Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
1
SECURITY PAPER OR SPECIAL PAPER INCORPORATING HIGH
RESISTANCE SYNTHETIC ELEMENTS AND A PROCEDURE FOR
OBTAINING SAID PAPERS
DESCRIPTION
OBJECT OF THE INVENTION
The object of the present invention refers to a security or special paper
that incorporates high resistance synthetic elements (fibres,
microspheres,...), as well as a security document manufactured with said
support.
These synthetic elements incorporated in the security paper or special
paper are usually provided different qualities such as been fluorescent,
phosphorescent, luminescent, with magnetic characteristics, etc,
characteristics that are visible to the naked eye all that can be observed
under certain conditions, such as under ultraviolet light, magnetic sensors,
etc
The synthetic elements incorporated by the security paper or special
paper proposed by the invention provide that such characteristics conferred
to these elements are embedded within them, such that the loss of properties
inherent to these elements becomes more difficult as time goes by, resisting
the harsh conditions that security and special documents are subject to, such
as bank notes or the like.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The use of security documents incorporating fluorescent fibres and
other synthetic elements with different verification and detection responses
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
2
that are introduced during the paper manufacturing process such that some
elements are embedded within the paper as it is formed is known in the state
of the art.
These elements, in the case of the fibre is, for example, are generally
manufactured in viscous or polyamide, substances that are related to water
since they have hydrogen free radicals. These are, therefore, substances
that can be easily integrated in water dispersions, which are the base of the
paper manufacturing process, since the fibres the paper is made of are
introduced in the paper manufacturing machine as an aqueous dispersion
that will form the sheet of paper as the water is extracted.
The fibre manufacturing procedure is generally performed by obtaining
extremely fine filaments in an extrusion line that are cut to a certain
length.
Certain pigments are added to this type of elements to confer them the
desired characteristics of fluorescence, phosphorescence, luminescence,
magnetism etc, these pigments being applied after manufacturing said fibres,
such said fibres are superficially impregnated.
The pigments usually used can basically be of two types, inorganic-
based pigments are the main characteristic of which is offering good
resistance to preserve the fluorescent, phosphorescent, luminescent,
magnetic, and other properties, although in contrast they offer deficient
response intensity.
The second type of pigments that can be used organic-based
pigments and have bad resistance, the effects lasting little, but however,
offering good response intensity.
The synthetic element impregnation procedure provides introducing
these inside pressure tanks, until they are totally dyed by the pigments.
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
3
These elements, in order to be incorporated into the paper
manufacturing process, are prepared in the form of a water suspension
provided to the paper manufacturing process, thus being embedded inside
the paper at different depths that are randomly arranged.
It has been demonstrated that superficially arranged pigments lose
their features prematurely since light deteriorates their properties very
easily,
since there are only protected by the possible fibres in the paper. Moreover,
since these pigments remain on the surface they can easily deteriorate by
friction or the use given to the security paper they are on.
It has thus been demonstrated that security papers integrating
elements with fluorescence, phosphorescence, luminescence, and other
features lose such qualities with use, making these authentication and
recognition measures practically useless for such security documents.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
It is the object of the invention to obtain a security paper or special
paper which, based on the previously mentioned technology, internally
incorporates synthetic elements that are provided with pigments, either
fluorescent, phosphorescent, luminescent, magnetic, etc., that confer them
security features, that such pigments are highly resistant to the detachment
of their own synthetic elements and that they can be easily integrated in the
manufacturing process of a security paper or special paper used to
manufacture security documents or special documents such as banknotes,
bills of exchange, security labels, etc.
It is also the object of the invention to achieve the security or special
document, either a banknote, bill of exchange, security label, etc that has as
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
4
a substrate this security paper or special paper integrating synthetic
elements
with the qualities of being highly resistant to wear factors of the document
itself without their characteristics being altered.
Also the object of the invention is an improved procedure for
incorporating said synthetic elements in the paper forming process,
preventing their caking and therefore favouring their dispersion and
integration in the paper paste.
In order to carry out the object of the invention we propose using
synthetic elements with the pigments or products to be conferred singular
characteristics, inside the material of the element itself. The material of
the
element itself will protect said pigment or product provided to the fibre and
conferring it the appropriate security characteristics.
The pigment introduced in the paste for forming the synthetic element
will be protected by the material of the element itself, preventing wear by
friction and being protected from attacks from physical and chemical agents
that the security document may suffer and from light, so that the features
incorporated in the pigments are kept unchanged with time.
The material of these synthetic elements that allows integrating the
pigments in the paste without their deterioration in is not viscous or
polyamide but polypropylene, and has the difficulty of being a material
without hydrogen free radicals and is therefore a product that is not related
to
the water surrounding it, that is, it is not impregnated in the water of the
aqueous solution it is in, producing caking of the synthetic elements and
therefore not providing a homogeneous dispersion thereof in the water.
An aqueous solution has been achieved in which the synthetic
elements are dispersed without caking, with the addition of dispersing and/or
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
penetrating and/or antifoaming agents in the appropriate proportion. This
allows them to be incorporated in the aqueous paper forming solution,
achieving the homogenous dispersion of such synthetic elements inside the
paste of the paper that is being formed, preventing the caking of the
synthetic
5 elements.
This homogeneous incorporation of the synthetic elements in the
paper forming paste alarms though to be distributed inside the paper, which
is compared to the effect is achieved with the viscous or polyamide fibres but
with a material that does not present affinity towards water.
