Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02429278 2006-03-29
ELECTRIC RADIATOR
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to heating equipment, and in particular to an
electrical heater for indoor use.
Background of the Invention
With people's living standards steadily improving, more and more families are
using portable electrical heaters. Existing portable electrical heaters can
generally be
categorized into one of two forms.
The iarst kind has a reflector located in the body. The reflector radiates
heat
energy produced by heating elements to heat and warm the local space. Some
electrical heaters of this kind also have a fan in the body. However,
electrical heaters
of this kind only raise the temperature within the immediate surrounding
space. When
the heaters are switched on for some time, even if the temperature of the
local space
is increased significantly, the space temperature of other parts in the same
room are
only marginally raised. People will still feel cold when they leave the heated
local space
for another part of the room. The electrical heaters of this kind can just
heat the
limited space, and then a lot of heat energy is wasted with a low heat effect.
A second kind of heater has a body formed of a series of hollow columns. The
hollow columns are interconnected to form a chamber. This chamber is filled
with oil
which has good thermal conductivity properties. The oil is heated by a heating
element
generally situated at the bottom of the heater. This causes the oil in the
heater to
circulate due to convection so that the oil in the columns is evenly heated.
The large
surface area of the columns transfers heat to the surrounding air which in
turn rises
and initiates a convection current in the room. However, this form of
electrical heater
heats slowly and it takes a long time after switching on for people to feel
warm.
Furthermore, the heater itself is big, heavy, and difficult to move. And,
since the
columns are filled with oil, high hermetic sealing is required, resulting in
relatively high
manufacturing costs.
CA 02429278 2006-03-29
It is an object of the present invention to overcome or ameliorate at least
one
of the disadvantages of the prior art, or to provide a useful alternative.
Accordingly, the present invention may be considered as providing an
electrical
heater for heating a space by means of radiant heating and convective heating,
the
heater comprising a casing, the casing including: a body compartment; a
heating
element within the compartment; a reflector having a reflective surface facing
the
heating element; and a spaced array of radiant conductive fins of a heat-
tolerant
material disposed within the compartment so that the heating element passes
through
apertures in the fins.
Furthermore, the present invention may be considered as providing an electric
heater comprising: a casing having a body compartment, an air inlet for the
ingress
of air to the compartment and an outlet for the egress of air from the
compartment;
a plurality of spaced radiant conductive fins in the compartment, the fins
defining an
air heating channel between each two of the radiant conductive fins, the air
heating
channels aligned between the air inlet and the air outlet for guiding air to
flow along
the air heating channels from the air inlet to the air outlet; an electrical
heating
element, for electrical connection to a power source, the heating element
being
transversely extended through the radiant conductive fins; and a heat
reflector, having
a heat reflecting surface, disposed within the compartment at a position
transversely
extended from the radiant conductive fins at side edges thereof; wherein when
the
heating element generates heat, such heat is distributed through the radiant
conductive fins in a planar manner for heating the air within the air heating
channels
so as to create heat flows therewithin to outside through the air outlet.
Advantageously, at least in a preferred form, the radiation from the reflector
quickly heats the required space. Furthermore, the radiant conductive sheets
manufactured with a heat-resistant material advantageously exploit the
principle that
air will rise when heated and fall as it cools, thus starting a convection
flow and thereby
exchanging heat in a vertical way. This cycle heats the air in the room and
raises the
temperature of the whole room.
2
CA 02429278 2006-03-29
Brief Description of the Drawings
A preferred embodiment of the invention will now be described, by way of
example only, with reference to the accompanying drawings in which:
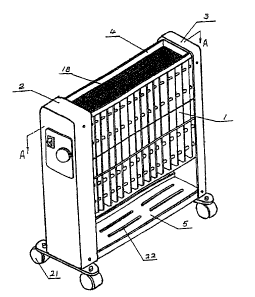
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of an electrical heater according to the present
invention;
Fig. 2 is an enlarged view showing the heating elements of the heater in Fig.
1;
Fig. 3 is an end view of Fig. 2 from direction B;
Fig. 4 is a cross-sectional view along the line A-A in Fig. 1;
Fig. 5 is a detailed view illustrating an embodiment of the connection between
the radiant conductive sheets and the link rods;
Fig. 6 is an end view illustrating an embodiment having apertures opened in
the
radiant conductive sheets; and
Fig. 7 is another end view illustrating another embodiment having slots opened
in the radiant conductive sheets.
Detailed Description of the Preferred Embodiment
The present invention, thus, relates to an electrical heater, which comprises
a
casing 1, defining a compartment for receiving heating elements 11 and a
reflector 14.
