Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
2144396
PAINT FILM-PROTECTIVE SHEET
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a paint film
protective sheet which is hard to cause a paint film
deformation and suitable for the surface protection of
automobile bodies and parts, coated steel plates, etc.
BACKGROLiND OF THE INVENTION
In the case of loading trucks or ships with coated
automobiles, the parts thereof, etc., and transporting those to
remote places such as overseas, an effective means is desired
to prevent the paint films of the automobiles, etc., from being
damaged, dulled, discolored, etc., by various suspended matters
such as dusts or rains, or impinging matters.
Hitherto, a method of applying a coating material
comprising a wax as the main component at a thickness of from
5 to 40 um has been known as such a prevention means.
However, this method has various problems such that it
is difficult to form the wax coating at a uniform thickness,
whereby a uniform protection of the paint film is not obtained;
the coated layer is liable to be stained and has a poor
resistance to acidic rain; the wax and the like penetrate into
the paint film to cause discloration or other defects; the -
formation and the removal of the wax coating require much
labors; and the use of a solvent, the treatment of waste
liquids, etc., are liable to cause environmental problems.
- 1 -
2~4439~
On the other hand, various surface protective sheets
comprising a substrate having formed thereon a pressure-
sensitive adhesive layer are known, and a surface protective
sheet comprising a substrate having formed thereon a radiation-
curable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer having a lowered
glass transition point (Tg) is proposed for use on adherends
having a paint film as disclosed in JP-A-2-199184 (the term
"JP-A" as used herein means an "unexamined published Japanese
patent application"). Such a sheet system can overcome the
problems described above.
However, where such a surface protective sheet is
adhered to the surface of the paint film of an automobile or
the like, low molecular weight components contained in the
paint film, such as a fatty acid glycerol ester, migrate into
the surface protective sheet side due to a temperature rise in
the outdoor transportation, whereby a step mark phenomenon
occurs in the paint film to cause a problem that the adhesive
marks of the protective sheet clearly appear on the surfaces of
the paint film. In particular, in a low Tg type paint film,
the adhered traces having a depth of from about 0.1 to 0.5 Pm
usually occur during the adhesion of the protective sheet for
about 10 hours under 50°C.
The present inventors have previously proposed a
surface protective sheet in which a rubber-based polymer such
as a polyisobutylene is used as a pressure-sensitive adhesive
(EP 0 519 278 A2). This sheet is hard to cause the deformation
_ 2
21443J~
of a paint film and does not have a problem on adhesive
remaining. Thus, this sheet is a practical surface protective
sheet. However, this sheet has in some cases a problem that
the adhesive marks may not completely be eliminated where the
paint film contains a fatty acid glycerol ester.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to
provide a paint film-protective sheet which can prevent the
occurrence of the step marks as illustrated in the Figure onto
a paint film by the migration of the low molecular weight
components contained in the paint film into the paint film-
protective sheet even in the case of being accompanied by the
temperature rise in the outdoor transportion of automobiles,
etc., whereby the adhesive marks of the protective sheet are
not formed on the surface of the paint film, and is excellent
in the protective property for paint films and in the releasing
property without leaving the pressure-sensitive adhesive which
becomes a staining material.
According to the present invention, there is provided
a paint film-protective sheet comprising a supporting substrate
having formed thereon a rubber-based pressure-sensitive
adhesive layer compounded with a fatty acid glycerol ester.
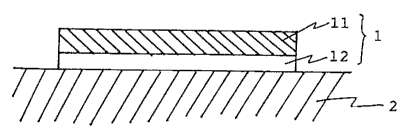
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a view showing a state that a paint film-
protective film 1 comprising a supporting substrate 11 and a
pressure-sensitive adhesive layer 12 is adhered on a paint film
- 3 -
2144396
2;
Figure 2 is a view showing a state that low molecular
weight components contained in a paint film 2 have migrated
into a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer 12 of a paint film-
s protective sheet 1; and
Figure 3 is a view showing a state that a step mark 3
is formed on a paint film 2 after removing a paint film-
protective sheet 1.
DETAILED DE CRIPTION 9F THE INVENTIQN
The present invention is described in detail below.
In the present invention, by using the rubber-based
pressure-sensitive adhesive compounded with a fatty acid
glycerol ester, the migration of the low molecular weight
components in a paint film into the protective sheet can be
prevented even in the case of involving the temperature rise in
an outdoor transportation of automobiles, etc., and the step
mark phenomenon of the paint film does not occur, whereby the
adhesive marks of the protective sheet are not formed on the
surface of the paint film. Further, the paint film-protective
sheet of the present invention is excellent in the protective
property for the paint film in the state that the protective
sheet is adhered thereon, and also can be easily released from
the paint film without leaving the pressure-sensitive adhesive
which becomes a staining material on the paint film.
