Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02548983 2010-02-25
1
Device And Method For Manufacturing Wrapped Tubes
Background of the Invention
Field of the Invention
The invention relates to a device as well as a method for manufacturing
wrapped tubes by helically winding up a thermoplastic, preferably strip-
shaped plastic profile onto a winding core in an overlapping manner, a plas-
ticizing aggregate supplying the plastic profile via a profile nozzle.
Description of Related Art
Devices for manufacturing a tubular object by helically or spirally winding up
a band material of thermoplastic plastics are known, for example, from
German Patent No. 1281676 issued on October 31, 1968 to Manfred
Hawerkamp. Immediately after the band material has emerged from an ex-
truder or has been heated, it is wound up, in a deformable state, onto a
winding core with an overlapping and/or abutting, particularly obliquely
abutting overlapping winding seam and welded by applying pressure and, if
necessary, additional heat in the region of the winding seam in such a
method.
Summary of the Invention
It is an object of the invention to provide a device as well as a method for
manufacturing wrapped tubes by which pressure tubes with a larger tube
diameter are producible without an extreme enlargement of the wall thick-
ness as would bb the case in the present wrapped tube production.
CA 02548983 2006-06-09
2
The invention advantageously provides that the plasticizing aggregate is a
kneading means supplying the winding core with a thermoplastic plastic
mixed with reinforcing fibers via the profile nozzle.
Because of the use of a screw kneading aggregate, reinforcing fibers with
greater fiber lengths can also be mixed homogeneously with the thermoplas-
tic plastic without shortening or grinding the fibers. The screw kneading ag-
gregate permits the exactly metered addition of fibers into the processed
molten mass, the fiber length of the added fibers being preserved. The in-
crease in pressure-resistance and tensile strength due to the fiber strength-
ening permits to manufacture, e.g., larger tube diameters with a tube wall of
lesser wall thickness and thus of small weight. Due to the strengthening,
pressure tubes with an outer diameter of, e.g., up to 4 m and more are pro-
ducible as wrapped tubes.
Such a homogenized mixture of fibers and thermoplastic plastic while pre-
serving the fiber length of the fibers cannot be produced by a conventional
extruder because of the very high shearing forces, since the fibers are
shortened and ground due to the occurring shearing forces.
Preferably, the thermoplastic plastic consists of polyethylene or polypropyl-
ene. No granules with fillers are used but polyethylene granules or polypro-
pylene granules are plasticized in the kneader and provided with fiber-
shaped reinforcing agents, in principle, all strength-increasing reinforcing
fibers being suitable.
Preferably, the reinforcing fibers consist of plastic, glass and/or metal,
glass
fibers in particular, but also aramide fibers and/or carbon fibers being
highly
strength-increasing.
When several layers of the plastic profile are wound up, this is effected un-
der a different supply angle so that the fiber-reinforced superposed winding
CA 02548983 2010-03-17
3
layers cross each other whereby the internal pressure resistance of the
wrapped tubes is additionally increased.
On the outside of the wrapped tube, a profile, preferably a tube profile, may
be additionally wound onto the outer tube wall to increase the tube stiffness
and the moment of inertia.
The fiber length of the reinforcing fibers amounts to at least about 2 mm,
but preferably to more than 4 mm up to endless fibers.
The screw kneading aggregate is adapted to process such fiber lengths up to
endless fibers.
The fiber-reinforced thermoplastic mixture homogenized in the screw
kneader consists of about 60 to about 94 percent by weight of polyethylene
or polypropylene, about 1 to about 10 % of the bonding agent as well as of
about 5 to about 40 percent by weight of reinforcing fibers arranged in an
uniformly distributed manner in random orientation in the plastic profile.
The bonding agent particularly serves to improve the adhesion between the
polyethylene or polypropylene and the fibers.
In addition to the at least one layer formed of the fiber-reinforced plastic
profiles, an innermost and/or an outermost winding layer of polyethylene
without fiber reinforcement may also be wound up onto the winding core.
