a top
horizontal bar. Each horizontal bar has a trough
formed in its upper surface within which each load
cell beam is disposed, there being four load cell
beams, one at each corner of the bed.
WO 93/06807 PCIf/US92/08329
211945
Brief Description of the Drawings
The several features and objectives of the
present invention will become more readily apparent
from the following detailed description taken in
conjunction with the accompanying drawings in which:
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of the inven-
tion;
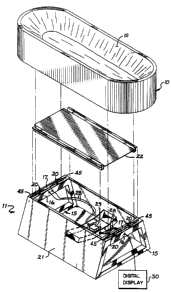
Fig. 2 is a diagrammatic, disassembled
perspective view of the invention;
Fig. 3 is a disassembled cross-sectional
view through one end of the bed; and
Fig. 4 is an enlarged cross-sectional view
showing the load cell mount.
Detailed Description of the Tnvention
Referring to Fig. l, a fluidized patient
support system is shown. A deep tub 10 is mounted on
base 1I, the base being trapezoidal in cross-section.
The tub 10 is filled with a ceramic granular material
which is covered by a flexible sheet 12. A blower
z0 system (not shown) drives air through the granular
material in the tub creating a fluidized bed which
supports the patient while resting on the sheet 12.
The blower is connected to the bed by a hose of
~i
sufficient flexibility that it does not add a force
component to the weighing system. The bed is particu-
larly useful for patients who have been immobilized
for long periods of time and have developed bed sores.
dV0 93/06807 P('T/US92l08329
_5_
As shown in Fig. 2, the base 11 has as
principal structural elements two horizontally-spaced
' trapezoidal structures 15. Each trapezoidal structure
includes a top bar 16. The upper surface .of the top
bar 16 is formed as a trough 17 within which four load
cells 20 are mounted, one load cell being at each
corner of the bed. A wrapper 21 is wrapped around the
sides and bottom of the base 11 to enclose the base.
A stiffener plate 22 extends between the two trape-
zoidal structures 15 and is bolted at its ends to the
trapezoidal structures while leaving the troughs 17
exposed.
Referring to Fig. 4, each trough has a
bottom wall 23. A spacer 25 is welded to the bottom
wall 23. Each load cell 20 has a beam 26 secured by
two anchor bolts 27 passing through the bottom wall 23
and spacer 25. Each load cell has a bridge connection
of four strain gauges, not shown, forming a transducer
connected by conductors 28 (Fig. 2) Which are in turn
connected to a load cell summing junction box 29 and
from there to a digital display 30.
The anchor bolts 27 secure one end of the
load cell beam 26 in the trough leaving a cantilevered
' free end 32 free to flex vertically. A lower ball cup
stud 35 is threaded into the free end 32 of the load
cell 20. A similar ball cup stud 36 is secured by a
nut 37 to the bottom of the tub and precisely overlies
the ball cup stud_35. The ball cup studs have facing
WO 93/06807 PCT/US92/08329
_6_
surfaces 38 in the lower stud and 39 in the upper stud
which are generally hemispherical. A 5/8 inch harden-
ed stainless steel ball 40 is mounted between the
surfaces 38, 39 to provide the sole connection of the
S tub to the load cell and base. Collectively, the four
load cells provide the entire support of the tub
through the hardened balls 40. The diameter of the
sphere that defines the surfaces 38, 39 is approxi-
mately 7/8 inch. The surfaces are hardened to about a
Rockwell 62. "
A clearance hole 45 is formed in the top bar
16 of the trapezoidal structure 15. A stop bolt 46
passes through a clamp plate 43, the bottom wall 47 of
the tub 10 and a tub plate 44. A cylindrical spacer
48 is mounted on the bolt 46 below the tub and is
secured thereto by a nut 49 and washers 50 and 51.
The nut 49 passes through the clearance hole 45 in the
top bar 16. The clearance hole 45 is of a diameter
substantially greater than the transverse dimension of
the nut 49 so that there is no contact between the nut
or any part of the bolt 46 and the elements attached
to it and the base 11.
' ~~ A retainer clip 55 is attached by a bolt 56
to the side of the trapezoidal structure 15 at each
corner of the base. The retainer clip has a hori-
zontal section 57 that terminates in an edge 58 having
a semicircular recess 59 of greater diameter than the
spacer 48. The spacer 48 is received in the recess
tY0 93/06807 PCd'/LJS92/08329
~1~.J~J~
59, but the dimension of the recess is greater than
the diameter of the spacer so that normally there is
' no contact between the retainer clip and the spacer.
The retainer clip cooperating with the bolt
S as well as the clearance hole 45 cooperating with the
nut 49 provide assurance that there will be no lateral
movement of the tub great enough to cause the ball cup
studs to become dislodged from the balls.
In the operation of the invention, the tub
is supported only by the engagement of the studs 35,
36 with the ball 40 at each corner of the tub. The
weight of the tub and patient stresses the load cell
beams causing their transducers to provide signals
proportional to the weight that is stressing them.
The weight of the patient is displayed on the digital
display 30. Each ball 40 provides single point
contact with its upper and lower cup stud 36, 35 so
that only vertical components of force are applied to
the load cell beam. ,any tendency of the tub to move
laterally with respect to the base is resisted by the
cup stud and ball interconnection. The upper stud
must roll uphill over the ball to be dislodged and/or
the ball must roll uphill over the lower stud to be
' dislodged. The greater the mass contained within the
tub, the greater is the lateral force that would be
required to cause the dislodgment of the cup and ball
interengagement. Thus, under normal conditions of
transportation and the like, the tub remains securely
CA 02119456 2002-10-31
_g_
seated on the base. If there is unusual lateral stress
of the tub with respect to the base, that is resisted by
the bolt 46 and its engagement with clearance hole 45
and/or clip 55.
From the above disclosure of the general principles
of the present invention and the preceding detailed
description of a preferred embodiment, those skilled in
the art will readily comprehend the various modifications
to which the present invention is susceptible.
Therefore, we desire to be limited only by the scope of
the following claims and equivalents thereof: