Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
~ 02200 008
Packet Delay Measurements
This invention relates to a method of measuring the delay of encountered by
packets passing through a packet switched network.
A packet network traditionally comprises a series of intermediate nodes that
fol ~v~d individual data packets to the next node along the route until the packets reach
their destination. Measuring the delay encountered by data frames as they are traverse
through such packet networks, such as frame relay networks, traditionally has been solved
by several methods. One such method involves occasionally sending a test packet, or
ping, through the network. The packet is retnrnefl~ back through the network, to the
sender when it reaches the receiving node, and the sending node uses the time elapsed
between sending and receiving the packet to give an indication of the net~,vork delay.
Another method is to add timing information, which can be used by the receiving node to
determine network delay, into the. packet itself.
While the two methods cited above can give indications of delay, they have
shortcomings. For example, the ping method suffers from numerous limitations including
the fact that the size of the ping packet likely does not match a given data frame's size and
that it is sent at a di~e~ instant in time than the data frame. It may therefore have a
di~elelll delay associated with it, and more seriously, the ping packet may not follow the
same route as a user data frame, again resulting in a dirr~ L network delay value.
The second method of adding timing information into the packet results in a
proprietary implemen~ation that would not work in standards based networks, such as
frarne relay networks.
An object of the invention is to alleviate these problems.
According to the present invention there is provided a method of measuring packet
delay in a packet switched network comprising the steps of measuring the queuing time
for each packet at each node on a connection through the network; applying statistical
methods to determine a representative value at each node; summing said representative
values across the connection; and adding to said summed representative values a value
representing tr~n~mi~sion delay and switching delay.
~~ 02200008
The delay of a packet through a packet network is the sllmm~tion of the time it
takes for the packet to traverse each physical link of the network (T_tr~nqmi.cqion for each
link), which is a function of the line speed of the link and the packet size, plus the
switching delay incurred when the packet is moved from one physical link to another
through the network (T_switching for each sw;tch) normally a constant value incurred at
each switching point, plus queing delay at each switching point (T_queing), which is a
function of how many other packets are attempting to use the same physical link at the
same time. T_tr~nsmisqion and T_switching are essentially fixed values for a given
packet route.
The invention is based on the realization that in effect the only variable is in fact
T_queing. Thus by measuring and storing over set time intervals the exact T_queing at
each switch for every packet of a connection where timing information is desired,
applying statistical mathematics to the resulting values such as mean, variance and
standard deviation, and ~.".. i--~ up these values across the involved switches, then
adding in T_tr~nqmiqsion and T switching values, an accurate statistical view of the delay
encountered by packets of a connection can be realized.
This statistical view is equivalent to the information arrived at by using test
packets, for although a test packet returns an actual delay value, several test packets must
be sent to arrive at a true value since a single test packet cannot be trusted to be typical of
delays encountered, similar statistical analysis of the test packets results must be done.
The invention will now be described in more detail, by way of example only, withreference to the accompanying drawings, in which the single ~igure shows a packet
switched network.
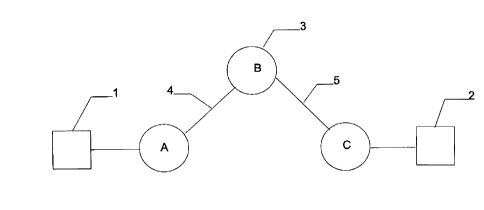
In the Figure, users I, 2, are communicating over a virtual connection 2
established over a frame relay network 3 consisting of switch nodes A, B, C. The virtual
connection is carried over physical links 4, 5.
As each packet traverses the virtual connection it encounters a tr~nqmi.q~ion delay
T-tr~n~mi.qqion, which is the time taken to traverse the physical links 4, 5, and a switching
delay T-switching, which is a substantially constant delay incurred at each switching
point. These values can be treated as constants that can be determined for each
connection.
-
0 2 2 0 0 0 0 8
T_queing, for exarnple at node B, is calculated by using the line speed of the link
4 and the number of bytes of data from other frames that are using the physical link but
are queued ahead of the frame in question. The switch is capable of knowing thisinformation when it processes the frame. For example, a frarne arrives at a switch after
taking T_tr~n~mi~ion to arrive from its previous location. This frarne is switched inside
the switch B taking T_switching time, and is queued to the physical link 5. Due to its
arrival time (and other factors), this frarne is behind 3 frarnes of identical length. ~t
follows then that r_queuing would equal 3 * T_tr~n~mi~ion, as the other frames must
leave the switch before the target frame can use the physical link.
The total delay for this switch (or "hop") would be T_tr~n~mi~sion + T_switching+ T_queing where for this exarnple T_queuing = 3 * T_tr~n~mi~ion This value is stored
in the switch for a given connection, and for each frame switched on the connection the
results are stat;stically added. By adding tlle statistical results from all switches involved
in a connection path, ~he statistical delay encountered by frames on a connection is
accurately measured.