Une partie des informations de ce site Web a été fournie par des sources externes. Le gouvernement du Canada n'assume aucune responsabilité concernant la précision, l'actualité ou la fiabilité des informations fournies par les sources externes. Les utilisateurs qui désirent employer cette information devraient consulter directement la source des informations. Le contenu fourni par les sources externes n'est pas assujetti aux exigences sur les langues officielles, la protection des renseignements personnels et l'accessibilité.
L'apparition de différences dans le texte et l'image des Revendications et de l'Abrégé dépend du moment auquel le document est publié. Les textes des Revendications et de l'Abrégé sont affichés :
| (12) Brevet: | (11) CA 2840275 |
|---|---|
| (54) Titre français: | PROCEDE D'ALIMENTATION BASE SUR UN CONTROLE EN UN SEUL POINT POUR UN DISPOSITIF D'ALIMENTATION D'UNE CELLULE DE REDUCTION D'ALUMINIUM |
| (54) Titre anglais: | SINGLE-POINT CONTROL BASED FEEDING METHOD FOR ALUMINUM REDUCTION CELL FEEDER |
| Statut: | Octroyé |
| (51) Classification internationale des brevets (CIB): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventeurs : |
|
| (73) Titulaires : |
|
| (71) Demandeurs : |
|
| (74) Agent: | SMART & BIGGAR LP |
| (74) Co-agent: | |
| (45) Délivré: | 2017-06-13 |
| (86) Date de dépôt PCT: | 2012-05-31 |
| (87) Mise à la disponibilité du public: | 2013-01-03 |
| Requête d'examen: | 2013-12-23 |
| Licence disponible: | S.O. |
| (25) Langue des documents déposés: | Anglais |
| Traité de coopération en matière de brevets (PCT): | Oui |
|---|---|
| (86) Numéro de la demande PCT: | PCT/CN2012/000750 |
| (87) Numéro de publication internationale PCT: | WO2013/000270 |
| (85) Entrée nationale: | 2013-12-23 |
| (30) Données de priorité de la demande: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
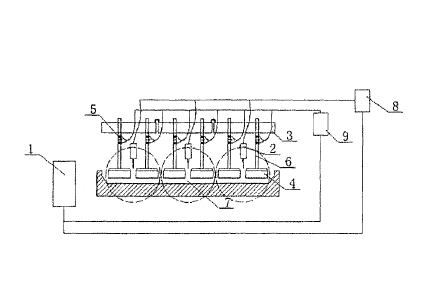
L'invention concerne un procédé d'alimentation basé sur un contrôle en seul point pour un dispositif d'alimentation de cellule de réduction d'aluminium à anodes précuites. Un orifice d'alimentation est divisé en différentes régions. Des signaux de chute de tension équidistants sont échantillonnés sur des conducteurs d'anode dans différentes régions. Le courant anodique est calculé selon les signaux de chute de tension équidistants. La concentration d'oxyde d'aluminium dans des régions de l'orifice d'alimentation est comparée selon la tendance de variation du courant anodique. Un contrôle d'alimentation est effectué de façon distinctive pour des états des régions de l'orifice d'alimentation. Par ce procédé, un contrôle ciblé peut être effectué sur la concentration d'oxyde d'aluminium dans chaque région de la cellule électrolytique, permettant ainsi d'améliorer la précision du contrôle d'alimentation, d'éviter la production ou la fréquence d'effet d'une précipitation, ce qui est avantageux pour un fonctionnement stable de la cellule électrolytique, et ce qui permet de parvenir à l'effet d'économiser de l'énergie, de réduire une consommation et d'améliorer le rendement en courant.
Disclosed is a single-point control based feeding method for a pre-baked anode aluminum reduction cell feeder. A feeding port is divided into different regions. Equidistant voltage drop signals are sampled on anode leaders in different regions. The anode current is calculated according to the equidistant voltage drop signal. The aluminum oxide concentration in regions of the feeding port is compared according to the variation trend of the anode current. Feeding control is performed distinguishingly for states of the regions of the feeding port. Through the method, targeted controlling can be performed on the aluminum oxide concentration in each region of the electrolytic cell, thereby improving the accuracy of the feeding control, avoiding precipitation production or effect frequency, being beneficial to stable running of the electrolytic cell, and achieving the effect of saving energy, reducing consumption and improving current efficiency.
Note : Les revendications sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
Pour une meilleure compréhension de l'état de la demande ou brevet qui figure sur cette page, la rubrique Mise en garde , et les descriptions de Brevet , États administratifs , Taxes périodiques et Historique des paiements devraient être consultées.
| Titre | Date |
|---|---|
| Date de délivrance prévu | 2017-06-13 |
| (86) Date de dépôt PCT | 2012-05-31 |
| (87) Date de publication PCT | 2013-01-03 |
| (85) Entrée nationale | 2013-12-23 |
| Requête d'examen | 2013-12-23 |
| (45) Délivré | 2017-06-13 |
| Date d'abandonnement | Raison | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2015-10-09 | R30(2) - Absence de réponse | 2016-08-26 |
Dernier paiement au montant de 263,14 $ a été reçu le 2023-12-07
Montants des taxes pour le maintien en état à venir
| Description | Date | Montant |
|---|---|---|
| Prochain paiement si taxe applicable aux petites entités | 2025-06-02 | 125,00 $ |
| Prochain paiement si taxe générale | 2025-06-02 | 347,00 $ |
Avis : Si le paiement en totalité n'a pas été reçu au plus tard à la date indiquée, une taxe supplémentaire peut être imposée, soit une des taxes suivantes :
Les taxes sur les brevets sont ajustées au 1er janvier de chaque année. Les montants ci-dessus sont les montants actuels s'ils sont reçus au plus tard le 31 décembre de l'année en cours.
Veuillez vous référer à la page web des
taxes sur les brevets
de l'OPIC pour voir tous les montants actuels des taxes.
Les titulaires actuels et antérieures au dossier sont affichés en ordre alphabétique.
| Titulaires actuels au dossier |
|---|
| CHINA ALUMINUM INTERNATIONAL ENGINEERING CORPORATION LIMITED |
| Titulaires antérieures au dossier |
|---|
| S.O. |