Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02842909 2014-01-23
Spring System for an Aircraft
The present invention relates to a spring system for an aircraft, a traveling
gear for
an aircraft with at least one spring system as well as an aircraft, in
particular
airplane.
In spring systems for aircraft, in particular spring systems for traveling
gears of
aircraft, a tension spring usually is mounted on a spring receiving means.
This
. spring receiving means includes a lug head or a sleeve, onto which a thread
with
a constant thread pitch which approximately corresponds to the spring pitch in
the
unloaded or untensioned condition is screwed.
Since at the beginning of the thread the pitch of the spring is changed very
much
due to the tensioning operation of the spring, the spring tends to jump off
the first
thread groove of the thread or even undergo a plastic deformation. For
example, a
permanent gap or kink formation of the spring thereby can occur.
Further approaches by using so-called pre-cylinders, certain material pairings
such as stainless steel and titanium turned out to be disadvantageous, because
these constructions were quite susceptible to seizing. Here, for example the
inside
CA 02842909 2014-01-23
2
diameter of the titanium spring scrapes on the pre-cylinder and on the last
thread
groove of the lug head of stainless steel.
It has also been attempted to prevent the spring from jumping or to prevent
deformations of the spring by bonded connections. These approaches, however,
have the disadvantage that the fatigue strength or stability of the spring is
not
high.
Therefore, it is the object of the present invention to develop a spring
system as
mentioned above in an advantageous way, in particular to the effect that the
durability of a spring system is increased and a safe attachment of the spring
of
the spring system becomes possible.
In accordance with the invention, this object is solved by a spring system
with the
features of claim 1. Accordingly, it is provided that a spring system for an
aircraft
is provided with at least one spring and with at least one spring receiving
means,
wherein the spring receiving means includes at least one lug head to which the
spring is attachable or attached, wherein the lug head includes a thread onto
which the spring can be screwed or is screwed, and the thread includes at
least
one thread portion which has a thread pitch in the region of the operating
pitch of
the spring.
The aircraft in particular can be an airplane and the spring system in
particular
can be a spring system of a traveling gear of an aircraft. The spring in
particular
can be a tension spring, i.e. a spring subjected to tension.
The operating pitch of the spring in particular corresponds to the pitch of
the
spring which is reached in operation of the spring, i.e. the pitch of the
spring in the
loaded condition. This pitch of the spring is determined by the elongation of
the
spring to a certain length or a certain length range, to which the spring is
expanded or deflected in operation.
CA 02842909 2014-01-23
3 =
In particular, this provides the advantage that a reduction of the
deformations and
the forces at the transition from the clamping region of the spring, which is
attached b the spring receiving means, and the resilient region of the spring
is
achieved. Advantageously, the spring deformation and the spring force are
built
up slowly. In particular, it thereby is achieved that the spring no longer
tends to
so-called jumping, i.e. jumps out of the thread as a result of the load, as
the forces
which effect jumping are minimized from the start very simply and very
effectively.
In particular, the spring now no longer can jump off the first thread groove
of the
lug head, since the deformation is greatly reduced in this region.
It is possible to use a short lug head, as now the forces to be transmitted
can be
reduced or are reduced. By using a shorter lug head, weight and material
advantageously can be saved. This also provides the advantage that the
stiffness
jump at the end of the thread can greatly be reduced. Advantageously, no more
rubbing takes place at the pre-cylinder or at the spring receiving means, and
rubbing between the first thread groove and the spring also is reduced
distinctly.
The fatigue strength of the spring advantageously can be increased distinctly.
The spring can be a titanium spring. Furthermore, it can be provided that the
spring receiving means is made of stainless steel
Furthermore, it can be provided that the thread at least partly has a constant
pitch.
It is conceivable that the thread exclusively has a constant pitch.
It is possible that the thread at least partly has a variable pitch. A
variable pitch in
particular provides the advantage that the spring deformation and spring force
is
built up slowly in the clamping point. The tendency of the spring to jumping
thereby is reduced distinctly.
In addition, it can be provided that there is provided at least one further or
second
thread portion with a first constant pitch.
CA 02842909 2014-01-23
4
Furthermore, it is conceivable that there is provided a further or third
thread
portion with a variable or a first variable pitch.
It is possible that there is provided a further or fourth thread portion with
a variable
or a second variable pitch.
In addition, it can be provided that the thread is an external thread or an
internal
thread and/or that the thread is a round thread or a conical thread or a
rectangular
thread or a trapezoidal thread.
In addition, the present invention relates to a traveling gear with the
features of
claim 9. Accordingly, it is provided that a traveling gear for an aircraft is
provided
with at least one spring system according to any of claims 1 to 8.
