Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02302978 2000-03-07
WO 99/12798 PCT/N098100270
Device for vehicles and method for manufacturin~~ the device
The invention concerns a device for vehicles, comprising a metallic frame
which forms the supporting part for a body composed of large body units of
plastic, preferably thermoplastic and especially coloured thermoplastic,
wherein the frame comprises pillars projecting upwardly from a base
structure to support the vehicle's body and possibly also roof/side beams. The
invention also concerns a method for manufacturing a vehicle of this kind.
The present day manufacture of vehicles, particularly cars, is to a great
extent based on the construction of bodies by welding together plates and
panels into a unit with a structure which has the necessary strength and
rigidity, permitting the body to be assembled together with a chassis. with
springs and wheel suspension and with installation of the engine and other
parts. This construction method constitutes a substantial advance over the
original vehicle construction, which consisted of a strong frame, where
panels and body parts were mounted on the frame.
The development has largely been based on the utilization of steel, with
plates which are stamped out as panels and welded together on highly
rational and effective, robotized assembly lines. This production method is
therefore highly advanced with regard to control and precision, with
associated very high investments. A production method of this kind will
therefore be appropriate and financially justifiable in the manufacture of
large production volumes.
To-day the trend in further development is towards the building of vehicles
and cars which are both smaller and lighter, and which above all should be
capable of being driven with a reduction in energy consumption, thereby
reducing the strain on the environment. For this purpose modern materials
and new production methods are employed. A further feature in this
development trend is the production of vehicles or cars which are intended to
cover a special requirement or a niche in the market, i.e. they are not
intended for universal use, e.g. over long distances. Such "niche" vehicles,
which are also regarded as conveyances or means of transport, will not
normally satisfy the requirements for manufacture in very large production
volumes, and for such vehicles there have therefore been developed special
CA 02302978 2000-03-07
WO 99/12798 PCT/N098/00270
2
production methods and materials employed which until now have not been
widely used in car production.
In the case of these vehicles too, however, it is very important for the
vehicle
to offer a sufficiently high degree of safety for the user and it is therefore
crucial that in this case too it is possible to incorporate the necessary
strength
and deformation conditions in the design in order to be able to meet modern
safety requirements.
The use of profiles, e.g. in aluminium, has been shown to provide interesting
construction methods for future vehicle development through so-called
"space frames". These frames are built up by joining the profiles together by
means of welding, gluing or by other mechanical attachment means. Such a
frame, e.g. in aluminium, is light in weight and can be calculated and
dimensioned to provide a very high level of safety. In order to be able to
construct a final vehicle, panels and body parts have to continue to be built
together on this frame. For this purpose metal, possibly aluminium panels or
plastic panels may be used which are mounted on the frame by substantially
known means. Even though this may indicate a step backwards towards
conventional construction technology, where frames were employed, the only
difference being that modern materials such as aluminium and plastic are
used, while at the same time greater safety is built into the frame, a
construction method of this kind will also be of very great interest for the
above-mentioned new vehicle types. One of the reasons for this is that
considerably lower investments are required in order to be able to develop a
vehicle on this basis. At present the method is most suited to smaller
production numbers.
Supporting frames of this kind can also relatively simply be built in a steel
structure where a simple surface treatment then has to be carried out for
corrosion protection. This treatment is substantially simplified compared to
surface treatment of a traditional car body, which subsequently has to be
sprayed.
"Space frames" is a term for frames of this kind which are composed of
profiles with connection points. These are employed in several types of
vehicle and are of considerable interest. A major challenge, however, is to be
able to achieve a simplified and rational installation of body parts and
panels.
CA 02302978 2000-03-07
WO 99/12798 PCT/N098/00270
3
It is known in the prior art to use plastic in body parts in various design
variants in combination with an aluminium frame or steel frame. Polyester or
epoxy body parts have been most used, but other types of plastic have also
been employed, by means of vacuum forming, injection moulding or where
panels are produced by means of spraying and fitting.
Examples of such known designs can be found, e.g., in DE 19500361 which
discloses a body/frame structure, where the rear frame section and outer roof
beams consist of a part, which in turn is attached to a lower floor section.
The outer panel on the rear is in turn attached to the outside of this. In EPO
584576 an outer structure is employed which forms the actual cabin, on
which is mounted a front module, these parts being glued together. A similar
design, based on a complete cabin, is also described in EPO 547583.
