Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
LIGHTING DEVICES FOR CONTROLLED DISTRIBUTION
AND FOR PANEL RADIATION
This is a divisional application of Canadian Patent Application Serial No.
2,219,239 f led on October 23, 1997.
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates in general to lighting devices for controlled
distribution of light or for uniform radiation through the panels of such
lighting
devices. It should be understood that the expression "the invention" and the
like
encompasses the subject matter of both the parent and the divisional
application.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The conventional methods of controlling distribution of light of a lamp are to
redirect or control flux of a light source with a reflector or a lens, or to
cut a part of
flux with an absorption body in order to eliminate the light which goes to
outside of
the desired area. However, the elimination of a part of the flux of a lamp for
such an
improvement has resulted in a low energy efficiency. Many of the conventional
lighting devices for uniform radiation through the panels of such lighting
devices have
a plurality of fluorescent lamps behind each of the translucent diffusion
panels and
radiate the flux of lamps out through each of the diffusion panels.
Such devices have failed to have sufficiently uniform light intensity
throughout the radiation panel due to cause of light and dark bands on the
surface of
the radiation panel along the arrangement of the fluorescent lamps.
Elimination of
such tight and dark bands by arranging the lamps closer to one another or by
using a
high diffusion panel of conventional translucent material for the radiation
panel
decreases the energy efficiency.
-1-
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
It is an objective of the present invention to pro'v'ide a lighting
device in a distribution control type which forwards much greater
amount of the flux of a lamp (lamps) into a specified range of
light distribution and much less amount of the flux to the outside
of the range than any conventional device does, ie. a lightir~g device
in a distribution c~trol type which provides a desired light
distribution with a high energy efficiency.
It is a further objective of the present invention to provide a
lighting device in a radiation. panel type with no cause of light
and dark bands an the radiation panel, i.e. uniform radiation
throughtout the panel arith a high energy efficiency in exploitation
of the above light distribution control technology.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A lighting device in a controlled distribution type in regard to
the present invention comprises an artificial light source, a means
to redirect the flux of the light source and a light diffuser which
diffuses such redirected flux in specific directions, wherein the
diffuses has a transparent or reflective body comprising a plurality
of ridges or ridges and grooves arranged, whereby redirected flux
of light incident to a face of the arrangement is diffused.
More specifically, the present invention provides a lighting device
for a controlled distribution of light, comprising a light source; a flat
reflector positioned in front of the light source and angled to redirect a
flux from the light source, an ellipsoidal reflector positioned behind the
light source and positioned to reflect light toward the flat reflector, and a
diffuser which diffuses such redirected flux into specific directions,
-2-
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
wherein the diffuser is a transparent body or a reflective body embodying
a plurality of ridges or ridges and grooves arranged, wherein each of the
ridges in the arrangement of ridges, or at least each of either ridges or
grooves in the arrangement of ridges and grooves has a cross-sectional
shape that is partially circular, elliptic, sine curved or curved in other
way, whereby redirected flux incident to either face of the diffuser is
diffused in specific direction.
The present invention also provides a lighting device in a radiation
panel type, comprising a substantially rectangular enclosure, a pair of
substantially planar optical component parts within the enclosure and
having optically smooth faces which are facing each other in distances
varying gradually in traveling from one end to an opposite end of the pair
of optical component parts, wherein one of the optical component parts is
transparent and the other is reflective, and a light source apparatus to
enter light between the faces at an end of the optical component parts and
the enclosure, whereby the entered light reflects off of the reflective
optical component part and radiates out through the transparent optical
component part.
The redirection of the flux of the light source may be made
with a reflector which provides the fluz of the light source in
specific beam angle. Optical fibers or a light guide pipe may
transmit such beam of flux to the diffuser at a distant place. A
higher energy efficiency can be obtained by further redirecting
a part of diffused rays which were to be directed to outside of
-3-
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
a desired range of light distribution, into the desired range arith
an additional reflector.
A lighting device in a radiation panel type in regard to the
present invention comprises a pair of optical component parts
having optically smooth faces which are facing each other in
distances varying in traveling from one end to the opposit end
of the optical component parts, wherein at least one of the said
component parts is transparent, 'and one or a plurality of light
sources so placed at one end or both the opposit ends of the said
component parts that the flux of the light sources) enters between
the said faces and radiates out through the transparent component
part.
