Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
- WO OOf37395 PCT/IB99/01971 _
1
A DETONATION INITIATING DEVICE
INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND TO THE INVENTION
This invention relates to a detonator and to a detonation initiating device
for
a detonator.
Conventional electric or electronic detonators are usually provided with a
detonation initiating device, which often comprises a metal resistive wire
embedded in primary explosives compositions based on lead styphnate or
lead picrate. Alternatively, the metal resistive wire may be embedded in
pyrotechnic compositions based on intimate mixtures of heavy metals such
as cerium, tantalum or boron in combination with an oxidiser. Such
detonation initiating device is commonly known as a fuse head.
Alternatively to the fuse head, various other detonation initiating devices,
for
use with electrical or electronic detonators, are known. Examples of these
are thick film, printed, resistive bridge initiators; vacuum deposited thin
film
bridge initiators; and so-called SCB initiating devices.
A thick film bridge initiator usually comprises a printed resistor extending
between two conductors which are insulated from each other, the resistor
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
- WO OOf~37395 PCT/IB99/01971
2
being either polymeric or ceramic in nature, as is common in hybrid electronic
technology. The bridge is trimmed or printed to value.
A thin film bridge usually comprises a central conductor; and an annular
conductor surrounding the central conductor, the conductors being spaced
by a glass substrate. A metal layer forming a resistor is vacuum deposited
on the glass substrate to connect the conductors, with the metal layer often
being trimmed to value.
A SCB initiating device uses silicon doping compositions to generate plasma
between two spaced conductors, when an electrical current is passed
through.
To amplify the electric energy flowing through the resistors or plasma of the
above initiating devices, into a flame or detonation able to initiate
explosives
in proximity to the resistor, the resistor or SCB is disposed in close contact
with either a primary explosive or pyrotechnic compositions of the type
commonly used in fuse head manufacture.
A disadvantage of the explosive or pyrotechnic compositions of the type
commonly used with fuse heads or other initiating devices is that they are
usually mechanically and electrically sensitive to uncontrolled initiation.
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
WO 00/37395 PC'C/IB99/01971
3
Another disadvantage of such compositions is that toxic heavy metal
particles are released into atmosphere upon explosion of the initiating
explosives.
OBJECT OF THE INVENTION
It is accordingly an object of the present invention to provide a detonator
and
a detonation initiating device for a detonator with which the aforesaid
disadvantages may be overcome or at least minimised.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
According to a first aspect of the invention there is provided a, detonation
initiating device for a detonator, the device including:
- two spaced electrical conductors;
- a resistive substance extending between the electrical conductors, for
releasing energy upon application of an electrical current to the
resistive substance; and
- an explosive composition including diazodinitrophenol (DDNP),
covering the resistive substance.
Diazodinitrophenol (DDNP) has been used in the past as a main explosive
charge in detonators. However, because it is as such relatively insensitive to
mechanical and electrical initiation, it has thusfar not been considered as an
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
- WO OOf37395 PCT/IB99/01971
4
initiating explosive in detonation initiating devices, for electric and
electronic
detonators.
The resistive substance may constitute a thick film bridge for an electronic
detonator.
Alternatively the resistive substance may constitute a thin film bridge.
Further alternatively the resistive substance may comprise a dope substance
for creating plasma upon the application of the electrical current.
The explosive composition may further include a binder.
The binder may be an energetic material. Preferably the binder is selected
from the group comprising nitro-cellulose and polyvinylnitrate.
Alternatively the binder may be non- energetic. Preferably the binder is
selected from the group comprising acrylate and natural gum.
Yet further according to the invention, the explosive composition includes
DDNP in fine particulate form as well as in a relatively larger particulate
form.
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
- WO OOf37395 PCT/IB99/01971
The DDNP in fine particulate form may have a particle size which is
magnitudes smaller than the DDNP in relatively larger particulate form.
The DDNP in particulate form may be a precipitate of a mixture of DDNP and
5 said binder.
The DDNP in particulate form may be in a crystalline or modified crystalline
form.
The DDNP in particulate form may be prepared substantially as described in
the patent specification of DE 4117717.
The DDNP in particulate form may include compounds selected from the
group comprising explosives, oxidisers, fuels and/or reducing agents.
The oxidisers may be selected from the group comprising chlorates, nitrates,
perchlorates, and oxides and the fuels may be selected from the group
comprising metals and metal sulphides.
