Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 0220~229 1997-0~-13
W 096/12438 PCT~EP95/04095
DESC~IPTION
BLOOD VESSEL GRAFT QUALITY EVALUATI~N
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the evaluation of Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
(CABG) surgery and other medical procedures, which involve blood vessel
surgery.
There are provided a process for the evaluation of graft patency and means
for carrying out such process. The invention enables to evaluate grafts and
anastomotic site occlusions, leakage and proper location.
BACKGROUNi~ OF THE INVENTION
While myocardial revascularization has been employed for many years, the
graft patency depends to a iarge extent on the location and quality of the
anastomosis. The determination of possible blood flow through such a
vessel is of cardinal importance, and exact determination of this parameter is
critical for various types of surgery, and especially of coronary artery bypass
grafts (CABG) surgery.
There are several methods known today to measure the blood flow rate
through grafts including electromagnetic flow-meters, ultrasonic flow-meters,
thermal imaging etc.
CA 0220~229 1997-0~-13
WO 96/12438 PCT/EP95/0409~
The prior art does not provide direct flow measuring systems, and most of the
evaluations can be carried out only towards the end of the operation, after
the proximal side of the graft is connected to the aorta, and blood start flow
through the graft as the result of blood pressure produced by the heart.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the determination of flow rates through blood vessels
involved in surgery. Means and methods for effecting such measurements
are provided which are exceedingly simple, yet highly efficient and which
provide real time data for the surgeon performing surgery.
Coronary bypass surgery of the type referred to in the present invention
generally involves the attachment (anastomosis) of a graft blood vessel to an
existing blood vessel of the patient, which is of the order of diameter of a fewmillimeters, carrying out the control and evaluation according to the
invention, and after ascertaining that such attachment is in order, attaching
the second end of the graft to the aorta.
The device of the invention and the method of evaluation is also applicable
to other types of blood vessel surgery, such as that of blood vessels of the
feet etc.
CA 0220~229 1997-0~-13
WO 96/12438 PCT/l~P95/04095
There is provided a device for measuring the flow rate of a liquid through the
graft to be used in surgery while it is already connected with a blood vessel
of the patient, which fluid can be saline, a buffered solution or blood. The
device comprises a liquid container provided at one end with means for
applying a predetermined pressure, and at another end with exit means,
means for applying controlled pressure (continuous or in pulsed form) to a
liquid (saline, blood) in said container, where the pressure is applied to the
free end (proximal end) of the blood vessel used as graft, after the
anastomosis to the coronary artery is made to the other end (distal end) of
the graft, means being provided for the accurate measurement of the
parameters involved such as pressure curve, pressure inside the vessel,
liquid volume, time and flow rate calculation.
Preferably a syringe or syringe-like container is used, to the piston of which
there is applied the desired pressure, which can be essentially constant or
which can be pulsed, with a pulse rate and form similar to that provided by
the human heart.
There is provided a closed servo loop which monitors and adjusts the
pressure applied to the liquid in said container (syringe). According to t'ne
invention the flow rate measurement through the blood vessel intended to be
used for the graft is made before connecting the proximal end of the graft to
the aorta; it is not required to reactivate the heart to produce pressure and
establish the flow through the vessel. Thus, the surgeon is able to determine
in real time the graft patency whether the attachment to the artery does not
CA 0220~229 1997-0~-13
WO 96/12438 PCT/EP95/0409
leak or get blocked, and if this is not entirely satisfactory, to repair it or
replace it by another graft. This determination is made right after the
anastomosis to the coronary artery.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention is described with reference to the schematical drawing, in
partial section, and not according to scale, of a device for use in
measurements according to the invention.
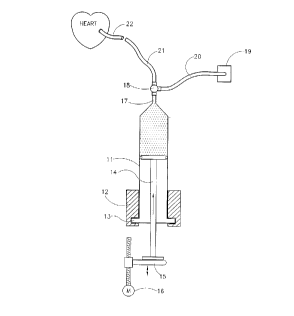
In this Figure there is illustrated a device of the invention, which comprises asyringe 11, having a piston area of about 10 cm2 which is held in holding
means 12, which grasp the flange 13 of syringe 11. The syringe piston 14 is
attached to a movable pushing plate 15. There is provided a linear motor 16,
that moves the pushing plate 15, which is used for pushing piston 14 into the
body of the syringe 1 1. To the tip 17 of the syringe 11 there is attached a 3-
way stopcock 18, to which there are attached tubes 20 and 21, tube 20 being
connected with pressure transducer 19, the other tube, 21 being attached to
the blood vessel to be used as graft 22. There can be applied a constant
pressure on the syringe piston, thus ejecting liquid from said syringe, through
the vessels to be used as graft to the patient arteries, the pressure and
displacement of the syringe piston are measured automatically, for a
predetermined time interval, thus indicating flow rate versus applied pressure
and testing the graft patency.
CA 0220~229 1997-0~-13
WO 96/12438 PCT/EP95/04095
Instead, there can be applied to the piston of the syringe a pulsatile
pressure. This can be of values which correspond to natural pressure
applied to blood in blood vessels in the human body. For example, a pulsed
pressure can be applied to the piston which mimics a systolic pressure of
100 mm Hg and diastolic pressure of 70 mm Hg, at a frequency of 90 per
rninute.
Example:
A GO ml syringe was connected as part of a device shown in Fig. 1 and filled
with saline solution. A pulsative pressure of 100 mm Hg (mean value) was
applied for 10 seconds.
During this 10 second period the displacement of the piston of the syringe
was measured and at the end of this period of time the flow rate through the
8raft was calculated based on the cross-section of the syringe and the
displacement of the piston during this time interval.
The average expected flow rate through a vein graft is about 75 ml per
minute.
Generally it is convenient to use saline as test liquid, and after measuring theflow rate through a blood vessel intended as graft, the surgeon can decide in
real time whether the graft can serve as by-pass.
.