Une partie des informations de ce site Web a été fournie par des sources externes. Le gouvernement du Canada n'assume aucune responsabilité concernant la précision, l'actualité ou la fiabilité des informations fournies par les sources externes. Les utilisateurs qui désirent employer cette information devraient consulter directement la source des informations. Le contenu fourni par les sources externes n'est pas assujetti aux exigences sur les langues officielles, la protection des renseignements personnels et l'accessibilité.
L'apparition de différences dans le texte et l'image des Revendications et de l'Abrégé dépend du moment auquel le document est publié. Les textes des Revendications et de l'Abrégé sont affichés :
| (12) Brevet: | (11) CA 2187096 |
|---|---|
| (54) Titre français: | MACHINE ELECTRIQUE TRIPHASEE A COUCHES CONDUCTRICES ENTRELACEES |
| (54) Titre anglais: | THREE-PHASE ELECTRIC MACHINE WITH INTERLACED CONDUCTOR LAYERS |
| Statut: | Réputé périmé |
| (51) Classification internationale des brevets (CIB): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventeurs : |
|
| (73) Titulaires : |
|
| (71) Demandeurs : |
|
| (74) Agent: | RIDOUT & MAYBEE LLP |
| (74) Co-agent: | |
| (45) Délivré: | 2004-06-29 |
| (86) Date de dépôt PCT: | 1995-04-05 |
| (87) Mise à la disponibilité du public: | 1995-10-19 |
| Requête d'examen: | 2002-04-04 |
| Licence disponible: | S.O. |
| (25) Langue des documents déposés: | Anglais |
| Traité de coopération en matière de brevets (PCT): | Oui |
|---|---|
| (86) Numéro de la demande PCT: | PCT/DE1995/000457 |
| (87) Numéro de publication internationale PCT: | WO1995/028027 |
| (85) Entrée nationale: | 1996-10-03 |
| (30) Données de priorité de la demande: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
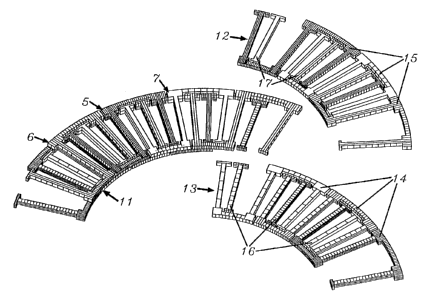
Dans les machines électriques triphasées connues, à enroulement en couches, les éléments conducteurs remplissent insuffisamment l'espace disponible dans les rainures ou bien les conducteurs de phase constituent des éléments de dimensions importantes, insérables les uns dans les autres, qui sont complexes et onéreux à produire. Selon l'invention, tous les conducteurs de phase (5-7) d'une couche conductrice (11) triphasée sont de structure identique et leur configuration se répète tous les quatre pas polaires. Alors que les conducteurs de phase (5-7) occupent toute la hauteur de la couche dans le champ magnétique, deux conducteurs de phase (5-7) qui se chevauchent dans le sens de la profondeur des rainures, se partagent l'espace dans les têtes de bobine (9). La section transversale du conducteur est augmentée à la sortie de la rainure et ce n'est que plus loin, dans la tête de bobine (9), qu'elle est réduite de moitié, d'un seul côté, à chaque passage à travers la tête de bobine. Des surfaces de contact, importantes comparativement à la section transversale des conducteurs, permettent d'alterner les moitiés de couches et la structure entrelacée des couches conductrices permet quant à elle d'utiliser de manière homogène les deux têtes de bobine (9). La production de couches conductrices triphasées par application alternée de couches conductrices et de couches isolantes s'applique notamment aux machines électromagnétiques de petites dimensions. En effet, avec un nombre réduit d'étapes, ce procédé permet une utilisation homogène de l'espace et par conséquent d'obtenir de manière économique, des rendements et des puissances volumiques élevés.
In prior art three-phase electric machines with a layered
winding, the conductor elements either make non-optimum use of
the space in the slot or the conductors for each phase are in the form
of large elements designed to be fitted into each other and whose
manufacture is complicated and costly. The invention calls for the
conductors (5-7) for each phase in the three-phase conductor layer
(11) to be identical in construction and for the construction to be
repeated every four pole pitches. While the phase conductors (5-7)
occupy the full height of the layer within the magnetic field, two
phase conductors (5-7) superposed one above the other in the slot
share the space at the coil ends (9). At the slot exit, the conductor
cross-section increases and only later, at the coil end (9), halved
from only one side at each passage through the coil end. In order
to alternate the layer halves, contact surfaces are available which
are large in comparison to the conductor cross-section and the two
winding ends (9) are uniformly utilized by virtue of the plaiting
of the layers. The production of three-phase conductor layers by
laying alternate conducting and insulating layers is particularly suitable for small electromagnetic machines, giving uniform space utilization
and hence high effectiveness and a high power density at low cost, and requiring only a few operations.
Note : Les revendications sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
Pour une meilleure compréhension de l'état de la demande ou brevet qui figure sur cette page, la rubrique Mise en garde , et les descriptions de Brevet , États administratifs , Taxes périodiques et Historique des paiements devraient être consultées.
| Titre | Date |
|---|---|
| Date de délivrance prévu | 2004-06-29 |
| (86) Date de dépôt PCT | 1995-04-05 |
| (87) Date de publication PCT | 1995-10-19 |
| (85) Entrée nationale | 1996-10-03 |
| Requête d'examen | 2002-04-04 |
| (45) Délivré | 2004-06-29 |
| Réputé périmé | 2010-04-06 |
Il n'y a pas d'historique d'abandonnement
Les titulaires actuels et antérieures au dossier sont affichés en ordre alphabétique.
| Titulaires actuels au dossier |
|---|
| HILL, WOLFGANG |
| Titulaires antérieures au dossier |
|---|
| S.O. |