Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
1
Material layer and method for manufacturing said layer
The present invention relates to a material layer of
either wet- or dry-laid soft paper, including mixtures
of polymer and cellulose fibres, fibre fabric or poly-
mer film, the layer being intended for use as a sepa-
rate layer, or at least in one layer, loosely laid on,
or bonded to one or more material layers or webs such
as to achieve the controlled diffusion of liquid de-
posited on at least this separate layer or web, or such
as to be a part of a bulkier and thicker material layer
or web, the invention also relating to a method of
manufacturing the material layer.
A laminate including soft paper in one or more layers
is usually the basic material on the market today for
table covers, napkins, cleaning rags, face-flannels,
bibs, underpant protectors, sanitary towels, absorption
products or other table and hygiene products, as well
as materials used in the packaging industry. A problem
with these known laminates has been that hardly any of
them is able to equal, as far as possible, a woven
material with characteristics of flexibility and drapa-
bility. In addition, the materials used for absorption
and in particular such laminates that are used for
absorbing body liquids, have limited capacity for
controlled diffusion of liquid deposited on them,
resulting in that the absorption layer is not optional-
ly utilized.
The object of the present invention is to provide a
material layer of the kind mentioned in the introduc-
tion, and comprising a quality-determining, flexible
material which is able to provide a laminate with a
controlled diffusion capacity on the one hand and on
the other hand a laminate with bulk.
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
2
With the first-mentioned ability of the inventive
material layer there is achieved controlled diffusion,
at least over the layer, of a liquid deposited thereon,
whereby practically optimum utilization of the material
absorption capacity may be reached. To this end, the
layer is provided with a plurality of slit formations
extending over it, laterally in optionally spaced
relationship such as to form separate strip formations.
These strip formations may be laterally in greater or
less spaced relationship, depending on the field of
use. In the case where mutual spacing is small and the
layer is laminated against a material web with the
propensity of being a liquid barrier, effective diffu-
sion of liquid deposited on the layer is effected in
the longitudinal direction of the strip formations.
This is particularly suitable when the layer is used as
a material layer in diapers, sanitary towels or under-
pant protectors, and with absorption products in gene-
ral, where controlled diffusion of a liquid deposited
on the layer is desirable. The slits may be made with
an orientation on the layer according to the functional
requirements, i.e. in any attitude from longitudinally
to transverse the layer. The slit formations may either
be continuous along the entire layer in some suitable
direction, or may consist of a plurality of disconti-
nuous slits, between which are formed longitudinal,
free-cut strips of the web. If the inventive layer is
made up using a less strongly absorbent or diffusive
fibre quality, only limited absorption or diffusion
takes place in the layer tself, and thus the deposited
liquid migrates in the longitudinal direction of the
strip formations and in the spaces between the strip
formations, while absorption then also occurs on the
material webs laminated to the upper or lower faces of
the layer.
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
3
A method of producing a material layer in accordance
with the invention consists of cutting or stamping
slits in different patterns in a material, e.g. soft
paper, although material having other characteristics
and compositions may be used. The slitted layer may be
subsequently drawn apart such as to afford different
covering percentages of the material surface and to the
extent appropriate to the field of use to which the
layer is put. It may then be positionally fixed by
laminating against one or more adjacent material layers
or webs.
In utilizing the other ability of the material layer in
accordance with the invention it is placed interiorly
in a laminate in combination with other material layers
or webs included in the laminate. Since greater bulk is
desired here, the layer is drawn apart as in the pre-
vious case, causing reticulations to be formed where
the slits are, with the strip portions becoming warped
as the reticulations are formed. The reticulations may
also be filled with foam. The reticulate layer may have
a colour differing from the other material webs in-
cluded in the laminate, and several reticulate layers
may be put together in different patterns or be provid-
ed with different fillers to obtain such as greater
weight, softness, colouring, workability, embossing
properties, and absorption capacity. In addition, the
laminate containing the inventive reticulate layer can
provide a thicker material of a lower weight than would
otherwise be possible, and as a result the layer also
affords the possibility of liquid being absorbed into
the material better. There is also less material needed
in the laminate containing the inventive, reticulate
layer.