In EP Patent 485457 and 697974 methods are described as to how a metal
frame can be used in combination with large body parts which in a simple
1 S design can form the whole body.
The object of the present invention is to provide a new form of assembly for
a vehicle, where the vehicle body can be manufactured from large plastic
units, preferably thermoplastic and specially preferred coloured
thermoplastic, where the body parts can also be made in smaller production
series and where these can be mounted in a simple and rapid manner on a
vehicle frame structure, e.g. of aluminium, without the use of complicated
aids.
This object is achieved according to the invention with a device of the type
mentioned in the introduction, which is characterized by the features
presented in the patent claims. The invention also comprises a method for
manufacturing a vehicle of this kind, which method is characterized by the
features presented in patent claim 13.
The invention differs from the previously known designs, representing a
highly simplified design. The problems with the previously known designs
are that it is a long-winded and difficult process to mount solid cast bodies
or
large parts of the body, since these are difficult to integrate and mount in a
prefabricated framed structure.
CA 02302978 2000-03-07
WO 99/I2798 PCT/N098/00270
4
In some cases there is a need to divide the framed structure in order to be
capable of installing the large body elements. This not only results in an
extra work operation with the frame assembly, but also often means an
impairment of the framed structure and costly steps in order to ensure a
simplified mounting and a satisfactory degree of safety. For example, the
design according to DE 19500361 requires welded-on and integrated metal
plates in the framed structure, since the body panels only give the vehicle
the external shape and appearance without a closely connected body module.
In the present invention the wish is to unite style and external appearance to
a greater extent with utility and functional solutions by a combination of a
metal frame and plastic panels. This is done in a manner whereby the plastic
body part has more integrated functions than simply being a cover with
exterior and visual advantages. In addition, a construction method is
employed where the plastic body parts include functions such as sealing and
separation of the vehicle's interior and exterior environment, and the parts
may include elements such as wheel arches, mudguards, etc., inset lights,
sealing edges, etc.
A special feature of the invention is also that moulding methods and
materials can be used for production of the body parts which eliminate the
need for painting of the body parts. Painting is an undesirable operation on
account of environmental conditions and costs.
In a special embodiment of the invention the front and rear vehicle body
parts are designed to overlap, resulting in a reinforced central part in the
vehicle. This provides a further reinforcement and separation between the
external and internal environments, which can be advantageous in special
applications.
The invention will now be explained in more detail by means of
embodiments which are illustrated in the drawings, in which:
figure 1 is a completely schematic view illustrating the design of the device
according to the invention, with the parts separated from one another,
figure 2 is a second embodiment of the invention, viewed in a schematic
horizontal section,
CA 02302978 2000-03-07
WO 99/12798 PCT/N098/00270
figure 3 is an embodiment corresponding to figure 2 in a lateral sectional
view, in connection with a cabriolet design, and
figure 4 is a side view of the cabriolet design in figure 3.
As mentioned above, the drawings are purely schematic representations,
$ which are only intended to illustrate the principal design of the device
according to the invention and the method for manufacture thereof. In the
drawings only those elements are included with are necessary for illustrating
the inventive concept, since the other features can be varied and will be a
technique which can be implemented without difficulty by a person skilled in
the art.
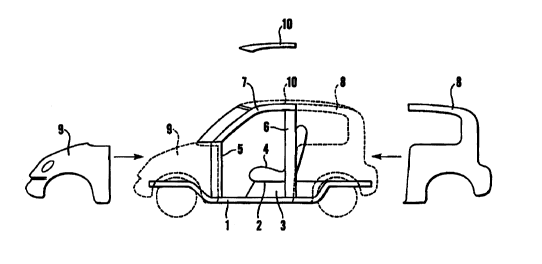
Figure 1 illustrates the principle of the device according to the invention,
some of the body parts having been pulled out to the side, while the final
assembled shape is illustrated by means of broken lines.
The basic element in the design is a metallic frame, e.g. a frame of the
"space
1$ frame" type, which is designated 1 and on which the necessary mechanical
components and systems are mounted in a simple and rational manner. The
frame is open with easy access. The vehicle can therefore be constructed with
chassis systems in the front and rear, an engine and other technical
connections without any hindrance from closed areas in the frame.
Depending on the transmission system, i.e. whether the engine is installed at
the front or the rear, possibly electrically powered, requiring room for
placing batteries, the floor system 2 can be made flexible, thus making room
for these said transmission systems under the vehicle, e.g. in the area
designated 3. The floor system is designated 2.