The paint film-protective sheet of the present
invention has on a supporting substrate a rubber-based
- 4 -
pressure-sensitive adhesive layer compounded with a fatty acid
glycerol ester.
The supporting substrate used in the present invention
can be any appropriate material, and examples thereof are
plastic films, porous films, papers, nonwoven fabrics, etc.
The thickness of the supporting substrate is generally 300 um
or less, and preferably from 10 to 100 um, although the
invention is not limited to the thickness.
The pressure-sensitive adhesive layer can be formed by
using an appropriate rubber-based pressure-sensitive adhesive
comprising one or more kinds of rubber-based polymers such as
natural rubber, polyisobutylene, an A-B-A type block polymer,
etc., as the main components and, if necessary, a tackifier or
a softener. Further, the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer may
contain appropriate additives such as a filler, a pigment, an
antioxidant, a stabilizer, etc.
Examples of the more preferred rubber-based polymer
from the point of the stability of the performance of the paint
film-protective sheet over a long period of time are a non-
curable polyisobutylene-based polymer and an A-B-A type block
polymer comprising a polystyrene block, an ethylene-butylene
copolymer block, and a polystyrene block. Further, the
polyisobutylene-based polymer which is preferably used is a
mixture of a high molecular weight type polymer having a
viscosity average molecular weight of at least 100,000 and a
low molecular weight type polymer having a viscosity average
- 5 -
2~4439~
molecular weight of less than 100,000 at a weight ratio of 95
to 80 : 20.
The tackifier or the softener which may be contained in
the rubber-based pressure-sensitive adhesive can be any
5 appropriate material, but the tackifier or the softener having
a good compatibility with the rubber-based polymer is
preferred. In general, Examples of the tackifier are
hydrocarbon resins, alkylphenol resins, and terpene resins.
Examples of the softener generally used are a
polyisobutylene having a low molecular weight when the rubber- _
based polymer is a polyisobutylene, and a paraffin oil when the
rubber-based polymer is the A-B-A type block polymer.
Examples of the fatty acid glycerol ester to be
compounded with the rubber-based pressure-sensitive adhesive
layer in the present invention are a (mono, di, or tri)capric
acid glycerol ester, a (mono, di, or tri)lauric acid glycerol
ester, a (mono, di, or tri)myristic acid glycerol ester, and
coconut oil. Of those, coconut oil is preferably used.
The fatty acid glycerol ester is used in the state that
it is compounded with the rubber-based pressure-sensitive
adhesive, and the compounding amount thereof is appropriately
determined by the thickness of the pressure-sensitive adhesive
layer formed. When the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer
having a thickness of 15 ~m is a standard, the compounding
amount of the fatty acid glycerol ester is from 0.5 to 20 parts
by weight, and preferably from 3 to 10 parts by weight, per 100
- 6 -
2144396
parts by weight of the rubber-based pressure-sensitive
adhesive. If the compounding amount is over 20 parts by
weight, it sometimes happens that the fatty acid glycerol ester
bleeds on the surface of the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer
to stain the surface of the paint film. On the other hand, if
the compounding amount of the fatty acid glycerol ester is less
than 0.5 part by weight, the addition effect thereof is poor
and the adhesive marks are liable to form.
The paint film-protective sheet of the present
invention can be formed according to a conventional method of
forming an adhesive sheet, such as a method of coating a
supporting substrate with a solution of the rubber-based
pressure-sensitive adhesive compounded with the fatty acid
glycerol ester or a hot-melt liquid of the rubber-fatty acid
glycerol ester, or a method of transferring the pressure-
sensitive adhesive layer formed on a separator onto a
supporting substrate, etc.
The thickness of the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer
formed may be appropriately determined, but is generally 200 ~m
or less, and preferably from 5 to 50 um. The pressure
sensitive adhesive layer is, if necessary, protected by pre-
fixing thereto a separator, etc., before use.
The paint film-protective sheet of the present
invention is advantageously used to protect the surfaces of
adherends having a paint film, such as bodies and parts of
automobiles coated with a paint film such as a melamine-alkyd
_ 7 _
21~439~
type, melamine-acryl type or urethane type paint film, or metal
plates (such as steel plates) or the shaped articles thereof
coated with the paint film, from impinging of fine matters,
chemicals, etc. In particular, the paint film-protective sheet
of the present invention can be advantageously used in the case
which involves the temperature rise as in the case of the
outdoor transporting of the automobiles, etc., or in the case
that the paint film-protective sheet is adhered to paint films
of automobiles, etc., over a long period of time.
