Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02443255 2003-10-02
- 1 -
WING FORA WINDOW OR A DOOR
1. Field of the invention
The invention relates to a wing for a window or a door with a profile frame,
which
forms a rabbet receiving an insulating glass component and has a perimeter
surface that surrounds the insulating glass component on the end side thereof
and a rabbet surface that extends beyond the edge of the insulating glass
component, and with an adhesive layer for securing the insulating glass
component within the rabbet, said adhesive layer filling, at least in
perimeter
areas, a perimeter slot between the end surfaces of the insulating glass
component and the perimeter surface of the rabbet located opposite said end
surfaces.
2. Description of the Prior Art
To simplify the installation of an insulating glass component, it is known (EP
1 070
824 A2) to bond the insulating glass component into a rabbet of the profile
frame.
For this purpose, a stripe of adhesive is applied along the rabbet surface of
the
perimeter frame rabbet, which is parallel to the insulating glass component,
prior
to inserting the insulating glass component into the rabbet. During insertion,
the
insulating glass component is therefore pressed against the perimeter stripe
of
adhesive which performs the function of joining together the insulating glass
component and the profile frame. The disadvantage of this known construction
however is that the load resulting from the insulating glass component is only
to
be carried away onto the profile frame through the ridge of the rabbet that
extends
beyond the insulating glass component. Moreover, the inner pane only is
supported by the frame, the outer pane however not, said outer pane being
carried by the inner pane through the edge connection between inner pane and
outer pane, which involves the risk that the outer panes will sag on one side
because of the perimeter slot provided between the end surfaces of the
insulating
CA 02443255 2003-10-02
- 2 -
glass component and the perimeter surfaces of the rabbet which are oriented
parallel to said end surfaces.
To permit easy fixation of a laminated glass in a profile frame of an
explosion
proof window, it is known (EP 1 004 740 A2) to bond the laminated glass
inserted
into a frame rabbet using a layer of adhesive that fills the perimeter slot
between
the laminated glass and the rabbet. In order for the adhesive layer to be
confined
to the end surface areas of the laminated glass, a profile bar that defines
the
adhesive layer can be bonded in the transition area between the perimeter
surface of the rabbet and the adjacent rabbet surface overlapping the edge of
the
laminated glass. Even if the adhesive layer is cut through, this profile bar
impairs
the replacement of the laminated glass because there remains, above the
profile
bar, a bonding bridge to the profile frame. Moreover, the profile bar makes it
more
difficult to remove the humidity entering between the laminated glass and the
frame profile, leaving the adhesive layer exposed to the adverse effect of
humidity.
Although it is known (DE 41 42 151 Al), for the purpose of exchanging an
insulating glass component that has been secured by bonding, to provide for an
auxiliary frame that is removably secured to the wing of the window and
carries
the insulating glass component, this very auxiliary frame complicates the
construction. Furthermore, the auxiliary frame, which is secured to the
insulating
glass component through an adhesive layer, cannot be removed from the
insulating glass component.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is therefore the object of the invention to improve, using simple means, a
wing
of a window or a door of the type mentioned herein above that retains the
advantages of the known bonding connection between the insulating glass
component and the profile frame, more specifically in regard to assembly,
without
presenting the disadvantages, above all with respect to the exchangeability of
the
insulating glass component.
CA 02443255 2003-10-02
- 3 -
The objective of the invention is accomplished by providing, at a distance
from the
front of the rabbet surface, in the region of a cover pane of the insulating
glass
component that faces the rabbet surface, a perimeter boundary ridge for
confining
the adhesive layer.
The boundary ridge not only permits to locally confine the adhesive layer to
the
end surface area of the insulating glass component, but also to provide
advantageous conditions for replacing the insulating glass component because
the adhesive layer may be cut through as far as the boundary ridge without
risk of
damage to the profile frame, since the boundary ridge is disposed a distance
from
the front of the rabbet surface overlapping the edge of the insulating glass
component and may thus be damaged without impairing the frame. The boundary
ridge may be assigned to the insulating glass component or to the profile
frame. In
both cases, the boundary ridge is allowed to unrestrictedly perform its
functions.
With the boundary ridge ending at a distance from the front of the insulating
glass
component or of the perimeter surface of the rabbet, the existing allowance
not
only makes it more easy to insert the insulating glass component into the
frame
rabbet but also facilitates replacement of the insulating glass component when
the
need arises because the adhesive layer can be cut through throughout its
extent
without residual bonding bridges in the region of the allowance provided
between
the securing ridge and the insulating glass component or the perimeter surface
of
the rabbet. The size of the possible allowance depends on the flow behavior of
the not yet cured adhesive as it is being introduced into the perimeter slot
provided between the insulating glass component and the perimeter surface of
the
rabbet, though. Another possibility to completely separate the adhesive layer
consists in severing the boundary ridge together with the adhesive layer,
which
requires the boundary ridge to be designed accordingly.
