Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02232578 1998-04-08
WO 97/13215 PCT/US96/15981
POS STATION OUTPUT SIGNAL CONVERSION METHOD AND SYSTEM
Field of the Invention
This invention relates generally to so-called "POS"
(Point of Sale) systems, such as are found in retail
r
facilities, and pertains more particularly to systems and
methods for use in adapting POS systems to host computer
equipment.
Background of the Invention
It is customary in current day retailing practices, to
have checkout counters at the exit of a facility, each
equipped with a clerk-controlled POS station effecting
checkout of articles through bar code scanning, retrieval of
article price from a storage unit containing article price
cross-correlated with article bar code, display of the
description and price of each article selected for checkout
to a customer, and selected article price totalization, and
providing the customer with a printout of the customer's
transactions in purchasing articles.
A data structure disparity exists as between signals
generated by a POS station for use in providing the printout
of customer's transactions and signals processable by host
computer equipment. For instance, bar code lookup for
bottled or canned goods, e.g., baked beans or tomato soup,
yields single line data, decodable as so-called "SLD" (single
line decoding). The respective single line data would read
"BAKED BEANS 0.35" and '°TOM SOUP 0.30". This type of
data is readily processable by host computer equipment.
However, for other goods, typically unpackaged produce,
bar code lookup yields multiple line data, decodable as so
called "MLD". For example, the data furnished at the POS to
its printer in this instance may comprise a first line "LOOSE
CARROTS" and a second line "1.0 Kg @ 0.25/Kg 0.25". Since
the POS and printer software for decoding is readily managed
a
independently of the host computer equipment, no difficulty
attends the data structure disparity as between SLD and MLD
at the POS station level.
The data structure disparity, however, takes on
significance in transmissions from POS stations to host
1
CA 02232578 1998-04-08
WO 97/13215 PCT/US96/15981
computer equipment. The latter is manufactured without
facility for input tolerance of data having decoding meaning
only under MLD constraints and, evidently, the manufacturer's
of POS equipment have no interest in or desire to adversely
r
make inroads on their products to accommodate data structure
disparities as between their equipment and host computer
equipment. Thus, POS equipment is presently operated at or
close to its performance limits and any additional processing
requirements are perceived by the manufacturers and their
client to hinder the essential function of POS equipment.
summary of the Invention
The present invention has as its primary object the
provision of systems and methods for overcoming the foregoing
data structure disparity problem as between POS stations and
host computer equipment.
In attaining the primary object, the invention provides
a method for processing single line data and multiple line
data generated at a POS station for driving a printer thereof
into common structure data, e.g., single line data, the
method comprising the steps of defining a first lookup table
having first signal content corresponding to literal article
identifications of articles and article price encompassed in
the single line data and having second signal content
corresponding to literal identifications of articles
encompassed in the multiple line data and flag data, defining
a second lookup table having signal content corresponding to
article identifications of articles encompassed in the
multiple line data cross-correlated with additional multiple
line data, furnishing the single line data and multiple line
data generated at the POS station for driving the printer
thereof to the first lookup table and determining
correspondence of literal identifications in the single line
data and the multiple line data with literal identifications
stored in the first lookup table and detecting flag data
therein. Upon determinations of correspondence of literal
identifications without accompanying detection of flag data,
the contents of the first lookup table are furnished as
single line output data. Upon determinations of
2
CA 02232578 1998-04-08
WO 97/13215 PCT/US96/15981
correspondence of literal identifications with accompanying
detection of flag data, the contents of the second lookup
table are furnished as single line output data.
Systems implementing the foregoing methods are set forth
hereinafter.
The foregoing and other objects and features of the
invention will be further understood from the following
detailed description thereof and from the drawings, wherein
like components are identified by common reference numerals
throughout.
Descrit~tion of the Drawings
Fig. 1 is a flowchart indicating steps of loading a
first lookup table in accordance with the invention.
Fig. 2 is a flowchart indicating steps of loading a
second lookup table in accordance with the invention.
Fig. 3 is a flowchart of steps of a signal conversion
practice in accordance with the invention.
Fig. 4 is a functional block diagram of a system in
accordance with the invention.
Detailed Description of Preferred Practices and
~bodiments
Referring to Fig. 1, the practice for loading a first
lookup table involves outset step S1, PROVIDE SLD AND MLD
DATA FOR SYSTEM PARTICIPATING ARTICLES INCLUSIVE OF ARTICLE
LITERAL
IDENTIFICATIONS AND MLD DATA ADDITIONAL TO ARTICLE LITERAL
IDENTIFICATION DATA. In this step, one collects all signal
data for single line and multiple line from the POS printer
drive signals, e.g., signals indicative of the foregoing
exemplary "BAKED BEANS 0.35"
"TOM SOUP 0
30'
d "L
,
.
an
OOSE
CARROTS" and its second line "1.0 Kg @ 0.25/Kg 0.25".
In step S2, STORE LITERAL IDENTIFICATIONS OF SYSTEM
PARTICIPATING ARTICLES WITH ALL SLD DATA, all literal
identifications collected in step S1 (SLD and MLD) are stored
as is all single line data associated therewith, i.e. , the
price information for the SLD packaged, bottled, etc., goods.
The MLD data additional to the article identification data
is
not stored.