A procedure for incorporating the synthetic elements with this material
is to achieve a dispersion of water and synthetic elements that is
continuously stirred. Dispersing agents and/or penetrating agents and/or
antifoaming agents are added to this dispersion in appropriate proportions,
thus preventing the caking of the synthetic elements. The dispersion is
prepared in several loading and homogenising deposits prior to it being
pumped to the paper production circuit in the machine.
Incorporation of these synthetic elements can be performed randomly
in the entire paste of the paper being formed or it can be performed in a
localised manner at specific points of the paper paste, thus obtaining
longitudinal strips of synthetic elements located at different levels on the
thickness of the paper with such elements, which increases the degree of
security of the final document thus obtained.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In order to complete the description being made and to aid towards a
better comprehension of the features of the invention, according to our
preferred practical embodiment thereof, we incorporate as an integral part of
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
6
said description a set of drawings that are illustrative and not limiting in
nature, and represent the following:
Figure 1 shows an enlarged section of paper incorporating this type of
synthetic elements in its paste, such as that shown in the invention.
Figure 2 equally represents an enlarged section of the paper
incorporating the synthetic elements of the invention in strips.
Figure 3 represents a schematic diagram of the tanks for preparing the
aqueous solution of synthetic elements before being introduced in the paper
manufacturing machine.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 shows an embodiment of a security paper or special paper
(3) with the synthetic elements integrated in its paste, in this case in the
shape of fibres (1) of the invention, in the same manner as in a traditional
embodiment of the state-of-the-art, achieving that, despite these fibres being
made in polypropylene, which does not present affinity towards water, such
fibres are not caked or superficially retained on the paper itself, but
randomly
distributed inside the paper formed.
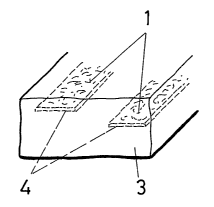
Figure 2 is a variant of the embodiment of a security paper or special
paper (3) wherein the synthetic elements of the invention, in this case again
in the form of fibres (1), can be integrated in strips (4) by means of
controlled
insertion techniques for inserting such fibres inside the paper during their
manufacture, controlling the depth at which said fibre strips are introduced,
so that they remained superficially or embedded inside the paper thus
formed.
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
7
Figure 3 represents a schematic diagram for the procedure of
preparing an aqueous solution of the synthetic elements, wherein these are
initially conditioned inside an aqueous dispersion in a tank (5), wherein an
amount of dispersing and/or penetrating and/or antifoaming agents is
conditioned in an adequate amount, as well as the synthetic elements and
the aqueous base for the suspension thereof, said suspension being stirred.
The dispersion thus prepared then goes through a homogenising step
(6) and is then dosed by means of appropriate pumps (7) towards the entry in
the paper manufacturing machine (8) for said synthetic elements to be
integrated en masse or in a controlled manner.
PRACTICAL EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION
Examples of dispersing products would be POLISAL by BASF or
AMP-90 by ANGUS. POLISAL is an aqueous solution of a yellowish
sodium polyacrylate with an approximate density of 1.3 gr/cm3, which is a
very active product for dispersion and refinement of the pigments used in the
paper industry, especially for coating pigments.
The dispersing agent AMP-90 is an aqueous solution of 2-amino-2-
methyl-1-propanol. This disposing agent is colourless, with a relatively low
viscosity and remains liquid at pretty low temperatures, such as -37 C, which
allows easy and adequate handling in industrial plants. This product is a very
efficient dispersing agent for pigments in plastic paints and, as a fatty acid
salt, emulsifier in non-mixing water-liquid systems. It also provides pH
stability, low odour and anticorrosive properties, and would even increase the
acceptance of universal colorants. This product's density is of 0.949 gr/cm3
at 25 C.
As a penetrating product we can mention NOPCOWET LO , which is
a synergic mixture of surface-active humectants and detergents such as Alkyl
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
8
phosphate and potassium salt, which in the alkaline bleaching process
facilitate the uniform impregnation of bleach in the entire paste to be
treated,
facilitating the elimination of waxy compounds coating the fibres. Due to its
detergent effect it carries away the dirt on the fibres
As an antifoaming product we can mention AFRANIL MG by BASF,
which is a mixture of aliphatic hydroxide compounds in an aqueous emulsion.
It has a density of approximately 0.960 gr/cm3 and a pH of approximately 9.
This product has a good deaeration effect for the mixtures it is inserted
into,
with the advantage that water-repellent impurities do not accumulate, that is,
it has a dispersing effect.
Security paper manufacturing tests have been performed, in which the
synthetic elements of the invention have been inserted en masse in the form
of fibres with a fluorescent feature, comparing it with the security paper
with
viscous or polyamide fibres as performed in the known state of the art. These
security papers have been subjected to several tests in order to verify the
stability of the fluorescence characteristics of the fibres with spectacular
results. These tests are basically of three types: the first are subjecting
these
security papers to acids, the second subjecting them to the action of
detergents and the third subjecting them to extreme heat and light situations.
As an example we enclose a comparative table of fibres with
fluorescent response.
TEST PERFORMED WITH FLUORESCENT FIBRES
The results are clearly in favour of the paper of invention.
CA 02603937 2007-10-05
9
% OF FLUORESCENCE REMAINING
Security paper Security paper of the
according to the state invention
of the art
Acetic acid 45-93 79-100
Hydrochloric acid 7-92 94-100
Sulphuric acid 11-100 96-100
Soapy solution at 95 7-87 95-100
Synthetic sweat 94 94-100
Heat 82-90 85-100
Light 3-25 25-96
The differences may vary according to pigment colour or the type of
response expected but always with an improvement upon the current state of
the art.