In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the mate-
rial layer is drawn out so as to be reticulated, caus-
CA 02251477 2006-02-09
.
23038-104
4
ing the strip configurations to become warped, and then
cured or "frozen" in this condition with the object of
forming a bulky material layer.
According to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a material layer of soft paper, polymer
fiber or polymer film having a plurality of slit formations
extending over the layer, the plurality of slit formations
laterally arranged at an optimal, mutual spacing, defining a
number of completely free-cut or partially separated,
longitudinally aligned strip formations, wherein, when the
material layer is drawn apart, different reticulation or
opening widths are obtained at the slit formations, the slit
formations inducing, by capillary action, a controlled
diffusion, in the strip formations and in the longitudinal
direction of the slit and strip formations, when a liquid is
deposited on the material layer.
According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided the material layer as described
herein, wherein the slit formations are longitudinally
aligned at a given material spacing in each of a plurality
of rows, alternate rows of slits are mutually,
longitudinally displaced a given distance in relation to the
other rows, and the material layer is expanded transversely
of the slits, forming reticulated strip formations.
According to still another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided the material layer as described
herein, wherein when the layer is drawn apart in a direction
transverse to the slits, different amounts of warping occur
in the strip formations extending between the slits, thereby
forming the reticulated strip formations.
CA 02251477 2006-02-09
23038-104
4a
According to yet another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided the material layer as described
herein, wherein the material layer is laminated to a
material web with a bonding agent.
According to a further aspect of the present
invention, there is provided the material layer as described
herein, wherein the reticulated strip formations of the
material layer laminated to the material web provide
bulkiness.
According to yet a further aspect of the present
invention, there is provided the material layer as described
herein, wherein the material web is in the form of a liquid
barrier.
According to still a further aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a multi-layer comprising the
material layer as described herein, wherein the material
layer is laminated to a material web in the form of a liquid
barrier, said layer having slit formations comprising
longitudinal slit openings to form completely free-cut,
slightly drawn-apart strips, so that a noticeable diffusion
of the deposited liquid is achieved on the layer in the
longitudinal direction of the strips.
CA 02251477 2005-02-16
23038-104
4b
The invention will now be described in more detail
below with the aid of some prefered embodiment examp-
les,'and with reference to the accompanying drawings,
where
Fig..1 illustrates an inventive material layer, which
is laminated against a material web in the
form of a liquid barrier, with the slit forma-
tions in the layer only slightly parted for
forming slit openings with completely free-cut
strips which effectively propagate the depo-
sited liquid in their longitudinal direction,
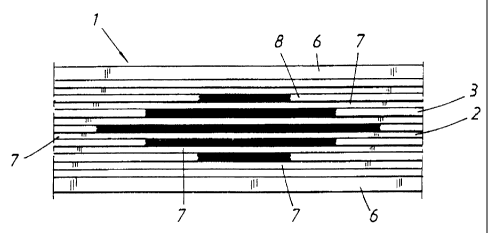
Fig. 2 illustrates a material layer in accordance
with the invention, this layer having a plura-
lity of discontinuous slit formations in the
form of slits, situated in line over its sur-
face and in given, mutually spaced relation-
ship and thus forming partial strips,
Fig. 3 illustrates the material layer of Fig. 2 after
it has been opened out transverse the slits
and laminated against a material web in the
form of a liquid barrier, such as to obtain
controlled migration of liquid in the longi-
tudinal direction of the strips,
Fig. 4 illustrates a layer of soft paper, without
slit formations and with the same fibre orien-
tation as in Fig. 3, that has been applied to
a material web formed as a liquid barrier, a
drop of liquid having been deposited on the
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
soft paper layer to demonstrate the diffusion
of the liquid in the laminate,
Fig. 5 illustrates the layer of Fig. 2 after it has
5 been further opened out such as to form a
reticulate layer with warped strip formations,
this layer being positionally fixed, with the
aid of a bonding agent, between two adjacent
material layers, and thus constituting a
spacer layer between these two for providing
bulkiness, and
Fig. 6 illustrates how completely free-cut strips in
an inventive material layer are brought into
given, mutually spaced relationship before
being positionally fixed to an adjacent mate-
rial web with the aid of deflecting apparatus.