The present invention is described below in more detail
by reference to the following examples and comparative
examples, but it should be understood that the invention is not
construed as being limited thereto. Unless otherwise
indicated, all percents, parts, ratio and the like or by
weight.
EXAMPLE 1
To a toluene solution of a rubber-based pressure- -
sensitive adhesive composed of a mixture of 75 parts of a
polyisobutylene having a viscosity average molecular weight of
1,000,000 and 25 parts of a polyisobutylene having a viscosity
average molecular weight of 80,000 was added 5 parts of coconut
oil followed by compounding. The resulting liquid was coated
on a film having a thickness of 40 um composed of polypropylene
and polyethylene (9/1 by weight ratio), and dried at 80°C for
2 minutes to obtain a paint film-protective sheet having a
pressure-sensitive adhesive layer having a thickness of 15 Vim.
_ g
CA 02144396 2001-08-31
EXAMPLE 2
A paint film-protective sheet was obtained in the same
manner as in Example 1 except that the compounding amount of
coconut oil was changed to 10 parts.
EXAMPLE 3
A paint film-protective sheet was obtained in the same
manner as in Example 1 except that the compounding amount of
coconut oil was changed to 20 parts.
A paint film-protective sheet was obtained in the same
manner as in Example 1 except that trilauric acid glycerol
ester was used in place of coconut oil.
EXAMPLE 5
A paint film-protective sheet was obtained in the same
manner as in Example 1 except that a mixture of 100 parts of an
A-B-A type block polymer comprising a polystyrene block, an
ethylene-butylene copolymer block, and a polystyrene block
(KratonTM G-1657, made by Shell Chemical Co. ) and 40 parts of
a hydrogenated petroleum resin (ArconTM, made by Arakawa
Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was used as the rubber-based
pressure-sensitive adhesive.
COMPARATIVE EXAMPLE 1
A paint film-protective sheet was obtained in the same
manner as in Example 1 except that coconut oil was not
compounded.
_ g -
214436
COMPARATIVE EXAMPLE 2
A paint film-protective sheet was obtained in the same
manner as in Example 1 except that the compounding amount of
coconut oil was changed to 30 parts.
Evaluation Tests
Each of the paint film-protective sheets obtained in
the examples and the comparative examples was subjected to the
following tests.
Adhesive Remaining:
The paint film-protective sheet was adhered at room
temperature to a plate having an alkyd-melamine paint film
having a glass transition point of 60°C and containing the
fatty acid glycerol ester. The resulting plate was placed in
an atmosphere of 80°C for 24 hours, taken out therefrom, and
then allowed to stand at room temperature for 3 hours.
Thereafter, the paint film-protective sheet was stripped off,
and the presence of the pressure-sensitive adhesive remained on
the paint film of the plate, in particular, the presence of the
pressure-sensitive adhesive remained on the portion of the
paint film of the plate corresponding to the peripheral portion
of the paint film-protective sheet was examined.
Adhesive Mark:
The alkyd-melamine paint film after the above adhesive
remaining test was observed, and the presence of the adhesive
marks in the paint film, in particular, the presence of the
adhesive marks in the portion corresponding to the peripheral
- 10 -
~144~9~
portion of the paint film to which the paint film-protective
sheet had been adhered was visually examined. In this test,
when the adhesive mark (concaved portion) of the paint film
caused by the migration of the fatty acid glycerol ester
contained in the alkyl-melamine paint film into the paint film-
protective sheet was not observed, the case was evaluated as
"none" and when such an adhesive mark was observed, the case
was evaluated as "found".
The results obtained are shown in the table below.
TABLE
Comparative
Example example
1 2 3 4 5 1 2
Adhesive Hone None None None None None None
Remaining
Adhesive None None None None None Found Found
Mark
According to the paint film-protective sheet of the
present invention, even in the case that the glass transition
point of a paint film is low and a temperature of the paint
film rises, the migration of the low molecular weight
components in the paint film into the paint film-protective
sheet adhered onto the paint film can be prevented, whereby the
occurrence of the step mark phenomenon of the paint film can be
prevented and the adhesive marks of the protective sheet are
not formed on the surface of the paint film. Further, the
- 11 -
paint film-protective sheet of the present invention is
excellent in the paint film-protecting property in the adhered
state and can be easily released from the paint film without
leaving thereon the pressure-sensitive adhesive which becomes
a staining material.
While the invention has been described in detail and
with reference to specific embodiments thereof, it will be
apparent to one skilled in the art that various changes and
modifications can be made therein without departing from the
spirit and scope thereof. -
- 12 -