According to an aspect of the present invention there is provided a device for
manufacturing wrapped tubes by helically winding shaped thermoplastic onto a
winding core, the device comprising:
a plasticizing unit for supplying the shaped thermoplastic to the winding core
via a nozzle,
CA 02548983 2010-03-17
3a
wherein the plasticizing unit is a kneading means supplying the shaped
thermoplastic via the nozzle, and the shaped thermoplastic comprises
thermoplastic material mixed with reinforcing fibers, and
wherein the kneading means is a screw kneading unit, such that the
reinforcing fibers can be homogeneously mixed with the thermoplastic
material, while fiber length of the reinforcing fibers is maintained.
According to another aspect of the present invention there is provided a
method for manufacturing wrapped tubes by winding shaped thermoplastic
onto a winding core in an overlapping manner, the shaped thermoplastic being
supplied to the winding core from a plasticizing unit and a nozzle, the method
comprising the steps of.
heating a thermoplastic material to a predetermined melting temperature;
homogeneously mixing the heated thermoplastic material with reinforcing
fibers in a kneading means, wherein the kneading means comprises a screw
kneader and is employed as the plasticizing unit for manufacturing said
wrapped tubes with an increased internal pressure resistance; and
supplying the fiber-reinforced homogenized thermoplastic material mixture to
the winding core via the nozzle.
According to a further aspect of the present invention there is provided a
wrapped tube manufactured according to the method as described herein,
wherein the fiber-reinforced homogenized thermoplastic material mixture
comprises:
- 60 to 94 percent by weight of polyethylene or polypropylene;
- 1 to 10 percent by weight of bonding agent; and
- 5 to 40 percent by weight of the reinforcing fibers arranged in random
orientation.
CA 02548983 2010-03-17
3b
Brief Description of the Drawings
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the invention is explained with reference to
the drawings, in which
Fig. 1 shows, in side view, a device according to the invention, for manu-
facturing wrapped tubes;
CA 02548983 2006-06-09
4
Fig. 2 shows the device according to Fig. 1 in top view; and
Fig. 3 shows the winding of several winding layers.
Detailed Description of the Preferred Embodiment of the Invention
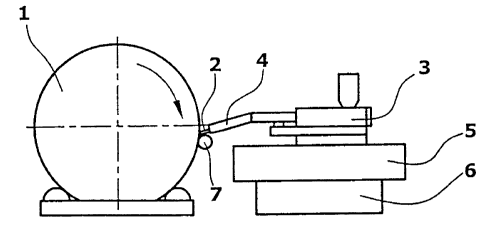
Figure 1 shows a device for manufacturing a wrapped tube by helically wind-
ing up a thermoplastic, preferably strip-shaped plastic profile 2 onto a tem-
perable or heatable winding core 1 in an overlapping manner.
A screw kneading aggregate 3 used for plasticizing is seated on a reciprocat-
ing slide 5 that is adapted to be displaced to and fro along a guide 6
parallel
to the winding core 1, the plastic profile 2 being supplied to the winding
core
1 from the screw kneading aggregate 3 via a profile nozzle 4.
As can be seen from the top view of Fig. 2, the plastic profile 2 is supplied
to
the winding core 1 via the profile nozzle 4 under an oblique angle. In the
reversal position of the slide 5 at the ends of the winding core 1, there
arises
an oblique angle with the same amount but with opposite direction because
of the reversal of the direction of movement of the slide 5 so that succeed-
ing winding layers 9a,9b cross each other. Preferably, it is provided that the
start of a new winding layer is respectively effected at different ends of the
winding core 1 so that the winding process can substantially be continued
continuously. The first plastic profile 2 of a winding layer may also be sup-
plied straight to obtain a straight end at the end faces of the wrapped tube.
From Fig. 3, the different orientation of the plastic profile 2 of superposed
winding layers 9a,9b is apparent.
While the slide is thus moved to and fro, the winding core 1 rotates to wind
up the strip-shaped plastic profile 2 in an overlapping manner, which profile
is welded at the points of overlapping and abutment.