Furthermore, the present invention relates to an aircraft with the features of
claim
10. Accordingly, it is provided that an aircraft, in particular airplane, is
provided
with at least one spring system according to any of claims 1 to 8 and/or with
at
least one traveling gear according to claim 9.
Further details and advantages of the invention will now be explained in
detail with
reference to an exemplary embodiment illustrated in the drawing,
in which:
Figure 1: shows a top view of the spring system according to the invention in
the
loaded condition;
Figure 2: shows a top view of the spring system according to the invention in
the
partly loaded condition;
Figure 3: shows a top view of the spring system according to the invention in
the
unloaded condition;
CA 02842909 2014-01-23
Figure 4: shows a sectional drawing of the spring system shown in Figure 3,
Figure 5: shows a detail drawing of a traveling gear of an aircraft in the
extended
condition; and
Figure 6: shows a detail drawing of a traveling gear of an aircraft in the
retracted
condition.
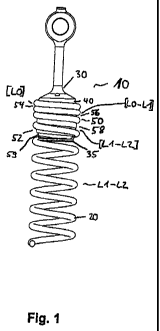
Figure 1 shows a top view of the spring system 10 according to the invention
in
the loaded condition, here a deflection of the spring 20 to a length in the
range Li-
L2.
In the Figures, the spring pitch is indicated such that the spring pitch in
the
designated range is indicated put in brackets with reference to the length of
the
spring corresponding to this spring pitch with a corresponding deflection.
The essentially new and advantageous aspect of the spring system according to
the invention consists in that now a reduction of the deformations and forces
at
the transition from the fixed to the resilient region of the spring 20 is made
possible. This is achieved in particular by fastening the spring 20 to the
thread 50
with a variable pitch. The spring deformation and force thereby is built up
slowly in
the clamping point.
The thread pitch of the thread 50 rises continuously from the thread portion
54
with a first constant spring pitch [LO] at the head in direction of the spring
20. The
pitch of the thread 50 at the end approximately is the pitch of the spring at
[L1] or
advantageously approximately is a spring pitch between [1_1-1_2].
At the transition from the fixed to the resilient region, the spring 20
thereby is
pretensioned and deformed already to the values occurring in operation.
The thread 50 is arranged on the lug head 40, in particular cut or milled in,
wherein the lug head 40 is part of the spring receiving means 30. The spring
CA 02842909 2014-01-23
6
means 30 also includes a cylinder portion 35, over which the spring 20 can be
pushed. The cylinder portion also can be designed such that it also stabilizes
the
spring 20 from inside, in particular when the cylinder portion is designed
with a
length greater than in the exemplary embodiment.
The thread 50 is divided into different portions, namely into the thread
portion 52
which has a thread pitch [L1-L2] in the region of the operating pitch of the
spring
20. Furthermore, in the thread portion 54 two thread grooves with a constant
pitch
[LO] are provided, in the thread portion 56 one thread groove with a variable
pitch
of [LO-L1], and a further thread portion 58 with a variable pitch of [L1-1_21.
The portions 52 and 58 overlap in the exemplary embodiment shown here, which
however is not absolutely necessary.
The thread groove 59 in the thread portion 58 can be widened or lined. The
assembly of the spring 20 thereby is facilitated and the spring 20 is unwound
in a
controlled way on the flank of the first thread groove facing away from the
lug by
varying the length (L1 to L2 or vice versa). Stress and deformation peaks
thereby
are excluded.
In principle, it is also conceivable that the thread or individual thread
portions are
tapered or set at a lower level. The thread shape can be round or also have
any
other shapes, such as e.g. rectangular shapes or trapezoidal shapes. The
requirements placed on a spring system also can be satisfied by threads with
constant pitch, which lies in the region of the operating pitch [L1-L21. In
principle, it
is also possible that the thread 20 also is designed as internal thread. To
secure
the attachment of the spring 20 to the lug head 40, adhesives and/or further
elements such as e.g. a shrink sleeve can be used.
Figures 2 and 3 show a further top view of the spring system 10 according to
the
invention in the partly loaded condition (cf. Figure 2) with a deflection to a
length
L1 or in the partly unloaded condition (cf. Figure 3) with a deflection to a
length
LO. Figure 4 shows a sectional drawing of the spring system 10 shown in Figure
3.
CA 02842909 2014-01-23
7
Figure 5 shows a detail drawing of a traveling gear of an aircraft in the
extended
condition. The traveling gear 100 of the aircraft includes a spring system 10.
Figure 6 shows the traveling gear 100 of the aircraft as shown in Figure 5 in
the
retracted condition-
.