A lighting device in a controlled distribution type in regard to
the present invention may be used for the light source of the above
lighting device in a radiation panel type as well as a fluorescent
lamp with a reflector which redirects its flux between the said
faces.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
Figure 1 is a schematic view of a structure of a lighting device
in a controlled distributuion type in regard to the present
invention ;
Figure 2 is a schematic presentations of a light distributuion
obtained with the lighting device described in Figure 1
Figure 3 is cross- sectional schematic views of the diffuser in
Figure 1 in variation, wherein "C" or a single solid line represents
a circle, a cizrular arc or a curve, and a double solid line represnts
-4-
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
a Straight line
Figure 4 is a schematic view of the structure of a lighting device
in a controlled distributuion type in regard to the present invention
using a set of reflectors to further control diffused rays :
Figure 5 is schematic presentations of a lgith distributuion
obtained with the lighting device described in Figure 4, wherein
"(a)' represents the light distributuion in the cross- section at
Line A, and "(b)' represents the same at Line B ;
Figure 6 is a perspective view- of flux obtained with the lighting
device described in Figure ~
Figure 7 is a perspective view of a lighting device in a radiatiaan
panel type in regard to the present invention, wherein the distance
between the face of the radiation panel and the face of the
reflection parcel gradually decreases in traveling from the light
entering end to the opposit end
Figure 8 is a presentati~. of the distributuion of light intensities
obtained on the radiation panel of the lighting device described
in Figure ?, wherein a conventional acrylic translucent diffusion
paael is used as the radiation panel ;
Figure 9 is a presentation of the distribution of light intensities
obtained on the radiation panel of the lighting device described
in Figure 7, wherein a diffuser described in Figure 3 is used as
the radiation panel ;
Figure 10 is a perspective view of the structure of a lighting
device in a radiation panel type, wherein the distance between the
face of the radiation panel and the face of the reflection panel
gradually decreases towards the middle line of the radiation panel,
-5-
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
and light enters from both the opposit ends of the optical
component ;
Figure 11 is a perspective partial view of the lighting device
descn'bed in Figure 10, wherein fluorescent lamps are used as the
light sources.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
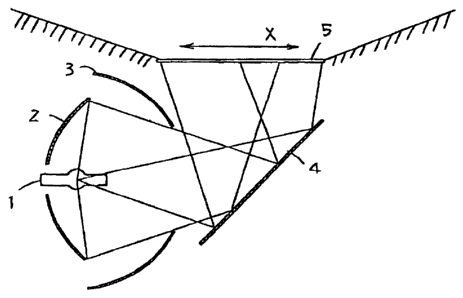
Figure 1 shovsrs that the flux of a 35 watt short-arc metal-halide
lamp 1 is collected and redirects into a condensed beam with an
ellipsoidal reflector 2 and a spherical reflector 3, and partially
further redirected the beam with . a flat reflector 4 to a transparent
diffusion body 5 which has a "diffusion axis X". All the said
reflectors are made by making specific optical coating on their
glass bodies so that they ref lect visible rays, transmit infrared rays
and consequently eliminate most of infrared rays from the beam
incident to the diffuser 5. The ellipsoidal reflector 2 alone or
together with the spherical reflector 3 constitutes the first means
to redirect the flux, and the flat reflector 4 constitutes the second
nneans for the redirection in regard to the present invention.
Projection of the diffused rays from the diffuser 5 to a wall
provides a light distribution ~ as shown in Figure 2.
The diffuser 5 is a transparent acrylic plate which emobodies
a plurality of ridges nexting to ane another on a face of the said
plate. wherein each of the ridges has cross - sectional shape of a
circular arc. The diffuser 5 may also be a transparent plate
emboding an arrangement of a plurality of either ridges or ridges
and grooves each of which has a cross- sectional shape that is
-6-
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
partially circular, elliptic, sine curved or curved in any other way
as shown in Figure 3. The diffuser 5 may also be either a
transparent or a reflective body of plurality of mono-filaments
or cylinders bundled together.
Optical fibers or a light guide pipe may receive the flux
condensed by the ellipsoidal reflector 2 alone or with the spherical
reflector 3, directly from the ellipsoidal reflector 2 or through the
flat reflector 4, in order to transmit the flux to the diffuser S
at a distant place. Projection of the diffused rays to a wall with
the flux thus redirected and transfe~d provides a light distrifution
similar to one shown in Figure 2.
As shown in Figure 4, a set of flat riflector 6 is so placed. in
front of the diffuser 6 that such set of reflectors controls the
direction of the diffused rays. Projection of the flux of such
controlled diffused rays to a wall at distance A and B are shown
in Figure 5 - (a) and (b). The shapes of the light distribution
at distance A and B represent the cross- sectional shapes of the
flux at distance A and l~ This implies that the diffusion from the
diffuser 5 is controlled into a shape of a fivstum of pyramid which
expands forwards.
Figure 7 shows a thin box having thickness of 15 cm, bight of
50 cm and width of 100 do is used as the radiation panel ?, and
a 3 nun thick acrylic reflection panel 8 is placed behind the
radiation panel ?, keeping the reflective surface faced to the
radiation panel 7. The distance between the said panels is set to
be 13.? cm at one of the shorter ends 9 of the box and gradually
decreased towards the opposit end 10, in a straight line. Reflection
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
panels 11 and 12 are placed at both the longer ends, keeping the
reflective faces fnside.
Flux of light which has a shape of a frustrum of pyramid as
shown in Figure 6, enteres between the radiation panel 7 and
reflection panel 8 at the end 9 of thus structured optical component
13. The distribution of the light intensities on the surface of the
radiation panel 7 is shown in Figure 8. Each number on the
radiation panel shows the intensity in lux at each point where
such number is shown. The result implies the following
Average intensity . 1873 lux
ty ~ Max. intensity ~ : 2200
Uniformi ~ intensity 1700 ~ 1.3
Total flux radiated 1873 x 0.5 i 0.3~
Total flux radiated ~ ' 2700
In the above optical component 13, the translucent radiation panel
7 is replaced with a transparent diffusion panel which has the
structure the same to the diffuser 5. The diffusion panel is so
placed that its ridges face outside and is orthogonal to the
longitudinal axis of the optical compornent 13. Light intensities
vn the radiation panel ~ made of such diffusion panel is shown
in Figure 9_. The result implies the following
Average intensity . 2I73 lua
Uniformity M~ intensity ~ .~ 1.25
Min. intensity ~ ' 20p0
. Total flux radiated 1086 x 0.5 i
°~ ~ Total flux radiated , ~ X00 -~ 0.4
Figure 10 shows the optical component 13, wherein the distance
between the radiation panel 7 and the reflection panel 8 gradually
decreases in traveling from both the said opposit ends 9 and 10
_g_
CA 02488271 1997-10-23
to the middle line of such two ends. Flux of a fluorescent lamp
enters between the said panels at each of the said opposit ends
9 and 10.
In any of the above lighting devices in a radiation panel type,
an increase of the distance between the said panels T and 8 towards
the opposit end or the middle line for a short distance from each
light entering end improves the uniformity of the radiation over
the surface of the radiation panel '~.
-9-