CA 02548983 2006-06-09
The screw kneading aggregate 3 supplies a homogenized mixture of a ther-
moplastic plastic of polyethylene or polypropylene and reinforcing fibers of
plastic, glass and/or metal to the profile nozzle 4. Upon emerging from the
double screw kneader, the fibers are arranged in the mixture so as to be
distributed homogeneously in random orientation in the thermoplastic plastic
and then, they are supplied to the winding core 1 via the profile nozzle 4.
Preferably, the screw kneading aggregate consists of a double screw
kneader where the screws arranged in parallel next to each other do not ro-
tate in opposite directions but have the same rotational direction. The
kneading means is also referred to as double screw kneader with the same
rotational direction. In dependence on the processed mixture, the tempera-
ture of the thermoplastic plastic amounts to about 170 to 240 C.
Single-screw as well as double screw extruders rotating in opposite direc-
tions, however, are not suited to produce the mixture of fiber-reinforced fi-
bers and thermoplastic plastic because they do not have a sufficient ho-
mogenizing effect and shorten or grind the fibers because of the occurring
shearing forces so that the pressure resistance required for the production of
pressure-resistant wrapped tubes with large diameter cannot be achieved.
Preferably, reinforcing fibers of glass fibers are employed, for particular ap-
plications and particularly high strength requirements, however, aramide
fibers and/or carbon fibers or a mixture of different fibers can be used as
well.
The fiber length should amount to at least 2 mm, preferably, however, to
more than 4 mm. In a preferred embodiment, the fiber length amounts to
about 6 mm. It is also possible, however, to use longer fibers up to endless
fibers.
The fiber-reinforced thermoplastic plastic mixture emerging from the screw
kneader 3 preferably consists of about 60 to about 94 percent by weight of
CA 02548983 2006-06-09
6
polyethylene or polypropylene, about 1 to about 10 % of bonding agent as
well as of about 5 to about 40 percent by weight of reinforcing fibers.
Therefore, a double screw kneader 3 is used as a plasticizing aggregate for
manufacturing wrapped tubes with an increased internal pressure resis-
tance, a thermoplastic plastic being brought to a predetermined melting
temperature in the double screw kneader 3 and then being homogeneously
mixed with reinforcing fibers. Subsequently, the fiber-reinforced homoge-
nized thermoplastic plastic mixture can be supplied to the profile nozzle 4.
As a whole, the wrapped tube may be formed of several winding layers,
where the innermost and/or the outermost winding layer may be formed of
polyethylene without fiber reinforcement. Preferably, the fiber-reinforced
winding layers are wound crosswise, i.e., radially adjacent winding layers
9a,9b extend under different angles such that the orientation of the fibers
crosses each other in the individual winding layers.
By means of the described device and the manufacturing method, wrapped
pressure tubes with large dimensions and very high internal pressure resis-
tance are producible, the wall thickness, due to the fiber reinforcement, be-
ing substantially, i.e., by about 50%, smaller than with conventional manu-
facturing methods without fiber reinforcement.
In a wrapped tube with a diameter of about 4 m, for example, the wall
thickness amounts to about 100 mm to 200 mm, each winding layer 9a,9b
being formed of a plastic profile 2 with a thickness of about 5 to 10 mm.
Such pressure-resistant wrapped tubes are suitable for the conveyance of
drinking water, for example.
As is apparent from Fig. 1, the winding core 1 rotates clockwise so that the
plastic profile 2 is wound downward onto the winding core 1, a pressing
means 7 pressing the plastic profile 2 against the winding core 1. The screw
kneader 3 extends under an angle of 901 to the longitudinal axis of the
CA 02548983 2006-06-09
7
winding core 1, the oblique angle of each winding layer 9,11 resulting solely
from the advance of the slide 5.
Although the invention has been described and illustrated with reference to
specific illustrative embodiments thereof, it is not intended that the
invention
be limited to those illustrative embodiments. Those skilled in the art will
rec-
ognize that variations and modifications can be made without departing from
the true scope of the invention as defined by the claims that follow. It is
therefore intended to include within the invention all such variations and
modifications as fall within the scope of the appended claims and equivalents
thereof.