Said resistive substance may constitute a resistive bridge and the fine
particulate DDNP may have a particle size which is at least five times smaller
than the smallest dimension of the resistive bridge. Preferably the fine
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
- WO 00/37395 PCT/IB99/01971
6
particulate DDNP has a particle size which is at least ten times smaller than
the smallest dimension of the resistive bridge.
The ratio between the fine particulate DDNP and the DDNP in relatively
larger particulate form may be between 1:99 and 20:80 on a mass per mass
basis. Preferably the ratio between the fine particulate DDNP and the DDNP
in relatively larger particulate form is 5:95 on a mass per mass basis.
The arrangement may be such that when an external current is applied to the
contacts, the fine particulate DDNP ignites, to initiate ignition of the DDNP
in
relatively larger particulate form, which in turn ignites a detonator charge.
Further according to the invention, the DDNP in fine particulate form may be
applied separately to the resistive bridge, in ink of the type used to print
polymer thick film bridges substantially as disclosed in South African patent
number 95/1680. This increases the reliability of ignition of the explosives
in
contact with the resistive bridge.
Further according to the invention, the DDNP is enclosed. Preferably the
DDNP is enclosed by a layer comprising a polymeric material or a resin.
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
- WO OO~f37395 PCT/IB99/01971
7
According to a second aspect of the invention there is provided a detonator
including a detonation initiating device according to the first aspect of the
invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
The invention will now be described further by way of a non-limiting example
with reference to the accompanying drawing, which is a diagrammatical
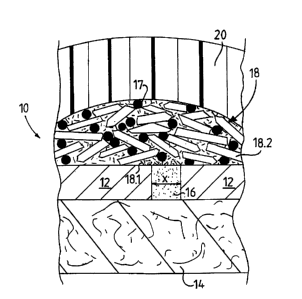
cross-sectional view of a detonation initiating device 10 according to a
preferred embodiment of the invention for a detonator (not shown).
DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION
The detonation initiating device 10 includes two spaced electrical conductors
12 located on an insulating substrate 14; a thick film 'resistive bridge 16
extending between the electrical conductors 12, for releasing energy upon
application of an electrical current to the resistive bridge 16; and an
explosive
composition, generally designated by reference numeral 18, covering the
resistive bridge 16.
The explosive composition 18 is prepared from an energetic nitro-cellulose
binder 17 and diazodinitrophenol (DDNP), substantially as described in the
patent specification of DE 4117717, to include DDNP in fine particulate form
18.1 as well as in a relatively larger particulate form 18.2. The DDNP in fine
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
- WO OOf37395 PCT/IB99/01971
particulate form 18.1 has a particle size which is magnitudes smaller than the
DDNP in relatively larger particulate form 18.2 and at least ten times smaller
than the smallest dimension X of the resistive bridge 16. The ratio between
the fine particulate DDNP 18.1 and the DDNP in relatively larger particulate
form 18.2 is 5:95 on a mass per mass basis,
The DDNP in particulate form is preferably in a crystalline state and the
explosive composition 18 includes additional compounds such as other
explosives, oxidisers, fuels and/or reducing agents. The oxidisers are
selected from the group comprising chlorate, nitrate, perchlorate, and oxides
and the fuels are selected from the group comprising metals and sulphides.
Preferably the oxidiser is lead monoxide (Pb0) and the fuel metal is
zirconium.
The DDNP in fine particulate form 18.1 may alternatively be applied
separately to the resistive bridge 16, in ink of the type used to print
polymer
thick film bridges substantially as disclosed in South African patent number
95/1680.
The explosives composition 16 is enclosed by a polymeric layer 20.
In use, an external current is applied to the contacts 12 to energise the
CA 02355256 2001-06-13
- WO OOf37395 PCT/IB99101971
_ .
resistive bridge 16, which ignites the fine particulate DDNP 18.1. The one
particulate DDNP 18.1 initiates ignition of the DDNP in relatively larger
particulate form 18.2, which in tum ignites a detonator charge (not shown).
The detonation initiating device according to the invention, is not only very
stable and resistant to accidental explosion, but also very reliable due to
the
presence of the fine particulate DDNP.
Furthermore, the explosive composition of the detonation initiating device
can be initiated even at the low energy levels at which electronic initiating
devices usually operate.
It will be appreciated that no heavy metal particles are released by the
detonation initiating device according to the invention, during explosion.
It will be appreciated further that variations in detail are possible with a
detonator and a detonation initiating device according to the invention
without departing from the scope andlor spirit of the appended claims