The free spacing between the boundary ridge and the rabbet surface overlapping
the edge of the insulating glass component constitutes an advantageous drain
for
humidity at worst entering this region. To assist in removing humidity
alongside
CA 02443255 2003-10-02
4 -
the frame legs, the perimeter surface of the rabbet may form a recessed groove
on the side of the boundary ridge that faces the rabbet surface.
To manufacture a wing in accordance with the invention, the insulating glass
component is at first inserted into the rabbet of the profile frame and then
the
perimeter slot provided between the end surfaces of the insulating glass
component and the perimeter rabbet surface located opposite said end surfaces
is filled up to the boundary ridge, at least in perimeter areas, with an
elastic
adhesive. After the adhesive layer that fills the perimeter slot has been
cured, the
wing may be fully loaded. If the adhesive is injected into the perimeter slot
around
the entire perimeter, a sealed connection is established between the profile
frame
and the insulating glass component around the perimeter without additional
provisions being required. The adhesive may hereby be injected or forced under
pressure, into the perimeter slot. If the adhesive were applied prior to
inserting the
insulating glass component, there would be a risk of shearing it off during
jointing,
with the resulting connection not providing a material positive connection.
The adhesive layer in the perimeter slot provided between the insulating glass
component and the rabbet of the profile frame that surrounds the insulating
glass
component is intended to provide good support for the individual panes of the
insulating glass component relative to the profile frame. This may be
advantageously ensured if the perimeter slot is filled with adhesive to a
depth
corresponding to the thickness of the insulating glass component so that the
width
of the thus obtained stripe of adhesive corresponds to the overall thickness
of the
insulating glass component. The adhesive must be sufficiently elastic so as to
be
capable of undergoing tensile stresses generated by different thermal
expansion
coefficients between the bonded materials without impairing the bonding
connection.
A hot melt adhesive is preferably utilized. Such a hot melt-type adhesive may
be
processed when hot and is capable of fixing the insulating glass component in
the
profile frame as a result of the increase in viscosity during the cooling
stage so
that the wing may undergo further processing shortly after the adhesive has
been
CA 02443255 2009-12-11
31149-1
-5-
applied. If, in addition, said adhesive is capable of thermoplastic
deformation, it is
ensured that, when the wing is caused to move, the bonding connection remains
intact and the adhesive will not peel off the frame profile as this could be
the case
with crystalline thermoplastic adhesives. It has been found out that, with the
adhesive bond hardening within about 30 seconds to two hours after the hot
melt
adhesive has cooled down, the needs of window and door construction can be
well met. The use,of a reactive adhesive constitutes another possibility. It
has
been found that two-component adhesives, more specifically polyurethane-based,
epoxide-based or (meth)acrylate-based ones, are particularly suited. Such type
reactive adhesives allow for fast hardening in conjunction with strong
manipulability.
To be suited, the adhesive has to exhibit a certain stability and an
appropriate viscosity. It is hereby to be taken into account that the adhesive
is to
be applied to a sufficient coating thickness on the one side and that the
force
needed to process the adhesive under pressure is not too large on the other
side.
In accordance with an aspect of the invention, there is provided a
wing for a window or a door with a profile frame, which forms a rabbet
receiving an
insulating glass component and has a perimeter surface that surrounds the
insulating glass component on the end side thereof and a rabbet surface that
extends beyond the edge of the insulating glass component, and with an
adhesive
layer for securing the insulating glass component within the rabbet, said
adhesive
layer filling, at least in perimeter areas, a perimeter slot between end
surfaces of
the insulating glass component and the perimeter surface of the rabbet located
opposite said end surfaces, wherein there is provided, at a distance from the
front
of the rabbet surface, in the region of a cover pane of the insulating glass
component that faces the rabbet surface, a perimeter boundary ridge for
confining
the adhesive layer:
In accordance with another aspect of the invention, there is provided
a method for manufacturing a wing for a window or a door according to the
previous paragraph wherein the insulating glass component being inserted into
CA 02443255 2009-12-11
31149-1
-5a-
the rabbet of the horizontally positioned profile frame and being fastened
therein
by bonding, wherein the insulating glass component is first inserted into the
rabbet
of the profile frame and that the perimeter slot between the end surfaces of
the
insulating glass component and the perimeter surface of the rabbet located
opposite said end surfaces is next filled with an elastic adhesive, at least
in
perimeter areas, as far as the boundary ridge.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
The subject matter of the invention is shown by way of example in
the drawing wherein
FIG. 1 is a detail view of a wing for a window or a door in
accordance with the invention showing the cross-section of a frame leg,
FIG. 2 is a view of a design variant corresponding to the illustration
shown Fig. 1 and
FIGS. 3 through 5 are schematic top views of a line for
manufacturing wings in accordance with the invention in various work
positions.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
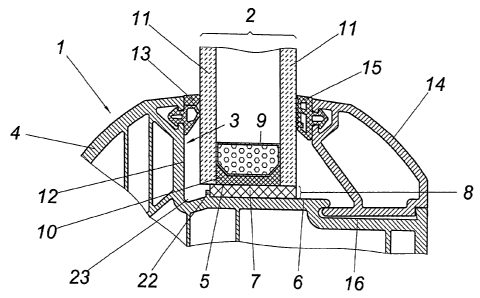
A wing of a window or a door in accordance with the invention
consists of a profile frame 1 and of an insulating glass component 2 that is
inserted in a perimeter rabbet 3 of the profile frame 1. To this purpose, the
rabbets 3 of the frame legs 4
CA 02443255 2003-10-02
- 6 -
form a perimeter surface 6 that is located opposite the end surfaces 5 of the
insulating glass component 2 and that encloses the insulating glass component
2.