In an embodiment of the invention illustrated in Fig.
2, a material layer 1 is comprised, for example, of
soft paper. This layer is intended to be utilized as a
separate layer, or at least in one layer to be placed
loosely, or to be bonded against one or more material
webs for achieving a bulkier and thicker material web.
This is obtained by pulling apart the layer 1, causing
the layer to become reticulated as the slit formations
2 open out and the strip formations 3 are warped or
twisted to suit, as will be seen from Fig. 5; or the
layer may become a laminate for an absorption product
according to Fig. 3. The twisted or warped strip forma-
tions 3 may, after reticulation, be fixed to two adja-
cent material webs, the reticulated layer 4 then con-
- stituting a spacer providing bulkiness. The reticulated
layer 4 is thus intended to be placed between two webs,
or against one web, and its reticulations may be filled
with different fillers with a foam, to obtain further
properties such as greater weight, softness, colouring,
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
6
workability, embossing characteristics and absorption
capacity in the finished laminate.
The laminate containing the reticulate layer 4, with or
without foam-filled reticulations, provides a thicker
material with lower weight than what would otherwise be
the case, and as a result of this the implementaton of
the layer 4 affords the possibility of rapid absorption
of any liquid spillage on the laminate.
The slit formations 2 allowing the formation of reticu-
lations comprise a plurality of slits 5, arranged in
lines in mutual spaced relationship both along the
lines and laterally. The slits 5 in one line are dis-
placed in relation to the slits 5 in lines on either
side, thus enabling special configuration of the layer
1 in response to its field of use. In a preferred
embodiment example the strip formations 3 formed by
slits 5 may have a width constituting a short, given
portion of the length of the slits 5.
In the case where the inventive layer 1 is intended for
inclusion in a laminate, where controlled liquid diffu-
sion of a liquid desposited on the layer is desired,
e.g. for a baby's diaper or an underpant protector, the
slitted layer 1 may be laminated against a material web
formed as a liquid barrier 6, with the strip formations
3 only slightly parted to form small slit openings 7
according to Fig. 1, or slit openings 7' according to
Fig. 3, whereby a noticeable and effective migration of
liquid in the longitudinal direction of the slit and
strip formations is achieved when liquid is deposited
, on the layer. What distinguishes the layer 1 when used
in absorbent materials, e.g. diapers or underpant
protectors, is that is has a plurality of slit forma-
tions 2. These may either be continuous slit openings 7
with completely free-cut strips 8 along the entire
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
7
layer 1 in some suitable direction, according to Fig.
1, or the slit formations 2 may comprise a plurality of
slits 5 arranged one after the other in lines at small
mutual spacing between the strip formations 3, accord-
ing to Fig. 2. It will be seen from the embodiment
example, illustrated in Fig. 3, how a drop of liquid is
diffused in the slit material, irrespective of the
fibre orientation in the layer 1. In Fig. 4 the layer
depicted here has the same fibre orientation as that
for the layer in Fig. 3, where a material layer in-
cluded in the laminate is not slitted in accordance
with the invention. It will be noted from this figure
that a drop of liquid diffuses mostly transverse the
fibre orientation, which particularly applies to soft
crepe paper. From Fig. 3, illustrating the same lami-
nate as in Fig. 4, but slitted in accordance with the
invention, it will be seen how liquid migrates in the
longitudinal direction of the strip formations 3, due
to the slits. In addition, by slitting the material web
controlled diffusion of liquid deposited on the layer
may also be obtained in a direction towards regions of
superabsorbent material (SAP) arranged in the laminate.