The heating elements 1i could be infrared heating elements, or be halogen
heating
elements, or other elements transforming electrical energy into heat.
The casing 1 comprises left side covers 2, right side covers 3, upper cover 4,
and
lower cover 5. An air outlet 18 is located at or near a top portion of the
casing and an
air inlet 22 may be located at or near a bottom portion of the casing. A
reflector 14 is
located so that a curved surface thereof faces towards the heating elements.
The
curved surface of the reflector 14 has a predetermined curvature of a concave
shape,
or may include several such adjacent surfaces as shown in Figures 2a and 3.
The
electric heater may be mounted for movement across a floor by way of castors
21.
An open side of the casing, opposite the reflector, is left uncovered so that
the
internals of the heater are exposed and heat may be radiated from the heater.
A
safety mesh, as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 4, screens the high temperature
heater
3
CA 02429278 2006-03-29
internals from being inadvertently touched. This open side may also function
either
partially or wholly as the air inlet and/or outlet.
A spaced array of radiant conductive fins 12 formed from radiant conductive
sheets manufactured with a heat-tolerant material, partitions the compartment
into a
series of air heating channels. The fins 12 are supported in the compartment
in a
vertically parallel manner via a plurality of transverse link rods 13. As
such, the air
heating channels are also vertically configured for guiding the air to be
heated by the
radiant conductive fins in an upwardly flow towards the air outlet.
By ~~heat-tolerant" it is meant that the sheets are manufactured from a
material
which does not change its chemical or physical properties substantially,
within the
operating temperature of the heater. Suitable radiant conductive, heat-
tolerant
materials include stainless steel, copper, aluminum, a heat-resistant nonmetal
and etc.
as such, each of the radiant conductive fins 12 is capable of transferring
heat from one
region to another region through conduction. It is worthwhile mentioning that
conduction ofthe radiant conductive fins 12 occurs between regions thereof at
different
temperatures.
The link rods 13 pass through the radiant conductive fins 12, as shown in Fig.
5. The two ends of the link rods 13 are bolt connected with left and right
side covers
2 and 3; therefore, the radiant conductive fins 12 are fixed in the casing 1,
as shown
in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. The heating elements 11 rank at a distance, and pass
through the
holes or apertures 19 provided in the fins 12. The inner diameter of the holes
19 is
greater than the outer diameter of the heating elements ll. There always is a
space
or gap of about 0.5mm - 5mm between the inner edge of the holes 19 and the
outer
edge or surface of the heating elements 11. This gap is large enough to
prevent the
possibility of any damage caused due to interference between the hot,
expanding fins
and heating elements 11, but is small enough to provide adequate heat transfer
to the
fins from the elements.
The fins 12 are generally rectangular but may be any other shape fitted with
the
shape of the casing 1, even an irregular shape. There can be various diversion-
grooves and corrugations on the fins 12 to focus the radiation heat and the
vertical
4
CA 02429278 2006-03-29
convection.
In one embodiment of the invention there are grooves on the casing 1. The fins
12 pass through the opening in the reflector 14, and are inserted in the
grooves on the
casing 1 and fixed in the casing 1 without link rods 13. The other structural
features
are unchanged.
In a further embodiment of the invention the holes 19 provided in the fins 12
can be circular sealed, or non-sealed slots. Vertically extending slots 19'
adjacent the
edges of a fin are shown in Fig. 6 with heating elements 11 located therein.
Horizontally extending slots 19" extending inwardly from side edges of a fin
are shown
in Fig. 7 with heating elements 11 located therein.
In operation, with the heater connected to a source of electrical energy and
switched on, the heating elements 11 radiate heat energy. Radiant heat energy
is
radiated out of the heater both directly, and indirectly reflected from the
reflector at
the rear of the heater. Advantageously, this radiant energy provides immediate
and
localized warming to the heater surroundings.
In addition, the radiant energy is absorbed by the radiant conductive fins 12
and
heat is conducted throughout the fins from high temperature areas adjacent to
the
heating elements to lower temperature areas remote from the heating elements.
The
combined effect of heat transfer to the air from the radiant conductive fins,
and both
directly and indirectly form the heating elements by conduction and radiation
through
the air, causes the air in the channels to become warm. As this occurs, the
air
warming in the channels rises and exits the heater through the air outlet 18.
This air
displacement causes cooler air to be drawn into the heater from the bottom
primarily
through the air inlet 22 but also through the open side. As a result, a
convection
motion is initiated and heater may advantageously provide far reaching heating
to a
room.
Although the invention has been described with reference to specific examples
it will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the invention may be
embodied in
many other forms.