An adhesive layer 7, which fills the perimeter slot 8 provided between the end
surfaces 5 of the insulating glass component 2 and the perimeter surface 6 of
the
rabbet 3, serves to secure the insulating glass component 2 in the rabbet 3.
As
the adhesive layer 7 has a width that is adapted to the thickness of the
insulating
glass component 2, the cover panes 11 of the insulating glass component 2,
which are joined together through a spacer profile 9 and a seal 10, are
supported
individually relative to the frame legs 4, which permits to advantageously
divert
the load from the insulating glass component 2 onto the frame legs 4. The
bonding achieved in this way has the advantage that the stiffness of the
insulating
glass component 2 may be used without restriction to confer stability to the
wing.
From the Figs. 1 and 2 it can be seen that the rabbet 3 of the profiles of the
frame
legs 4 forms a rabbet surface 12 that overlaps the edge of the insulating
glass
component 2; however, as opposed to conventional wings, this rabbet surface 12
does not serve to secure the insulating glass component 2, but is only
intended to
cover the perimeter edge of the insulating glass component 2, with a seal 13
that
fits said edge in the region of the rabbet surface 12 being provided. On the
opposite inner side of the insulating glass component 2, the edge thereof is
covered by a covering profile 14 and a seal 15 retained in the covering
profile 14,
said seal in turn only accomplishing sealing functions and playing no part in
retaining the insulating glass component 2. Therefore, the covering profile 14
only
needs to be snapped into a groove 16 of the frame leg 4.
To manufacture a wing in accordance with the invention, the profile frame 1,
which is formed by the assembled frame legs 4, is positioned onto an assembly
table 17 so that the insulating glass component 2 may be inserted into the
rabbet
3 intended to receive it using a hoisting device 18. Said hoisting device 18
is
comprised of a lifting device 20 provided with suction cups 19 in order to
align the
received insulating glass component 2 relative to the profile frame 1 on the
assembly table 17 and to insert it into the profile frame 1 using a swivel arm
21.
The perimeter slot 8 (Fig. 4) that remains between the inserted insulating
glass
CA 02443255 2003-10-02
- 7 -
component 2 and the rabbet 3 of the profile frame 1 may now be filled with an
adhesive, said adhesive being injected or forced under pressure into the
perimeter slot 8. To prevent the adhesive introduced into the perimeter slot 8
from
flowing out of the perimeter slot 8 toward the ridge 12 of the frame legs,
said slot
is closed by a boundary ridge 22 provided in the region of the outer cover
pane
11, said boundary ridge freely extending, according to Fig. 1, beyond the
perimeter surface 6 of rabbet 3 at a distance from the rabbet surface 12. As a
result, the perimeter slot 8 is only filled with adhesive to a depth that
corresponds
to the thickness of the insulating glass component 2 in order to make sure the
desired bonding connection between the end surfaces 5 of the insulating glass
component 2 and the frame legs 4 is achieved. After the adhesive introduced
into
the perimeter slot 8 has been cured by cooling or reactivity, the assembled
wing
may be lifted through the insulating glass component 2 from the assembly table
18 using the hoisting device 18 and may be moved to possible further
processing
stations. The manipulability of the wing is not dependent on the chemical
curing of
the adhesive, which may occur later.
The boundary ridge needs not be assigned to the frame legs 4. As can be seen
from Fig. 2, a boundary ridge 22 that is mounted to the cover pane 11
neighboring
the rabbet surface 12 also meets the requirements placed thereon with regard
to
the local confinement of the adhesive layer 7 to the area of the end surfaces
5 of
the insulating glass component 2, this providing the advantage that the
adhesive
layer 7 may be severed later on, either in the region of the slot remaining
between
the boundary ridge 22 and the insulating glass component (Fig. 1) or the
perimeter surface 6 (Fig. 2) resp., or in the region of the boundary ridge 22,
which,
in this case, must also be cut through.
According to Fig. 1, the perimeter surface 6 between the boundary ridge 22 and
the rabbet surface 12 may form a recessed groove 23 through which humidity
possibly entering between the seal 13 and the insulating glass component 2 may
be advantageously drained so that the adhesive layer 7 needs not be
disadvantageously affected by humidity.