3
CA 02232578 1998-04-08
WO 97/13215 PCTlUS96/15981
In step S3, STORE FLAG DATA WITH STORED LITERAL
IDENTIFICATIONS WHERE MLD DATA EXISTS FOR SYSTEM
PARTICIPATING ARTICLES, the lookup table is completed by
associating a flag with MLD data entries stored in step S2.
t
The flag data is of a nature which causes progress to the
second lookup table, now discussed in connection with Fig. 3.
In step S4, STORE LITERAL IDENTIFICATIONS OF SYSTEM
PARTICIPATING ARTICLES HAVING MLD DATA ADDITIONAL TO ARTICLE
LITERAL IDENTIFICATION DATA, article literal identifications
for only the articles having multiple line structure are
stored.
In step S5, STORE MLD ADDITIONAL DATA WITH STORED
LITERAL IDENTIFICATIONS, the second lookup table is completed
by storing the multiple line additional data with the
previously stored article literal identifications in step S4.
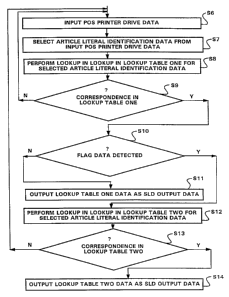
Turning now to Fig. 3, it depicts a flowchart of steps
of a signal conversion practice in accordance With the
invention. It is assumed that the practices of Figs. 1 and
2 have been completed, i.e., that the first and second lookup
tables have been established and are accessible.
In step S6, INPUT POS PRINTER DRIVE DATA, POS printer
drive data is entered in either single line or multiple line
structure, as determined by the nature of the input data.
In step S7, SELECT ARTICLE LITERAL IDENTIFICATION DATA
FROM INPUT POS PRINTER DRIVE DATA, that portion of the data
input in step S6 relating to article literal identification
is selected.
In step S8, PERFORM LOOKUP IN LOOKUP IN LOOKUP TABLE ONE
FOR SELECTED ARTICLE LITERAL IDENTIFICATION DATA, the first
lookup table contents are accessed.
In step S9, ? CORRESPONDENCE IN LOOKUP TABLE ONE,
inquiry is made as to whether there is a counterpart article
literal identification data in the first lookup table for the
selected article literal identification data. Upon negative
(N) reply to the inquiry, i.e., the establishment of the
first lookup table did not take into account the selected
article literal identification, return is to step S6 and a
suitable output alarm indication is provided to the system
4
CA 02232578 1998-04-08
WO 97/13215 PCT/LIS96/15981
user.
Upon affirmative (Y) reply to the step S9 inquiry,
progress is to step S10, ? FLAG DATA DETECTED, inquiry is
made as to whether flag data is stored in the first lookup
table along with the selected article literal identification
data. Upon negative reply to the inquiry, the data is
recognized as SLD data and progress is to step S11, OUTPUT
LOOKUP TABLE ONE DATA AS SLD OUTPUT DATA.
Upon affirmative reply to the step S10, the selected
article literal identification data is recognized as MLD data
and progress is to the second lookup table, i.e., to step
S12, PERFORM LOOKUP IN LOOKUP IN LOOKUP TABLE TWO FOR
SELECTED ARTICLE LITERAL IDENTIFICATION DATA and thence to
step S13, ? CORRESPONDENCE IN
LOOKUP TABLE TWO.
Upon negative reply to the step S13 inquiry, i.e., the
establishment of the second lookup table did not take into
account the selected article literal identification, return
is to step S6 and a suitable output alarm indication is
provided to the system user.
Upon affirmative reply to the step S13 inquiry, progress
is to step S14, OUTPUT LOOKUP TABLE TWO DATA AS SLD OUTPUT
DATA.
A system for implementing the practices of Fig. 3 is
shown in functional block diagram form in Fig. 4. Referring
thereto, INPUT BUFFER 10 receives and holds the data input in
step S6 of Fig. 3, i.e., the POS printer drive data in SLD or
MLD format. The buffer output signals are applied over lines
12 to CPU 14 (central processing unit - a microprocessor
programmed per the Fig. 3 flowchart). Lines 12 are
bidirectional and CPU 14 thus communicates readout commands
to buffer 10 as desired.
The CPU communicates bidirectionally with LOOKUP TABLE
ONE 16 over lines 18. SLD DATA OUTPUT ASSEMBLER 20 receives
content of LOOKUP TABLE ONE 16 over lines 22 when CPU 14
concludes that SLD data was input and is to be output as
system data.
Upon flag detection by CPU 14 in its examination of data
5
CA 02232578 1998-04-08
WO 97/13215 PCT/US96/15981
furnished to it by LOOKUP TABLE ONE 16, resort is made to
LOOKUP TABLE TWO 24 over bidirectional lines 26. MLD TO SLD
DATA OUTPUT ASSEMBLER 28 receives content of LOOKUP TABLE TWO
24 over lines 30 when CPU 14 concludes that MLD data was
r
input and is to be output as system data in SLD format.
System output data made available on output lines 32 and
r
34 is thus fully in SLD format, readily interpretable by host
computer equipment without need for modification of host
computer data recognition rules.
l0 Various changes to the particularly disclosed apparatus,
systems and practices may evidently be introduced without
departing from the invention. Accordingly, it is to be
appreciated that the particularly discussed and depicted
preferred embodiments and practices of the invention are
intended In an illustrative and not in a limiting sense. The
true spirit and scope of the invention are set forth in the
ensuing claims.
6