This superabsorbent material (SAP) may then be blended
into the fibre material of the layer 1 or disposed in
the slit formations 2. The SAP is suitably applied in a
pattern consistent with the intended field of use.
The invention also relates to a method of producing a
material layer 1, which is intended to be placed in at
least one layer, loosely against, or bonded to, one or
more material webs for providing a controlled diffusion
capacity for a liquid deposited at least on the layer
-- 1, or for providing a bulkier and thicker material web.
Distinguishing for the method in accordance with the
invention is that the layer 1 is slit to form longi-
tudinal strip formations 3, while the slit formations 2
thus formed extend a given distance from each other,
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
8
the layer 1 being positionally fixed to at least one
material web, after the strip formations 3 have been
drawn apart to a greater or less extent.
A deflecting apparatus 9 may be used for drawing apart
the completely free-cut strips 8 in accordance with the
embodiment illustrated in Fig. 1. As will be seen from
Fig. 6, the parallel strips 8 forming the layer 1 are
deflected about 900 over the apparatus 9. At its de-
flecting location 10, which can be an edge 12, the
apparatus 9 has a plurality of 45 sections 11 situated
one after the other and mutually relatively displaced
for guiding and separating the strips 8. At the appara-
tus 9 the free-cut strips 8 are separated and then
positionally fixed in relation to each other, e.g. on a
material web in the shape of a liquid barrier 6.
When a part of the inventive layer 1 is included in a
diaper or underpant protector as a diffusion layer for
liquid deposited on the article, the material from
which the layer is produced can be dry- or wet-laid
soft paper, or other fibre material possessing capill-
ary propertiAs and which can absorb and permit diffu-
sion, i.e. can have properties of liquid acceptance or
gain. The diffusion layer may be single or comprise
several layers one upon the other, and they may have
different densities for controlling liquid acceptance.
In special embodiments, different kinds of SAP may be
used in one or more layers and in different concentra-
tions, and of different types to suit desired product
properties. The SAP type used is suitably environment-
ally friendly, biologically decomposeable and made,
-- inter alia, from renewable raw materials.
The web-forming diffusion layer may have a coating,
which is either fully covering or perforated and is,
for example, a polymer film, dense paper or a liquid
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
9
product forming a film. When a polymer film is used the
slit cuts also result in downwardly bent cut surfaces,
which reinforce the diffusion effect, provide reduced
rewetting and also a reduced feeling of moistness.
To achieve a "dryness feeling" for the surfaces of the
diffusion layer, a coating of permeable material, e.g.
nonwoven or such as perforated polymer film, is lami-
nated to the diffusion layer, and this coating drains
deposited liquid such as to give a feeling of low
moistness in or on the outer material layers.
Different combinations of diffusion layers in accord-
ance with the invention can be envisaged, namely seve-
ral layers with varied location of any fibre layer with
a coating, partially reticulate layers for concentra-
ting absorption, reticulate layers with reticulations
of varying sizes for different purposes, diffusion
layers with narrow reticulations giving low feeling of
moistness, and those with wide reticulations giving
rapid liquid acceptance due to their large empty volu-
mes, diffusion layers with reticulations where the
slits have optional orientation, e.g. along or trans-
verse web length. Slit length and reticulation width
for the diffusion layer may be adjusted to suit re-
quirements, and openings in multilayer products may be
in register, or randomly arranged in the Z-direction.
Completely free-cut strips, forming the inventive
diffusion layer, may be set on edge in spaced mutual
relationship and uncoated, or placed close together if
they are coated with film.
In the case where knives are used to make the slits,
these knives may be implemented such that they provide
rough cut surfaces, which results in greater absorption
area, and thus better absorption. Finally, the coating
CA 02251477 1998-10-02
WO 97/36565 PCT/SE97/00557
and backing may be vacuum formed to each other with an
intermediate, inventive diffusion layer. In some appli-
cations it can be advantageous to have an "aspirating"
backing.