2$ A floor 2 can therefore be attached to the frame, e.g. on two levels in
order to
provide space and opportunity for mounting batteries under the vehicle in the
area at 3. In a design of this kind attempts will be made to lay the high
floor
level under the seats 4.
The vehicle's upwardly projecting pillars, which are designated A and B
pillars, and given the reference numerals $ and 6, are also mounted on the
frame, together with a roof frame 7 for closed vehicles. The upwardly
projecting pillars are preferably approximately vertically arranged, but may
also assume angled or curved shapes, according to the body design.
CA 02302978 2000-03-07
WO 99/12798 PCT/N098/00270
6
The body is mainly composed of a rear part 8, which constitutes a large body
part comprising both the rear sides, wheel arches and mudguards and floor
section which is then attached to the vehicle's B pillars 6, possibly also
other
points. In cases where the vehicle has 4 doors, this part 8 may be attached to
the vehicle's so-called C pillars, and the B pillar thereby becomes a middle
pillar. The front part 9 of the vehicle is designed as a cover which is open
below, thus enabling it to be laid over the engine and wheels and attached in
the area around the vehicle's A pillars 5. In the inside it is expedient to
construct a separate torpedo wall from the pedal set up to the dashboard in
order to close and seal the internal cabin. This cover 12 may also be an
extended part of the plate in the floor. A loose roof 10 may be attached to
the
frame over the window, and doors installed on the A and B pillars 5 and 6
respectively, possibly by using 3 pillars on each side, between the pillars.
In figures 2-4 there is illustrated a second embodiment of the invention,
where the rear and front parts 8 and 9 overlap each other. The rear body part
8 is thereby designed with the external form and the external measurements
required by the vehicle up to the area at the rear pillar or the B pillar 6,
while
the vehicle's front body part 9 extends backwards with the external
dimensions and design of the vehicle in the area up to the A pillars 5. In
this
embodiment the front part of the rear body part 8 is extended forwards on the
inside of the pillars 5 and 6, to the front area of the cabin's interior,
where it
forms an upwardly projecting or extending wall 11 between the cabin's
internal compartment and the external technical compartment or motor
compartment, where it can be terminated with an attachment or a seal against
the lower window frame 13. In the same way, this part may include the
vehicle's dashboard or the basic part of the dashboard 12, as illustrated in
figure 3.
By employing a suitable plastic material and moulding technology, a bumper
cover can be moulded into the front part 9, together with other details such
as
a grille, a recess and securing means for lights, etc.
The doors are installed as a subsequent part of the assembly process and are
attached on the front pillar 5 and locked in a closed state against the pillar
6.
An important feature of this design is that the split line between the door
and
rear body part can be adjusted in a simple manner by adjusting or shifting the
hinge point for the door on the pillar S. The front part can then be adjusted
CA 02302978 2000-03-07
WO 99/12798 PCT/N098/00270
7
towards a front door line, with the result that it is in perfect alignment
with
the door split.
When 3 pillars are used, i.e. A, B and C pillars, the procedure will be the
same, also when mounting the rear door. In figure 1 a device is illustrated
for
a vehicle with a roof structure. Figure 4 illustrates that the same vehicle
device can also be employed with a design without a roof.
The invention represents a highly rational and effective method of
constructing a vehicle. The body parts, both front and rear, i.e. 9 and 8 are
mounted after all the mechanical components, chassis, springs, engine, etc.
have been installed on the open frame. These can be made of different types
of plastic by means of different production methods which offer the
possibility of constructing three-dimensional large parts. An example of such
a part is a rotationally moulded part and vacuum forming and blowing may
also be employed in the case of given design criteria. A preferred material is
thermoplastic and particularly coloured thermoplastic, but other plastic
materials with similar properties may also be used.
The assembly of the plastic body parts and the metal structure offer the
possibility of providing a good seal since there are no more body panels
which have to be joined together and sealed. The plastic edges may be
pushed in and locked to the metal structure, e.g. by means of clamping.
Despite the fact that these relatively large body parts do not provide any
structural strength in the structure, they have an obvious functional effect
in
arriving at a complete vehicle.
The invention is described in purely schematic terms and the fact is referred
to, e.g., that 3 pillars may also be used on each side instead of 2. The
device
can be varied in many ways within the framework of the claims while
retaining the main features, viz. the use of a large construction part as the
front part and a large construction part as the rear part, these construction
parts being in three-dimensional form, which gives them great strength and
rigidity, thereby providing a safe body. It will be possible to vary the
actual
design and form.